Odontogenesis (Part 2)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
tooth germs
adjacent
Topic: Developmental Stages
The development of the _____ _____ is initiated, and the cells continue to proliferate faster than the ______ cells
tooth enamel
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
What is the main function of the certain epithelial cells of the tooth bud? To form the….
epithelial cells of the tooth bud
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
What is critical for a normal tooth development
columnar
polygonal
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
In the bud stage enamel organ consists of peripherally located low _______ cells and centrally located ______ cells
mesenchyme
mitosis
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
Cells of the tooth bud and surrounding ______ undergo _____
neural crest
ectomesenchymal
condense
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
Cells of the tooth bud and surrounding mesenchyme undergo mitosis results in:
Migration of ____ ___ cells into the _______ cells surrounding the tooth bud and ____
mitosis
Division of somatic cells
Dental papilla
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
The area of ECTOMESENCHYMAL CONDENSATION immediately subjacent to the enamel organ
ectomesenchymal condensation
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
Dental papilla, the area of ________ ______ immediately subjacent to the enamel organ
Dentin and Pulp
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
Cells in the Dental Papilla will form: ____ and ___
Dental sac
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
What is the condensed ECTOMESENCHYME that surrounds the TOOTH BUD and the DENTAL PAPILLA
tooth bud
dental papilla
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
Dental Sac, condensed ECTOMESENCHYME that surrounds the ____ ___ and the ____ ____
cap and bell
Topic: Tooth Bud Stage
Both the dental papilla and the dental sac become more well defined as the enamel organ grows into the ___ and ____ stages
cementum and periodontal ligament
Cells in the Dental Sac will form: _____ and ______ ______
Dental organ/Enamel organ
Dental papilla
Dental sac/Dental follicle
What are the three parts of the Tooth Bud?
oral epithelium
enamel
Topic: Parts of the Tooth bud
Dental organ/Enamel organ
Derived from:
Produces:
mesenchyme
pulp and dentin
Topic: Parts of the Tooth bud
Dental papilla
Derived from:
Produces:
mesenchyme
cementum and periodontal ligament
Topic: Parts of the Tooth bud
Dental sac/Dental follicle
Derived from:
Produces:
Ameloblast
Topic: Tooth Bud
What is the correct answer?
Dental organ/Enamel organ
A. Ameloblast
B. Odontoblast
C. Cementoblast
Odontoblast
Topic: Tooth Bud
What is the correct answer?
Dental papilla
A. Ameloblast
B. Odontoblast
C. Cementoblast
Cementoblast
Topic: Tooth Bud
What is the correct answer?
Dental sac/Dental follicle
A. Ameloblast
B. Odontoblast
C. Cementoblast
ectoderm
Topic: Tooth Bud
What is the correct answer?
Dental organ/Enamel organ:
Ectoderm or Ectomesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme
Topic: Tooth Bud
What is the correct answer?
Dental papilla:
Ectoderm or Ectomesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme
Topic: Tooth Bud
What is the correct answer?
Dental sac/Dental follicle:
Ectoderm or Ectomesenchyme
ENGKKK MALI KASI DI KA NAG PAALAM
ANO YUNG BONE BETWEEN THE TWO HEARTS?

