ESCI 402 Final Exam
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
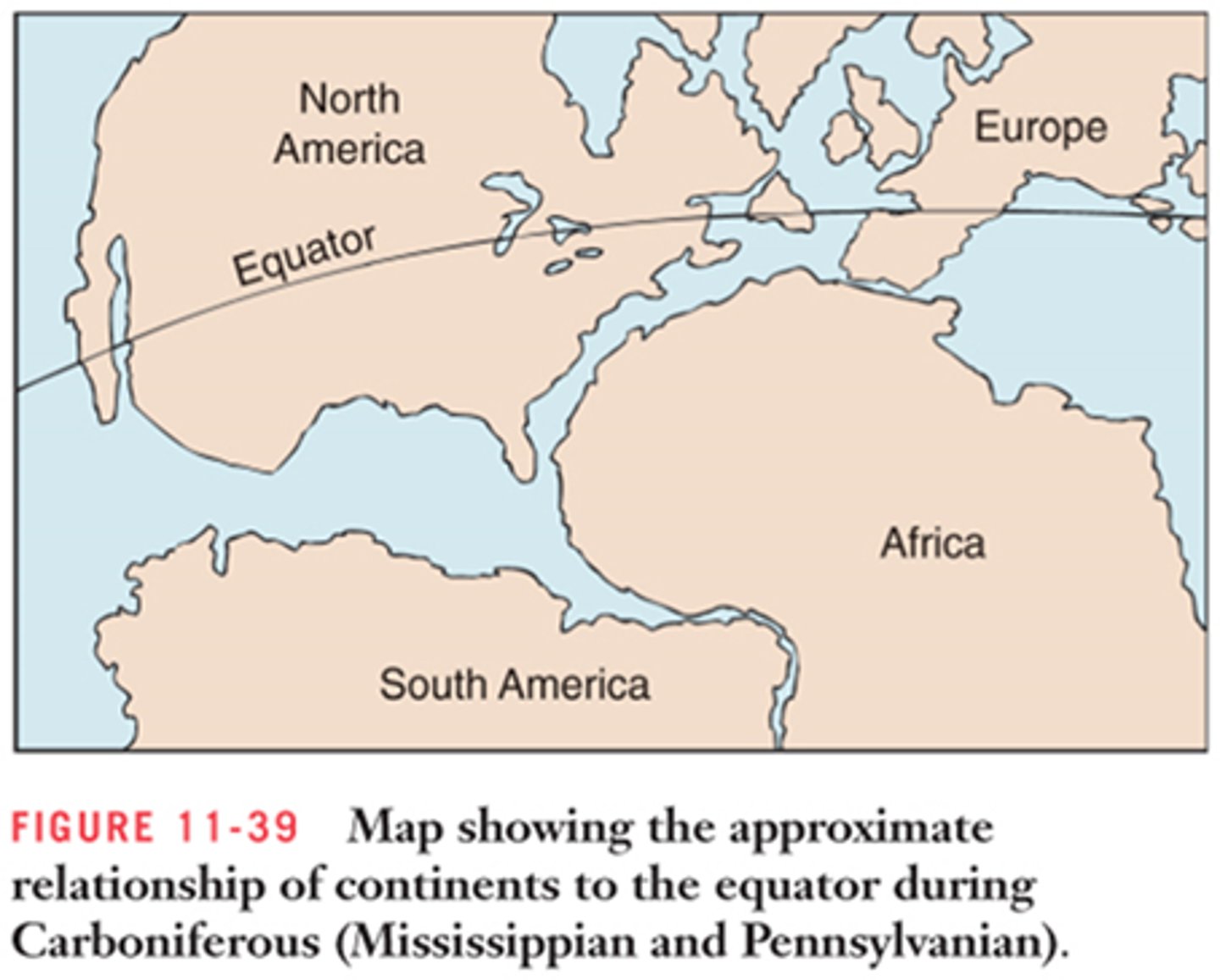
What is the Alleghenian Orogeny
Mountain-building event that occurred when the part of Gondwana that is now Africa began to collide with Laurasia during the Late Pennsylvanian. (300 ma)
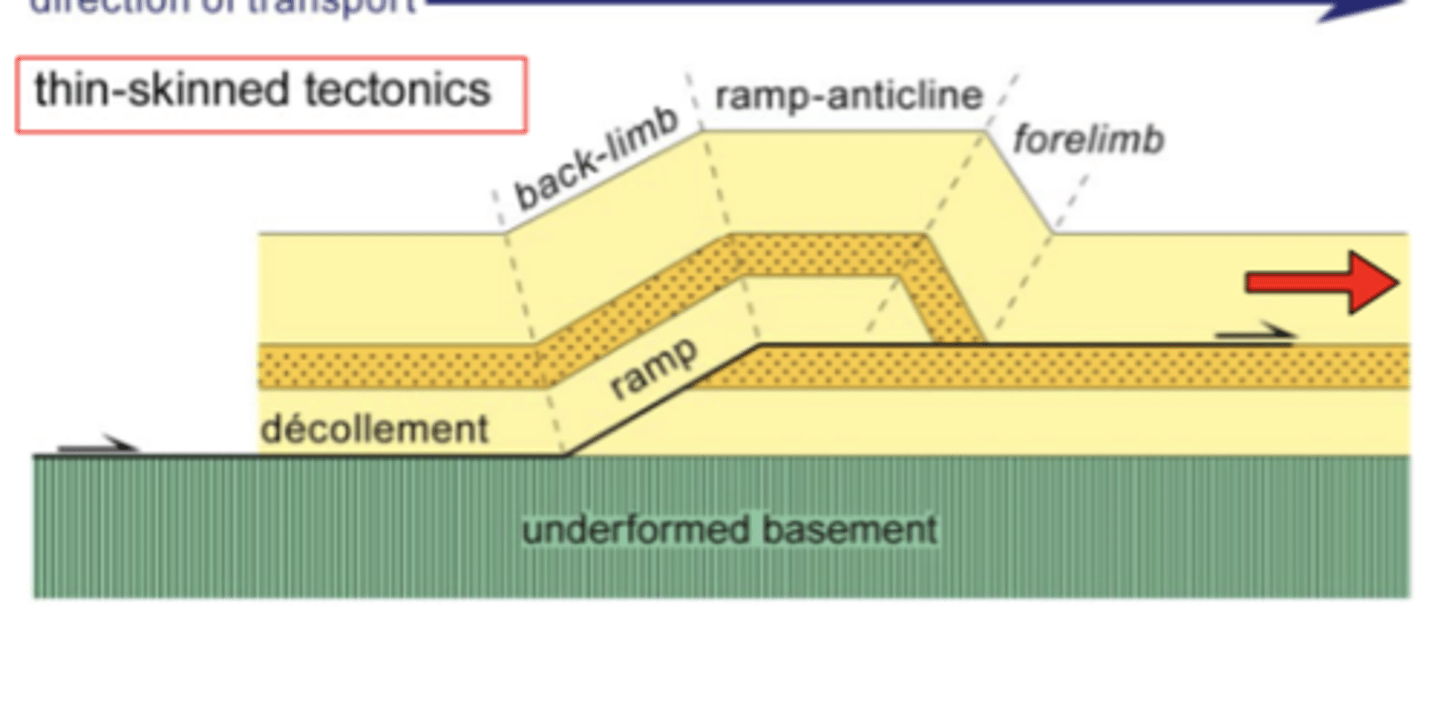
What is thin-skinned tectonics
A kind of deformation in which the basement rocks are largely unaffected and the overlying "skin" of weaker sedimentary rocks breaks into multiple-thrust faults.
How long did Pangea exist?
Pangea existed from 335-175 Ma. From the late Mississippian through the early- to mid-Jurassic
What are the 5 geologic evidences for Pangea?
1) Geographic fit of the continents. Too good to be a coincidence
2) Evidence from glaciation. Grooves left in rocks by glaciers all radiate from what was then the South Pole.
3) The Gondwana Succession. A unique succession of rocks found today on all southern continents and India.
4) Remanent (residual) magnetism tells us the past position of continents.
5) Distribution of fossils
What were the 3 things unique about Pangea's climate?
1. LOW EQUABILITY
2. HIGH SEASONALITY
3. CYCLICITY
What is low equability?
Low equability means temperatures are very different around the world
What indicated low equability in pangea?
Coal deposits form from plant material accumulating in swampy areas.
Permian-aged coal deposits in Antarctica
What is high seasonality?
Earth's climate has seasonality, which means it changes depending on the time of year.
High seasonality means the seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation (or other climate variables) are large
What indicated high seasonality in pangea?
Lungfish Burrows
As the water level falls lungfish burrow into the bottom mud to form a cocoon to survive the dry season. Some of these have formed trace fossils.
What was pangea's cyclicity like?
Pangea had natural variations in global climate, which caused changes in glacier extent and sea level
What would the climate of pangea look like in terms of geographic variances?
Similar to modern day Asia (except more intense).
On coasts climate was dependent on latitude and weather patterns.
Far more extreme climate inwards.
What was the Permian-Triassic extinction?
250 million years ago - period of enormous volcanic eruptions in current Siberia. Lava covered huge areas of land, carbon dioxide emitted caused the global climate to increase by 6C
What went extinct during the Permian-Triassic extinction?
96% of marine species
70% of terrestrial vertebrates
Many plants (especially larger ones)
Insects (only extinction event)
What are the 5 major classes of fish?
1. Agnathans
2. Acanthodians
3. Placoderms
4. Chondrichthyes
5. Osteichthyes
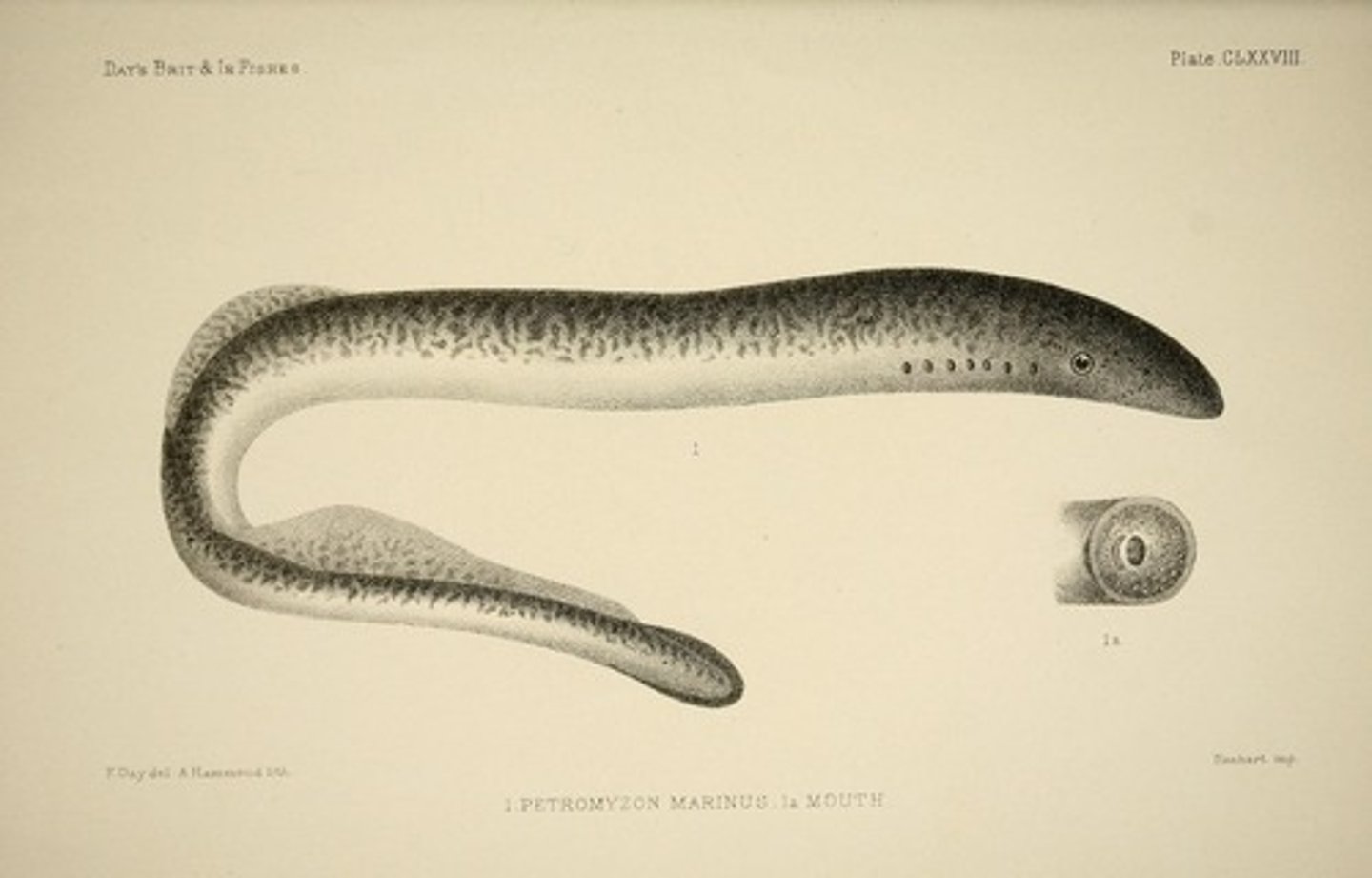
What are Agnathans?
Jawless fishes (lamprey, hagfish)
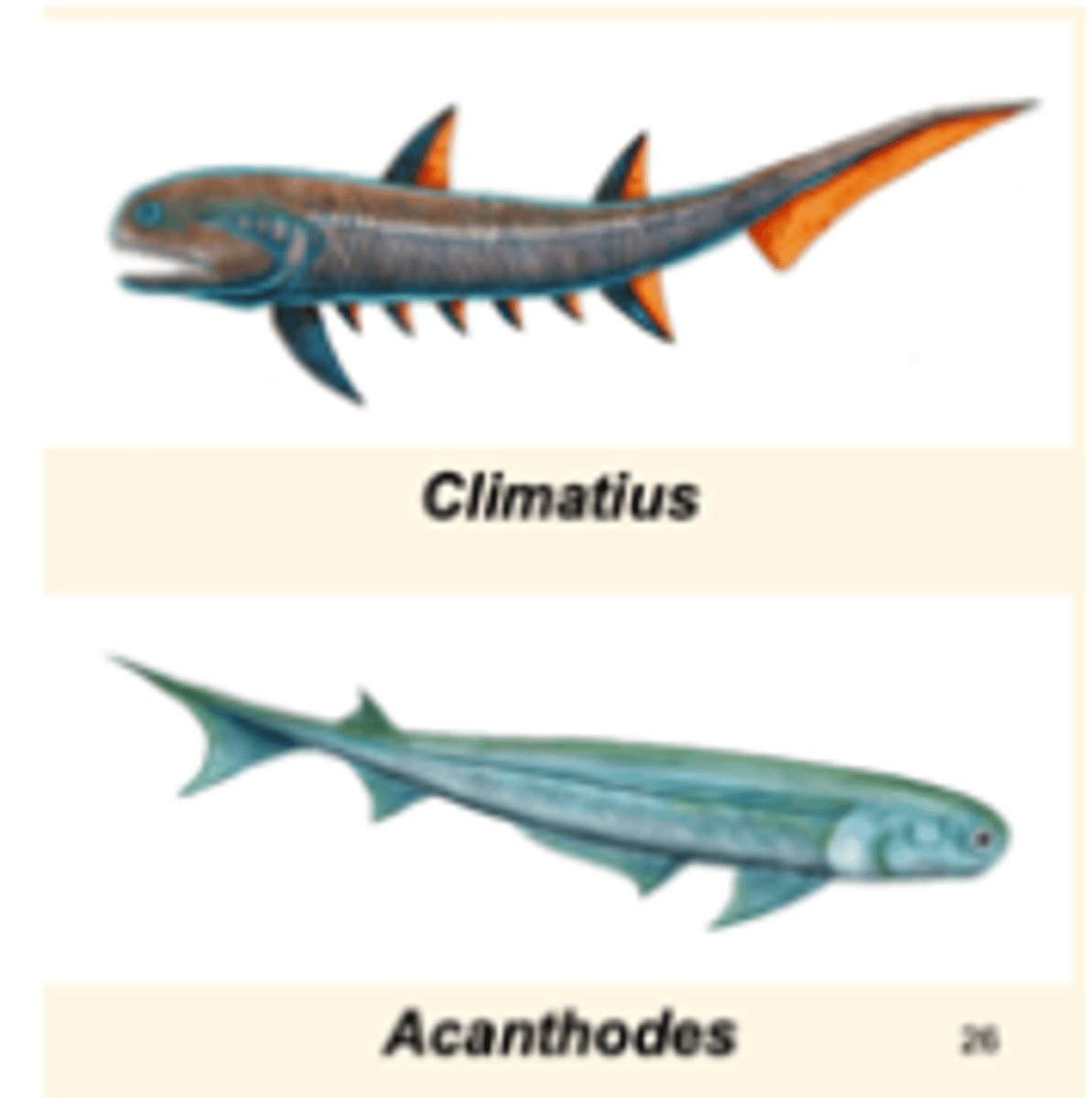
What are Acanthodians?
Spiny fishes with jaws

