Bio-1
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Hypothesis
a possible explanation for your question (HAS to be testable and falisfiable)
Steps of the Scientific Method
Observation, Question, Hypothesis, Design Experiment, Predict, Test hypothesis, analyze results
Variables
Independent (controlled/manipulated)
Dependent (measured)
Groups
Experimental Group (gets treatment) and Control (does not get treatment)
Blinds
Single-Blind experimenter does not know what group is what
Double-Blind neither experimenter nor participants know
Mass #
number of protons + number of neutrons
Compound
Substance with 2+ elements
Isotopes
Different number of neutrons
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons
Ionic Bond
formed by attraction of + or - Ions
Molecular Formula
Like C6H12O2
Non Polar
Covalent bond atoms share (covalent) electrons equally (non polar)
Polar Covalent Bonds
atoms share (covalent) electrons unequally (polar)
Hydrogen Bonds (H Bonds)
Weak attractions formed b/w partially + to a partially - atom of a different molecule
Chemical Reaction
Elements involved, Temp, and pH
Water
Cohesive and can Moderate Temperature
Solvent vs Solute
Solvent: Water
Solute: substance disolved by solvent
hydrophobic
afraid of water
hydrophilic
loves water (like a drugie loving drugs)
pH
1 Most Acidic, 7 Neutral, 14 base
Buffers
Substances that can minimize change in pH
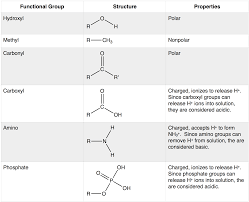
Hydroxyl
Carboxyl
Amine
Phosphate
Look of them
Molecules of Life
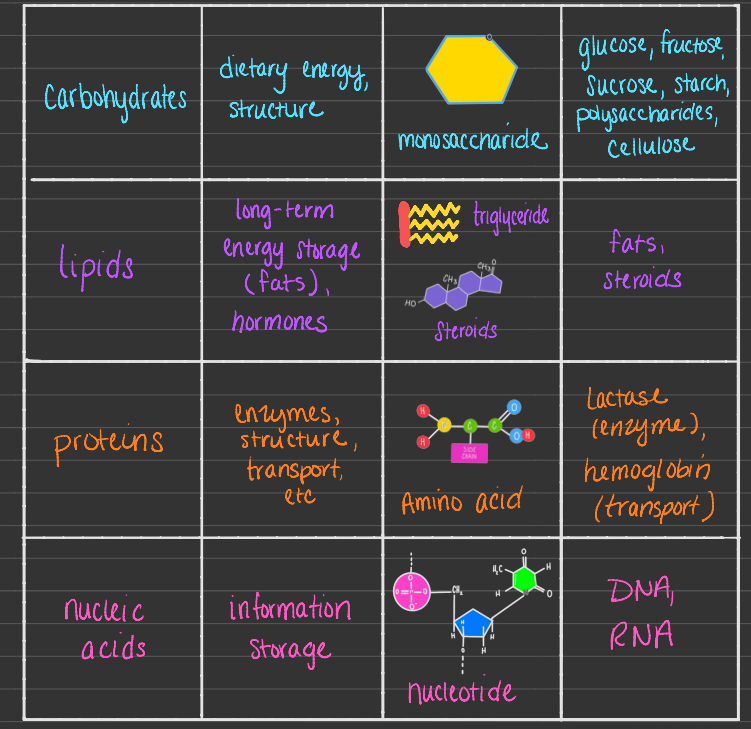
Proteins, Fats, Nucleic Acids, Carbs
Carbs
monomer (simple sugar) aka monosaccharide
glucose (C6H12O6), Fructose (C6H12O6) but fructose is much sweeter than glucose
Isomers
Same molecular formula, dif structure (shape makes a difference)
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides joined by dehydration reaction
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides (Carbs, Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose)`
Lipids
hydrophobic: does not easily dissolve in water
not large macromolecules
not true polymers
Saturated vs Unsatured bonds

Proteins
Monomer: amino acids
connected via Peptide Bonds
shape determined by specific sequence of amino acids
Nucleic Acids
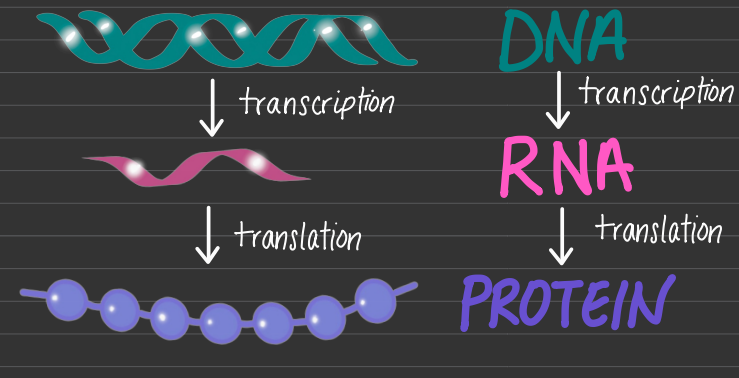
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acids)
DNA - Transcription - RNA - Translation - Protein
Biological Molecules
Cells
Procaryotic 3.5 bya smaller, simpler
Eukaryotic 2.1 bya larger, more complex
Organelles
Compartments seperated by membrane
Plasma Membrane
Seperate outside and inside of cell only letting things in and keeping others out
Cytosol
Thick fluid that contains organelles or “Cell juice”
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Smooth ER: Lipid factory and make more membrane
Rough ER
Golgi Complex
Recreate new proetins from Rough ER
Modify and ship new proteins
Lyosome
Full of diagnositic enzymes that break down materials
Vacuoles
Contractile Vacuole (pump out extra water)
Contral Vacuole (in plant cell)
Chloroplasts
Not in animal cell and for photosynthesis
Mitochondria
Energy powerhouse of the cell where glucose makes ATP