26.2 The properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Why does radiation make air conduct electricity?
it ionises air
How many types of radiation are there?
3
what are the three types of radiation?
Alpha, beta, gamma
How do magnetic fields affect alpha, beta and gamma particles?
alpha and beta are deflected in opposite directions
gamma is not affected
What can be concluded from how magnetic fields affect alpha, beta and gamma?
alpha is positive
beta is negative
How can the ionisation effect be measured?
ionisation chamber and picoammeter
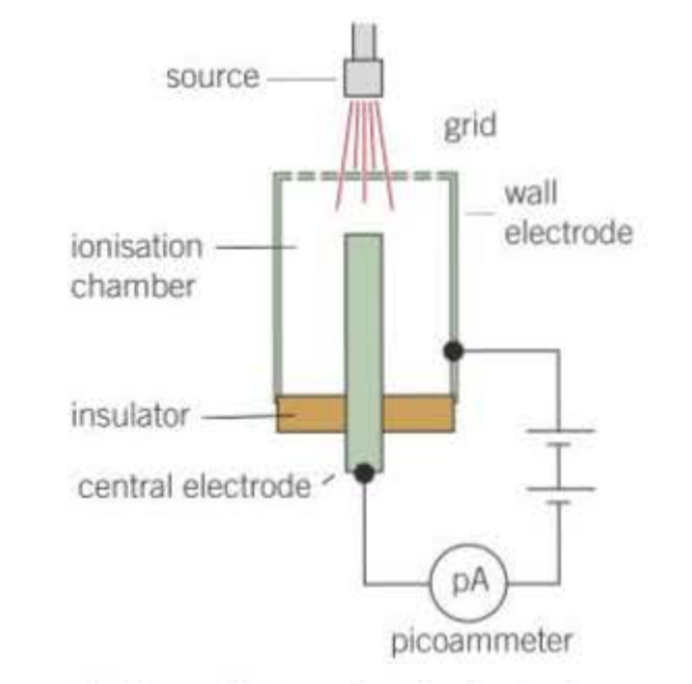
How does an ionisation chamber and picoammeter produce current?
ions created in the chamber are attracted to the oppositely charged electrode where they are discharged
electrons pass through the picoammeter due to ionisation is the chamber
the current is proportional to the number of ions per second created in the chamber
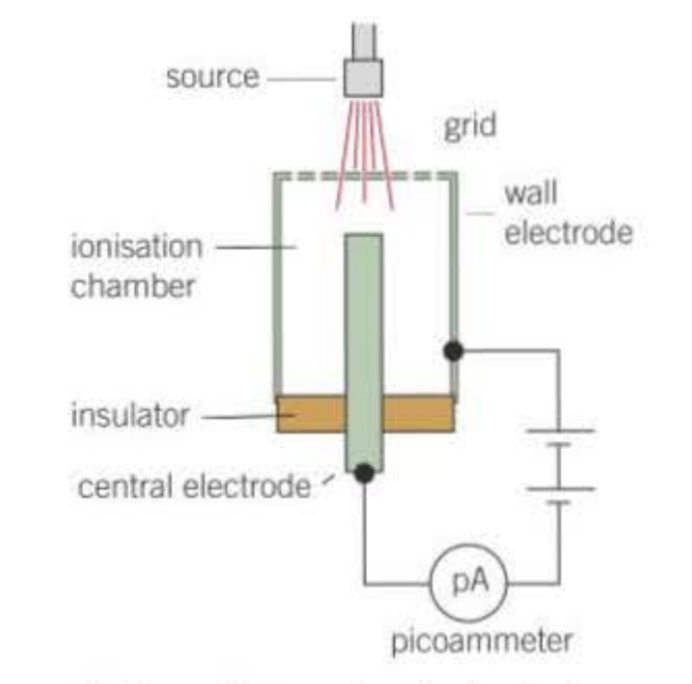
What type of radiation has the strongest ionisation?
alpha
What happens when you move the alpha source away from the chamber?
the ionisation effect weakens as alpha has a small range in air
Beta particles have ___________ range than alpha particles
larger
How long is a beta particle’s range?
