Antimicrobials
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is Antimicrobial Chemotherapy?
When a drug is used to control a infection.
What are Antimicrobial drugs?
A class of compounds which inhibit or kill microorganisms.
What are antibiotics?
NATURAL antimicrobal drugs.
What are synthetics?
Man made antimicrobials.
What are Semisynthetics?
Antibiotics which have been chemically modified.
What are Broad spectrum agents?
Agents that target a wide variety of pathogenic bacteria.
What are Narrow spectrum agents?
Agents target only a narrow subset of pathogens.
Who discovered pencicillin
Alexander Fleming.
What is the main source of our useful antibiotics?
Streptomyces and Bacillus which are bacteria
Penicillium and Cephalosporium which are fungi
What is the trick if one were to “design” an antibiotic?
find something the target pathogen has or does (e.g. a structure or pathway) which the host cell doesn’t.
What is the Therapeutic Index?
Ratio of a drug’s toxic dose to its minimum therapeutic dose.
Which is better:
20ug/ml toxic dose: 16ug/ml effective dose = 1.25
20ug/ml toxic dose: 2ug/ml effective dose = 10
The second option is better because it has a higher Therapeutic Index of 10, indicating a larger safety margin between toxicity and effectiveness.
If you’re marketing a new drug, which is better to have?
A high Therapeutic Index, as it implies a greater safety margin and reduced risk of toxicity.
What Inhibits of cell wall formation?
penicillins and cephalosporins
What Inhibits cell membrane function?
Polymyxins
What Inhibits DNA synthesis?
Ciprofloxacin
What Inhibits ribosomes/protein synthesis?
Tetracyclines, Erythromycin
What Inhibits metabolic pathways?
Sulfa drugs
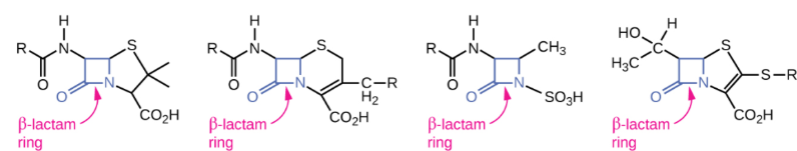
What are the 4 types of beta-lactam antibiotics? and what do they do?
Penicillins
cephalosporins
monobactams
carbapenems
They All have a “ß-lactam ring” and they inhibit cell wall synthesis.
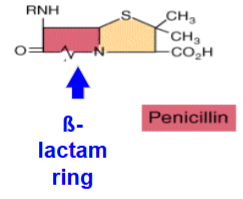
Name the members of the penicillin family. and what do they look like?
Penicillin
Amoxicillin
Ampicillin
Carbenicillin
They have a house like shape
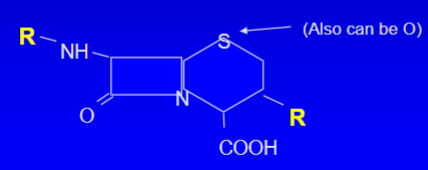
Where were Cephalosporins first found from.
They were first isolated from Cephalosporium acremonium and they are similar to penicillins due to their Beta-lactam ring. (most of them have the root “cef” in their name)
They also have two sites for the placement of R groups
Name some members of the Cephalosporins family?
Cephalothin (1st)
Cefotiam (2nd)
Moxalactam (3rd)
Cefepime (4th)
What are 2 Metabolic pathway inhibitors?
Trimethoprim
Sulfanilamides (sulfa drugs)
What are Trimethoprim and Sulfanilamides metabolic analogs of? What does this chemical do?
They are metabolic analogs of PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid), it is necessary for the synthesis of folic acid. Folic acid is required for the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines
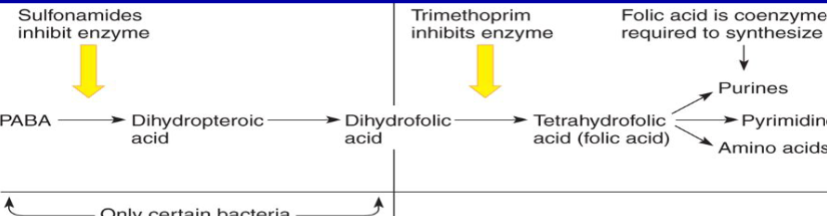
What inhibitor stops the creation of Dihydropteroic acid?
Sulfanilamides inhibit the enzyme responsible for this reaction.
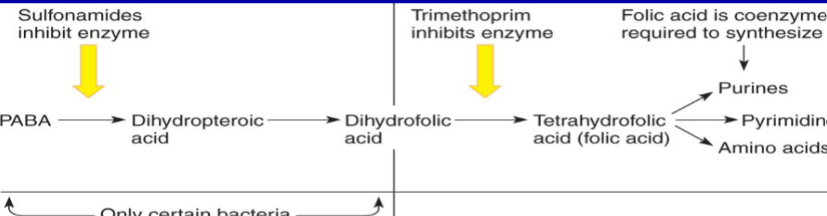
What inhibitor stops the creation of Tetrahydrofolic acid (folic acid)?
Trimethoprim inhibits the enzyme.
