Lab Quiz 5
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: Shape
Staphylococcus & streptococcus: cocci
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: ram reaction
Staphylococcus & streptococcus: gram +
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: arrangement
Staphylococcus: clusters
Streptococcus: chains
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: where found in the body
Staphylococcus: skin, nasal passage
Streptococcus: mouth, throat, GI tract, vaginal area
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: catalase reaction
Staphylococcus: + (lives on skin)
Streptococcus: - (aerotolerant anaerobe)
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: reaction to cold or dryness
Staphylococcus: not sensitive/resistant
Streptococcus: sensitive
difference between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus: salt tolerance
Staphylococcus: osmotolerant
Streptococcus: not osmotolerant
difference between S. epidermidis and S. aureus (staphylococcus): % of humans that carry it
S. epidermidis: 100% carries it
S. aureus: 25-20% (50% for healthcare workers)
difference between S. epidermidis and S. aureus (staphylococcus): pathogenicity
S. epidermidis: no
S. aureus: can be pathogenic
difference between S. epidermidis and S. aureus (staphylococcus): normal flora
S. epidermidis: yes
S. aureus: can be or 2/3 of people carry sometimes
difference between S. epidermidis and S. aureus (staphylococcus): fermenter of mannitol (sugar)
S. epidermidis: no
S. aureus: no
difference between S. epidermidis and S. aureus (staphylococcus): coagulase reaction
S. epidermidis: -
S. aureus: +
virulence factors of s. aureus
coagulase
beta-hemolysin
staphylokinase
coagulase as a virulence factor
forms clots (97% of staph)
helps protect the bacteria from the immune system
beta-hemolysin as a virulence factor
digests RBC and uses the contents for food and multiplies
staphylokinase as virulence factors
dissolves clot
helps for the spread of bacteria to neighboring tissue
Levels of staph infection
folliculitis
abscess
furuncle
carbuncle
systemic → sepsis
pneumonia
necrotizing fasciitis
common cause of food poisoning
toxic shock syndrome
folliculitis
pimple; infected hair follicle
abscess
localized region of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue
furuncle
boil; multiple local focal points of infection
carbuncle
subcutaneous; deep in the tissue (causes a fever)
purpose of MSA
to presumptively identify staphylococcus aureus and select for the growth of salt tolerant bacteria
beef extract, peptones in MSA
MSA: general growth
sodium chloride (7.5%) in MSA
MSA: high salt concentration → selective for osmotolerant bacteria
D-mannitol for MSA
MSA: sugar for fermentation - differential b/c S. aureus can ferment it
Phenol red in MSA
MSA
pH indicator