over a meter
A beta particles produces _______ ions per mm than an alpha
less
Gamma radiation has a __________ ionisation effect that alpha and beta
smaller
Why does a gamma particle have smaller ionisation effect?
photons do not carry a charge
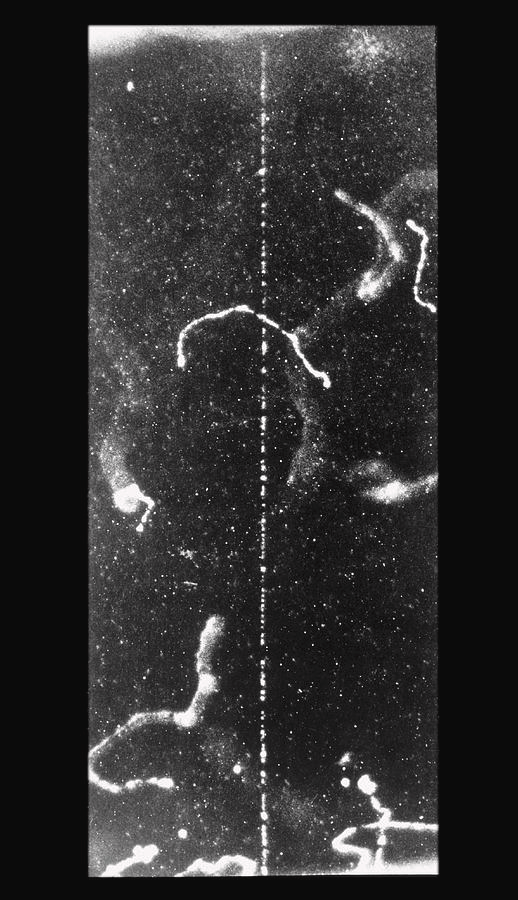
What does a cloud chamber contain?
air saturated with vapour at a very low temperature
Why do radiation particles leave a visible track in a cloud chamber?
ions produced by ionising particles trigger the formation of droplets in the supersaturated vapour
What kind of tracks do alpha particles leave?
visible straight tracks of the same length
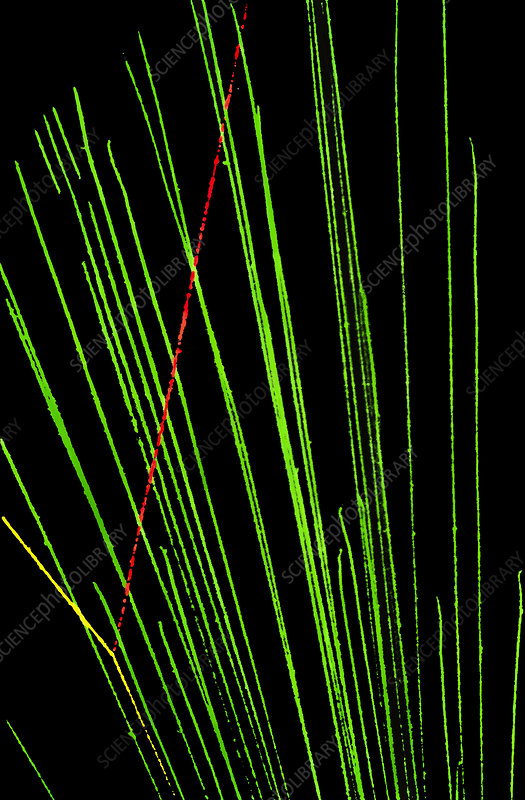
Why do alpha tracks have the same length?
same range
What kind of tracks do beta particles leave?
wispy
Why do beta particles leave wispy tracks?
collision with air particles
Why are beta tracks hard to see?
they are less ionising
count rate
number of counts/ time taken
How do you find the count rate using a Geiger tube?