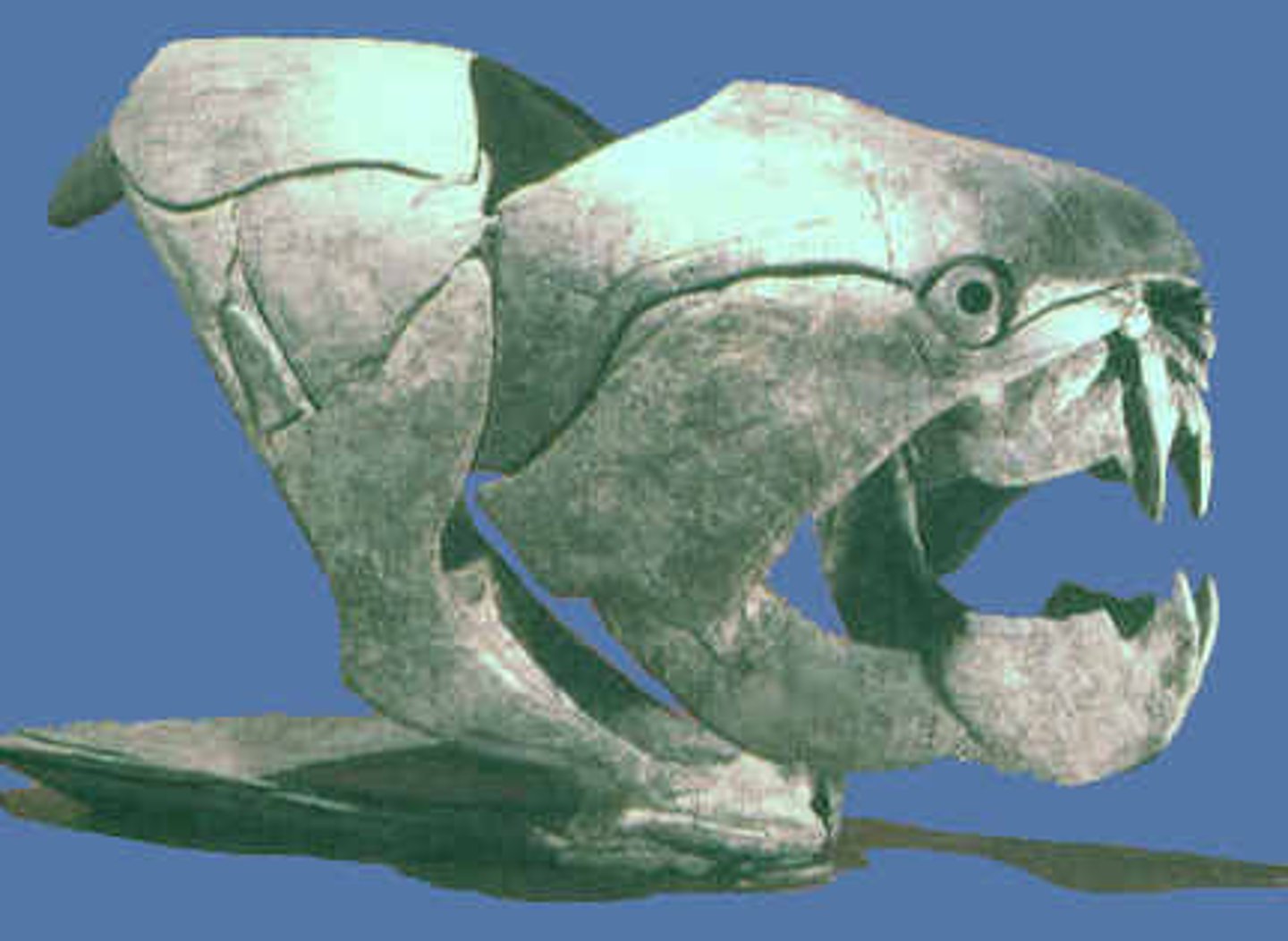
What are Placoderms?
Plate-skinned fishes with jaws (Dunkleosteus)

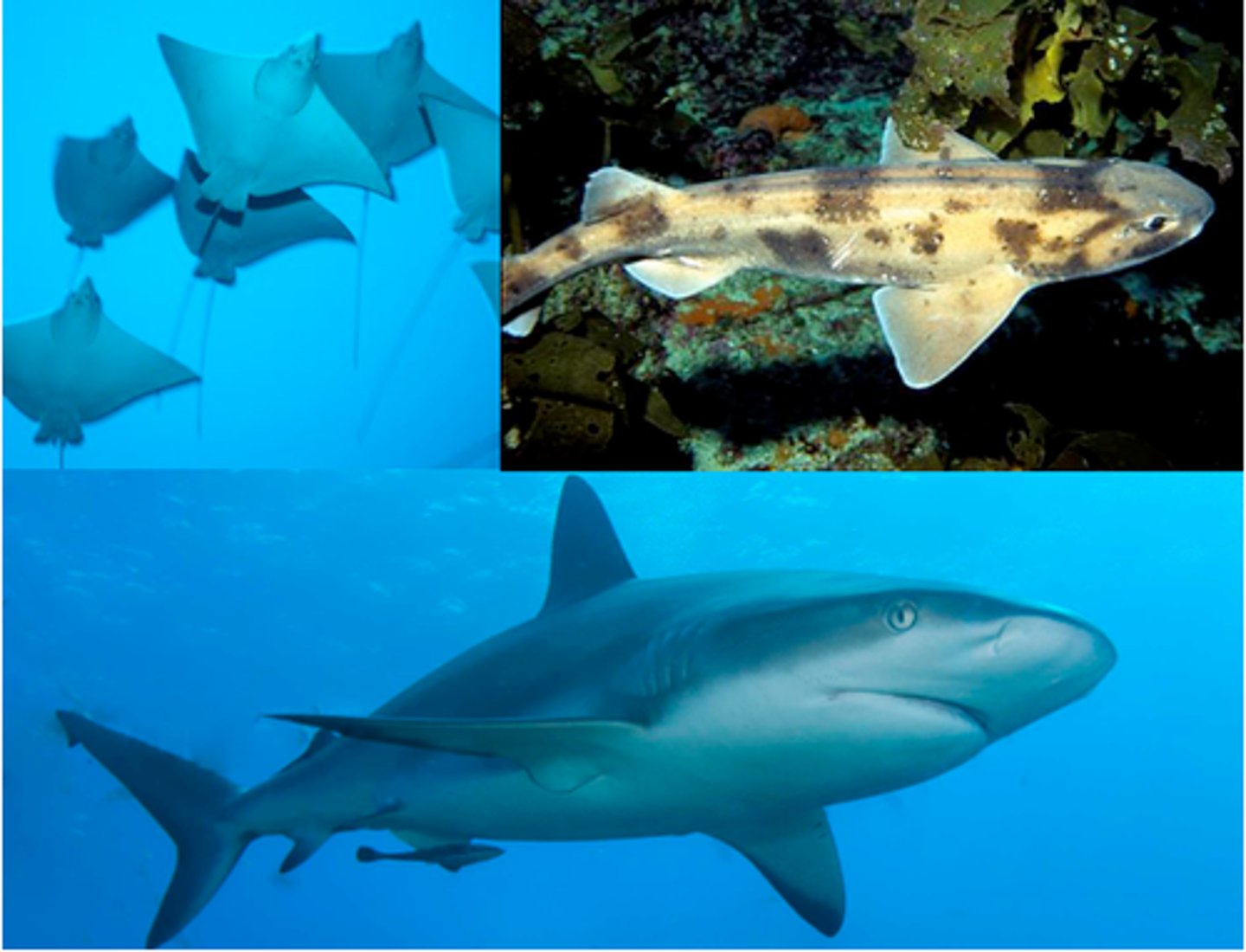
What are Chondrichthyes?
Cartilaginous fishes such as sharks, skates, and rays

What are Osteichthyes?
Fishes with bony skeletons (Actinopterygians)
What are Sarcopterygians?
lobe-finned fish (that eventually evolved into tetrapods)
What are Crossopyterigians? (fishapods)
Lobe-finned, bony fishes believed to have given rise to the amphibians and all other land vertebrates
What are Ichthyostegids?
Amphibian-like fish.
Still had fish-like tail, bony gill covers, fish-like vertebrae and skulls.
What are Labyrinthodonts?
Fish-like amphibians.
Followed the ichthyostegids in fossil record.
What is an Amniotic egg?
Embryo is enclosed in a membrane that allows oxygen to enter, but retains water (can develop out of water).
Where and when are the oldest amniote fossils recorded?
Oldest amniote fossils are found in swamp deposits from the Pennsylvanian Period
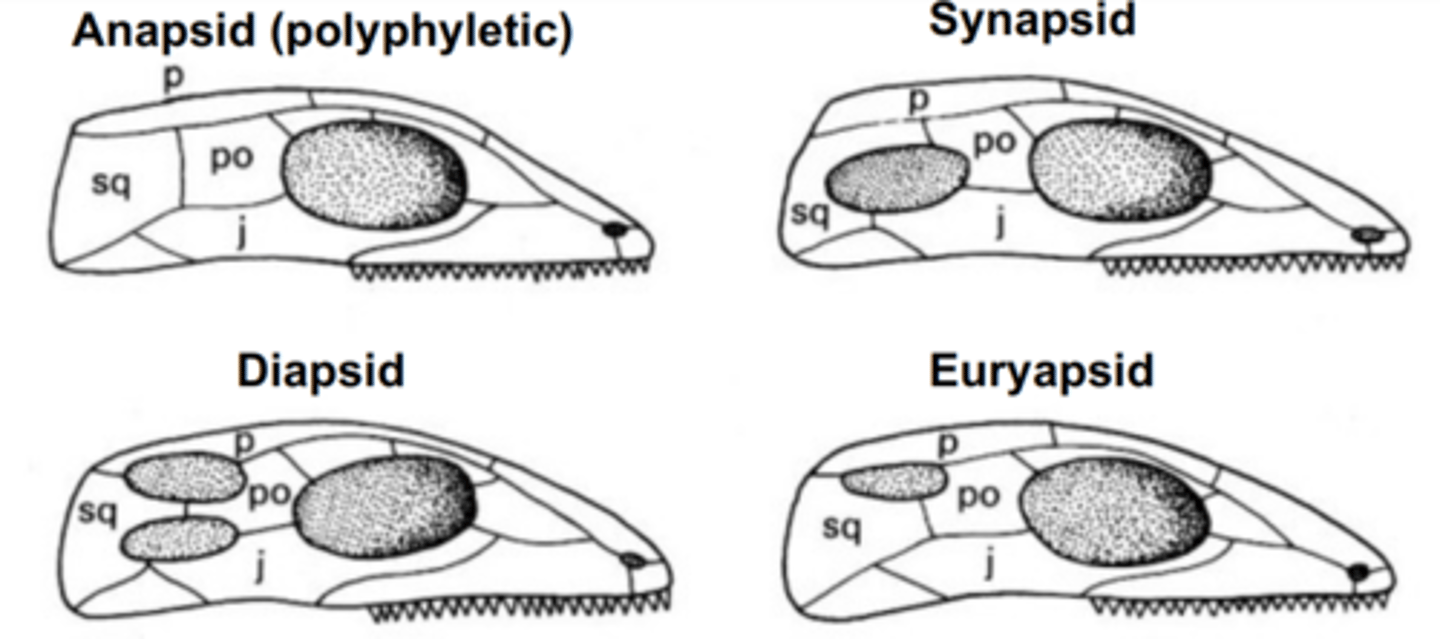
What are Synapsids?
Class of animals that includes mammals and everything more closely related to mammals than to reptiles and birds
What are Diapsids?
Group of reptiles that developed two holes on each side of their skulls.Includes crocodiles, lizards, snakes, and dinosaurs
What are Archosaurs?
Group of reptiles ancestral to dinosaurs, pterosaurs (flying reptiles), and crocodilians
What are the starting point of Archosaur evolution?
Basal archosaurs
What are the two main types of dinosaurs?
Ornithischians -"bird-hipped"
Saurischians -"lizard-hipped"
What were Ornithischians?
Bird-hipped plant eaters that eventually evolved into lizards
What were the Saurischians?
Lizard-hipped dinosaurs that eventually evolved into birds.
Sauropodomorphs - herbivorous
Theropods - carnivorous
What were the effects of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction?
The K-Pg extinction eliminated:
• Non-avian dinosaurs
• Pterosaurs (flying reptiles)
• Ammonoids (cephalopod molluscs)
• Large marine reptiles (ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs & mosasaurs)
• Rudists (bivalve molluscs) • Many other invertebrates
What caused the cretaceous-paleogene exinction?
1. Bolide impact
2. Continental flood basalt eruption
What is the evidence for the bolide impact?
Meteorite impact in Yucatan Peninsula
• Iridium anomaly
• Shocked quartz - minerals fractured by impact
• Tiny glass spherules or tektites - cooled droplets of molten rock from an impact
• Carbon soot - remnants of forests burned in a firestorm caused by an impact
What is the evidence for the continental floor basalt eruption?
Continental flood basalts around the time of K-Pg extinction
Amniote Skulls
anapsid, synapsid, diapsid
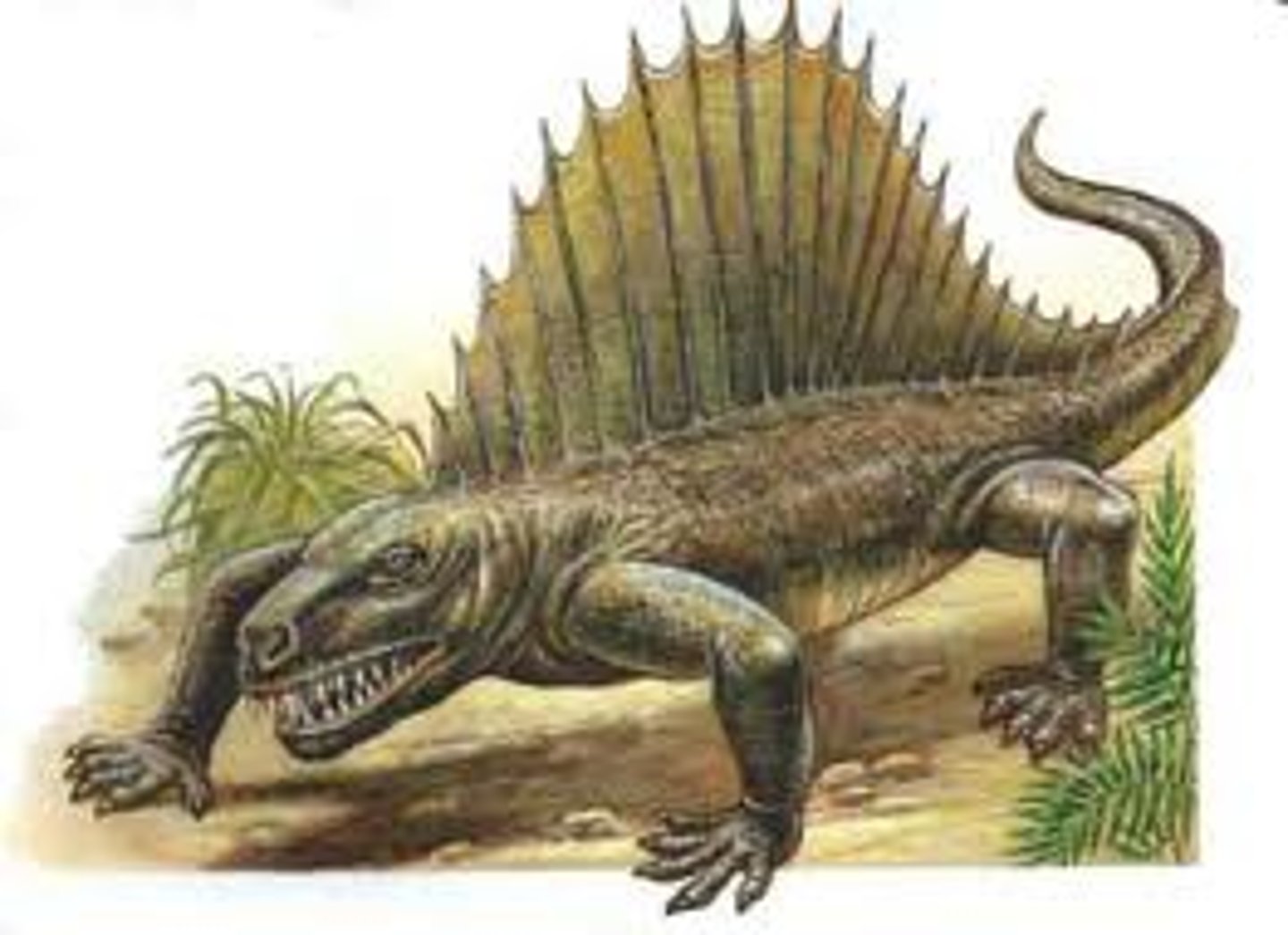
What are pelycosaurs (synapsids)?
A large extinct reptile of the late Carboniferous and Permian periods, typically having a line of long bony spines along the back supporting a sail-like crest.

