3A - cognitive processing
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
stages of memory
sensory memory
short term memory
long term memory
memory processes
encoding
storage
retrieval
what is encoding?
the conversion of incoming information into a mental construct that can be stored in the brain
types of encoding
acoustic encoding (incoming auditory input)
visual encoding (visual inputs like words images or faces)
elaborative encoding (connects or relates new inputs to existing memories)
semantic encoding (by meaning)
where does encoding happen?
in STM, where the main process is rehearsal of information
types of long term memories
explicit / declarative memories (requires some level of concious thought
> semantic (facts - WHAT)
> episodic (events - WHEN)
implicit / procedural memory (not in conscious behaviour)
> procedural (how to do)
types of amnesia
retrograde amnesia - loss of memories from BEFORE a time/event
anterograde amnesia - loss of memories from AFTER a time/event
the multistore model (diagram) and who it was made by
Atkinson and Shiffrin, 1968
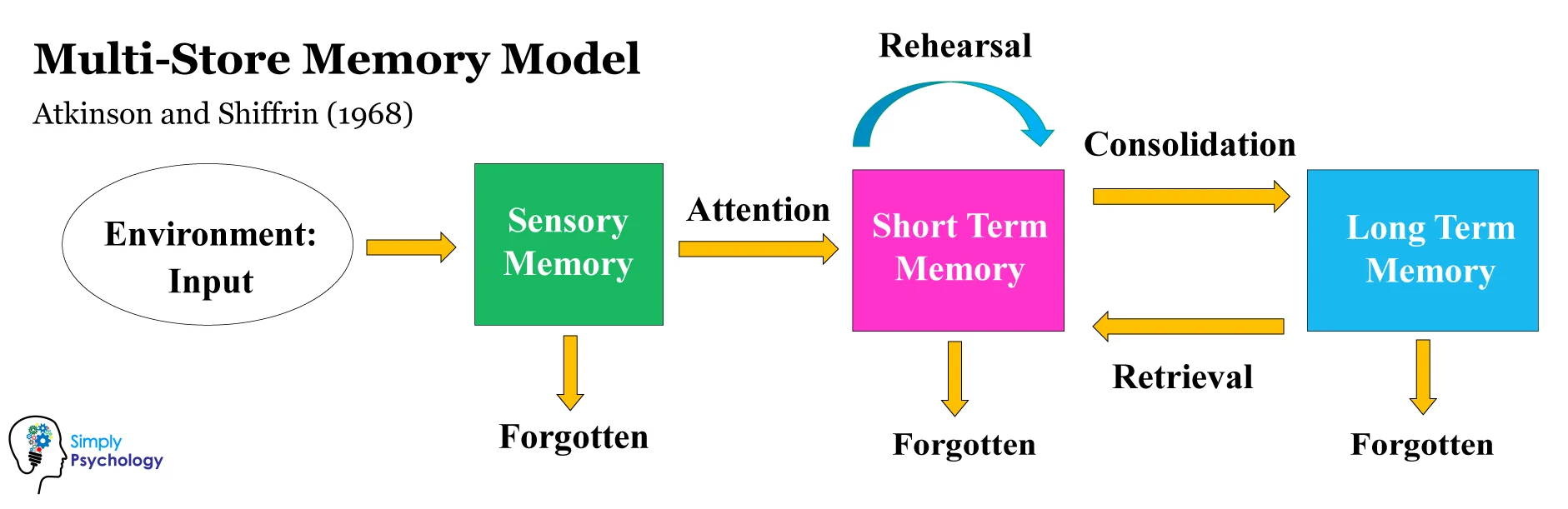
capacity and duration of sensory memory
unknown capacity
duration of ~500 milliseconds
*attention is a key factor
capacity and duration of short term memory
capacity of 7 ± 2 itens , or more recently suggested 4 chunks
duration of ~ 30 secs
*rehearsal is key for transferral to LTM. info not rehearsed is lost to either displacement or decay
capacity of long term memory
unknown capacity (thought to be unlimited)
information is though to be stored semantically
types of LTM memory loss
interference - different memories integrate and become indistinguishable
decay - memories fade over time
retrieval failure (aka cue dependent or context dependent forgetting) - memory cannot be retrieved due to missing stimulus / cue / context which likely was relevant to the initial encoding of it
types of rehearsal
elaborative rehearsal - thinking about the MEANING of a stimulus item
maintainance rehearsal - just repetition