R3.1: Proton transfer reactions
1/177
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
Acids are good
conductors of electricity
Strong acids
disassociate completely into ions in water
Boron is stable with just 6 electrons but can
accept 2 more although it’s an exception to the octet rule
Bases are proton
acceptors
Acids are proton
donors
Older (Arrhenius’ definition) concluded that all acids have
[H+] and all bases have [OH-]
More relevant Brønsted & Lowry theory proposes that
Brønsted & Lowry acids are proton donors and Brønsted & Lowry bases are proton acceptors. Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors and Lewis base are electron pair donors
Acid disassociation is as follows
HA + H2O → A- + H3O+
Hydronium (H3O+) is the
main ion in acidic solution and follow iconic acid base behavior theory. It can also be expressed as [H+]
Binary acids are made of a halide and hydrogen and increase in strength
across a period and down a group. They include HF, HCl, HBr, and HI
Oxyacids acids are polyatomic ions including
HNO3, H2SO4, H2CO3, and H3PO4
Weak acids have strong
conjugate base pairs and vise versa
Strong acids have weak
conjugate base pairs and vise versa
A conjugate pair is made up of a substance and its form after
protonation or deprotonation
Conjugate pairs should only differ by
1 proton
Organic acids are almost exclusively
weak acids
Acids chip away
bases by donating protons
Mineral testing for calcite (CaCO3) includes a drop of
acid that causes the solution to bubble in calcite presence due to the reaction forming gas (CO2)
Monoprotic acids can only donate
1 H+
Diprotic acids can donate only
2 H+
Triprotic acids can donate only
3 H+
Alkali or alkali earth metals and oxygen or hydroxides make
common bases
Some weak bases are
NaHCO3 (sodium hydrogen carbonate),Na2CO3 (sodium carbonate), NH3 (ammonia), and CH3CH2NH2 (ethanamine)
Amphiprotic substances include
HCO3- (hydrogen carbonate ion), HSO4- (hydrogen sulfate ion), H2PO4- (dihydrogen phosphate), HPO4(2-) (hydrogen phosphate), and H2O (water)
Amphiprotic means to be able to either
donate or accept protons
Amphoteric means to be able to either
display acid or base behavior
All amphiprotic substances are amphoteric but not
all amphoteric substances are amphiprotic
The disassociation of a strong acid is
exothermic the acid is happy and stable as an ion
NH4+ is a coordinate bond where H is
not very happy because its electron are lost to the more electronegative oxygen
the pH scale is between 0 to 14 but can extend to
infinity and negative infinity
Lithmus indicator turns blue in the presence of
base
Lithmus indicator turns red in the presence of
acid
pH is calculated with [H+] with the formula
pH=-log[H+] where base = 10
pOH is calculated with [OH-] with the formula
pOH=-log[OH-] where base = 10
[OH-] is calculated with pOH with the formula
[OH-]=10^(-pOH)
[H+] is calculated with pH with the formula
[H+]=10^(-pH)
To convert from pOH to pH, you
subtract it from 14 [14-pOH=pH] and vise versa
For strong acids and bases, the initial concentration of
[H+] or [OH-] is the same as the substance due to complete disassociation.
Methyl orange turns red in the presence of
base
Methyl orange turns yellow in the presence of
acid
Phenolphthalein turns colorless in the presence of
acid
Phenolphthalein turns purple/pink in the presence of
base
The iconic product of water is the value of equilibrium (K) of [H+] and [OH-] ions at 298K
Kw=1×10^(-14)
Since pH of water = 7
[OH-] = [H+] for ionic product of water @298K
H2SO4 is diprotic but
only its first disassociation is strong
The strength of an acid or base depends on its
degree of dissociation
Organic often see as little as
1% being dissociated into H3O+
Increased [H3O+] or [OH-] mean
stronger rather than weaker acids
Strong acids/bases have
good conductivity, more extreme pH values, and fast reactions with CaCO3 and Mg
The side of the reaction expression with the stronger acids/bases will
be the position to which equilibrium is leaning to
Log scales are used to
linearize data
Antacids neutralize
stomach acids
Metal oxides and acids create water and salt
M-O + H-A → MA + H2O
Metal hydroxides will react with water to create water and salt
M-OH + H-A → M-A + H2O
Hydrocarbons might react with water to create water, salt, and carbon dioxide
M-H-CO3 + H-A → MA + H2O+ CO2
Carbonates might react with water to create water, salt, and carbon dioxide
M-CO3 + H-A → MA + H2O + CO2
Amines might react with water to create water, salt, and carbon dioxide
RNH2 + H-A → NH4+ + A-
Ammonia might react with water to create water, salt, and carbon dioxide
NH3 + H-A → NH4 + A-
with a pH increase or decrease of 1, [H+] =
100 times stronger or weaker
Titration allows us to find
the concentration of an unknown acid or base and titrate it with a standard solution of which you know the concentration and understand its significance
The titrant is put into a small burette and added to a measured volume of acid w/ clear concentration
At half of its reaction, when the indicator is colored, and equivalence point is reached, acid and base are of equal concentrations and neutralization of reaction is reached.