What are therapsids?
Synapsids that eventually evolved from pelycosaurs
Arched cheekbones
Thin limbs, body raised off ground
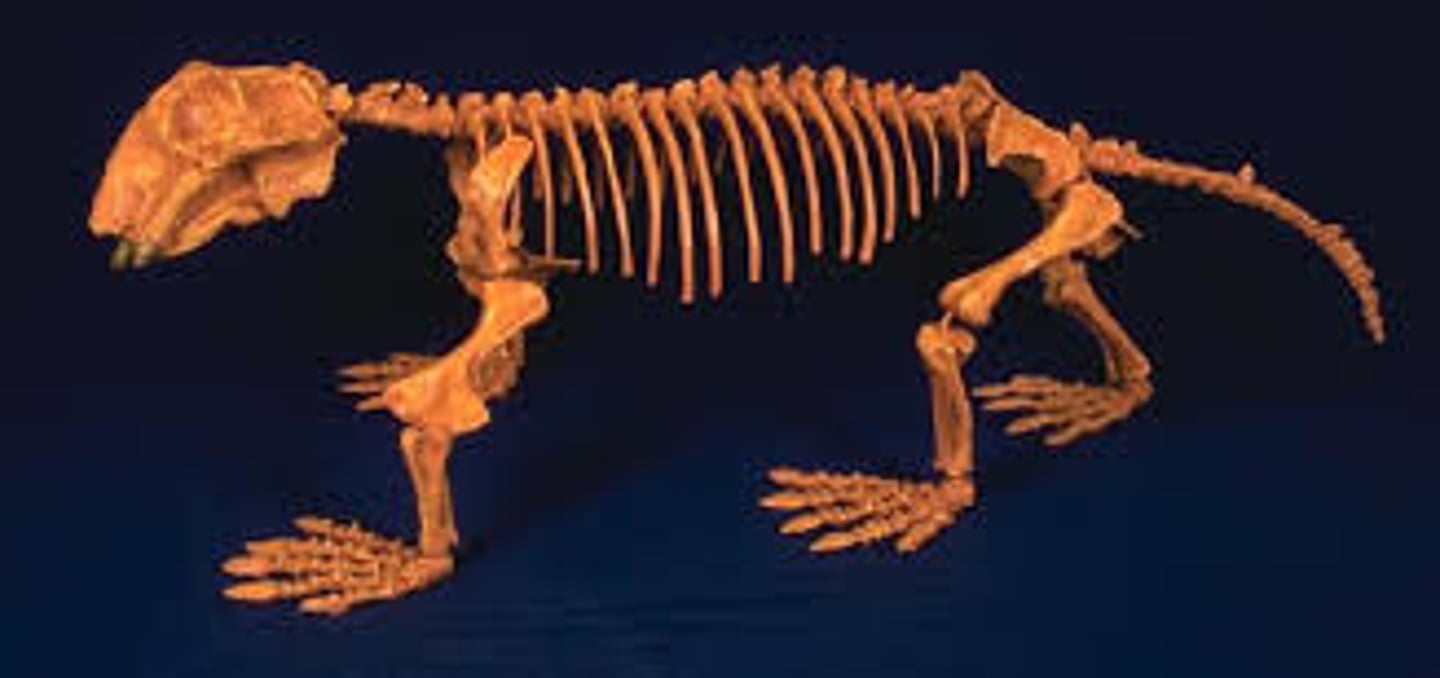

What are Cynodonts?
Animals with mammalian skeletal traits, including whiskers/hair, mammal-like teeth, and bones that let them breathe while eating
Mammalia Characteristics
Mammary glands, hair and subcutaneous fat, embryos develop in a uterus, in placental mammals the young develop in the womb, large brains, different teeth made of bioapatite
What is adaptive radiation?
Animals fill ecological niches that were left empty by extinct floras and faunas
How did mammals survive the cretacious-paleogene extiction?
Most animals under 2 kg, Led to adaptive radiation (65 mya)
What are some primate characteristics?
1) Opposable thumbs
2) Rotation of radius and ulna in forearm
3) Nails on digits
4) Forward-directed eyes
5) Postorbital bar (a vertical ridge of bone that separates the eye socket from the side of the skull)
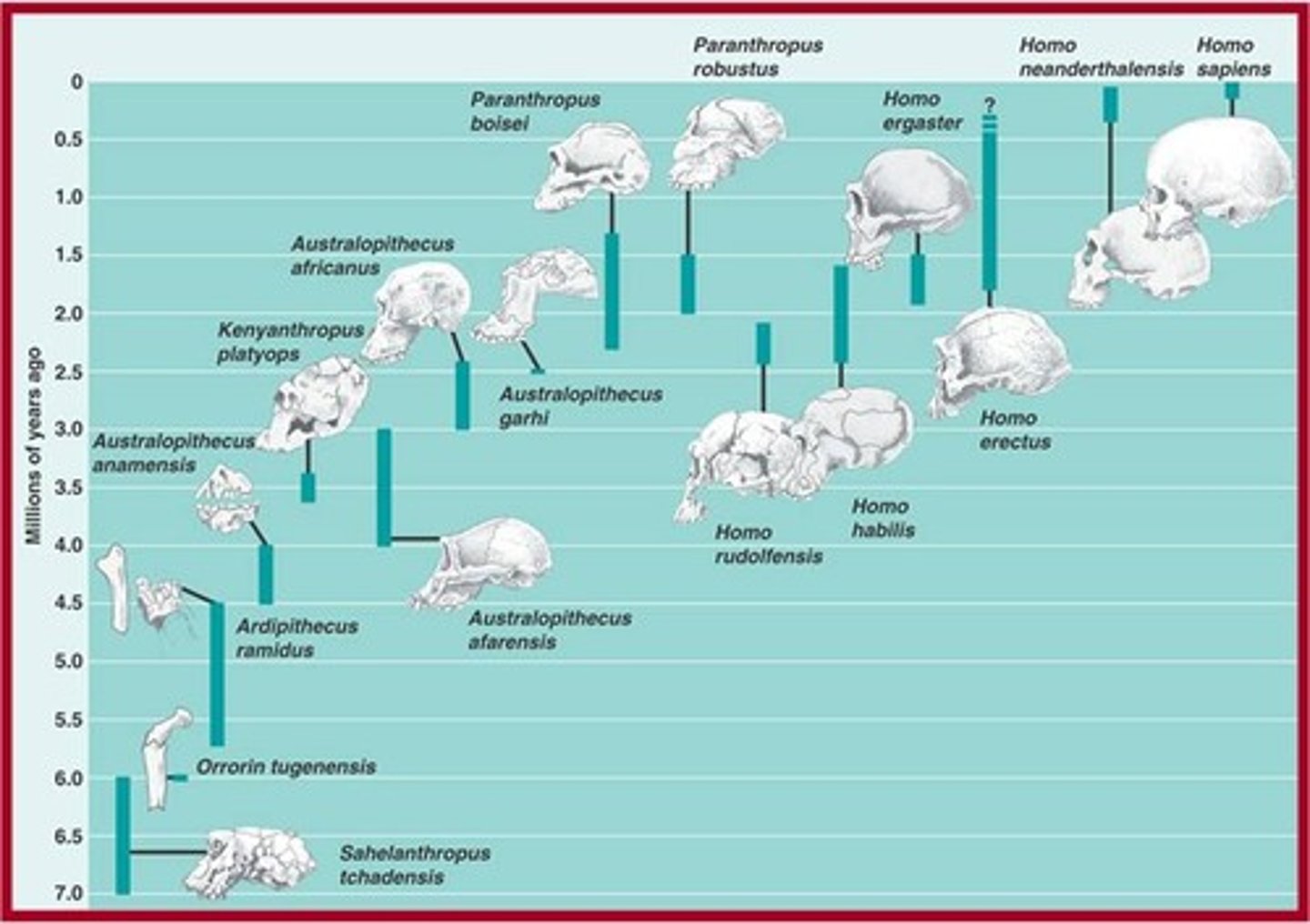
Timeline for human evolution
Timing of the Quaternary period, Pleistocene and Holocene
The Quaternary Period has been an ice age, with big swings between warm and cold climates. Now, in the Holocene, we are in an interglacial within the Quaternary ice age.
What is a glacier?
Glacier - a persistent mass of ice that flows under the influence of gravity
Mountain glaciers
flow from higher elevations to lower elevations and can take several forms
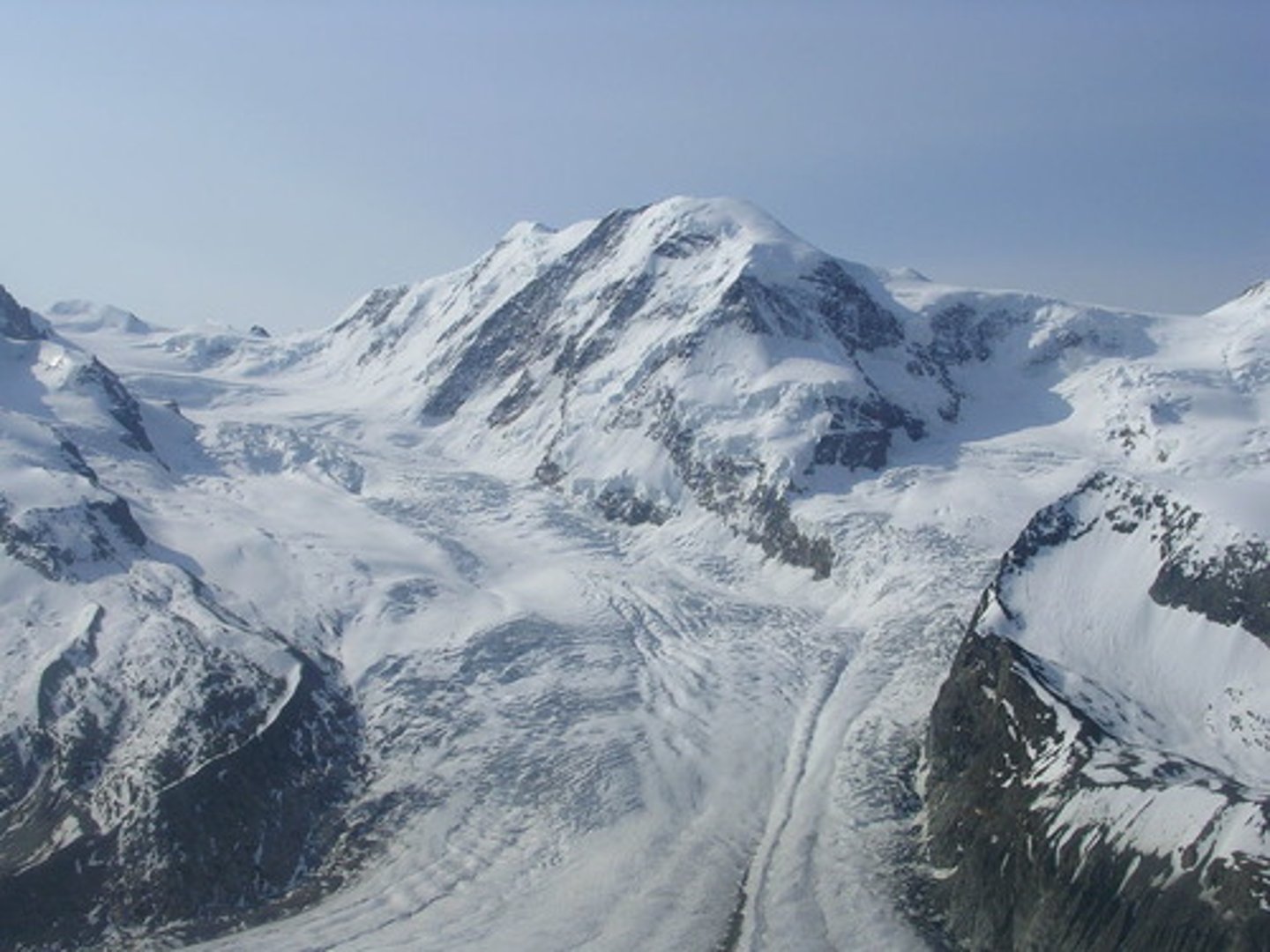

