topic 4 - the brain and neuropsychology
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms

label the diagram of the brain
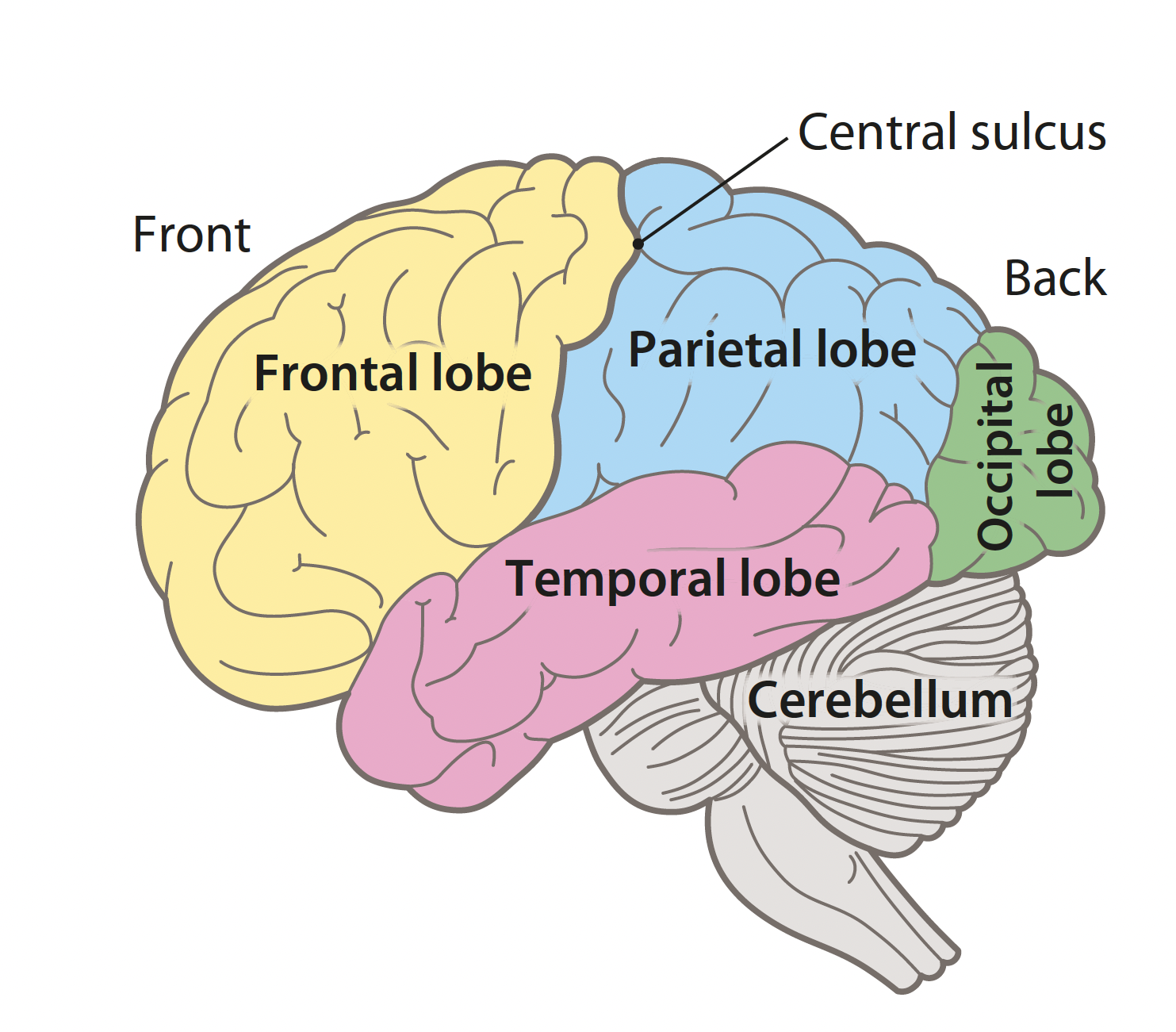
function of the frontal lobe
important role in decision-making, problem-solving skills and impulse control
the motor cortex is located towards the back of the frontal lobe and is responsible for the voluntary movements of the human body
function of the temporal lobe
helps with hearing and understanding sound as well as creating and understanding speech
said to contain the auditory cortex (controls our hearing)
function of the parietal lobe
helps with the ability to understand the world around us (perception) and it gives us the ability to recognise faces
function of the occipital lobe
deals with our ability to see and process visual information from our eyes so that we can understand what we are seeing
function of the cerebellum
plays a vital role in movement, coordination and balance (motor skills)
takes information from different senses and combined them to coordinate behaviour
lateralisation of function
the different jobs that are done by each half of the brain
asymmetrical function
the two hemispheres of the brain are not equal in terms of what they do
role of the left hemisphere
plays a big role in the processing of language
an area in the left hemisphere known as the Broca’s area controls the production of speech

role of the right hemisphere
plays a large role in our spatial awareness
controls our ability to recognise and perceive faces
often referred to as more creative

corpus callosum
a thick bundle of nerve fibres connecting the two hemisphere of the brain so that they can communicate with each other
sex differences in brain lateralisation
there is evidence that females have a thicker corpus callosum meaning they may use both sides of their brain to do some tasks
males tend to show dominance for one hemisphere for the same tasks with more activity in one hemisphere than the other hemisphere
strengths of lateralisation as an explanation of sex differences between males and females
Harasty et al. (1997) suggested that parts of the brain that process and produce language are slightly bigger in females compared to males
Rilea et al. (2005) found that males were better at spatial tasks
the experiments conducted have strong control over extraneous variables and are highly reliable