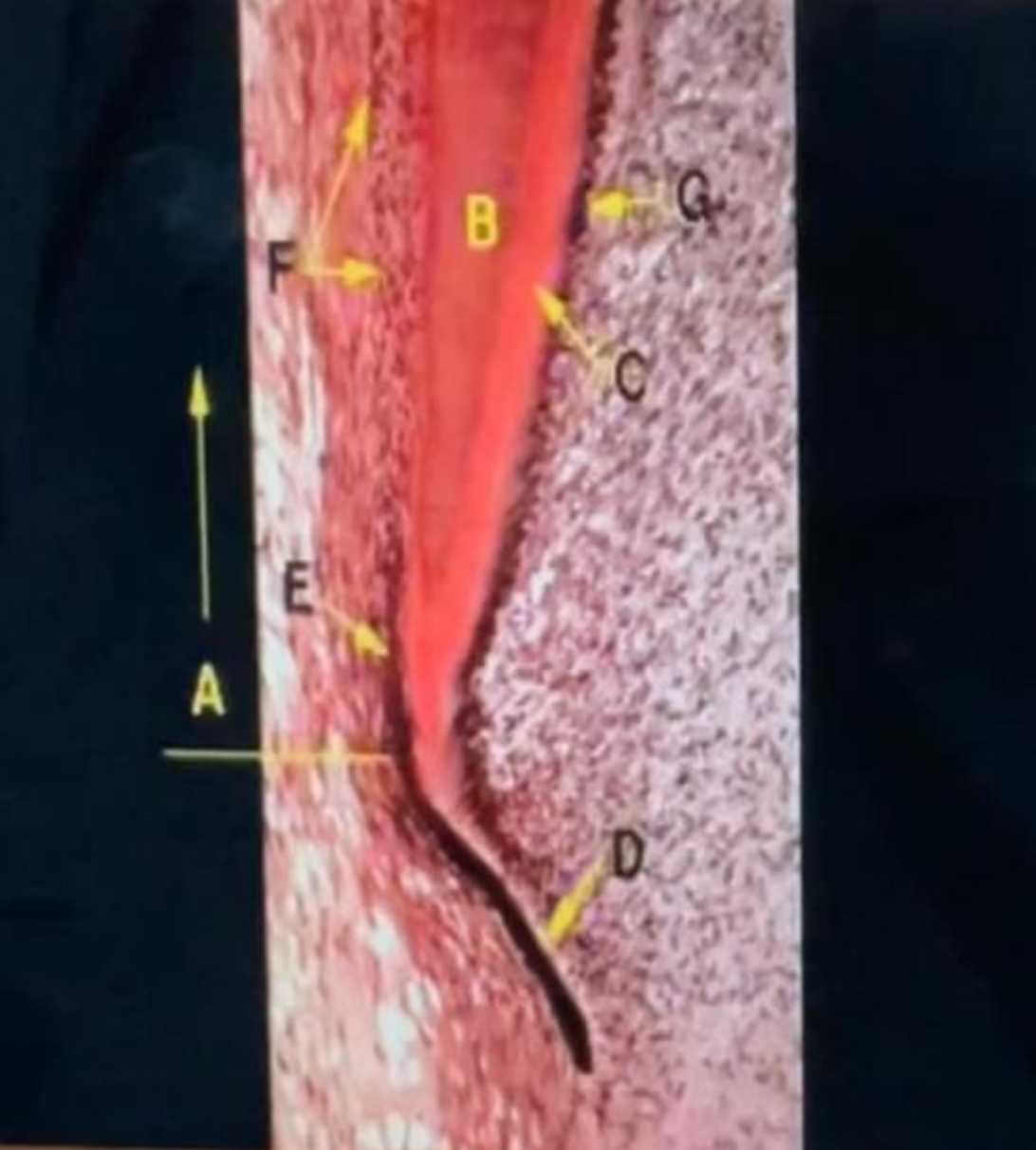
A - root of tooth
B – dentin
C – predentin
D – epithelial diaphragm
E – outer dental epithelium
F – epithelial rests
G – odontoblasts
Formation of the Epithelial Diaphragm
Identify each letter
Histodifferentiation or bell stage (early bell stage)
what stage is when the invagination of the epithelium deepens and its margin continue to grow, the enamel organ assumes a ___ _____
membrana performativa
Dental Papilla
The basement membrane that separated the enamel organ and the dental papilla, just prior to dentin formation called ______ ________
denser and more fibrous dental sac
what is important in the formation of cementum and periodontal ligament?