What inhibitors inhibits protein synthesis
Tetracyclines, Macrolides, and Aminoglycosides
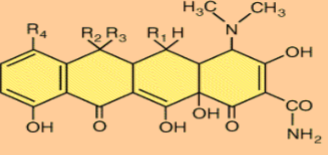
What is Tetracyclines and What is it derived from?
Tetracyclines is a semisynthetic drug that binds to ribosomes, is bacteriostatic, and is broad spectrum.
They are derived from the natural antibiotic Streptomyces species.
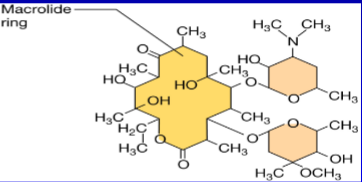
What is Macrolides and what is it derived from? What are examples of Macrolides?
It is a Ribosome-binding antibiotic derived from Streptomyces erythraeus it is also bacteriostatic. Examples: erythromycin,azithromycin
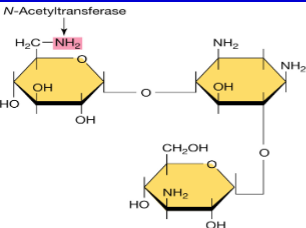
What is Aminoglycosides and what is it derived from? What are examples of Aminoglycosides?
Derived from Streptomyces, also ribosome-binding but bactericidal. Example: streptomycin, kanamycin, gentamicin, neomycin.
What is Fluoroquinolones and when was it discovered? How does it work? What are examples of Fluoroquinolones?
Fluoroquinolones are synthetic antibiotics, are broad spectrum and work well on Gram negatives. They were discovered 15 years ago and work by inhibits DNA replication (primarily binds to and interferes with DNA gyrase-DNA complex).
What are two newer classes of Antibiotics?
Synercid (dalfopristin/quinupristin) and Zyvox (linezolid)
How are Synercid and Zyvox used?
They are narrow spectrum drugs used primarily against Gram positive pathogens such as Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, and Streptococcus.
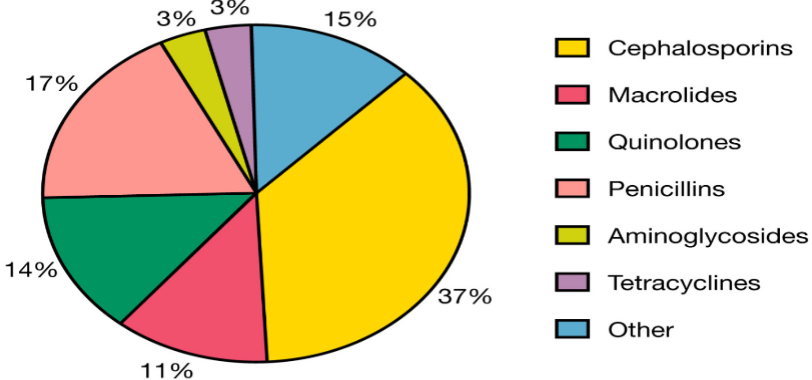
What is the most produced and used antibiotic?
Aminoglycosides.
What is a drug’s “therapeutic index”?
The toxic dose divided by the therapeutic dose
What was the estimated amount of antibiotics used in for agraculture? How much of that percentage is for “non-therapeutic” use.
84% and 70% of it was for “non-terapeutic use.
What is the One health concept?
The health of people is connected to the health of animals and the environment
What is a major factor in the rise in antibiotic resistance in bacteria?
Horizontal transfer of resistance genses
What family of antibiotics have a beta-lactam ring?
Penicillins and cephalosporins.
What antibiotic family inhibits a portion of the folic acid pathway?
Sulfonamides (Sulfa drugs) and Trimethoprim.
What are the mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance?
Efflux pump, Blocked penetration, Inactivation of enzymes and target modifications
Name the antibiotics effected by Efflux pump.
Fluroquinolones
Aminoglycosides
Tetracyclines
Beta-Lactams
Macrolides
Name the antibiotics effected by Blocked penetration.
Beta-Lactams
Tetracyclines
Fluoroquinolones
Name the antibiotics effected by Target modification
Fluroquinolones
Rifamycins
Vancomycin
Beta-Lactams
Macrolides
Aminoglycosides
Name the antibiotics effected by Inactivation of enzymes
Beta-Lactams
Aminoglycosides
Macrolides
Rifamycins
What is Beta-lactam?
A class of antibiotics that inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, including penicillins and cephalosporins.
What is a Beta-lactamase inhibitor?
A substance that blocks the action of beta-lactamase enzymes, allowing beta-lactam antibiotics to effectively target bacteria.
What is Beta-lactamase?
An enzyme produced by bacteria that breaks down beta-lactam antibiotics, rendering them ineffective.
What are the possible sides effects of antibiotics?
Tissue toxicity -- kidneys, liver, heart, skin, nerves, teeth and bones
Allergic reactions (sensitized on first contact) (often due to reaction to a metabolic byproduct)
Disruption of “normal flora” of the body
(frequent cause of diarrhea) (Superinfection-- secondary infection caused by destruction of normal microflora.)
How do you determine what the right antimicrobial drug?
Identify (if possible) the agent
Determine (if possible) the susceptibility of the agent
(Kirby-Bauer susceptibility test)
(Minimum Inhibitory Concentration = minimum concentration of a drug that visibly inhibits growth)