weaknesses of lateralisation as an explanation of sex differences between males and females
Rilea et al. (2005) found that males did not always perform better than females on spatial tasks
Sommer et al. (2004) suggested that there was no strong evidence that females used both hemispheres for language tasks
neurone
a nerve cell that transmits information
synapse
a gap between two neutrons that allows messages (in the form of neurotransmitters) to pass from one cell to another
neurotransmitters
chemicals released from neurons that pass messages from one neuron to another across a synapse
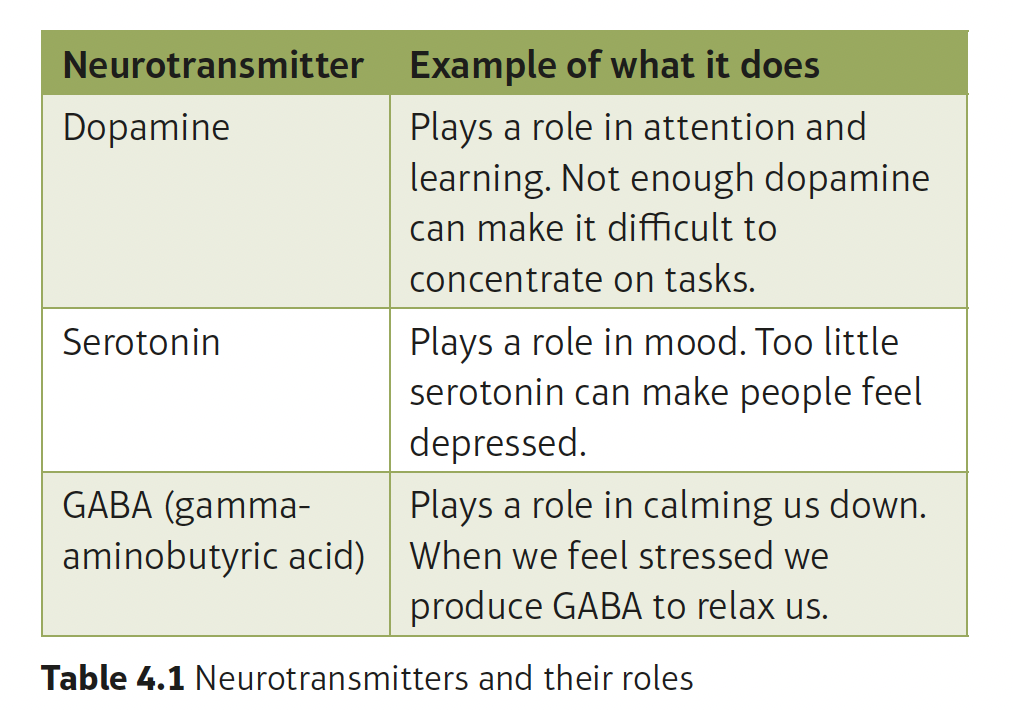
synaptic transmission
when messages are passed through the nervous system from one neuron to the next
central nervous system (CNS)
made up of the brain and the spinal cord
helps the brain and body communicate with another by passing messages forwards and backwards between them
neurological damage
refers to any kind if damage to parts of the nervous system
visual agnosia
the inability to recognise things that can be seen
a person can see perfectly well but cannot understand what that are seeing
this occurs as a result of damage to the parietal lobe because it is a disorder of perception
symptoms of visual agnosia
not being able to recognise the colour of an object
not being able to recognise objects and name them
not being able to recognise places you are familiar with
prosopagnosia
the inability to recognise faces
can be caused by damage to the back of the temporal lobe known as the fusiform face area
symptoms of prosopagnosia
difficulty in identifying people from their faces
seeing all faces as the ‘same’ and not being able to tell them apart
impact of damage to the pre-frontal cortex
the pre-frontal cortex helps us control our impulses and keep our emotions balanced
if it becomes damaged, a person may become aggressive and impulsive
Adrian et al. (1997) found that murderers had less activity in their pre-frontal cortex than a normal person, making them more aggressive and impulsive
background of Damasio et al. (1994)
in 1848, Phineas Gage was working in a railway line in the USA when an explosion caused an iron rod to pass through his head
it cause serious damage to his face and the frontal lobe of his brain
his personality underwent permanent damage