sac
ectomesenchyme
Dental ___:
Concomitant with the development of the enamel organ and dental papilla
There is a marginal condensation in the _________ surrounding the enamel organ and dental papilla
inner enamel epithelium
stratum intermedium
stellate reticulum
outer enamel epithelium
what are the types of epithelial cells that can be distinguished on bell stage of enamel organ? (x4)
inner enamel epithelium
Topic: Types of epithelial cells on bell stage of enamel organ
Consists of single layer of cells that differentiate prior to amelogenesis into tall columnar cells called ameloblasts
amelogenesis
ameloblasts
Topic: Types of epithelial cells on bell stage of enamel organ
Inner enamel epithelium, consists of single layer of cells that differentiate prior to ______ into tall columnar cells called ______
amelobasts
what do you call an epithelial cells from which tooth enamel is formed
4-5
40
mesenchymal
dental papilla
Topic: Types of epithelial cells on bell stage of enamel organ
Inner enamel epithelium
- These cells are ? - ? micrometers (um) in diameter and about _?_ (um) high
- The cells exert an organizing influence on underlying ________ cells in the ____ _____
stratum intermedium
Topic: Types of epithelial cells on bell stage of enamel organ
Few layers of squamous cells located between enamel epithelium and stellate reticulum
stratum intermedium
Topic: Types of epithelial cells on bell stage of enamel organ
what layer seems to be essential to enamel formation and is absent in the part of the tooth germ that outlines the root portions of the tooth
cap stage
what is characterized by shallow invagination on the deep surface of the bud
cap stage
As the tooth bud continues to PROLIFERATE ,it DOES NOT expand uniformly into a larger sphere,
INSTEAD, unequal growth in different parts of the tooth bud leads to ____ _____
outer enamel epithelium
inner enamel epithelium
stallate reticulum (enamel pulp)
what are the layers of cells seen in early cap stage? (x3)
outer enamel epithelium
Topic: Layers of cells seen in early cap stage
peripheral cells of the cap stage, cuboidal in shape that cover the convexity of the cap
cuboidal
Topic: Layers of cells seen in early cap stage
Outer enamel epithelium of the cap stage,
what covers the convexity of the cap?
inner enamel epithelium
Topic: Layers of cells seen in early cap stage
are the columnar cells in the concavity of the cap
stellate reticulum
Topic: Layers of cells seen in early cap stage
Polygonal cells located in the center of the enamel organ, between the outer and inner enamel epithelia, begin to separate as more INTERCELLULAR FLUID is produced and form the ______ ______
between the outer and inner enamel epithelia
Topic: Layers of cells seen in early cap stage
The polygonal cells of the stellate reticulum (enamel pulp) is located where?
intercellular fluid
stellate reticulum
Topic: Layers of cells seen in early cap stage
Stellate reticulum (enamel pulp):
Polygonal cells located in the center of the enamel organ, between the outer and inner enamel epithelia, begin to separate as more __________ _____ is produced and form the ______ ______
enamel knot
enamel cord
What are the accessory or temporary structures during cap stage?
enamel knot
Topic: Accessory or temporary structures during cap stage
cells in the center of the enamel organ that projects in part toward the underlying dental papilla, so that the center of the epithelial invagination shows a KNOBLIKE ENLARGEMENT
act as a reservoir of diving cells for the growing enamel organ
Topic: Accessory or temporary structures during cap stage
what is the function of the enamel knot and enamel cord?
