Tectonics
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Crust
thin, solid, outer layer of Earth
Mantle
thick, mostly solid layer of Earth
Outer core
liquid layer composed mainly of iron and nickel
Inner core
solid, dense centre made of iron and nickel
Lithosphere
crust and mantle, made up of 15 massive pieces known as tectonic plates
Asthenosphere
The thin zone of the mantle just beneath the lithosphere
Continental drift
movement of continents due to the motion of tectonic plates
Convergent (destructive)
where two tectonic plates collide, sometimes subduction occurs. Slow movement, forms ocean trenches and mountains
Divergent (constructive)
where two tectonic plates move apart
Transform (conservative)
where two tectonic plates slide past each other
Movement of plate tectonics
Convection currents circulate the mantle, hot magma rises to the surface where it cools, becoming denser and sinking back down
Fault
a break in the Earth’s surface where tectonic plates slide past each other
Epicentre
point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus
Intensity
measure of the amount of destruction caused by an earthquake
Magnitude
measure of energy released by the earthquake
Moment magnitude scale
logarithmic scale used to compare the amounts of energy released by earthquakes
Focus
point within the crust where an earthquake originates
Earthquake
shaking of the ground caused by the sudden release of energy along a fault line
Hotspot
hot magma rising through the surface, causing volcanic activity away from a fault line
Rift
zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart
Seafloor spreading
divergent plate boundaries creating a new ocean floor
Seismic wave
vibrations along the earth’s surface generated during earthquakes
Ocean ridges
underwater mountain ranges created by tectonic plates diverging, newest crust formed closest to it
Evidence of plate tectonics
Continental drift, sea floor spreading, subduction, fossil Evidence
Primary waves
Fastest, travel through solids, liquids and gases, longitudinal
Secondary waves
Slower than P waves, travel only through solids, transverse
Surface waves
Travel along the Earth’s surface, cause the most damage during earthquakes
Ring of fire
where most of the world's earthquakes and volcanoes occur, pacific plate
Volcano
opening in the crust where molten rock, gases and ash escape from earth's interior
What’s formed when 2 continental plates divide
great rifts and valleys
What’s formed when 2 oceanic plates divide
seafloor spreading, where molten lava rises to the surface to form new plate
Normal fault
when the crust is pulled apart and one block drops down
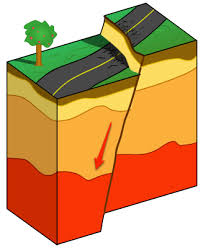
Reverse fault
when the crust is pushed together and one block is forced upward
Repeatability
getting the same result when same person uses the same equipment under same conditions
Reproducibility
getting same result with different people, equipment, or conditions involved