Musculoskeletal system
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Musculoskeletal System Provides
Supports upright posture
Provides wide range of motion / movement
Protects internal organs
Carries weight
General types of skeletons
Hydrostatic skeleton, Exoskeleton, Endoskeleton
The hydrostatic skeleton is formed by a
fluid-filled internal compartment, called the coelom
The coleum is under
hydrostatic pressure -- fluid, supports the organism and organs
A Hydrostatic skeleton is found in
soft-bodied animals such as sea anemones, earthworms, starfish, and other invertebrates
Movement in a hydrostatic skeleton
Muscle contraction and relaxation changes the shape of the coelom, pressure on the fluid produces movement.
An Exoskeleton is
External, consists of a hard encasement covering
An Exoskeleton provides
Provides defense and support the body
An Exoskelton is made of
30-50% chitin (polysaccharide); acellular
An exoskeleton allows for movment
through the contraction of attached muscles on the inside
Arthropods have a
exoskeleton (crustaceans and insects)
If you have an exoskeleton you have to
Molt to grow - shed exoskeletons because the exoskeleton does not
expand/grow
An Endoskeleton is
Hard, mineralized structures located within the soft tissue of
organisms
An endoskeleton is made up of
50 - 70% mineral
• 20 – 40% organic
• 5 – 10% water
• 3% lipid
An endoskeleton provides
support, protects internal organs, and allow for movement through contraction of muscles attached to the skeleton
The 2 divivsions of human endoskeletons are
Axial skeleton and Appendicular Skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of the bones of the
Skull
Ossicles of the middle ear
Hyoid bone
Vertebral column
Thoracic (rib) cage
The apendicular skeleton is made up of
SHoulder girdle
Arms
Hands
Pelvic girdle
Leg
Foot
Skull bones support
Support the structures of the face and protect the brain
Auditory Ossicles
Transmit sound from air to cochlea smallest bones in the body
Malleus
Incus
Staples
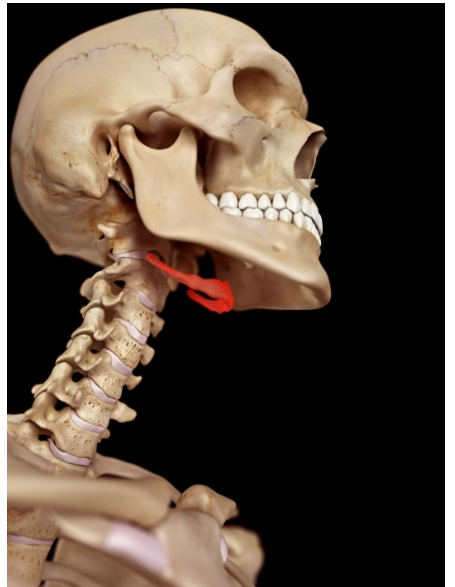
Hyoid Bone
Provides attachments for the muscles of the tongue, larynx (voice-box), and mandible (lower jaw)
The hyoid is important in
speech and swallowing
The hyoid bone is the only bone that
does not articulate with any other bone
The vertebral column is made up of
Cervical vertebrae (C1–7)
Thoracic vertebrae (Th1–12)
Lumbar vertebrae (L1–5)
Sacrum (5 fused)
Coccyx (4 fused)
The curve inscreases strength/Flexibility
The thoracic cage
or rib cage, protects the heart, lungs, pancreas, liver, and spleen.
The pelvic girdle
To adapt to reproductive fitness, the (a) female pelvis is lighter, wider, shallower, and has a broader angle between the pubic bones than (b) the male pelvis
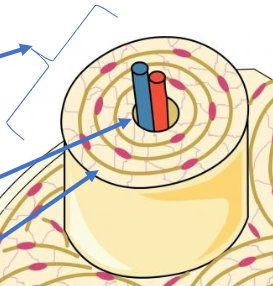
Osteon
Unit of bone
The haversion canal in osteon
is made up of vessels and nerves
Lamella
round layer of bone in osteon
lacuna
a small, microscopic cavity within the bone tissue that houses an osteocyte, a mature bone cell
osteocyte
bone cell in lacuna
caniculi
small canals where they connect osteocytes in lacunae for communication and nutrient exchange
osteogenic cell
bone stem cell
osteoblast
forms bone matrix
osteocyte
maintains bone tissue
osteoclast
reabsorbs bone
trabeculae
spongy bone
spongy bone is shaped like
rods and plates and triangles
sppongy bone id
light weight but strong
Ossification (Osteoblast)
Calcification –
begins 6M in utero and continues for 25
years for length, lifetime for thickness
Intramembranous Ossification
Ossification
of fibrous membranes into skull, mandible, clavicle – Ossification via mesenchymal cells – embryonic connective tissue
Endochondral Ossification
Mesenchymal(bone stem) cells differentiate
into osteoblast, leads to ossification of cartilage - All other bones
Bone Growth
Bones grow in length at the Epiphyseal plate
Growth is under control by
growth hormones produced by the pituitary gland as well as the
Ovaries and testes
Remodeling
Old bone replaced by new bone
Repair
healing a broken bone
hematoma
collection of clot
callas
fibruous tissue and cartilage
ossification
via osteoblas
osteoblast function
deposition of new bone
Osteoclast function
reabsorption of old bone
remodeling happens via
osteoclast + osteoblast
Joints and skeletal movement are classified by
Basic structure- the material and how the bones are connected
fibrous connection
connection by fibrous connective tissue
• No or little movement
cartilaginous
connection by cartilage
• More movement than Fibrous
synovial
Synovial capsule – space between bones
• Excellent movement
planar joint
wrist/ankle
hinge joint
elbow, kneee
pivot joint
neck
condyloid joint
thumb
saddle joint
hand
ball and socket
hip and shoulder
tendon
attaches muscle to bone
ligament
connects bone to bone or cartilage to cartilage
muscle cells are
specialized for contraction
skeletal muscle cell
Attach to bones and skin, locomotion and movement,
voluntary, long and cylindrical, striated, multiple nuclei
cardiac muscle cell
Heart muscle, striated, single nucleus, involuntary
smooth muscle cell
Walls of hollow organs (digestive system, blood vessels
respiratory system, bladder), no striations, involuntary, single
nucleus
sarcolemma
the plasma membrane that surrounds a skeletal muscle cell
sarcoplasm
the cytoplasm in myocyte
myofibrils
small subsection of myocyte; contractile filaments
myocyte striations
bands of proteins: Actin and Myosin
sliding filament model
actin slides over myosin(actin is pulled over myosin, shortening sarcomeres, which contracts the muscle)
T-tubule
(transverse) invaginations in muscle cells rich in ion channels
sarcoplasmic reticulum
membrane bound organelle
in muscle cells important in control
of Ca+ levels –release and uptake
(Sarcoplasmic reticulum