yellow = acidic
red/pink = basic
orange = neutral
meaning of yellow agar in MSA
+ result
acidic pH, osmotolerant
mannitol was fermented → possible S. aureus (confirm w. coagulase test)
yellow colonies can be micrococcus - nonpathogenic
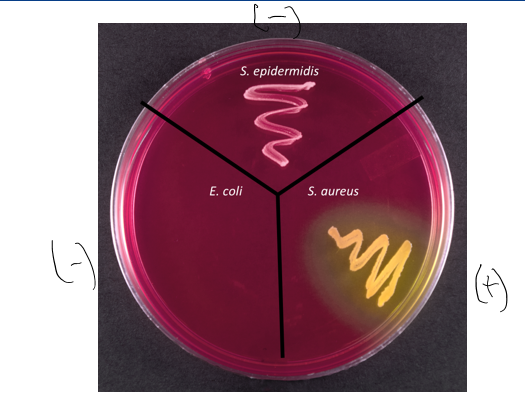
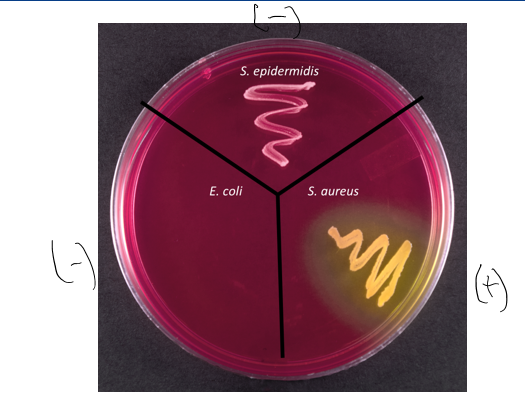
meaning of red or pink agar in MSA
- result
basic pH, osmotolerant
mannitol was not fermented; used peptones and raise the pH
no s, aureus, but an osmotolerant organism like s. epidermidis
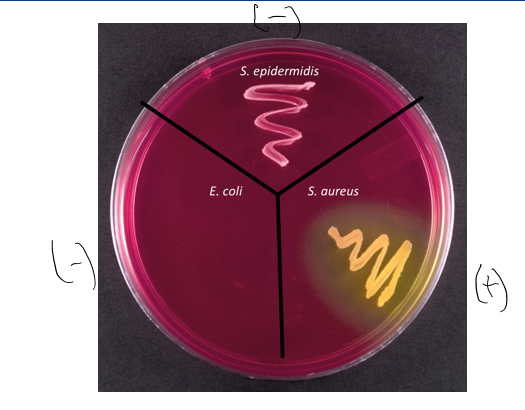
meaning of no growth in MSA
- result
no osmotolerant
purpose of coagulase test
to test whether bacteria produce coagulase (like s. aureus - can be a confirmatory test)
substrate of coagulase test
fibrinogen (l)
clotting factor that is liquid and source is rabbit plasma (liquids part of blood)
various enzymes in coagulase test
coagulase (exoenzyme)
product in coagulase test
fibrin clot (s)
result of solid in coagulase test
+ result
there is fibrin clot and confirmed for s. aureus
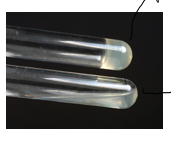
meaning of liquid in coagulase test
- test
there is no fibrin clot and s. aureus is not present
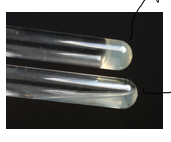
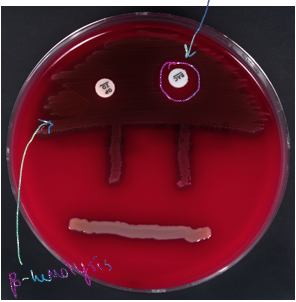
beta-hemolysis in throat culture
complete destruction of RBCs (get clear zones around colonies)
group A and B strep
sensitive to bacitracin
pathogenic and 50% are carriers
can cause step throat and scarlet fever
can cause flesh eating necrotizing fasciitis and form of toxic shock
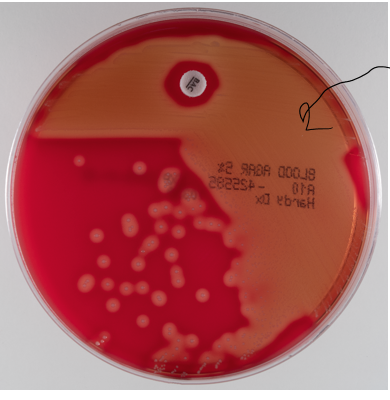
alpha-hemolysis in throat culture
partial desruction of RBCs (get green zones around colonies)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
sensitive to O2
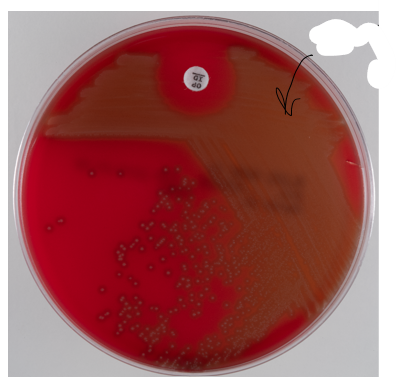
gamma-hemolysis in throat culture
no damage to RBCs (no change to agar)
S. mutans and group D strep
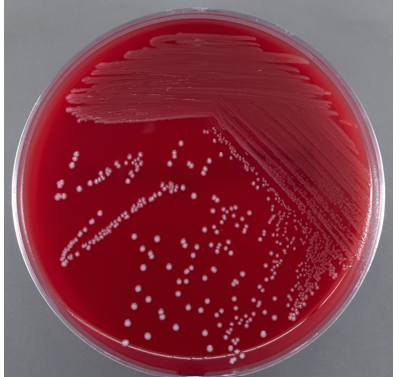
purpose of throat culture
rapid test to differenciate S. aureus (catalase +) from S. pyogenes (catalase -)
group B strep: beta-hemolytic
may be found as normal flora in GI
25% females - vaginal or anal carriers
women screened 35-37 weeks prior to birth
pathogen in immunocompromised patients
50% mortality rate for newborns if not treated immediately
neonatal pathogen → pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis
group D step: gamma- hemolytic
Enterococcus faecalis
100% carried as normal flora
can be outside of GI tract: sepsis and periotoneal cavity
Vancomycin resistant enterococcus has become a major nosocomial pathogen
non-lancefield
Streptococcus mutans (gamma-hemolysis)
Streptococcus pneumoniae (alpha-hemolytic)
purpose of CAMP test
to identify and confirm the presence of group B strep
positive result for CAMP test
look for triangular zone of enhanced beta-hemolysis (synergistic)