Cirque Glaciers
small, semicircular to triangular glaciers that form on the sides of mountains
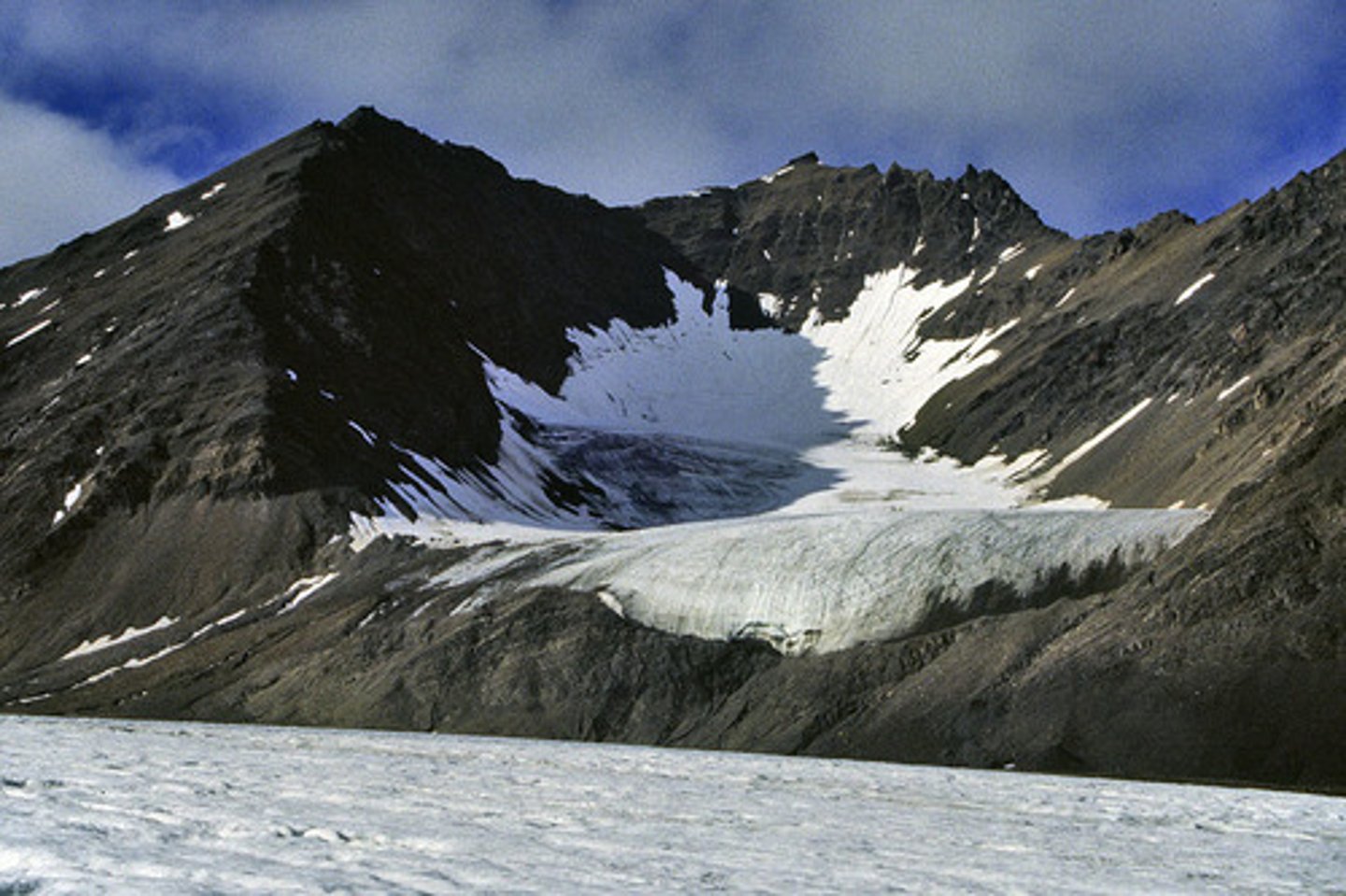

Valley Glaciers
long narrrow glaciers confined by mountains that usually move downhill through valleys already cut by rivers
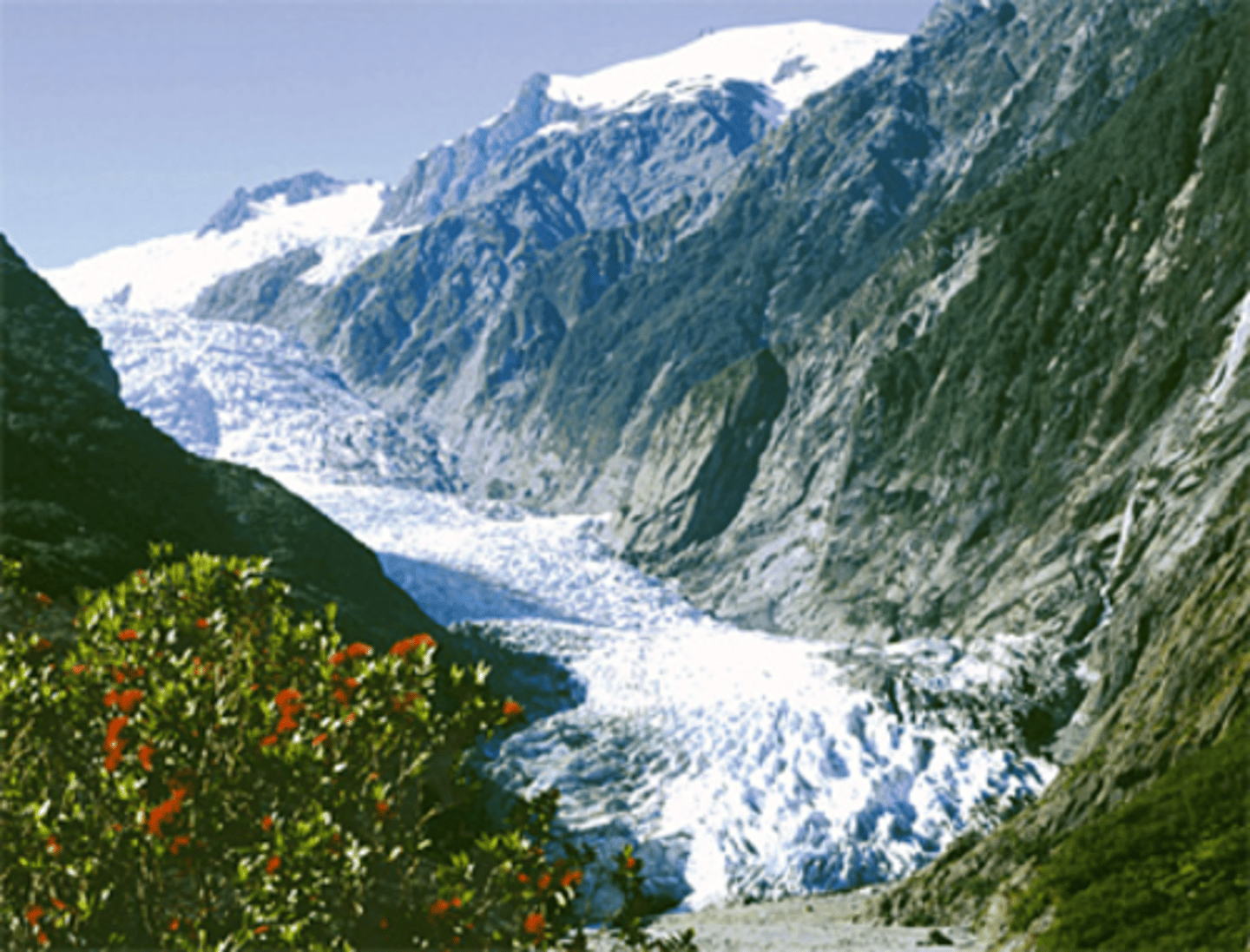

Piedmont Glaciers
mergers of two or more valley glaciers at the foot of a mountain range
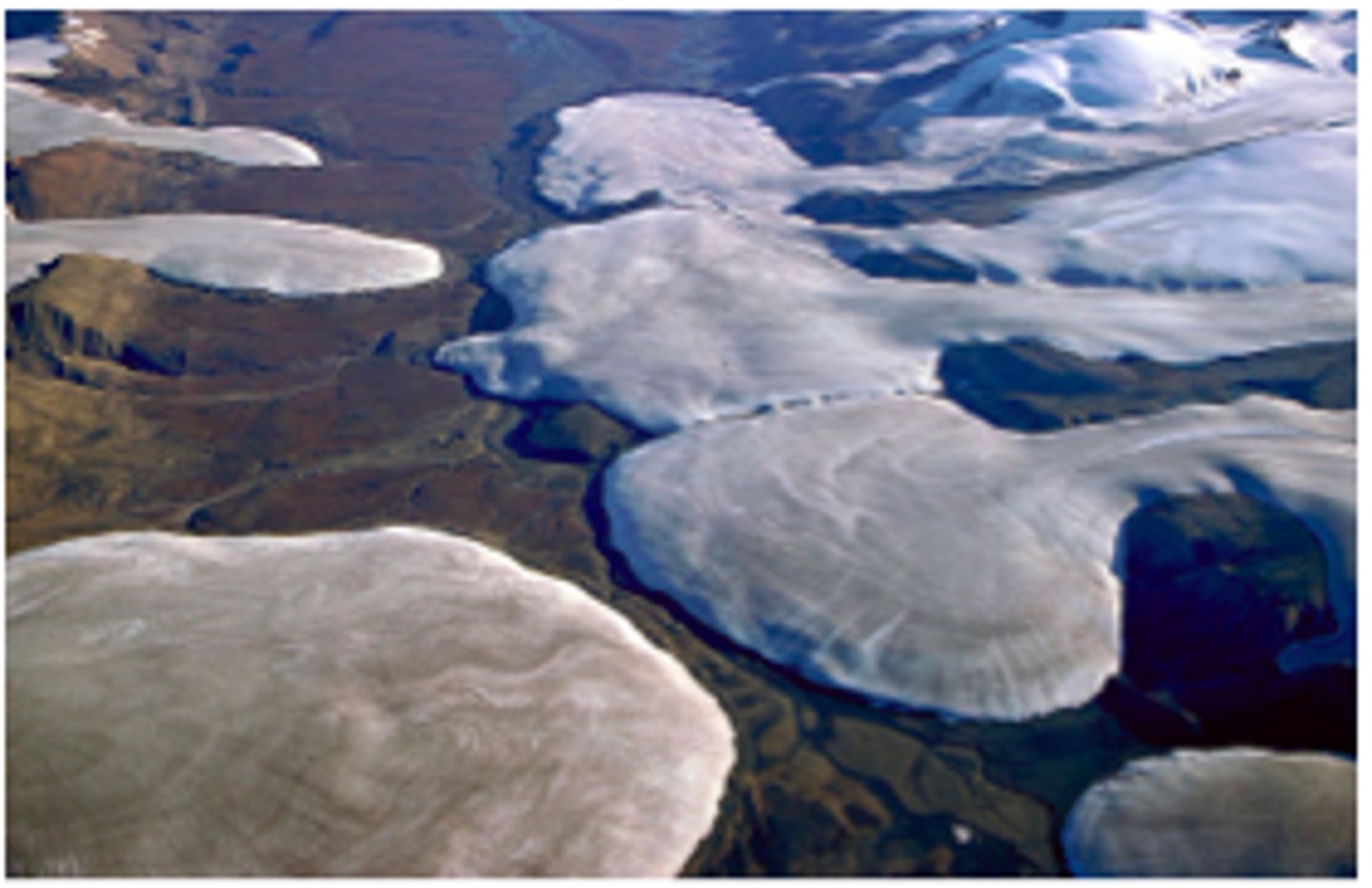

Tidewater Glaciers
glaciers whose terminus lies in the water
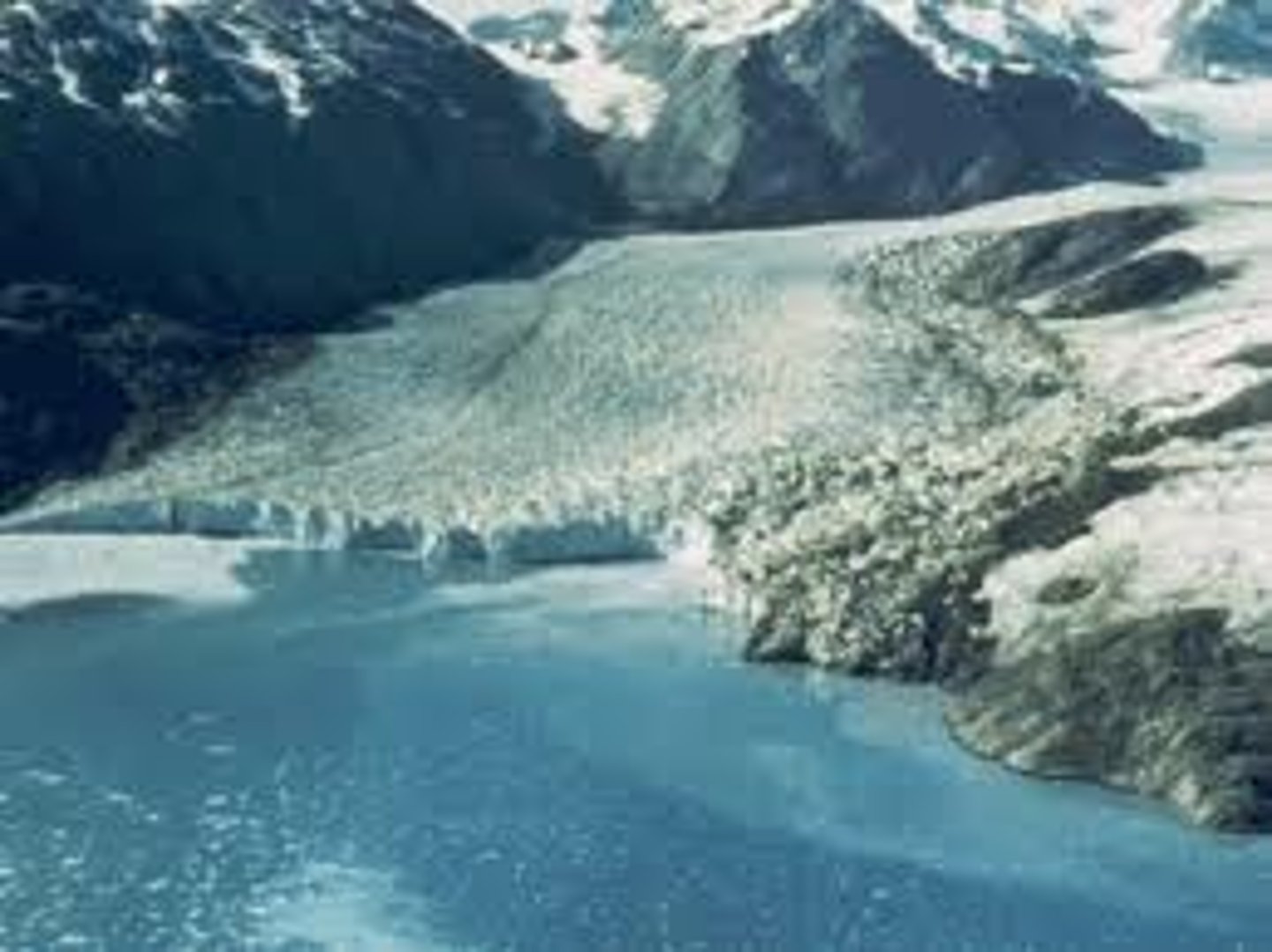

