ADH1 FINAL (Respiratory + DM)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Clinical Manifestations COPD: (9)
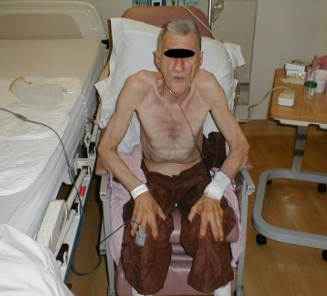
Chronic dyspnea (RR 40-50/min during exacerbations)
Barrel chest
Productive cough (worse in morning)
Crackles, Wheezing, Hypoxemia
Tripod
Accessory muscles
Pursed lip breathing
Cyanosis & Clubbing nails
Weight loss d/t dyspnea
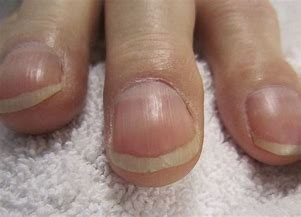
Why can’t u over oxygenate pt w/ COPD?
Range for O2 admin?
They will lose drive to breath
88-92%
What kind of chest shape will COPD have?
barrel chest
COPD pt should perform what kind of breathing?
Pursed lip breathing

Diagnostic tools for COPD: (3)
Pulmonary Functions Test (PFTs)
FVC/FEV1
Chest Xray
ABGs
What acid base imbalance would COPD pt have?
CO2 retention = Respiratory Acidosis (hypoventilating)
ratio of FEV1/FVC to confirm COPD:
Hypoxemia PaO2:
Hypercapnic PaCO2:
< 70% positive for COPD
PaO2 <80 mmHg
PaCO2 > 45mmHg
Complications of COPD: (3)
CO2 retention (Resp. Acidosis) —>
Respiratory failure
Cor pulmonale (R. sided HF)
Asthma is a chronic condition worsens based on what?
Triggers!!
What strongly triggers asthma?
ALLERGIES
Common asthma manifestations: (5)
Dyspnea
Chest tightness
Coughing
worse at night/ early mornings
Wheezing
Mucus production
Severe asthma attack signs: (3)
Accessory muscles
Prolonged expiration
Poor O2 saturation (low SaO2)
List meds for asthma:
2 main categories
5 classes
drugs in those classes (6)
Bronchodilators
a. SABA: albuterol
b. LABA: salmeterol
c. anticholinergics: ipratropium
Anti-inflammatory agents
a. Corticosteroids: Fludrocortisone; Prednisone
b. Leukotriene Blockers: Montelukast
Whats the most accurate diagnostic test for asthma?? *also for COPD as well
FEV1/FVC ratio
< 70%
Pneumonia manifestations: (8)
Fever
Sharp pleuritic CP
Dull chest percussion over consolidated areas
filled w/ exudate
SOB
Tachypnea
Productive cough
yellow, blood-tinged, purulent, rust colored
Crackles, Wheeze
Hypoxia
**similar to COPD!!
Lab/ Diagnostic tests for pneumonia: (7)
Sputum culture and sensitivity
bacteria
Blood culture
spread of infx—sepsis
CBCs
ABGs
BMP
CT
CXR
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) diagnosed when?
dx in community/ early in hospital admission (< 48 hrs)
Which of the 4 pneumonias is most common and whats it caused by?
CAP
influenza
Healthcare Associated Pneumonia (HCAP) diagnosed how?
Non-hospitalized pts have extensive contact w/ healthcare ppl
chemo, dialysis
HCAP is often caused by what pathogen, and linked to what rates?
Multidrug resistant pathogen (MDR) so also more likely to be resistant to abx tx
Linked to higher mortality rates
When does Hospital Acquire Pneumonia (HAP) develop? And what pathogen sources could pt be exposed to? (3)
> 48 hrs+ AFTER hospital admission
Medical equipment
Provider contact
Shared facilities
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia is sub-type of which other one? And HOW does it occur?
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP)
when condition manifests > 48hrs+ AFTER pt is INTUBATED
Nursing care for pt w/ pneumonia and why: (9)
Assessment
get baseline/ abnormalities
Breathing tx/ meds
open airways
O2 therapy
> 95%
Position
High fowlers max efficiency
Mobility
prevent atelectasis
loosen secretions
Promote nutrition/ hydration
2-3L to thin secretions!
Have rest periods
Conserve energy
Provide reassurance
bc they’re anxious
Monitor skin breakdown
around ears bc of mask
The 2 equipments to teach a pt w/ pneumonia how to use:
Incentive spirometer: encourage deep breathing
breath IN
PEP: opens alveoli and moves mucous from smaller airways larger airways and easier to expel

What members of interprofessional care would be consulted for pt w/ pneumonia? (3)
RT:
ABGs
breathing tx (inhalers)
O2 monitoring
Nutritionist:
high protein/calorie diet
Rehab (OT/PT)
Fine— OT
Gross— PT
get back to baseline functioning bc they’re weak
Nursing INTERVENTION to prevent Aspiration?? (6)
HOB > 30
Use few sedatives as possible
Confirm tube placement B4 enteral feedings
No stimulate gag reflex w/ suctioning
Have suction @ bedside tho
Thicken liquids for swallowing problems
DM1 & DM2 Fasting blood glucose and HA1c ranges:
Fasting blood glucose: > 126 mg/dL
HA1c: > 6.5%
What does HA1c measure?
> 6.5% measures avg blood glucose of past 2-3 months
Patho of DM1?
Absolute LACK of insulin d/t destruction of insulin producing beta-cells
Patho of DM2:
Cell membrane no transport glucose INTO cell aka pancreas beta cells FAIL (F-)
3P’s of T1 and T2 DM?
Polydipsia: really thirsty/ dehydrated form peeing
Polyphagia: really hungry
Polyuria: excessive urination
DKA usually found in what DM?
T1DM
Patho of DKA? (2)
no insulin for cells to get enough glucose for normal metabolism
breakdown of fat leads to fatty acids then converted by liver into KETONES
Clinical manifestations DKA: (5)
Kussmauls respirations (fast rate)
Fruity acetone breath
Poly-uria
-dipsia
-phagia
Specific labs for DKA:
Blood glucose level
Ketones
Anion gap
Serum Bicarb
pH
Serum osmolarity
Blood glucose level: > 250 mg/dL
pH: < 7.30 (met. acidosis)
Serum Bicarb: <18 mEq/L
Ketones: +
Anion gap: +
Serum osmolarity: > 300 mOsm/kg
How would u treat DKA? (3 steps) and whats the most important electrolyte??
Fluid replacement IV NS
Correct electrolyte imbalances B4 Insulin!!!—-especially K+
IV regular Insulin admission
HHS is usually in what type DM?
T2DM and higher mortality rate than DKA!!
Common causes of HHS? (4)
Infection
Stress
Trauma
Surgery
Patho HHS: (3)
there’s enough insulin to prevent rapid fat breakdown/ ketone release
BUT not enough to prevent HYPERglycemia
Extreme hyperosmolality —> osmotic diuresis
*cells are fed, just not enough to prevent hyperglycemia**
Specific labs for HHS:
Blood glucose level
Ketones
Anion gap
Serum Bicarb
pH
Serum osmolarity
Blood glucose level: > 600 mg/dL
Ketones : -
Anion gap: -
Serum Bicarb: > 15 mEq/L
pH: > 7.40
Serum osmolarity: > 320 mOsm/kg
Specific clinical manifestations of HHS: (2)
Profound dehydration
Altered LOC
How to treat HHS?? (3)
Fluid IV NS replacement
Tx for Altered mental status —AIRWAY management********!!!
Admin IV Regular insulin