purpose of bile esculin agar
to select for the growth of Enterococcus for presumptive indentification
pentones in bile esculin agar
bile esculin agar: general growth
oxgall (bile slats) in bile esculin agar
bile esculin agar: inhibit gram +, except enterococcus (selective)
sodium azide in bile esculin agar
bile esculin agar: inhibit gram - (selective)
esculin in bile esculin agar
bile esculin agar: special food source that contains glucose → E. faecalis can metabolize it (differential)
ferric citrate inbile esculin agar
bile esculin agar: turn brown with esuletin (product of esuclin metabolism); regent already in media
positive result in bile esculin agar
dark brown color = esculin digested
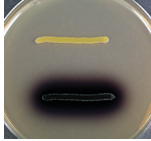
negative result in bile esculin agar
no brown color = esculin not digested
chart of species of Streptococcus
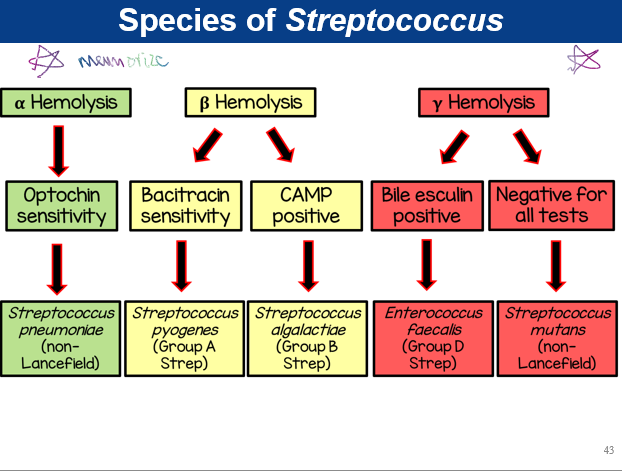
species of Streptococcus: streptococcus pneumoniae
alpha hemolysis (green)
non-lancefield
optochin sensitivity