How do glaciers form?
Glacers form only in areas where more snow falls than melts. Snow build up, and its weight compacts the snow, forming ice that then begins to move downhill
What is a moraine?
Till that is deposited at the edges of a glacier that forms a ridge
What is a terminal moraine?
A terminal moraine is a moraine ridge that marks the maximum limit of a glacier advance. They form at the glacier terminus and mirror the shape of the ice margin at the time of deposition.
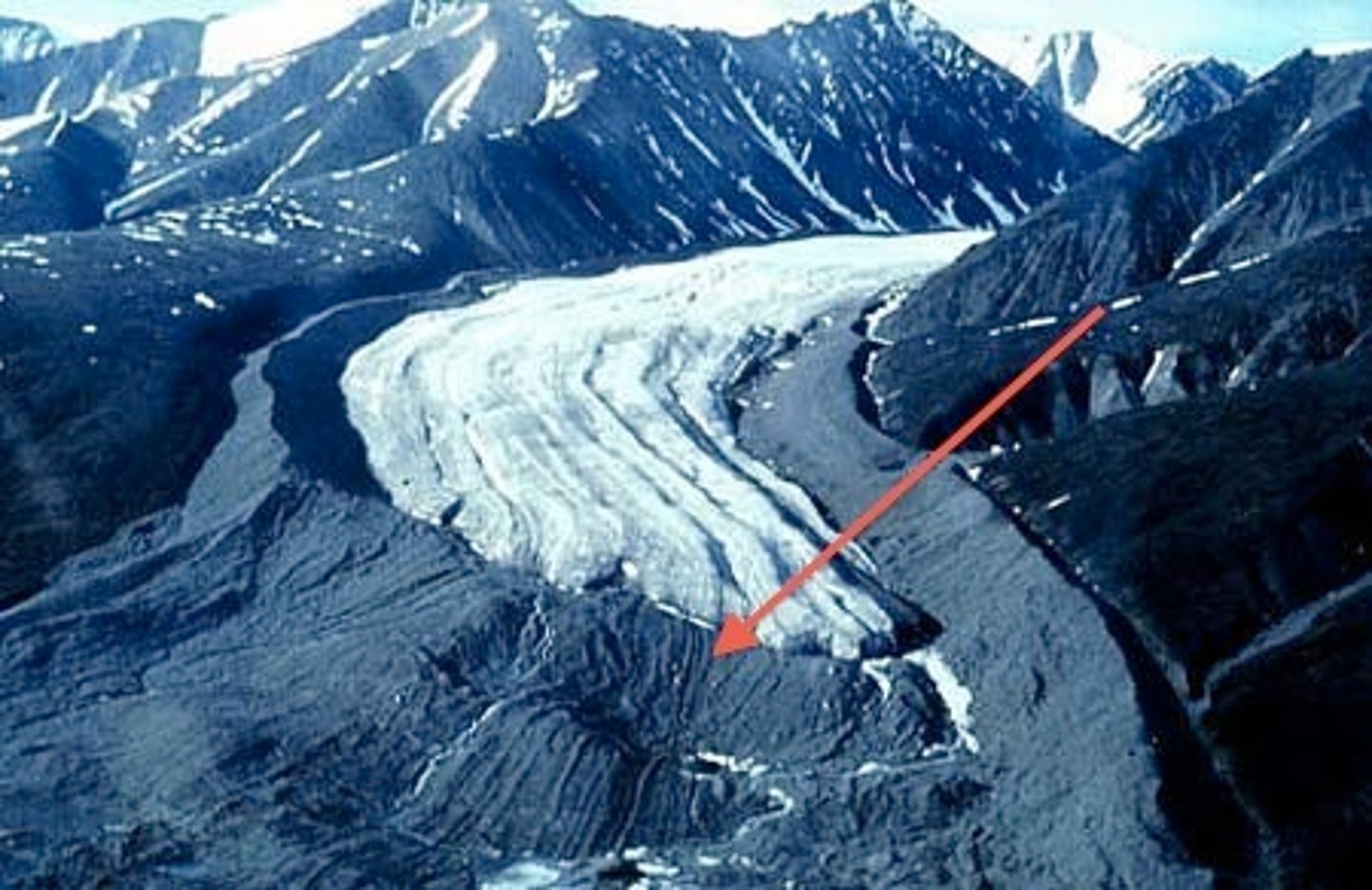

What is a lateral moraine?
Lateral moraines form along the glacier sides
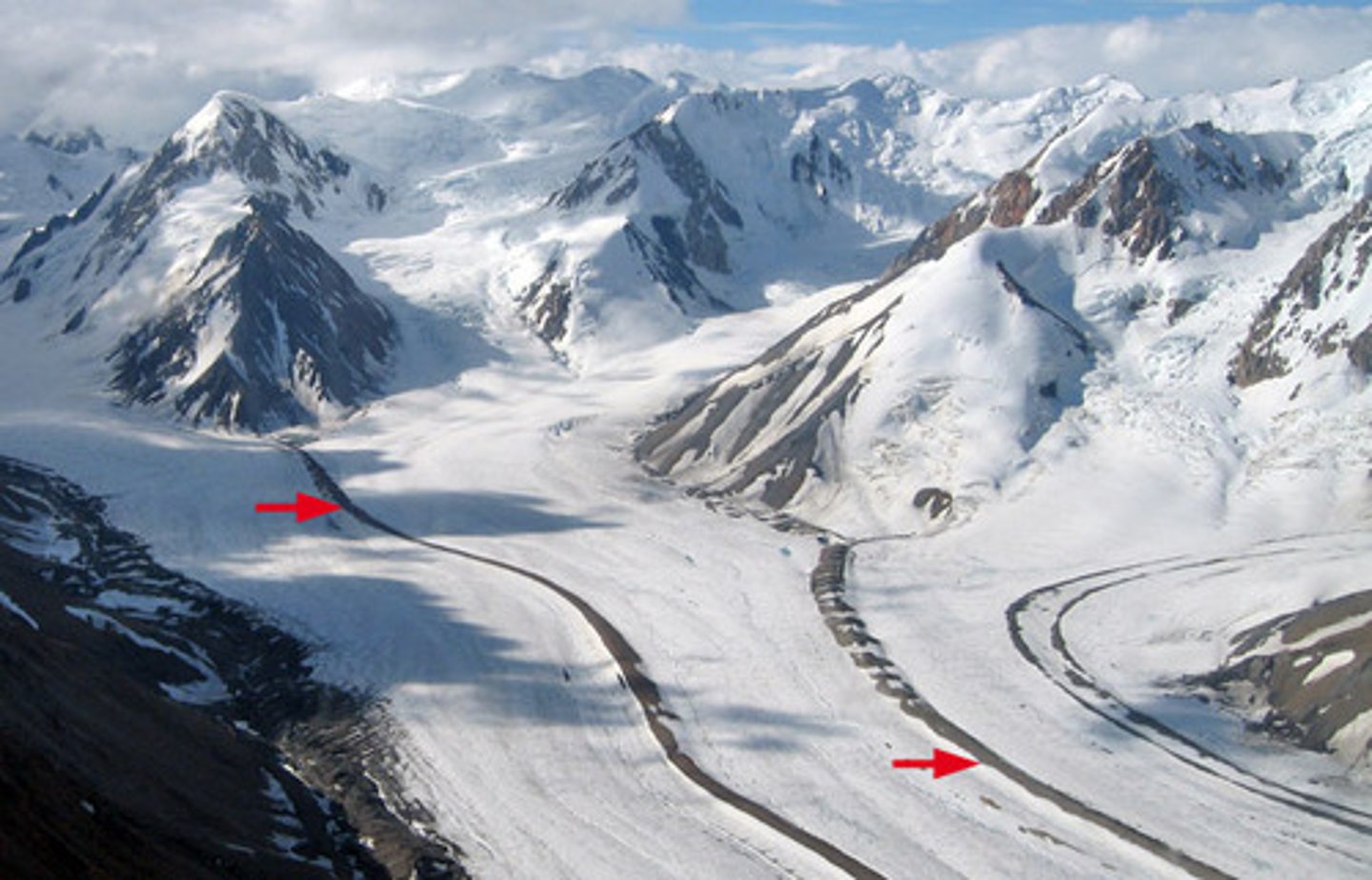

What is an outwash plain?
a layer of debris carried away from the terminus of a glacier and sorted and deposited by meltwater
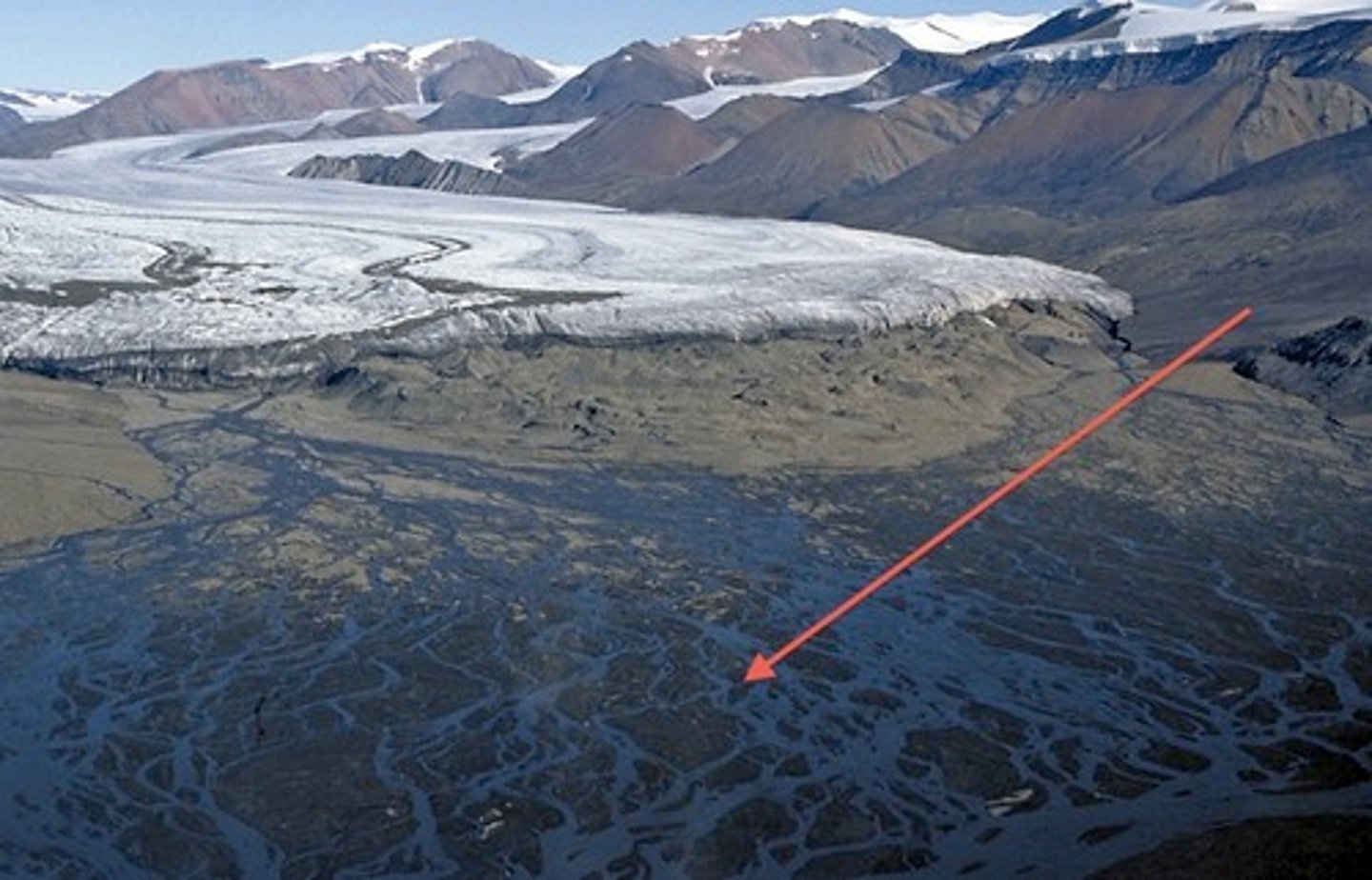

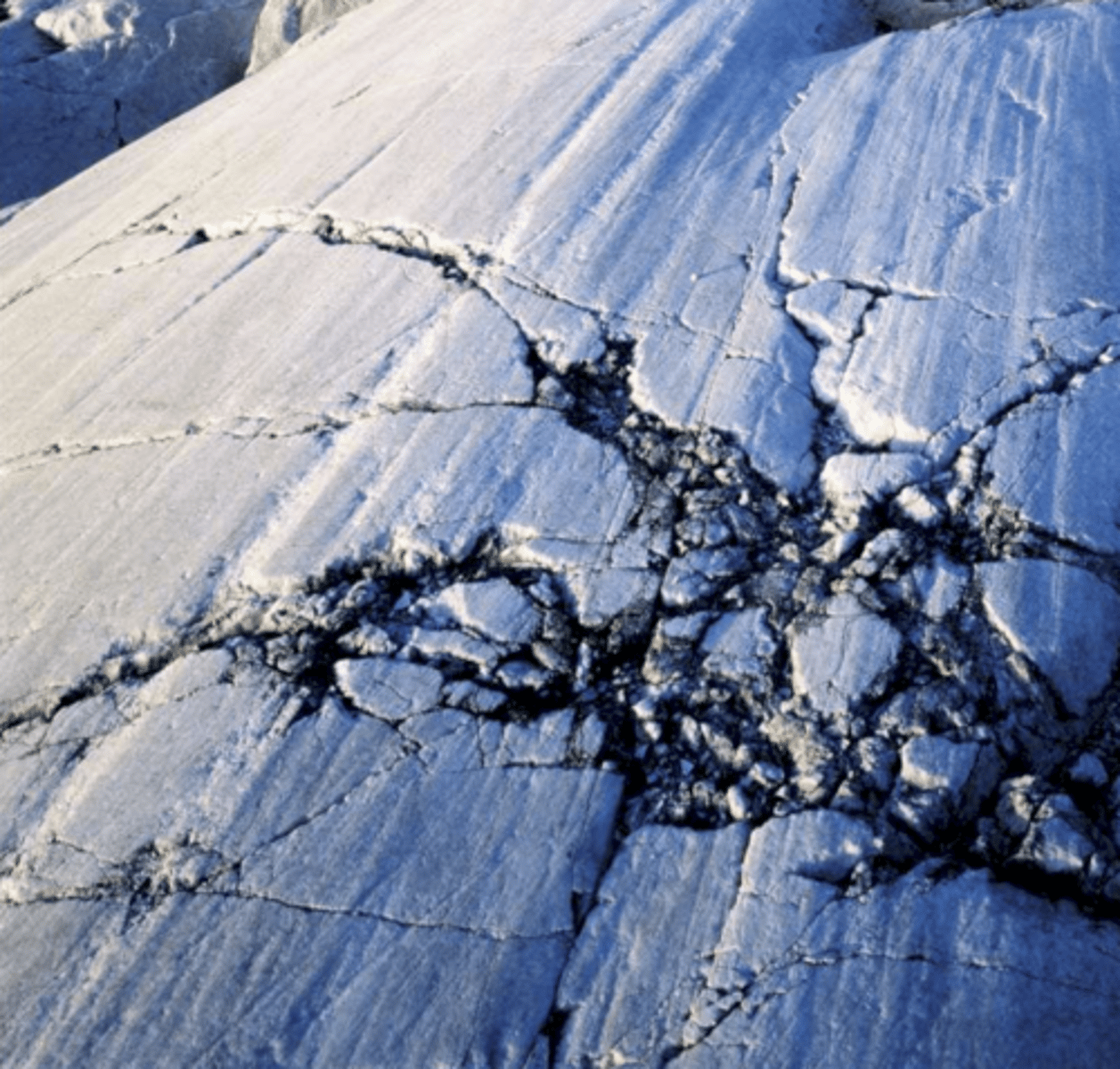
What are glacial scours?
Glacial scours or striationsform through the abrasion of bedrock by rocks incorporated into the bottom of a sliding glacier. They indicate past ice flowdirection!