before the accident, he was described as calm and responsible but after the accident, he was described as aggressive and rude
aims of Damasio et al. (1994)
wanted to build a model of Gage’s brain to figure out how the rod passed through his head
wanted to discover if any other parts of his brain had also been damaged
procedure of Damasio et al. (1994)
began by taking pictures and measurements of the skull of Phineas Gage
then they built a 3D replica model of a skull that matched the measurements of Gage’s skull
in total, 20 different entry points and 16 different exit points were tested
results of Damasio et al. (1994)
there was likely to have been damage in both the right and the left hemispheres of the frontal lobe
the damage was likely to have only affected the frontal lobe and no other parts of the brain
the iron bar would have passed through the left eye socket and upwards through the head
there was likely to have been more damage to the underlying white matter in the left hemisphere than in the right frontal lobe
the damage in both hemispheres seemed to be worse in the middle of the underside (ventromedial region)
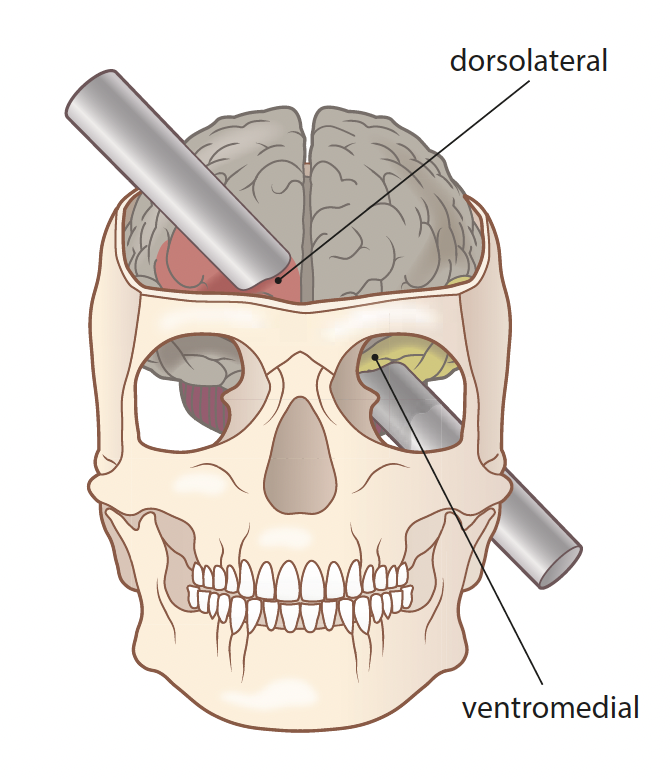
conclusion of of Damasio et al. (1994)
the ventromedial area of the frontal lobes seems to be important for making sensible decisions and controlling our impulses around people
it also seems to be important for the control of emotions
this knowledge can be used to predict the behaviour of someone who suffers brain damage in these areas in the future
strengths of Damasio et al. (1994)
researchers were able to use modern-day technology which made the results more scientific
we can now make predictions about what changes to behaviour we might expect if someone has damaged their frontal lobes
weaknesses of Damasio et al. (1994)
based on results that were originally gather 150 years ago which may make the information inaccurate and unreliable
holistic so there is a problem in generalising the results because it can only be applied to a certain individual
background of Sperry’s (1968) study
some patients with severe epilepsy who had not responded to treatment were offered surgery to help reduce their seizures
the surgery involved cutting down the corpus callous to disconnect/separate the right and left hemispheres
aims of Sperry’s (1968) study
what effects could be seen in split-brain patients by monitoring how they processed information