species of Streptococcus: streptococcus pyogenes
beta-hemolysis (yellow)
group A strep
bacitracin sensitivity
species of Streptococcus streptococcus algalactiae
beta-hemolysis (yellow)
group B strep
CAMP positive

species of Streptococcus: enterococcus faecalis
gamma-hemolysis (red)
group D strep
bile esculin positive

species of Streptococcus: streptococcus mutans
gamma-hemolysis (red)
non-lancefield
negative for all tests

purpose of plaque assay of viral titre
to determine the titer (PFU/mL) of the original phage stock solution
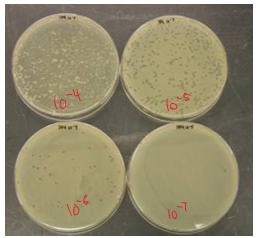
clear zone in plaque assay of viral titre
area of cell death known as a plaque b/c virus killed the bacteria
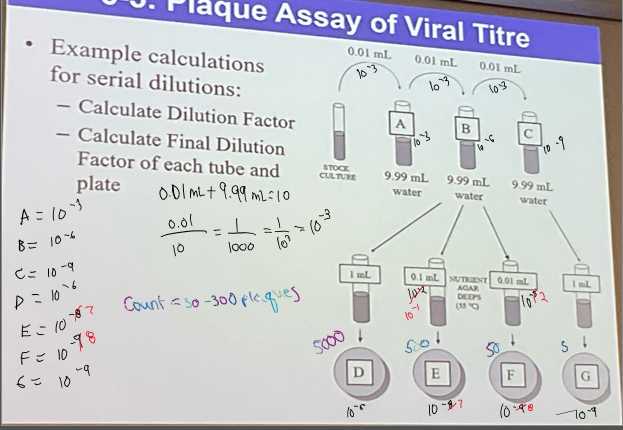
calculations for serial dilution
add 0.1 mL stock to 9.9 mL water to get 10
use formula stock culture/total fluid → 0.1 mL/10 mL
rearrange to scientific notation → 10^-2
for next dilution, 10^-2 × 10^-2 = 10^4 (when multiplying exponents, you add them together)
continue until plates are complete
PFU
plaque forming unit (the number of clear zones that developed on the plate
Titer
PFU/Final Dilution Factor (FDF)
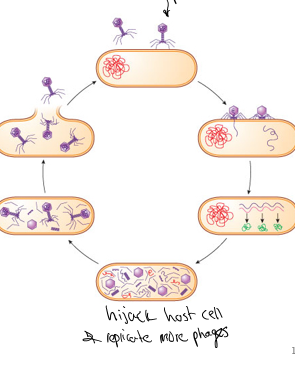
Plaque assay
can be used to enumerate viruses that lyse their host cells. The host cells and virus are incubated together for a short time to allow the virus to attach to and enter the host cell. Then the mixture in plated within a semi-solid agar plate.
general characteristics of fungi
eukaryotic (have a nucleus) with chitin in cell walls
heterotrophic
nonphotosynthesis
unicellular or multi cellular
reproduce by asexual or sexual spores and prefer moist, slightly acidic environments
What are two general categories of fungi
yeast
molds
mycology
study of fungi
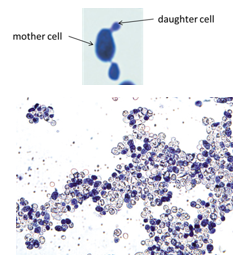
yeast
unicellular, round/oval, reproduce by budding/fission, and form smooth, creamy colonies
molds
multicellular, composed of hyphae (filaments) forming a mycelium, and reproduce using spores.
candida albicans
medically important yeast
causes yeast infection = candidiasis
vaginal area, mouth (causes thrush)
normally comes and goes
systemic in blood may result in endocarditis (may live 3-4 days)
antifungles usually work (nystatin)
most susceptible to Candida infections: diabetics, those w/ immunodeficiency, catheterized patients, infants, individuals taking antimicrobial medications
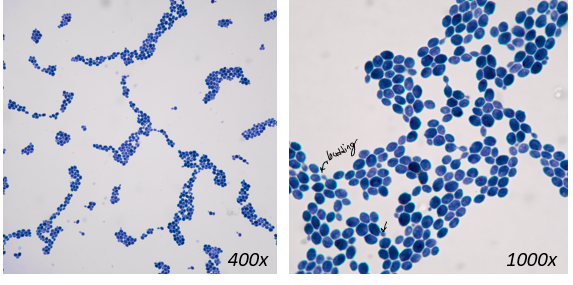
saccharomyces cerevisiae
important non-pathogenic yeast
name means “sugar fungus that makes beer”
brewers yeast - used to produce beer, wine, and bread
fermentation produces CO2 gas and ethanol (alcohol)
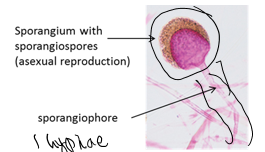
rhizopus stolonifer
black bread mold
hyphae are coenocytic (multinucleated cells)
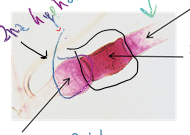
reproduce asexually (sporangiospore) or sexually (zygospore)
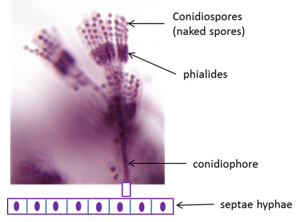
penicillium notatum
medically important mold
spores are green and hyphae are white
can cause a lung infection in immunocompromised patients
some strains are used to make blue cheese and brie cheese
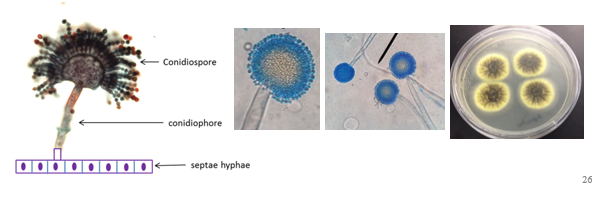
aspergillius niger
medically important black mold
black spores on top, yellow hyphae on bottom
names b/c it was thought to resemble an aspergillum which is a holy water sprinkler in the catholic church
most common mold (in wall sometimes)
causes lung infection - aspergillosis. Can cough up fungal balls which are not contagious
other species can be used to make soy sauce and soy paste
PFU
plaque forming unit (the number of clear zones that develop on the plate
Titer
PFU/Final Dilution Factor (FDF)
calculating titer example

