Phylogeny and evolution
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history and relationships among species or groups of organisms.
cladogram
a diagram based on shared characteristics.
monophyletic
describing a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all its descendants, forming a clade.
Paraphyletic
describing a group of organisms that includes an ancestor but not all of its descendants, resulting in an incomplete clade.
polyphyletic
diagram that represents evolutionary relationships among organisms. Phylogenetic trees are hypotheses, not definitive facts. A group of organisms that does not include the most recent common ancestor of the members, typically formed from multiple clades.
nodes on a phylogenetic tree
They tell use the age of the most recent or less recent common ancestor.
branch on a phylogenetic tree
refers to the line representing the evolutionary pathway between two nodes, showing the relationship between different lineages.
root on a phylogenetic tree
the common ancestor of all organisms in the tree, serving as the starting point for the evolutionary relationships depicted.
Taxonomy
the science of classifying organisms into groups based on their evolutionary relationships and characteristics.
What tells you how closely related two species are
two species are more related if they have a more recent common ancestor and less related if they have a less recent common ancestor.
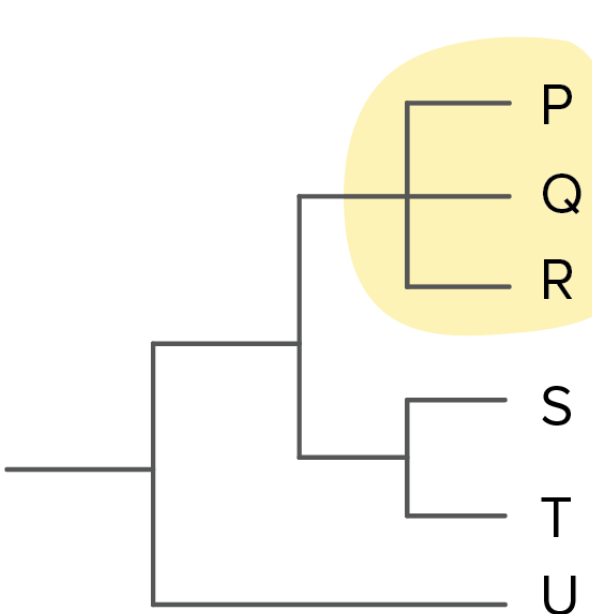
polytomy
a branch point in a phylogenetic tree where three or more descendant groups emerge, indicating uncertain relationships.
what can phylogenetic trees not tell us
we organize species into nested groups based on shared derived traits (traits different from those of the group's ancestor).it does not tell us the exact timing of evolutionary events or speciation.
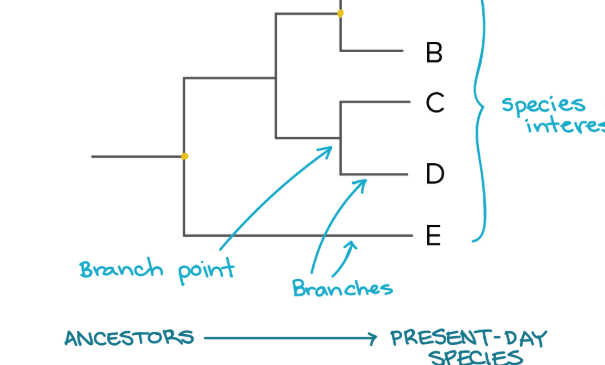
derived traits
traits that evolved within a group and differ from the ancestral trait.
In terms of DNA of relatedness
A larger number of differences corresponds to less related species
A smaller number of differences corresponds to more related species
Genomic changes
Changes in DNA and Cell divison and environmental disruptions
Continous change in fossil records
Transition fossils can show the evolutionary changes as one groups evolve into another
Resistance to various chemicals
Resistance can show evolutionary changes in terms of new mutations
Fitness
The ability of an organism to reproduce
Pathogens
infectious agent that produce dieases, evolves, can become chemically compatible with its host, and can change phenotypes.
Viruses
They evolve rapidly
Virus Recombination
two different viruses swap genetic material (DNA or RNA) when they have hosted the same cell to create a new viral strain, potentially leading to new characteristics or abilities.
Random mutation
A change in DNA sequence
Evidence for common ancestry in Eukaryotic
linear chromosomes, membrane bound organelles, and Genes that contain introns
Membrane bound organelles
Shown in Mitochondria and chloroplasts; have double membrane, endosymbiotic theory, and have ribosomes.
endosymbiotic theory
the hypothesis that eukaryotic cells evolved through a symbiotic relationship between different species of prokaryotes, leading to the formation of organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Linear Chromosomes
Found in all Eukaryotes. It differs from prokaryotic genomes (circular chromosomes ).
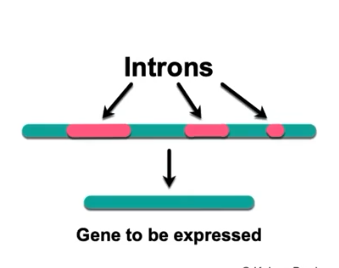
What is an Introns
non-coding sequences of DNA within a gene that are removed during RNA splicing.
Intron for common ancestry
Found in all eukaryotes.
Macroevolution
large scale evidence for evolution: anatomy, embryology, molecular biology, biogeography, and fossils.
homologous
variation in a structure that was present in a common ancestor
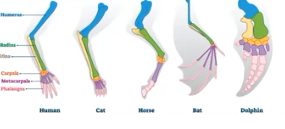
analogous
structures that evolved independently in different species due to similar environmental conditions/selective pressures
evidence 1- molecular biology
DNA sequence comparisons can show how different species are related.
evidence 2- biogeography
These patterns provide clues about how species, both alive and extinct, are related to each other
evidence 3- fossils
are preserved remains, impression, or trace of once living organisms from the past, it tells us age/geographical data
evidence 4 - anatomy/embryology
Anatomical features shared between organisms (including ones that are visible only during embryonic development) can indicate a shared evolutionary ancestry
vestigial structure
A reduced feature that serves little to no purpose for the organism; for example; the human tailbone
Biochemical evidence
A comparison of DNA nucleotide sequences and/or protein amino acid sequences provides evidence for evolution and common ancestry
True or False: Analogous features is convergent evolution
True
reduction of isotope - like carbon 14
is a method used in radiometric dating to determine the age of organic materials by measuring the decay of carbon-14 isotopes.