1.1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
systems architecture
comprises of hardware and the way all different components connect together
hardware
the physical component of a computer system both internal and external
the 4 components of a computer system
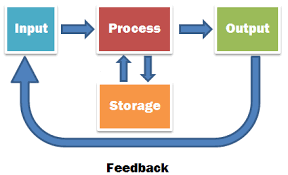
the necessity of 4 components
All computer systems have:
CPU
a minimum of one input device that gathers data
memory(primary storage) for program currently in use
a store/to store data in secondary storage
CPU(Central Processing Unit)
A small piece of hardware that performs all the calculation/processing in a computer
its main function is fetch-decode-execute
Transistors
Tiny switches that convert data into binary
billions of them make up a CPU
0 = off, 1 = on
RAM(Random Access Memory)
Where currently running programs/data/operating systems are stored.
All instructions need to be performed by the CPU are stored here
Stored Program Concept
Where program instructions/data are stored in the same memory(RAM)
this means the memory doesn’t need to be repeatedly entered
definition of Von Neumann Architecture
data vs program
programs- instruction/algorithm CPU executes
data- needs to be decoded in the CPU
Components of CPU
Internal Memory:
General Purpose Registers(Including program counter)
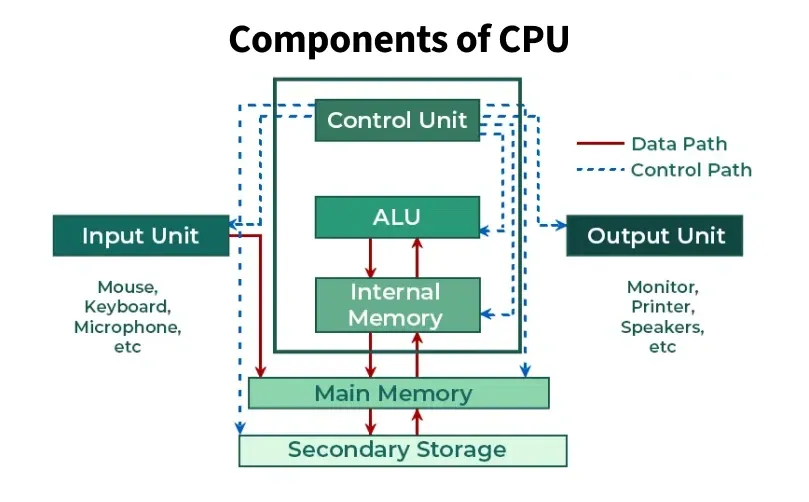
The ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
arithmetic operations(+,-,*)
logic operations(<,>,=)
shift operations(moving data , sort of alignment?)
The CU(Control Unit)
controls flow of data moving inside the CPU
times signals to other units
controls signals to direct operations within the CPU
Registers
a small amount of fast temporary memory within the processor where the ALU/CU can store & change values needed to execute instructions
Process in a register
program runs » stores value/calculations inside registers » small blocks of memory
works like a variable
Program Counter
a special purpose register that holds the address(location number) of the next instruction to be executed.
It’s located in the CU!
incremented(goes up by 1) after fetching an instruction.
Accumulator(ACC)
Stores the results of arithmetic/logic operations
speeds up process as data doesn’t have to be moved a further distance from main memory to CPU
MAR(memory address register)
holds the address of the current instruction being executed
MDR(memory data register)
stores:
data fetched from memory
data to be stored in memory
data from MAR addresses
(ASF)
cache
memory built into CPU storing recently used instructions
shortens distance when retrieving data instead of going to RAM to boost efficiency
relative distance of different cache memory
L1- located on CPU(low capacity, same speed as cpu)
L2- part of CPU module( a bit larger and runs at relatively same speed)
L3- on mother board, slower than L1-26
factors affecting CPU
clock speed(Hz)
number of processor cores
cache size + type
clock speed
number of instructions in a single processor core carried out per second
aka clock cycles, measured in hertz(Hz)
overclocking
increasing CPU speed in basic input/output system(BIOS) excessively
causes CPU to work too hard, leading to overheating
some instructions are not executed in time, which leads to corrupt data
core
processing unit which receives instructions & performs calculations
dual cores
2 CPUS working
each may have their own L2/3 cache, performing FDE at the same time & performing instructions
without a software that supports it, only 1 core can be used.
parallel processing
allows different instructions from the same program to be ran at the same time
dual core doesn’t mean twice the speed, as some tasks need to execute in order(sequential)