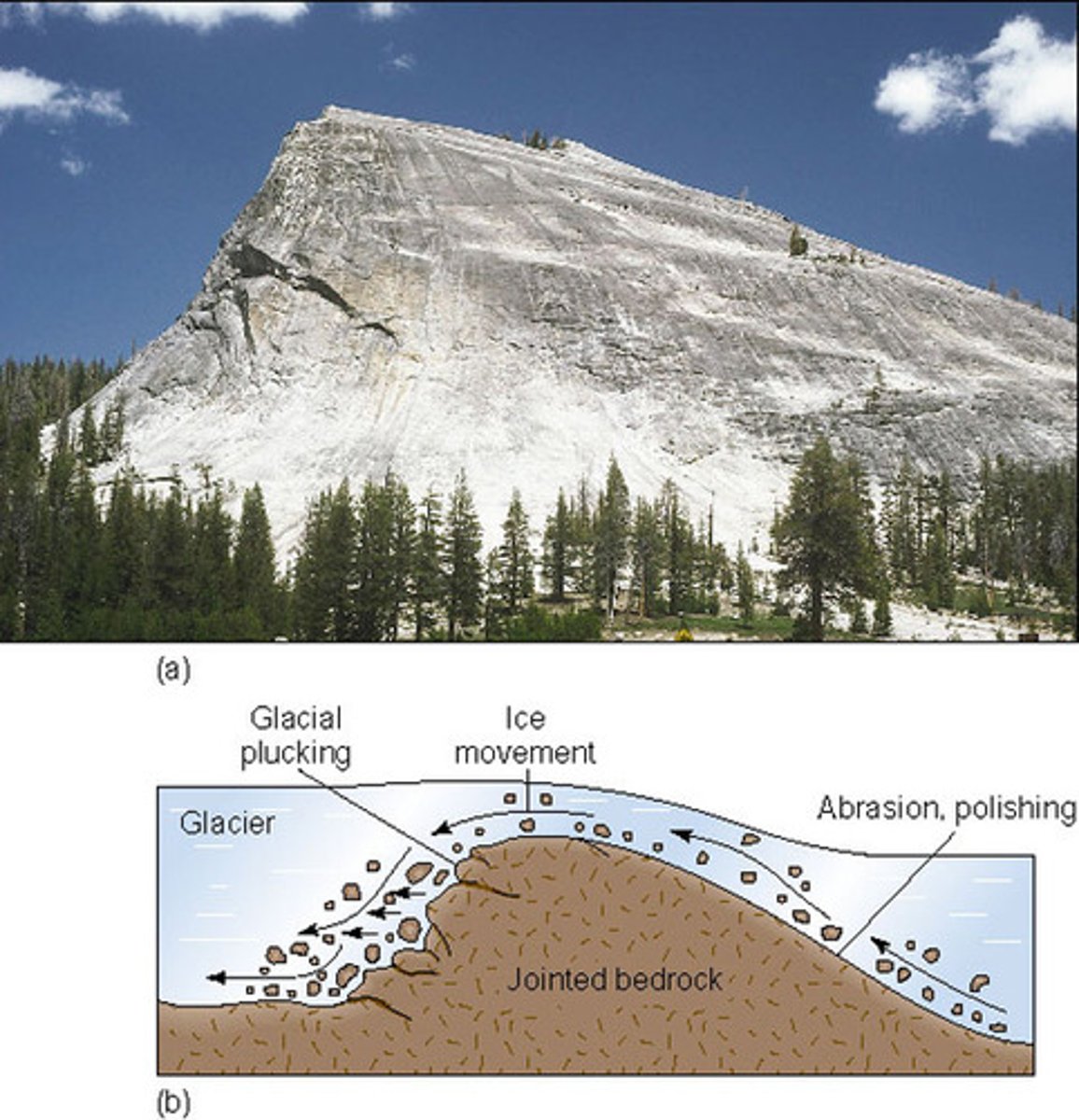
What are roche moutonnees?
rounded rock projections

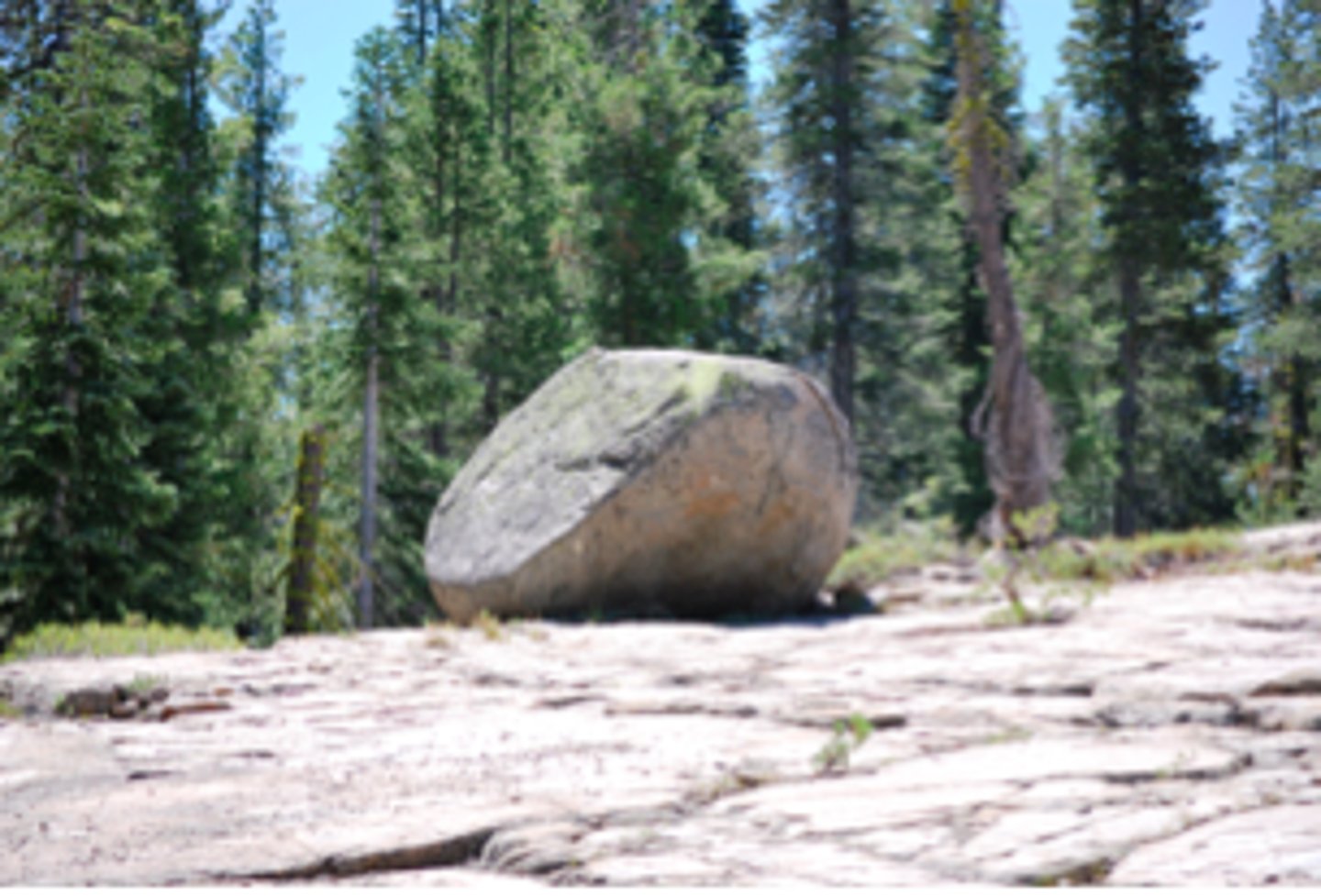
What is a glacial erratic?
Glacial erratic - a rock that has been transported by ice and deposited elsewhere