enamel cord
Topic: Accessory or temporary structures during cap stage
A VERTICAL extension of the enamel knot
disappear
formation
Topic: Accessory or temporary structures during cap stage
ENAMEL KNOT and ENAMEL CORD are TEMPORARY STRUCTURES that ______ before the enamel ______ begins
enamel organ
enamel knot
dental follicle
denta papilla
bone
Label the picture
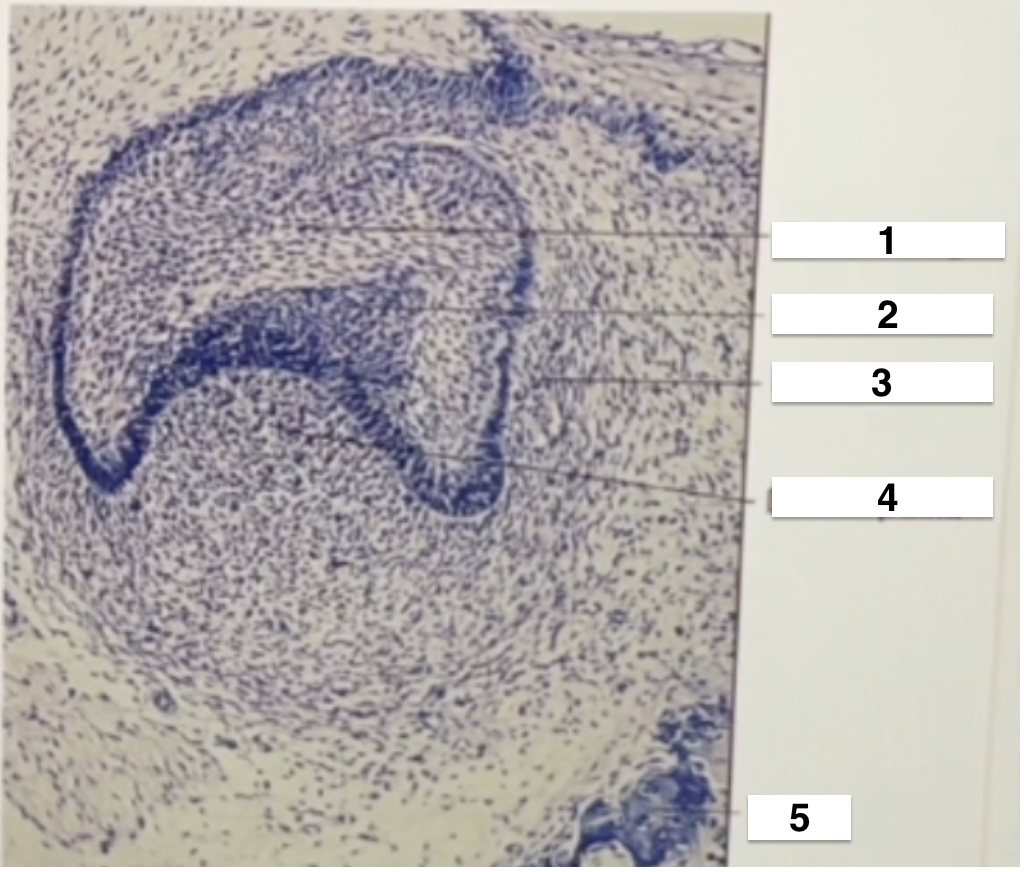
Histodifferentiation or Bell Stage (early bell stage)
What stage does the invagination of the epithelium DEEPENS and its MARGINS CONTINUE TO GROW?
dentinoenamel junction
Topic: Processes during Bell Stage
The boundary between inner enamel epithelium and odontoblast outline the future ________ ______
odontoblast
connective tissue cells that develop into dentin
Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath
Topic: Processes during Bell Stage
Cervical portion of the enamel organ gives rise to what?
Ameloblasts
Odontoblasts
Topic: Processes during Bell Stage
continuation of histodifferentiation
is where ______ and ______ are defined
crown
Topic: Processes during Bell Stage
Beginning of morphodifferentiation
- Tooth _____ assumes its final shape
startum intermedium
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
what type of epithelial cells is absent in portion of the tooth that OUTLINES THE ROOT PORTIONS of the tooth
intercellular fluid
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
In stellate reticulum it expands further and is mainly increased amount of ______ _____
star
processes
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
Stellate reticulum:
SHAPE: ____ shaped, with long _______
squamous
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
stratum intermedium has few layers of _____ cells
outer enamel epithelium
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
