Monera - Bacteria
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Is Bacteria Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic?
Prokaryotic
Define Prokaryotic
Does not have a nucleus
Is Bacteria Autotrophic or Heterotrophic?
Can be Both
Is Bacteria Multicellular or Unicellular?
Unicellular
How is bacteria identified?
By their shape
Name the shapes of bacteria
Round
Rod
Spiral
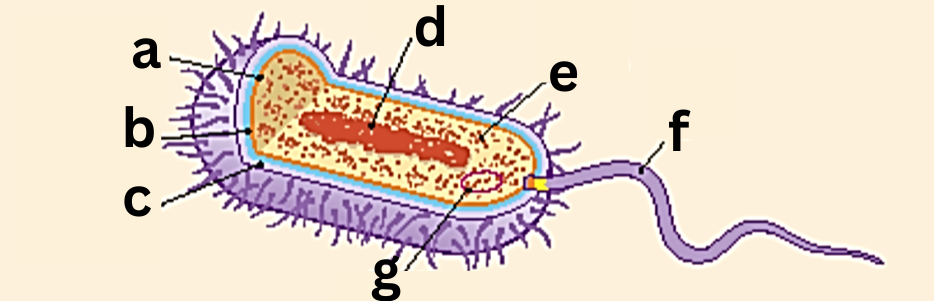
Label This Diagram
The Structure of Bacteria
a - Plasma Membrane
b - Cell Wall
c - Capsule
d - Nuclear Material
e - Ribosomes
f - Flagella
g - Plasmid
Define the function of the Plasma membrane
Semi permeable
Define the function of the cell wall
Protection and structure
Define the function of the Capsule
Protection
Define the function of the Ribosomes
Make Protein
Define The Function of the Flagella
Movement
Define The Function of the Plasmid
Antibiotic resistance
Define The Function of the Nuclear material
Reproduction
How do bacteria reproduce?
Binary Fission
Outline the steps of Binary Fission
1. DNA replication
2. Cell elongates
3. Two identical DNA move to opposite sides of the
cell
4. Cytokinesis occurs
Define Cytokinesis
Cell Division
Define Photosynthetic
Make their own food using light
Define Chemosynthetic
Use energy from chemical reactions
Define Saprophyte
Organism that takes in food from dead organic matter decomposers
Define Parasite
Organism that takes in food from a live host and causes harm
Name the factors that affect bacteria growth
Oxygen
Temperature
pH
Environmental concentration
How does Oxygen have an affect on bacteria growth
Bacteria are obligate anaerobes or aerobes
Define obligate anaerobe
Cannot live in the presence of oxygen
Define obligate aerobes
Can only live in the presence of oxygen
What is the optimum temperature for bacteria?
10 - 30 °C
How does cold temperature have an affect on bacteria
Slow bacterial growth due to enzymes slowing
How does hot temperature have an affect on bacteria
Bacteria die due to their enzymes being denatured
What is the optimum PH range for bacteria?
6-8PH
Define Acidophilies
Can live in acidic environments
Define Alkaliphilies
Cannot live in acidic environments
How does Environmental concentration have an affect on bacteria?
Concentration of solution around bacteria can affect how they grow
How can Bacteria withstand harsh and unfavourable condition?
By producing endospores
How long does the endospore stay dormant?
Until suitable conditions arise
What happens to the endospore under suitable conditions?
Breaks down and binary fission occurs
Name 3 Economic benefits of Bacteria
Produce antibiotics
Produce cheese and yogurt
Symbiotic
Name 2 economic disadvantages of Bacteria
Food decay
Disease
Define Antibiotic
Chemicals produced by micro-organisms to kill other micro-organisms without damaging human tissue
Define Pathogens
Disease causing micro-organisms
Name an example of a pathogen
Bacteria
Differentiate between Viruses and Bacteria
Antibiotics only work on bacteria
What are antibiotics used for?
Control bacterial infection
Name the first antibiotic and its creator
Penicillin - Sir Alexander Fleming
Name a disadvantage of Antibiotics
Overuse has led to the emergence of antibiotic resistance among bacteria
List out (in order) the stages of the growth curve
Lag Phase
Log Phase
Stationary Phase
Decline Phase
Survival Phase
Explain the Lag Phase
Microorganisms are adapting to the conditions
Explain the Log Phase
Numbers increase very rapidly as bacteria reproducing at their maximum rate
Explain the Stationary Phase
Production of new bacteria is equal to the death of existing bacteria
Explain the Decline Phase
Death of the microorganisms is much greater than reproduction.
Explain the survival phase
Endospores are produced
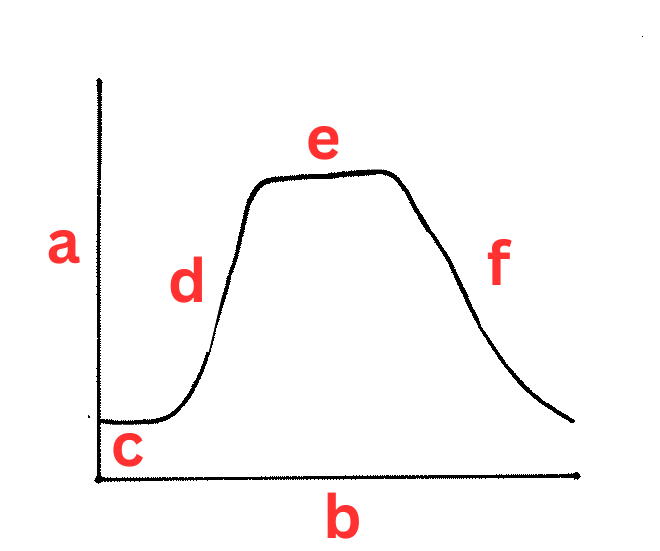
Label This Diagram
The Bacterial Growth Curve
a - Number of bacteria
b - time
c - lag phase
d - log phase
e - stationary phase
f - death phase
Name the ideal conditions for Bacteria
Food
Moisture
Space
Oxygen
Define Food Processing
The use of micro-organisms to form useful products
Define Bioreactor
Container in which living cells or their products are used to make a product
Explain the process of Batch Culture
Fixed amount of Nutrients added to micro-organisms in bioreactor
Growth curve occurs
Bioreactor is emptied
Explain the process Continuous flow culture
Continuous Nutrients added to micro-organisms in bioreactor
Stopped at stationary phase
Product is continuously removed
Define Sterile
Free from micro-organisms
Define Asepsis
Free from pathogens
Name 3 Aseptic techniques
Disinfectant
Flaming
Anti bacterial soap
Name 3 precautions when using microbes
Use sterile equipment
Dispose of all materials safely
All cultures should be considered as potentially dangerous