Place the geiger tube at a fixed distance from the source
measure the count rate with the source
measure the background count
count rate= count rate with source- background count
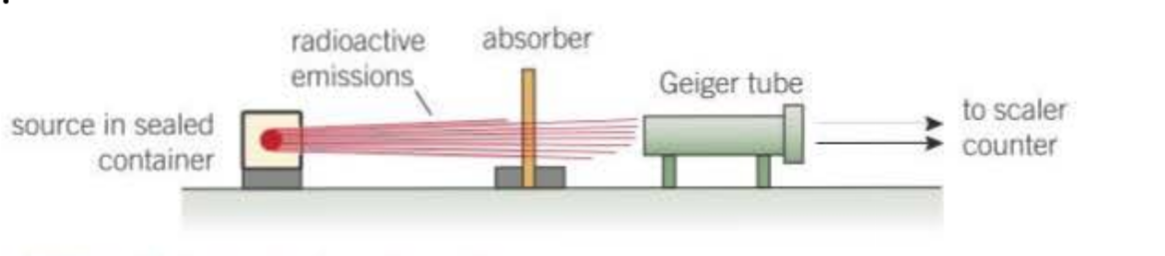
How can you measure the effect of absorbers on the count rate?
place absorbers of different materials/thickness and find count rate
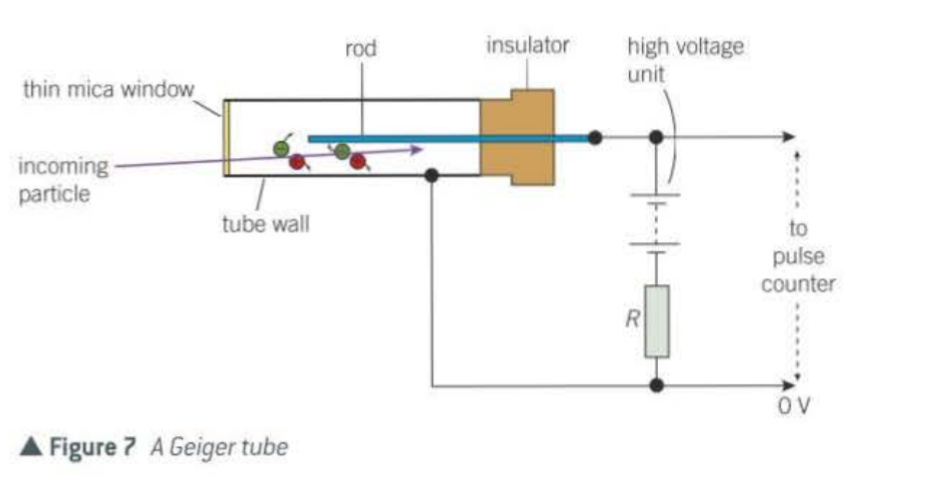
What does the Geiger tube consist of?
sealed metal tube with argon gas at low pressure
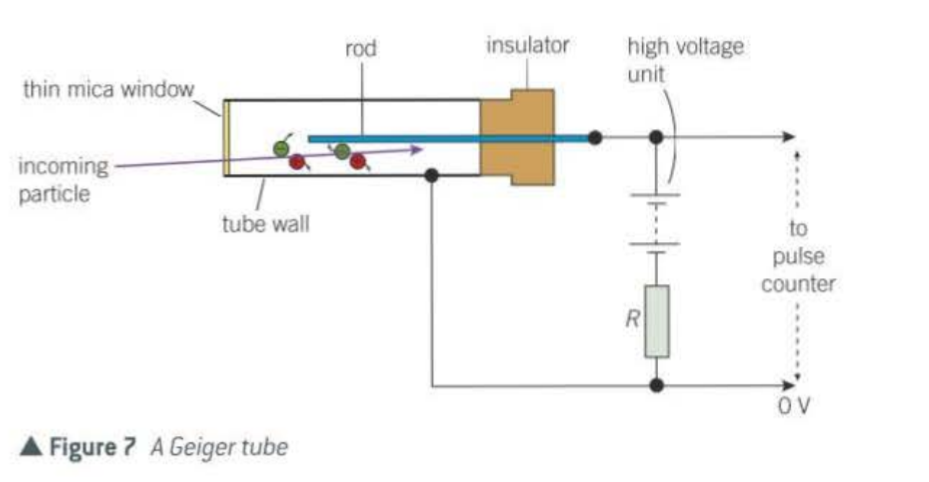
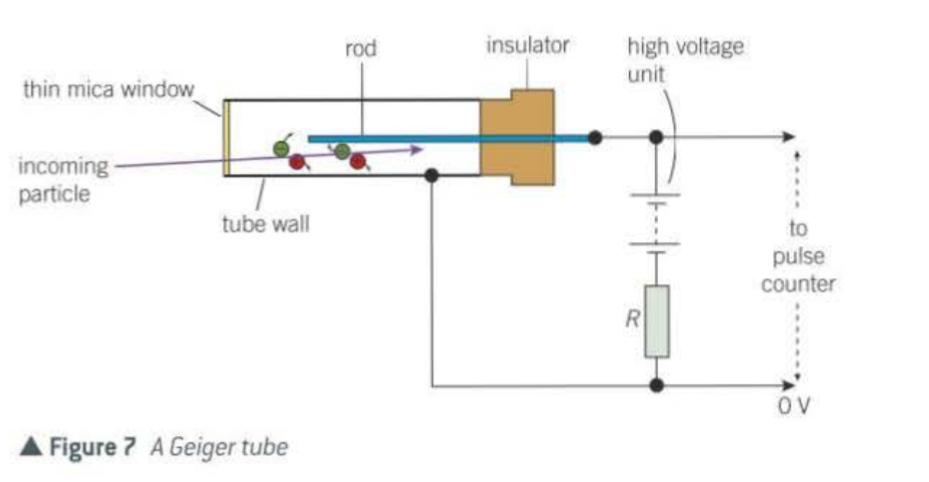
How does the Geiger counter work?
An ionising particle ionising the gas atoms when it enters
negative ions are attracted to the rod
positive ions to the wall
ions accelerate and collide with other gas atoms and create further atoms
until so many ions are created a pulse of charge flows through R causing a voltage pulse which is recorded as a count
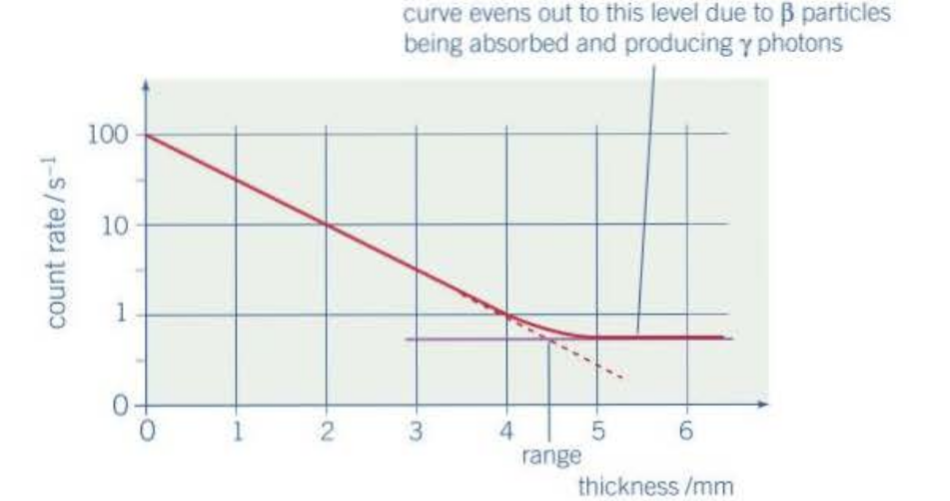
How do we know the range of particles?
count rate decreases as source is moved further
Why does the range differ for different sources?
different initial kinetic energies
Faster beta particles travel ___________ in air than slower beta particles
further
The proportion of gamma photons from the source entering the tube decreases according to the
inverse square law
Range of alpha in air
fixed range which depends on energy
up to 100mm
range of beta in air
up to 1m
range of gamma in air
inverse square law
deflection of alpha in a magnetic field
deflected
deflection of beta in a magnetic fiedl
deflected in the opposite direction to alpha
deflection of gamma in a magnetic field
not deflected
absorption of alpha
stopped by paper or thin metal foil
absorption of beta
stopped by ~5mm aluminium
absorption of gamma
stopped/reduced by thick lead
ionisation effect of alpha
produces ~10,000 ions per mm
ionisation effect of beta
produces ~100 ions per mm
ionisation effect of gamma
very weak
energy for a particle of alpha
cons
energy for a particle of beta
varies up to max for a given source
energy for a gamma photon
constant for a given source