How can we learn about global ice volume?
The ratio of 18Oxygen/16Oxygen (δ18Oxygen) in the ocean tells us about global ice volume (mostly large ice sheets)
What is an ice core?
a drill core of ice that can help tell the climates of the past (chemistry on the ice, dust, and trapped air bubbles)
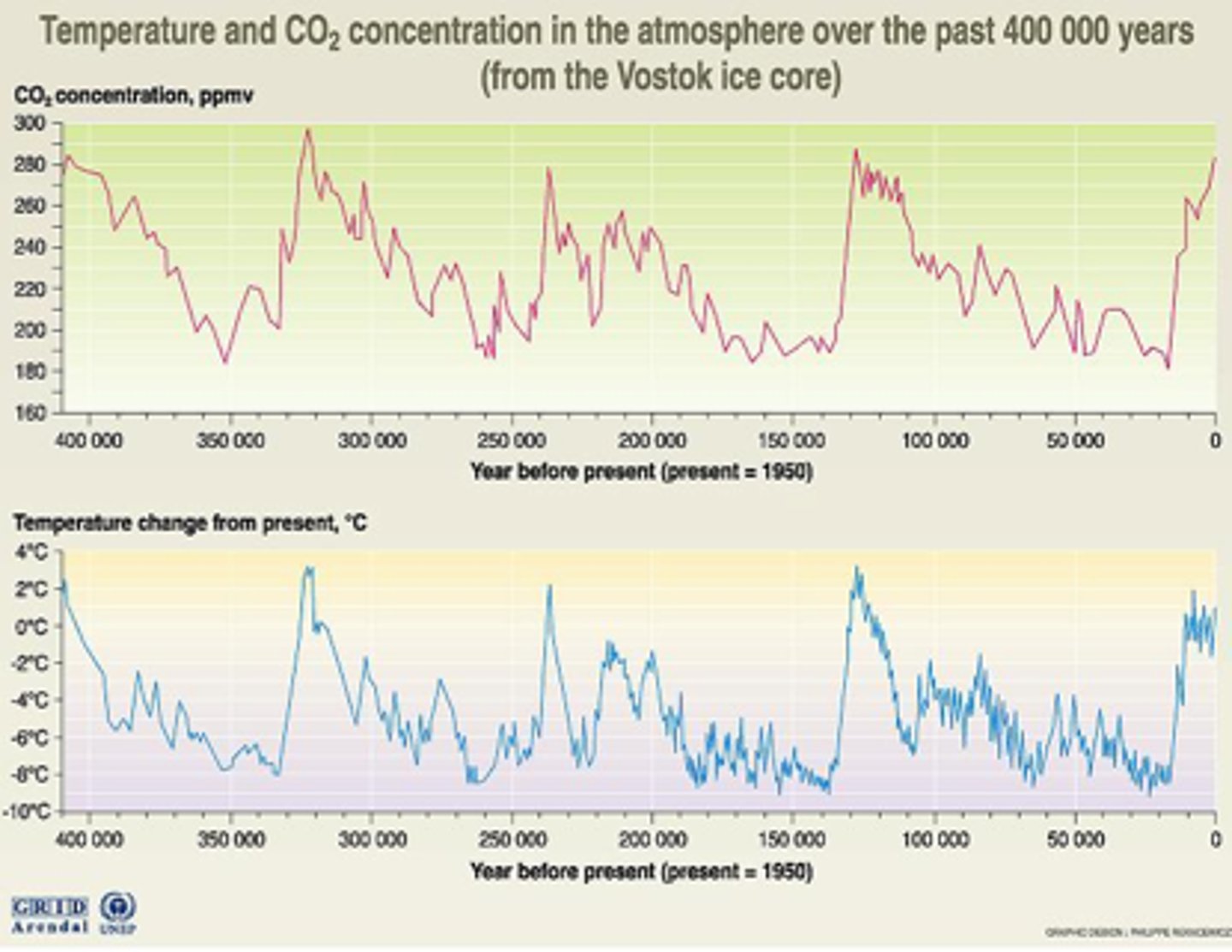
What are Milankovitch Cycles?
Milankovitch Cycles - natural variations in Earth's orbital configuration. They cause big changes in Earth's energy balance
Eccentricity(100,000 yr cycle)
Obliquity(41,000 yr cycle)
Precession(26,000 yr cycle)
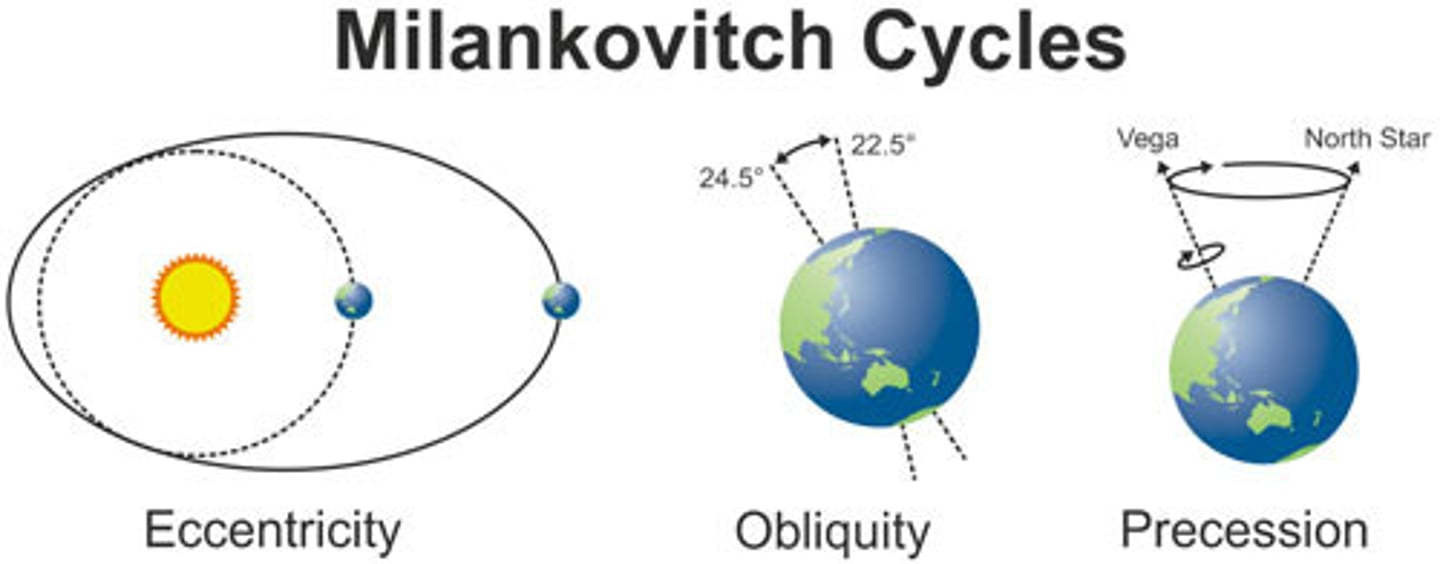
What is eccentricity?
Varies from a circular to elliptical orbit which lasts 90,000-100,000 years
What is obliquity?
Varies between 22.2° and 24.5°
Seasons are caused by this tilt
Tilt is 23.5° currently
Smaller angles = smaller differences in temperature between winter and summer
Cycle lasts 41,000 years
What is a precession of the Earth?
A slow change or wobble in the orientation of the Earth axis which affects the relationship between Earth's tilt and eccentricity. (26,000 yrs)
What are the orogenies in the western Cordillera?
1. Antler (Devonian-Pennsylvanian)
2. Sonoma(Permian-Triassic)
3. Nevadan(Jurassic-Cretaceous)
4. Sevier(Cretaceous-Paleogene)
5. Laramide(Cretaceous-Paleogene)
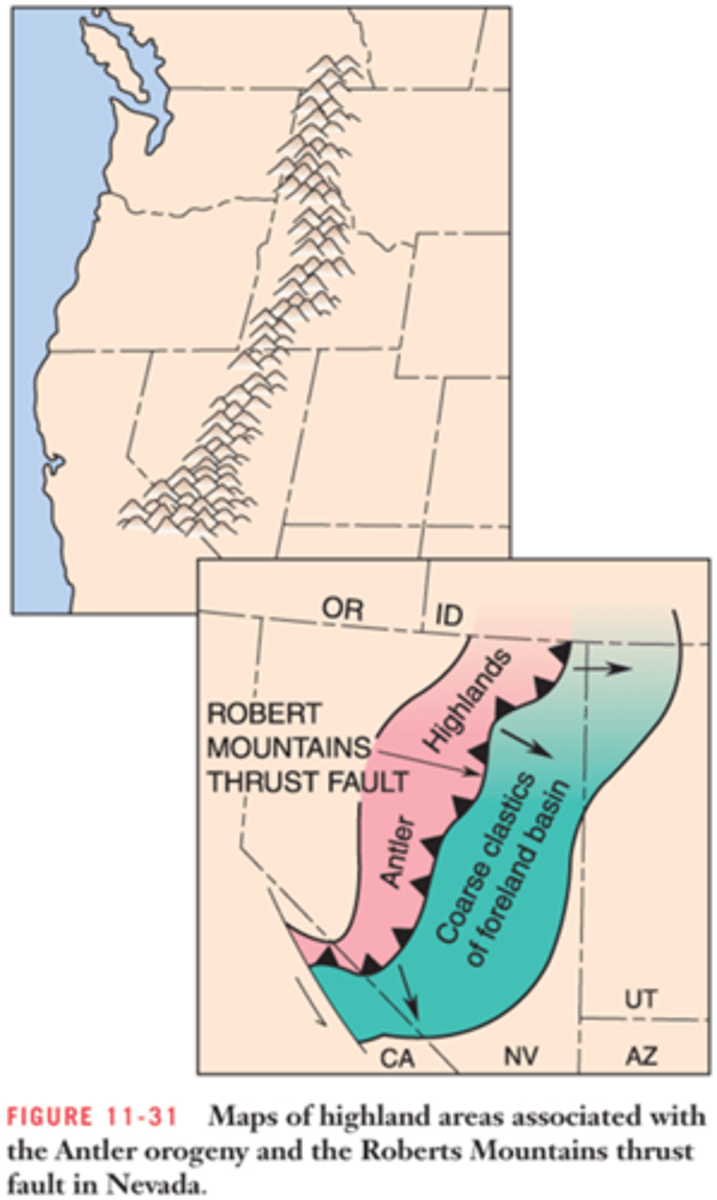
Antler Orogeny
Late Devonian to Mississippian deformation that affected the Cordilleran mobile belt from Nevada to Alberta, Canada.
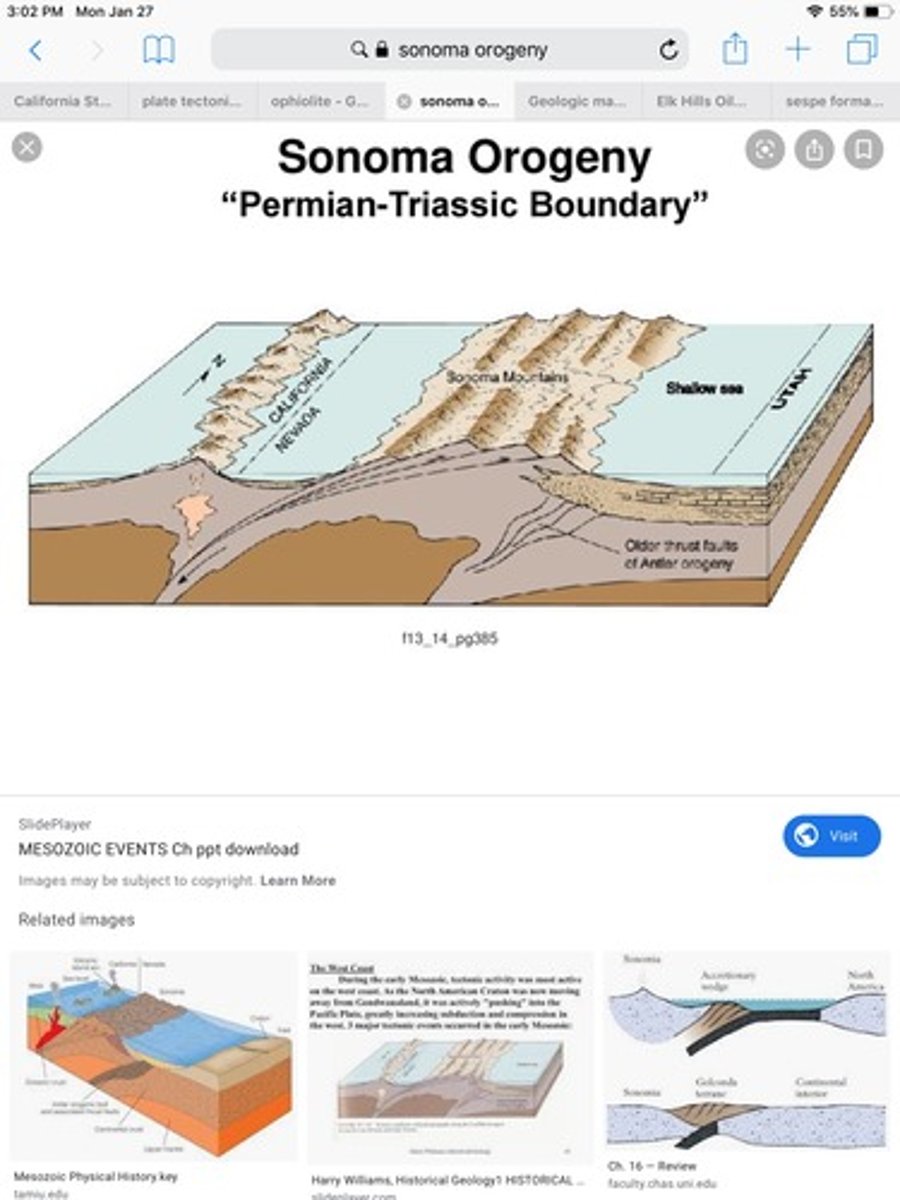
Sonoma orogeny
Permian-Triassic orogeny caused by the collision of an island arc with the southwestern margin of North America
