Chapter 5 - Electricity, Magnetism, and Electromagnetism
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
The smallest unit of electrical charge is the…
electron
__________ is the science of stationary electric charges.
electrostatics
__________ is the science of electric charges in motion.
electrodynamics
____________ describes how electrons are given electric potential energy (voltage) and how electrons in motion create magnetism.
electromagnetism
What is the primary function of an X-ray imaging system?
to convert electric energy into electromagnetic energy (x-rays)
More than 99% of the electron energy is converted into and less than 1% of energy is converted into .
heat, X-rays
What is the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles called?
electrostatic force (also called Coulomb's force / Coulomb's interaction)
A _______ is any substance through which electrons easily flow.
conductor
True or False: Copper is a great insulator.
False; it is a great conductor.
An ________ is any material that does not allow electron flow.
insulator
A ___________ is a material that under some conditions, behaves as an insulator and in other conditions, behaves like a conductor.
semiconductor
An ___________ is simply electron movement.
electric current (electricity)
True or False: Increasing electric resistance results in a reduced electric current.
True
Electric current is measured in ________.
amperes (A)
Electric potential is measured in _____.
volts (V)
Electric resistance is measured in _____.
ohms (Ω)
What does Ohm's Law describe?
The manner in which electric currents behave in an electric circuit. (V = IR, I = V/R, R = V/I)
What are the 3 electric factors that are part of an electric circuit?
resistance, current, and potential difference
________ is any property of the circuit that opposes the flow of current.
resistance
________ is the quantity of electrons flowing in a circuit.
current
___________ is the force or speed of the electron flow in the current.
potential difference
True or False: In radiology, all body parts require the same milliampere settings on the generator.
False; different body parts require different milliampere settings
X-ray voltage is measured in ___________.
kilovolts peak (kVp)
What does kilovolts peak refer to?
refers to the maximum voltage applied across the x-ray tube during the exposure
X-ray current is measured in ___________.
milliamperes (mA)
An ____________ is a continuous path for the flow of electric charges from the power source throughout one or more electric devices, and back to the source.
electric circuit
What are the two types of circuits?
series and parallel
Describe a series circuit.
In a series circuit, the wiring runs continuously from the source throughout the device and back to the source.
Describe a parallel circuit.
In a parallel circuit, the devices connected are wired across the circuit, making it more complex.
AC stands for….
alternating current
The process of an alternating current (AC) being converted so that it flows in one direction (DC) only is called?
rectification
A is a semiconductor device that essentially acts as a one-way switch for currents.
diode
What is the name of the special type of electrical generator that creates the process of rectification?
alternator
DC stands for…
direct current
The X-ray tube uses what kind of current?
pulsating direct current (DC)
True or False: The X-ray tube cannot produce X-rays unless the current is rectified.
True
True or False: Magnetic fields and electric energy are not interrelated.
False; they are interrelated
What are the three main ways to induce voltage into a conductor using electromagnetic induction?
Move a wire through a magnetic field.
Move a magnetic field across a wire.
Place a wire in a varying magnetic field.
A _________ can change the voltage of electricity.
transformer
What are the two types of transformers?
step-up and step-down
If there are more coil windings in the primary side than on the secondary side of the transformer, then it is a….
step-down transformer
If there are more coil windings in the secondary side than on the primary side of the transformer, then it is a….
step-up transformer
How does a transformer work?
by using different number of coil windings to change the voltage through electromagnetic induction
What is the primary function of the iron core in a transformer?
to provide a pathway for the magnetic field
Transformers only work with what kind of current?
alternating current (AC)
True or False: A step-down transformer decreases the voltage and current.
False; when the voltage is decreased, the current increases and vice versa.
True or False: Electromagnetic induction is the basis for the transformer.
True
The voltage supplied to a transformer is called the __________.
line voltage
The voltage coming into the transformer from the power source is called the ____________.
primary voltage
The voltage going out of the transformer is called the ____________.
secondary voltage
True or False: Voltage change is not proportional to the number of turns in coil windings.
False; they are proportional
Define transformer ratio (Turns ratio).
the ratio of the number of secondary turns (windings) in the secondary coil to the number of primary turns in the primary coil
True or False: A transformer always increases or decreases the incoming voltage by a set multiple called the transformer ratio.
True
The Turns Ratio is written as…
Ns : Np (Ns = # of turns in secondary coil; Np = # of turns in the primary coil)
What is the name of the process in which the current heats the filament, which leads to electrons being emitted?
thermionic emission
A(n) _ acts as a variable voltage source, allowing precise adjustment of the voltage applied to the step-up transformer; also helps regulate the filament current.
autotransformer
How many coils does an autotransformer use?
1
True or False: The autotransformer uses a singular coil that acts as both the primary and secondary windings.
True
In terms of the X-ray making process, what role does the step-up transformer play?
increases the voltage to the high levels (volts to kilovolts) necessary to accelerate electrons and produce X-rays.
In terms of the X-ray making process, what role does the step-down transformer play?
decreases the voltage and increases amperage to provide the necessary current for heating the filament and producing electrons
A ____ type transformer has its primary and secondary coils wrapped on top of each other, maximizing the effects of the mutual induction.
shell
What type of transformer is most commonly used among radiographic equipment?
shell-type transformer
The is the relationship between the voltage in the secondary coil and the voltage in the primary coil of a transformer.
voltage ratio
Voltage ratio is written as…
Vs = secondary voltage (output)
Vp = primary voltage (input)
Ns = # of turns in the secondary coil
Np = # of turns in the primary coil
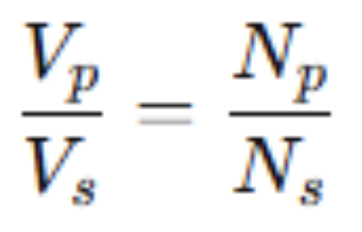
The ________ is a variable resistor that can be used to control the flow of electric current by raising or reducing its resistance.
rheostat
What is the primary function of a capacitor?
to store electrical charges
A ________ is a coil of wire (helix-shaped) that generates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it.
solenoid
A charged particle in motion creates a _________.
magnetic field
True or False: Induced current is always DC.
False; it is always AC
What is the SI unit of magnetic strength?
Tesla (T)
Electric power is measured in ____.
watts
On the surface of an electrified object, the charges concentrate on the?
sharpest curvatures
What is the primary function of a circuit breaker?
to automatically interrupt the flow of electric current when it exceeds a safe level
True or False: Any charge in motion induces a magnetic field.
True