fundus autoflorescence
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is lipofuscin
flourescent that accumulates in the RPE
byproduct of photoreceptor outer segments that have been phagocytosed
when does fundus autoflourescnce occur
when lipofuscin excited by short to med wavelength visible light
how can you detect lipofuscin
-confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope
-fundus autoflourescence camera system
-fundus spectrophotometer
what is the wavelength of lipofuscin
300-600nm
what kind of laser stimulates lipofuscin
low energy
what is the purpose of a barrier filter in AFA
allow only the RPE lipofuscin response to pass
what can AFA do
perform 30 scans & provide an avg calculated result
provides a single monochromatic images with contrast
what does the wideband barrier filter of fundus autofluorescence camera do
allows the lipofuscin response to pass through it before reaching the sensor of the retinal camera
high concentration of lipofuscin
hyperfluorescent signal
absence of lipofuscin appears as
hypofluorescent signal
how does normal fundus appear?
bc there is normal amount of lipofuscin in the RPE → ocular fundus appear diffuse, midly hyperfluorescent
what structures in the eye appear hypoflurescent
optic nerve
blood vessels
fovea
what do hypofluorescent signal
-RPE atrophy
-fresh hemorrhages
-exudative lesions
-areas of dense hyperpigmentation
-some types of hard drusen
what do hyperfluorescent signal
yellow lesions → best’s and stagardt’s disease
older hemorrhages
soft drusens
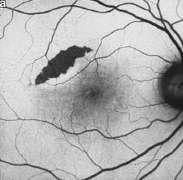
how do RPE tear appear
center: well demarcated → hypo fluorescence
edges: retracted → hyper-fluorescence
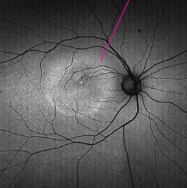
central serous choriotetinopathy
acute exacerbation of CSCR presents a macular detachment w/ hyper-fluorescence at the margin & inferior zone of detachment
in simpler terms: fluid build up → macular detachment → hyperfluorescence due to fluid leaking under the retina → most notable at inferior zone
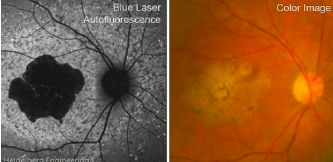
age related macular degeneration
For dry AMD, there’s no cure, but some people use vitamins or dietary changes to slow progression.
For wet AMD, doctors may use treatments like injections, lasers, or photodynamic therapy to stop the blood vessels from leaking.
While AMD doesn’t cause total blindness, it can make everyday tasks like reading or driving difficult, especially in its later stages.
stargardt disease
hyperfluorescent flecks with peripapillary sparing
appear as flecks surrounding a hypofluorescent central macula related to chorioretinal atrophy
what is the most common form of inherited macular degeneration in young people
stargardt disease
retinitis pigmentosa
robson-holder ring: border of active outer segment dysgenesis and abnormal lipofuscin production
what does robson-holder ring represent?
area where retina is active but damaged
retina is trying to work here but it is starting to break down
what is mottle hypoflourescence
Outside the ring
dark, uneven areas
area where photoreceptor cells are dead or severely damaged.
The dark spots mean the retina is no longer working properly in those areas.
best disease
genetic eye disorder that affects the macula
- mutations in the BEST1 gene, which leads to abnormal deposits of material under the retina, disrupting normal vision
what are the different stages of best’s disease
previtelliform
vitelliform
pseudohypopyon
vitelleruptive
atrophic
choroidal neovascularization
stage 1 - previtelliform
normal vision
subtle RPE changes
stage 2 - vitelliform
egg-yolk appearance
normal vision to mild vision loss
stage 3 - pseudohypopyon
layering of lipofuscin
normal to mild vision loss
stage 4 - vitellereptiove
break up of material
“scrambled egg”
stage 5 - atrophic
central RPE & retinal atrophy
20/30 → 20/200
stage 6 - CNV (choroidal neovascularization)
occurs in about 20% pts
significant decrease (20/200 or worse)