Nevadan Orogeny
Subduction led to deformation and magma generation (continental volcanic arc)
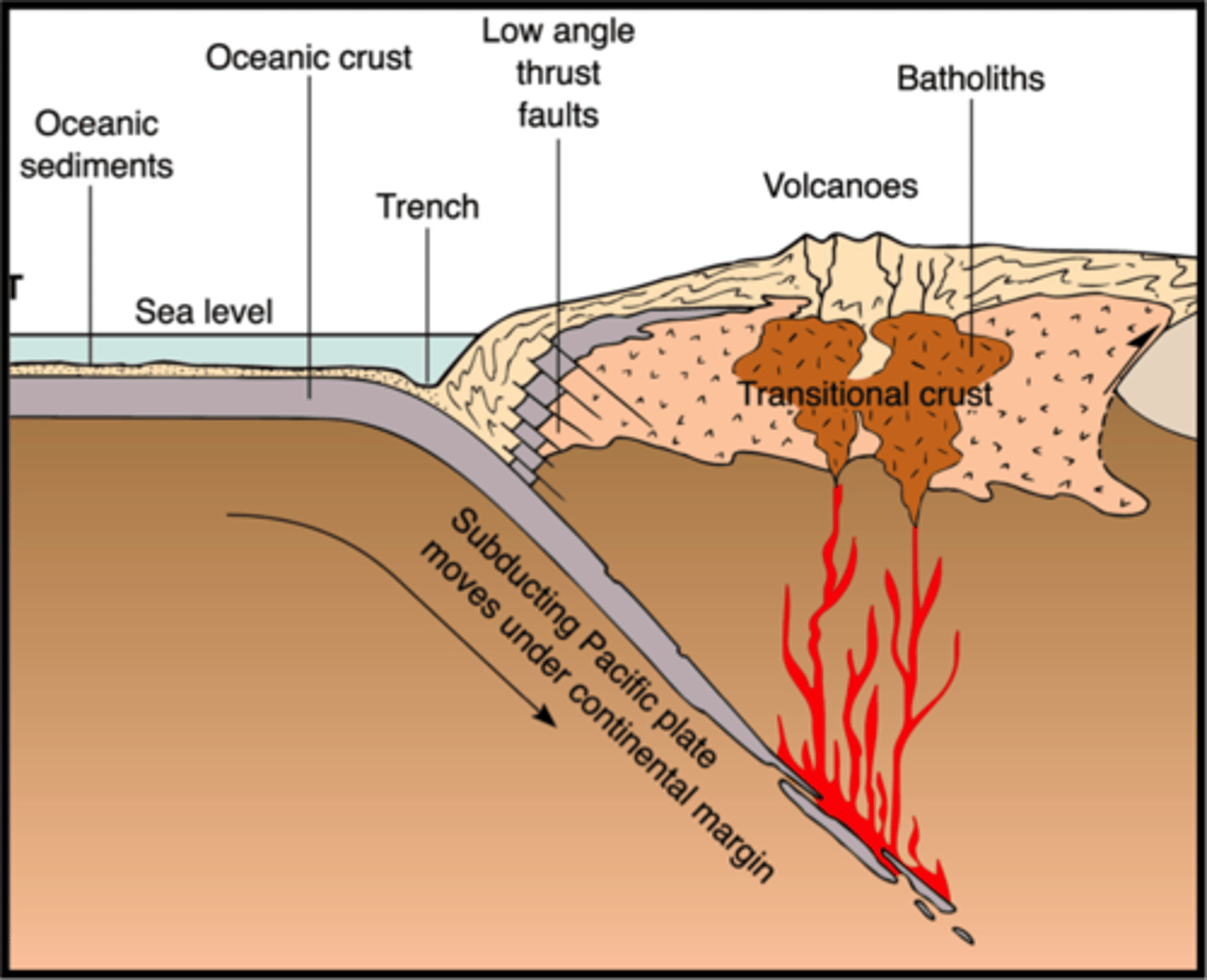
Sevier Orogeny
A mountain-building event that affected western North America between about 150 Ma and 80 Ma, a result of convergent margin tectonism; a fold-thrust belt formed during this event.
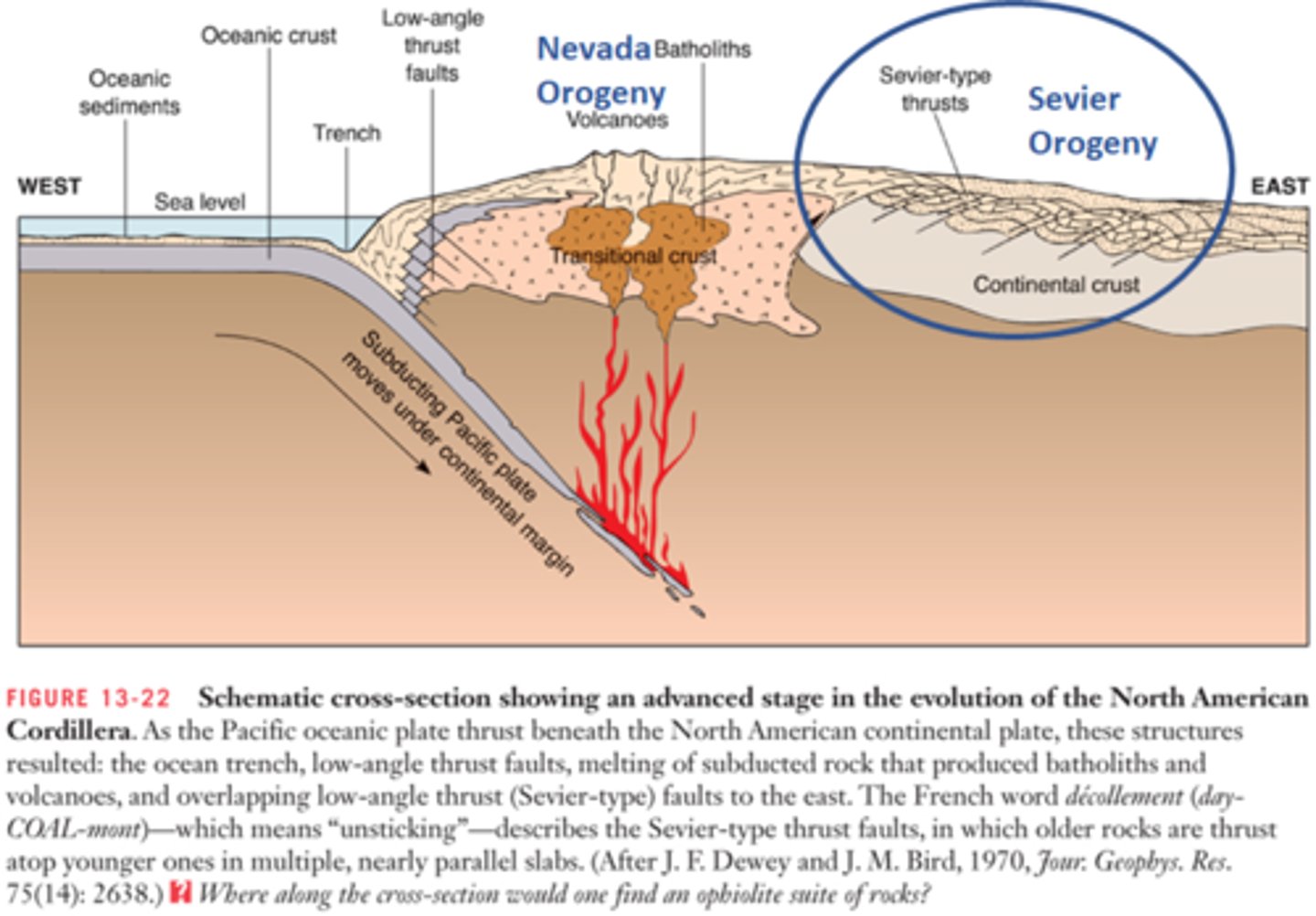
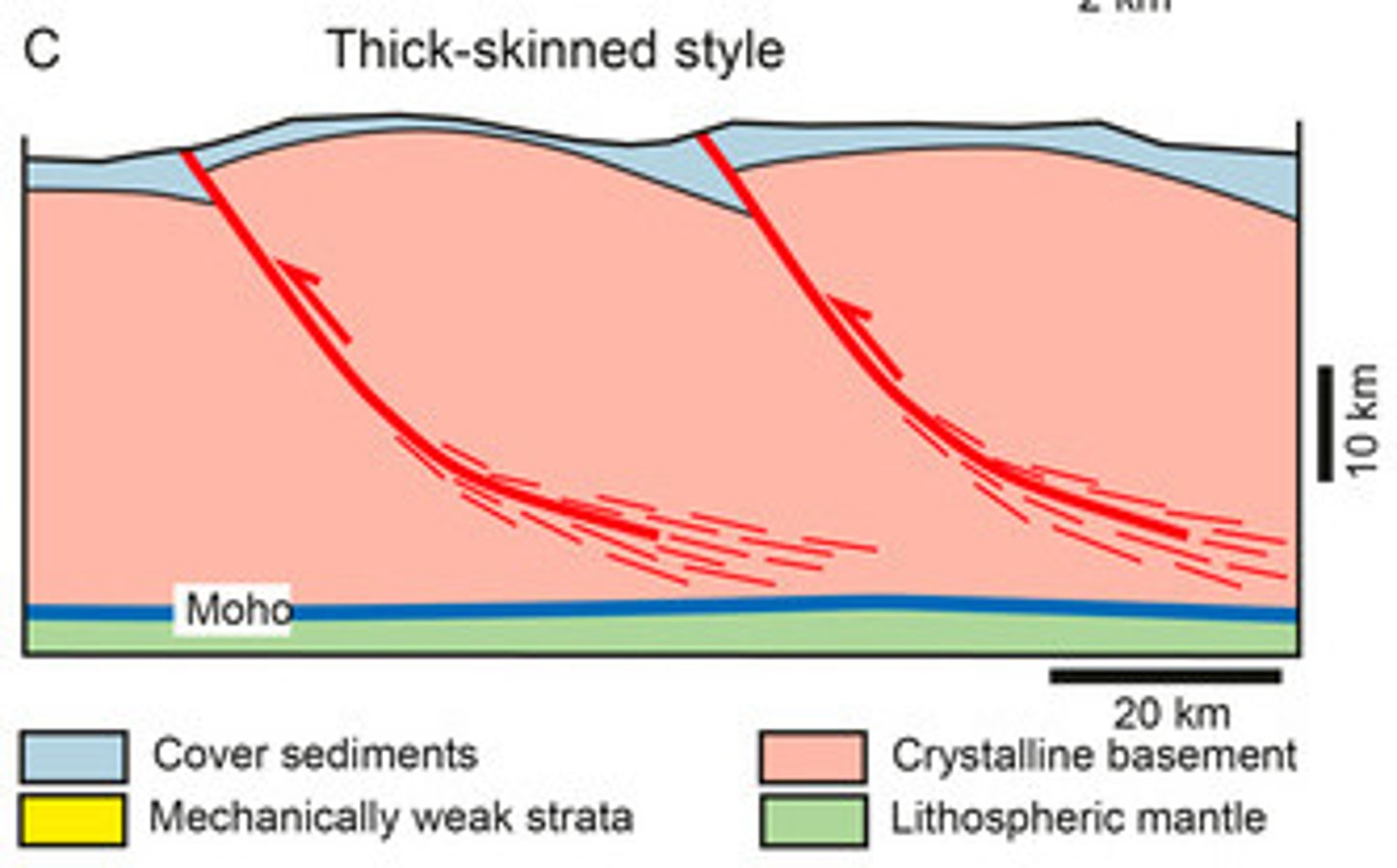
Laramide Orogeny
The mountain-building event that lasted from about 80 Ma to 40 Ma, in western North America; in the United States, it formed the Rocky Mountains as a result of basement uplift and the warping of the younger overlying strata into large monoclines.
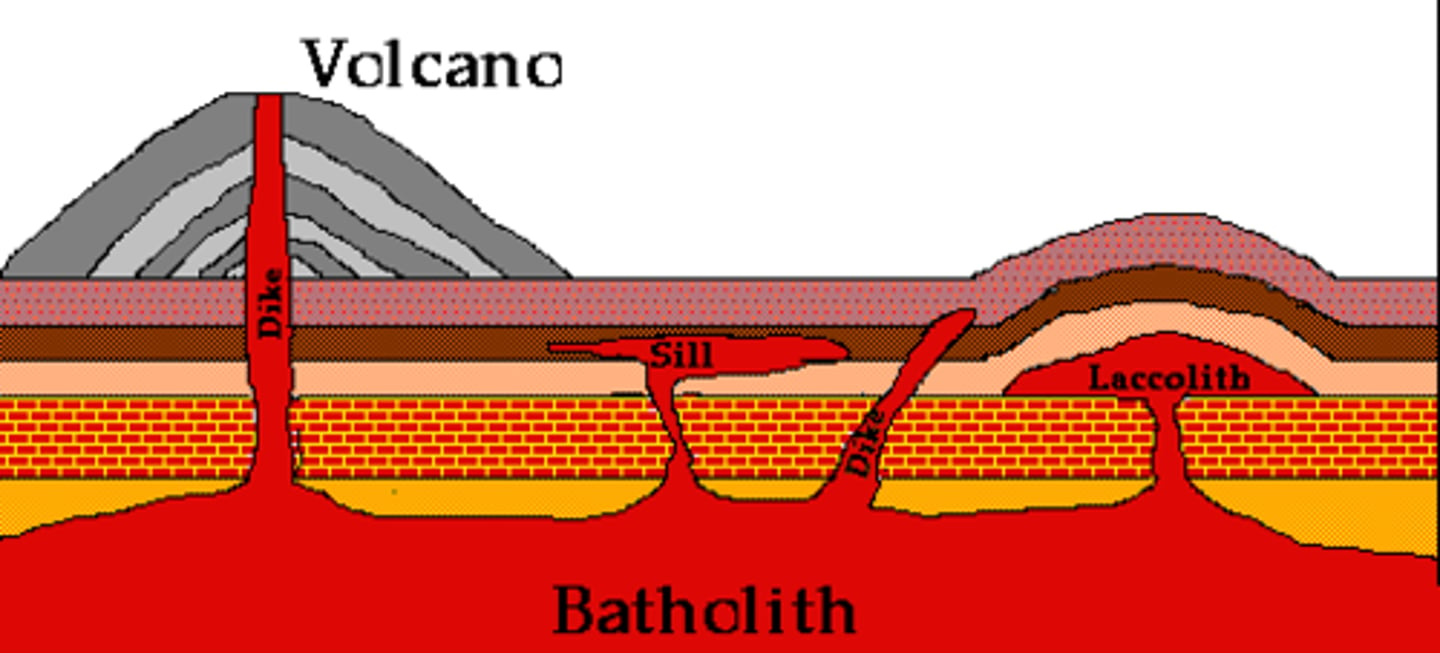
What is a batholith?
Batholith - large emplacement of intrusive igneous rock that cooled deep within the crust
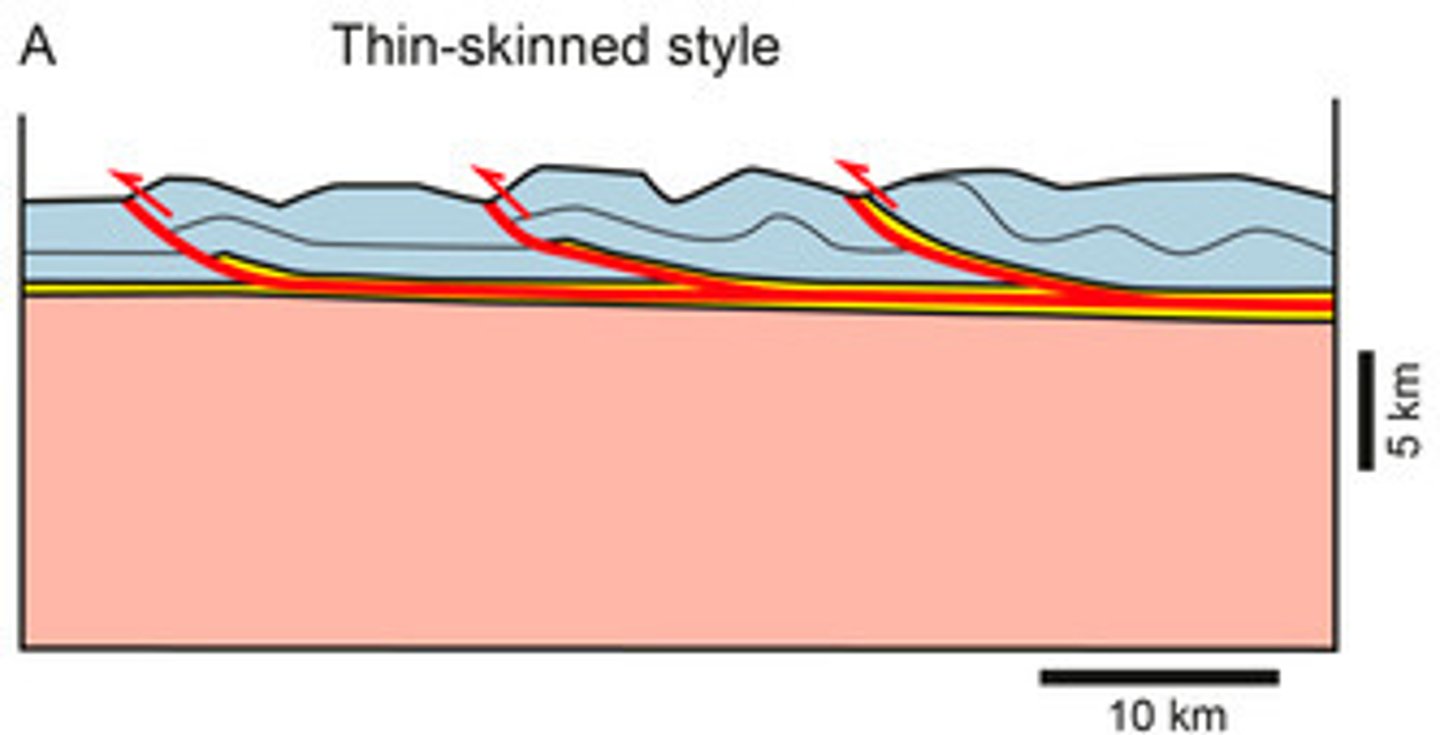
Thin-skinned deformation
refers to deformation without involvement of the basement (Sevier-type deformation)
Thick-skinned deformation
refers to deformation that involves basement (Laramide-type deformation)
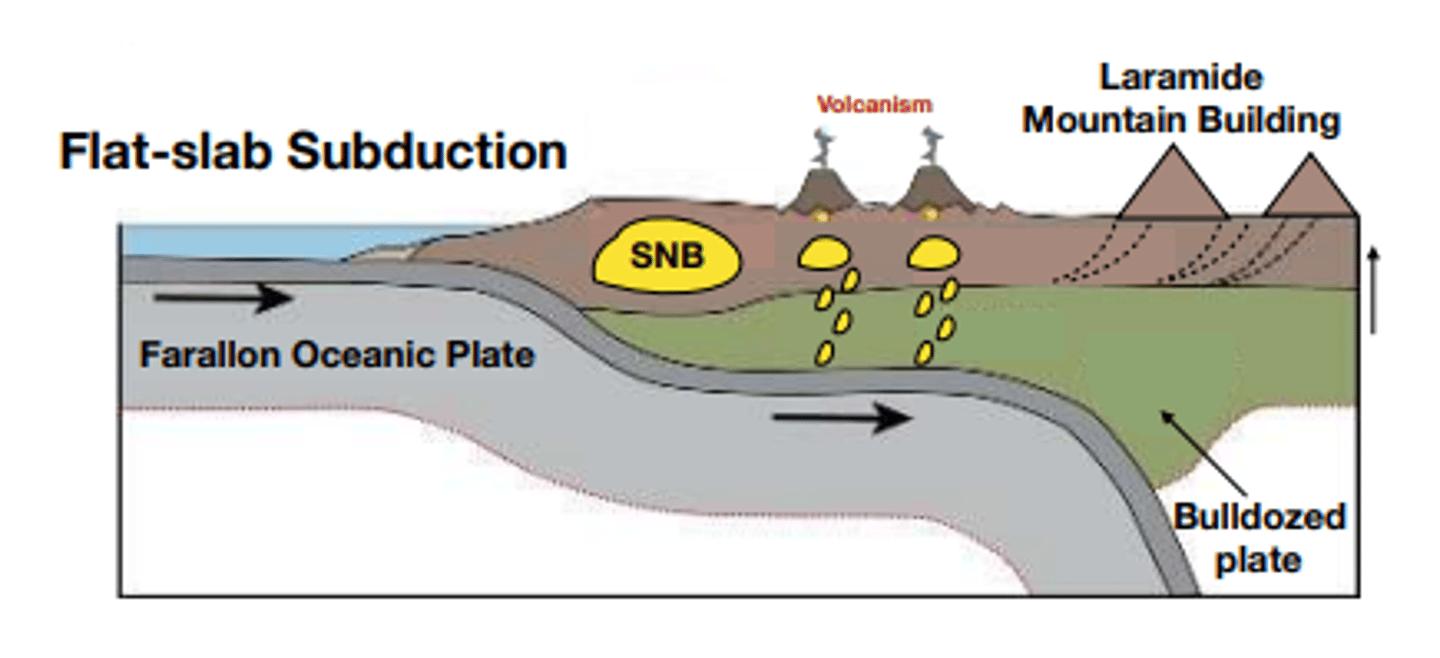
flat-slab subduction
The Farallon Plate subducted under the North American plate at a relatively low angle (Why? We don't really know...)
The underlying oceanic lithosphere caused drag on the root of the overlying North American Plate
What are the geologic time intervals?
Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Mississippian, Pennsylvanian, Permian, Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous, Paleogene, Neogene, Quaternary
Come Over Some Day, Maybe Play Poker, Try Jeff's Crazy Pizza-Nacho-Queso