→ SHAPE: flattened cells to a low cuboidal form (LOW CUBOIDAL)
→ laid in FOLDS during:
End of the bell stage
Preparatory to and during the
formation of enamel
capillary loops
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
Outer enamel epithelium:
→ BETWEEN THE FOLDS: papillae that contains ________ _____ form
capillary loops
Topic: Types of Epithelial Cells during Bell Stage
Outer enamel epithelium:
The _____ ____ provides rich, nutritional supply for the INTENSE METABOLLIC ACTIVITY
A – cervical loop
B – stellate reticulum
C – enamel septum
D – inner dental epithelium
E – stratum intermedium
F – dental lamina
G – outer dental epithelium
H – dental papilla
Label the picture from A-H
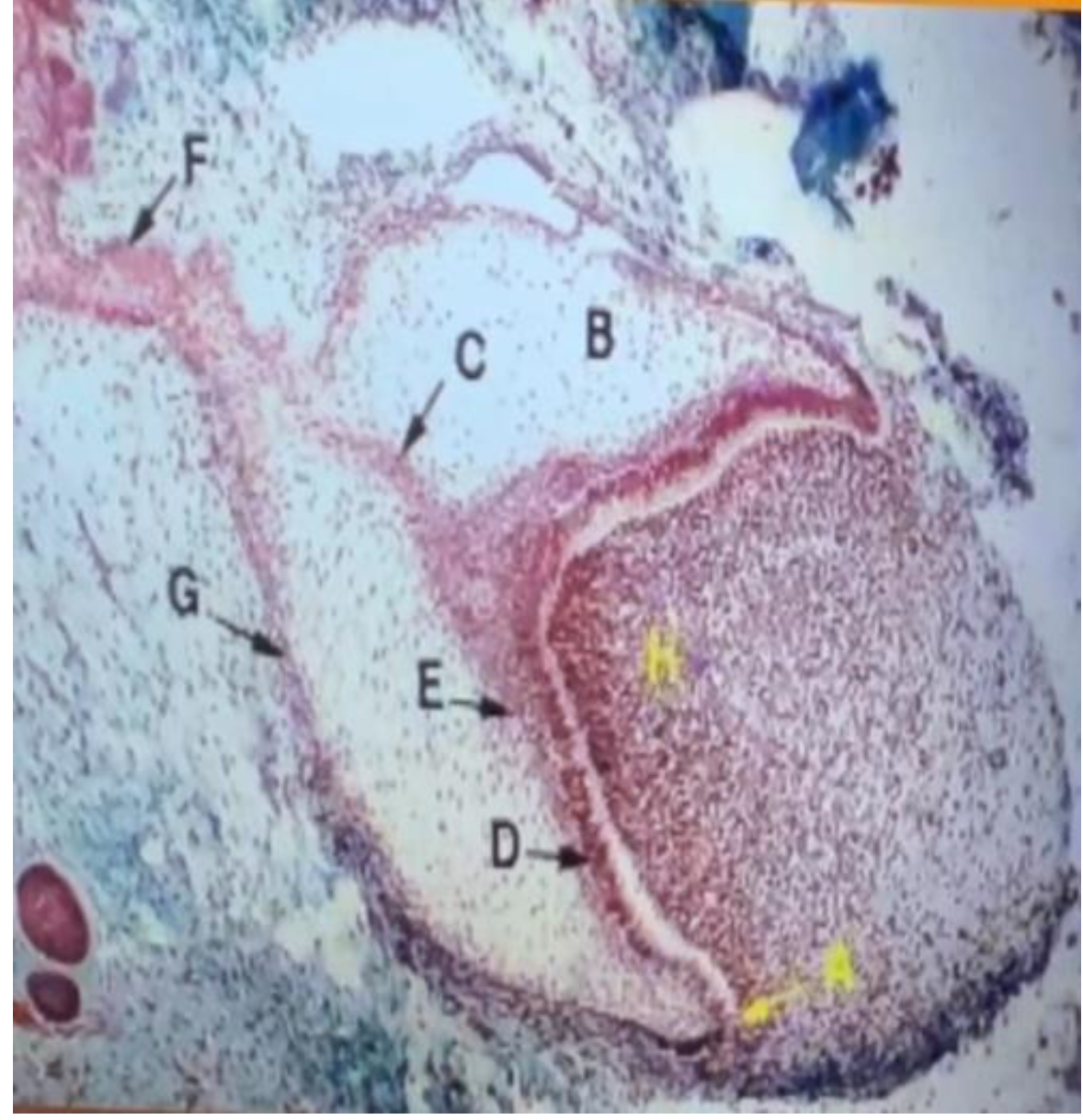
epithelial diaphragm
Prior to beginning of root formation, root sheath forms the ______ _____
CEJ
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
Development of the root begins after the enamel and dentin formation has REACHED THE FUTURE ___
calcified
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
Development of the root begins when the outline of the crown has been established BUT BEFORE the full crown is ______
enamel organ
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
plays an important part in root development and forms the Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath (HERS)
moulds the shape of the roots
initiates radicular dentin formation
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
functions of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath
cervical loop
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
_____ ____ is where the outer and inner enamel epithelium come together and where the cells continue to divide until the tooth crown attains its FULL SIZE
zone of reflexion
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
what is the other term for cervical loop?