procedure of Sperry’s (1968) study
group of 11 participants who had their corpus callosum cut
they were each given various tasks to test how they processed different types of information
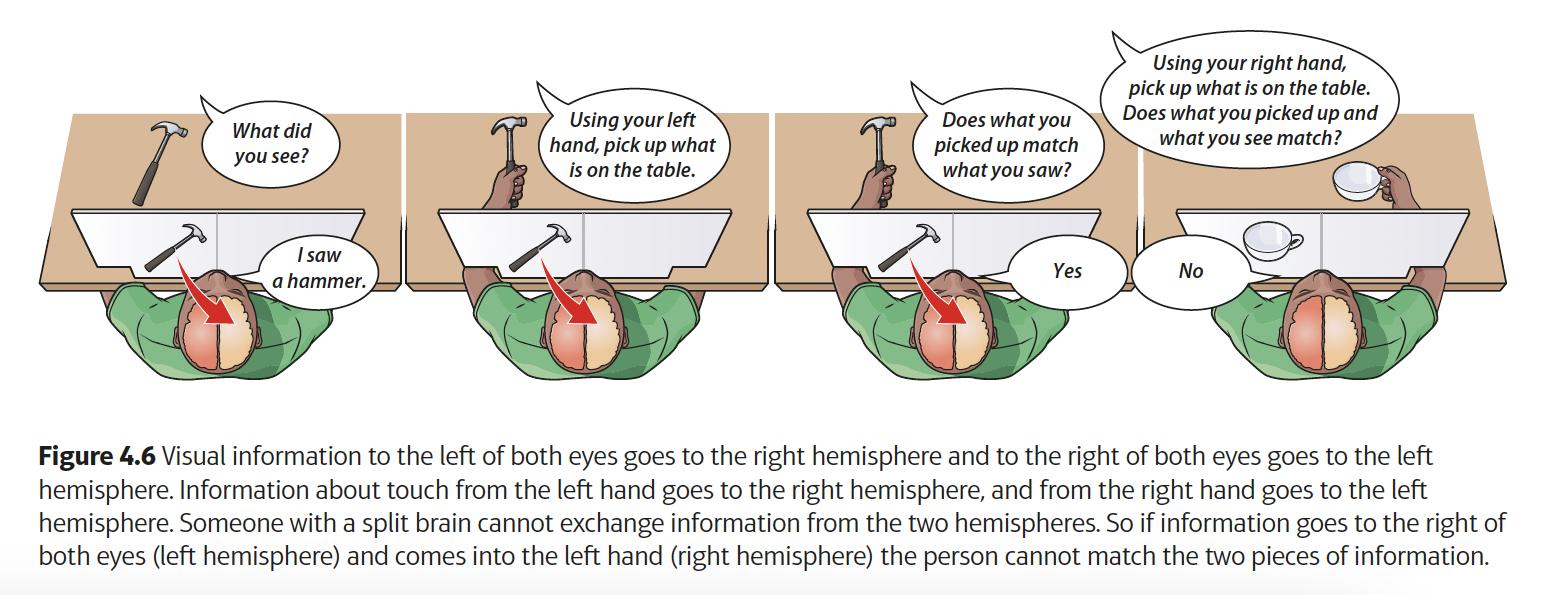
results of Sperry’s (1968) study
tasks involving reading words or selecting objects:
when words were shown to the right visual field, the patients had no problem
when they were shown the word to their left visual field, people had trouble saying what they had seen
if a word or picture was shown to the left visual field, participants had little trouble
when the word or picture was shown to the right visual field, the participants struggled to point to the correct object
when objects were presented to each hand:
when objects were felt by the right hand, they could name the object
when objects were felt by the left hand, it was more difficult
when two different objects were given to the participant and they were then asked to find it in a pile of objects, they could only identify each item with the hand that originally held it
conclusions of Sperry’s (1968) study
each hemisphere is perfectly capable of working well without being connected to the other side
the left hemisphere seems to be better at naming items using words when they had been held by the right hand
the right hemisphere was better at identifying objects by feeling for them with the left hand
the left hemisphere controls more language abilities and the right hemisphere controls more spatial abilities
strengths of Sperry’s (1968) study
gathered a lot of detailed information which made the study more reliable
data was gathered in a reliable way
weaknesses of Sperry’s (1968) study
the sample of 11 participants is too small to generalise the results
the results lacked ecological validity because the tasks down in the lab were in an artificial environment
how has psychology changed over time?
‘born’ in 1875 when William Wundt opened a laboratory in Leipzig, Germany to study people’s thoughts
studying the brain at that time could only be done post-mortem
in 1924, Hans Berger developed the EEG as a way to measure brainwave activity in a living brain
then, the MRI and PET scans were developed to show detailed pictures of what the brain looks like or how active different parts of the brain are at different times