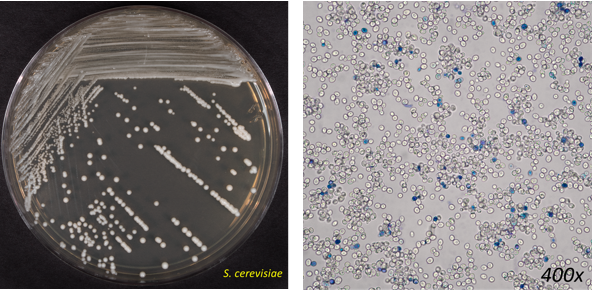
yeast simple stain of wet mouth of S. Cerevisiae
wet mount of S. Cerevisiae
Rhizopus stolonifer: reproduce asexually
sporangiospore
Rhizopus stolonifer: reproduce sexually
zygospore
Penicillium notatum: reproduce asexually
conidiospores

conidiophore
(in certain penicillum notatum & Aspergillus niger) a conidium-bearing hypha or filament.
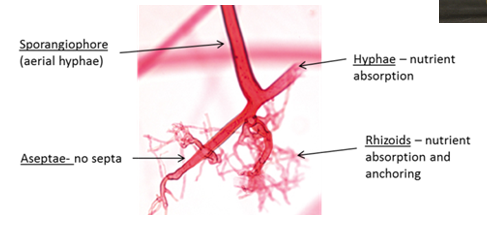
septae hyphae v. aseptae hyphae
septae = fungal filaments (hyphae) that are divided into individual cells by cross-walls called septa
aseptae = fungal filaments that lack internal cross-walls (septa), resulting in a continuous, multinucleated (coenocytic) cytoplasm within the tube-like structure
coenocytic
multinucleated cells
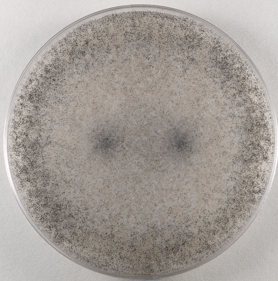
rhizopus stolonifer plate

rhizopus slide culture
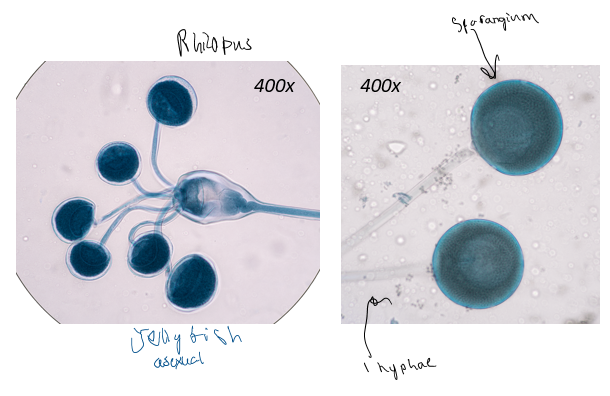
rhizopus stolonifer (sporangiophores)
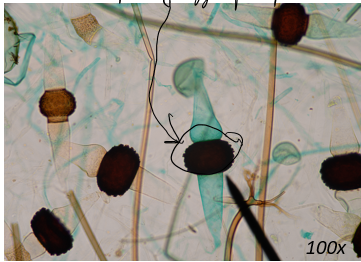
rhizopus stolonifer (zygospores)
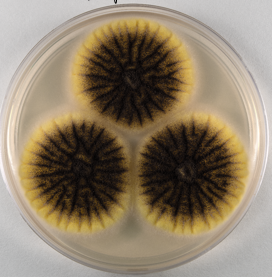
aspergillus niger plate

aspergillus niger - side culture
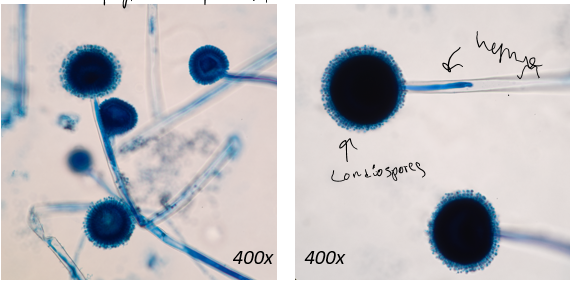
aspergillus niger - condiospores
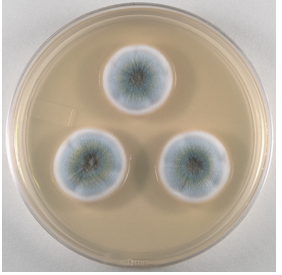
penicillum notatum plate
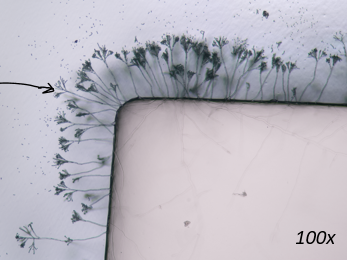
penicillium - side culture
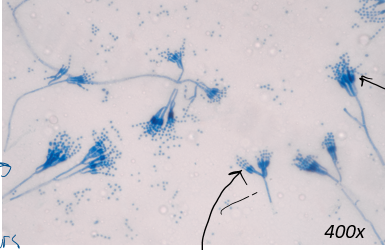
penicillum - condiospores