epithelial diaphragm
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
HERS bend sharply inward in order to form a plane known as ______ _____
apical boundary
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
HERS bend sharply inward in order to establish the ______ _________ of the dental papilla
guide the shape and number of the roots
Topic: Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath and root formation
function of HERS and Epithelial diaphragm
vertical epithelial root sheath
Topic: Determination of Number of Roots
what continues to grow longer, forming root LENGTH
horizontal epithelial diaphragm
Topic: Determination of Number of Roots
what continues to grow inward toward the midline of the tooth
- this inward growth will determine the number of roots
mono rooted
Topic: Determination of Number of Roots
what happens when the circumference grows EVENLY
bi rooted
Topic: Determination of Number of Roots
what happens when 2 areas opposite one another grows INWARD more rapidly and meet
- it will separate into 2 columns of root formation
tri rooted
Topic: Determination of Number of Roots
forms when 3 areas grow INWARD
multirooted teeth
Topic: Determination of Number of Roots
what do you call when the point where the epithelial diaphragm meet is the FURCATION/TRIFURCATION of the tooth
rest of malassez
what happens when HERS loses its structural continuity and close relation to the surface of the root and its remnants persists as an epithelial network of strands
periodontal ligament of erupted teeth
where is the rest of malassez located
morphodifferentation
basic form and relative size of future tooth is established by differential growth
Dentino enamel junction and dentino cement junction
In morphodifferentation what are the characteristic for each type of tooth, acts as blueprint pattern
morphodifferentation
Disturbances in _______ may affect form and size of tooth without impairing the function of amloblast and odontoblast
apposition
→ deposition of the matrix of the hard dental structures and has layer-like deposition of extracellular matrix
→ is the FULFILLMENT OF PLANS OUTLINE at the stages of histodifferentiation and morpho differentiation
calcification period
During what period is when the process by which organic tissue (matrix formed during apposition), becomes HARDENED
- By a deposit of CALCIUM or any mineral salts within its substance
eruption peiod
During what period is when the process through which the FORMING TOOTH comes into and tries to MAINTAIN OCCLUSION
→ continues throughout the LIFETIME of the tooth
Fusion
→ UNION of 2 separate tooth germs
→ if the contact occurs BEFORE CALCIFICATION:
- The 2 teeth may be completely united to form a SINGLE LARGE TOOTH
dens evanginatus
→ An ACCESSORY CUSP OR GLOBULE of enamel
→ LOCATION: Between the buccal and lingual cusps of premolars (unilaterally/bilaterally)
→ ALSO CALLED:
- Leong’s premolar
- Evaginated odontome
- Occlusal tuebrculated premolar
- Occlusal enamel pearl
hutchinson’s teeth
→ congenital
→ hypoplasia
→ involves permanent INCISORS (notched incisor) and FIRST MOLAR (mulberry molar)
enameloma
→ small island of enamel
→ LOCATION; usually found on the root surface, close to CEJ
hawk billed tooth
angulation or sharp bend/curve in the root or crown of a formed tooth
Fusion
Dens Evanginatus
Hutchinson’s teeth
developmental anomalies of the crown (x3)
Enamel pearls/enamel drops/enameloma
Dilaceration or hawk billed tooth
developmental anomalies of the root
dentino enamel junction and dentino cement junction
what are the characteristic for each type of tooth, acts as a blueprint pattern
inner epithelium and outer epithelium
Hertwig’s epithelial root sheaths consist of what?
notched incisors
Topic: Hutchinson’s teeth
what do you call if it involves permanent incisors