The indicator often used for titration is
phenolphthalein
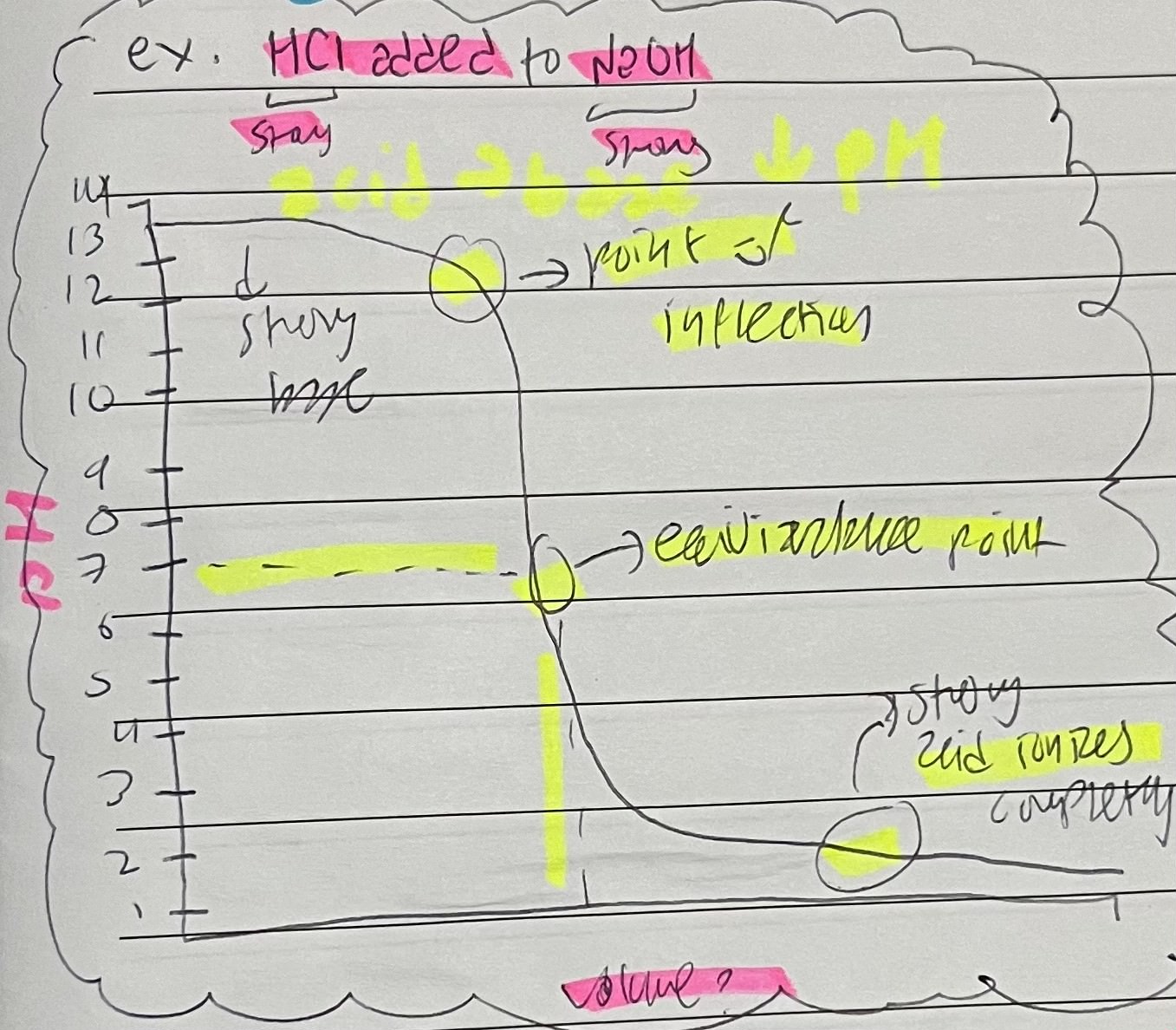
The sharp change in pH on a pH curve for the progression of a titration is called the
point of inflection (POI)
Base added to acid shows a
pH increasing curve
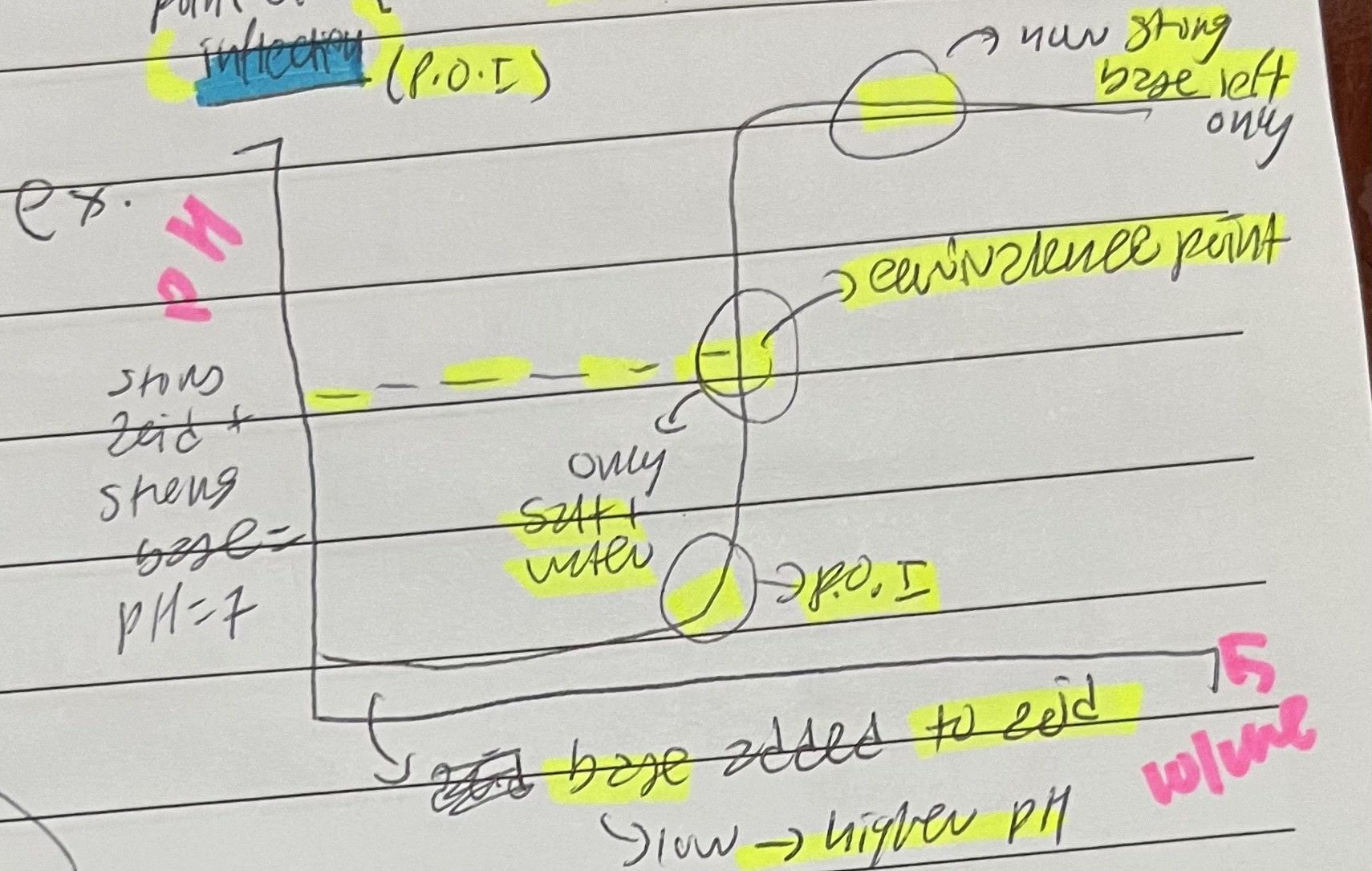
Acid added to a base shows a
pH decreasing curve
Complete disassociation is usually an
irreversible process
Organic acids can only donate hydrogens in their
carboxylic function groups because C-H is not polar so would not dissolve in polar substance
Bonds are better shorter as they are less
“diluted”
Water doesn’t break as much as acids break into
ions rather than form new molecules by breaking water
More concentrated acids are more
corrosive
More concentrated acids are not more
strong
Stronger acids mean they are
better proton donors
Oxyacids increase in strength with increased
oxidation of the central atom
Binary acids increase in strength
across the group and down a period
HCl is
hydrochloric acid
HNO3 is
nitric acid
H2SO4 is
sulfuric acid
HBrO is
hydrobromic acid
HI is
hydroiodic acid
HClO4 is
Perchloric acid
HClO3 is
chloric acid
CH3COOH is
ethanoic acid
HCO3 is
carbonic acid
H3PO4 is
phosphoric acid
HF is
hydrogen fluoride
H2SO3 is
sulfurous acid
HNO2- is
nitrous acid
LiOH is
lithium hydroxide
NaOH is
sodium hydroxide
KOH is
potassium hydroxide
BaOH2 is
barium hydroxide
NaO is
sodium monoxide
Ca(OH)2 is
calcium hydroxide
NH3 is
ammonia
C2H5NH3 is
Ethylamine
strong acid + strong base =
neutral salt
strong acid + weak base =
acidic salt
weak acid + strong base =
basic salt
Transition metals do not form very
strong bases
Effervescence is
the fizzing or pop that comes from gas being produced in liquid and coming out as bubbles (observable)