Lifespan Midterm Practice Questions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
You are a nurse taking a history on a patient in a clinic. You keep in mind that the most important aspect of primary prevention regarding risk-reduction practices is:
A. Reducing the number of partners
B. Treatment of sexually transmitted infections
C. Knowing one's partners
D. Getting tested annually for STIs
A. Reducing the number of partners
As a nursing student you know that the following is true about Bacterial STIs: (select all that apply)
A. There is no permanent cure
B. Treatment involves antibiotics
C. Should involve partner treatment
D. Can result in adverse pregnancy outcomes
E. Often exhibit no symptoms
B. Treatment involves antibiotics
C. Should involve partner treatment
D. Can result in adverse pregnancy outcomes
E. Often exhibit no symptoms
As a nursing student you know that the following is true about Viral STIs: (select all that apply)
A. Should involve partner treatment
B. Often exhibit no symptoms
C. They are chronic
D. Are cured with antibiotics
E. Are easy to detect based on obvious symptoms
A. Should involve partner treatment
B. Often exhibit no symptoms
C. They are chronic
When providing education to a patient regarding treatment of Chlamydia, an important piece of education is:
A. Wait at least 7 days after completing treatment to resume unprotected sex as you can still pass on infection
B. You can resume unprotected sex at any time after diagnosis
C. You can continue to have sex during treatment without risk of spreading the infection
D. You can have sex immediately after you complete taking the entire dose of medication
A. Wait at least 7 days after completing treatment to resume unprotected sex as you can still pass on infection
You are educating a patient on hormonal contraception. You let her know that combined hormonal contraceptives, which prevent ovulation from occurring, come in the following forms:
A. IUD, patch and pills
B. IUD, implant and patch
C. Ring, patch and pills
D. Ring, patch and IUD
C. Ring, patch and pills
You are educating a patient on contraceptive methods that do not contain hormones. You let her know that these include:
A. Implant, copper IUD and condoms
B. Ring, pills and implant
C. Condoms, natural family planning and levonorgestrel-releasing IUD
D. Copper IUD, condoms, natural family planning
D. Copper IUD, condoms, natural family planning
Case Scenario : You are caring for a 17-year-old girl who reports to the clinic with history of vaginal itching, abnormal vaginal discharge, and pain when passing urine and during sex.
Based on the information above which of the following diagnosis would potentially cause these symptoms. Select all that apply
A. Hepatitis C
B. Hepatitis B
C. Secondary Syphillis
D. Gonorrhea
E. Chlamydia
D. Gonorrhea
E. Chlamydia
Case Scenario : You are caring for a 17-year-old girl who reports to the clinic with history of vaginal itching, abnormal vaginal discharge, and pain when passing urine and during sex.
What would be the first thing that the provider should?
A. Educate the client about sex practices
B. Collect a urine and vaginal swab for a NAAT test
C. Conduct a vaginal exam to assess discharge and presence of sores
D. Ask history about sexual partners
D. Ask history about sexual partners
You are caring for a client on her initial visit. During interview she mentions that she got pregnant in 2010 and the pregnancy ended at 12 weeks; her second pregnancy was in 2012 and she delivered at 36 weeks and child is alive; her other pregnancy was twins delivered at 34 weeks gestations and both are alive; and she is currently pregnant. Calculate her GTPAL
A. G-4, T-0, P-3, A-1, L-3
B. G-4, T-0, P-2, A-1, L-3
C. G-4, T-1, P-2, A-1, L-3
D. G-5, T-0, P-3, A-1, L-3
B. G-4, T-0, P-2, A-1, L-3
You are caring for a client on her initial prenatal visit. Her LNMP is July 8th, 2020. Using Nagele's rule what is her estimated date of confinement (EDC)
A. 04/15/2021
B. 03/15/2021
C. 05/01/2021
D. 04/01/2021
A. 04/15/2021
Which of the following is considered a positive sign of pregnancy:
A. Ultrasound assessment of the fetal heart rate
B. Abdominal enlargement
C. A positive pregnancy test
D. Nausea, vomiting and a missed menstrual period
A. Ultrasound assessment of the fetal heart rate
You are caring for a patient who is 24 weeks pregnant. She is concerned about a recent dark pigmented color change in the form of a vertical line that goes from above the umbilicus to the top of the pubis. The best thing to tell her is:
A. This is not a normal finding in pregnancy and she should be referred to a dermatologist
B. This is called chloasma - it is normal in pregnancy
C. This is called linea nigra and is normal in pregnancy
D. This is normal in pregnancy but is often accompanied by itching and hives
C. This is called linea nigra and is normal in pregnancy
The following are part of all typical initial prenatal visits at approximately 12 weeks gestation (select all that apply):
A. Education about pregnancy symptoms and warning signs
B. Assessment of risk of intimate partner violence
C. Health history, nutritional history and family history
D. Measurement of fundal height
E. Lab tests, including CBC and blood type
A. Education about pregnancy symptoms and warning signs
B. Assessment of risk of intimate partner violence
C. Health history, nutritional history and family history
E. Lab tests, including CBC and blood type
Normal cardiovascular changes in pregnancy include:
A. Heart rate increases 10-15bpm
B. Blood pressure increases in late pregnancy
C. Cardiac output decreases
D. Blood volume decreases
A. Heart rate increases 10-15bpm
A nurse is examining fundal height in a pregnant woman in the third trimester. As the woman arises from her the bed she tells the nurse that she feels dizzy. The nurse explains:
A. This can be due to pressure on the vena cava and the woman should lie on her left side
B. This can be due to pressure on the vena cava and the woman should lie on her right side
C. This can be due to pressure on the legs and the woman should lie on her back with feet
D. This can be due to increased venous return from the increased circulatory volume, elevate legs.
A. This can be due to pressure on the vena cava and the woman should lie on her left side
When is urinary frequency most common during pregnancy?
A. First and second trimester
B. The first and third trimester
C. The second and third trimester
D. The third trimester only
B. The first and third trimester
A primigravida reports to the clinic at 37 weeks gestation . She explains that she has been experienced pressure on the diaphragm and shortness of breath in the past week, but she was told that everything was okay. She explains that her chest feels lighter and breathing has improved, but she occasionally feels sharp pain in the pelvis that comes suddenly and goes. All other findings are normal. Which of the following would be the most appropriate explanation of this condition?
A. "This is caused by increased oxygen demands due to growing fetus"
B. "This is a result of physiological anemia due to increased blood volume"
C. "Your body demands have increased with the increased body weight due to the enlarged uterus"
D. "This is called lightening as the fetus descends into the pelvic cavity"
D. "This is called lightening as the fetus descends into the pelvic cavity"
Cardinal movements of labor take the following order
A. Flexion, descent, internal rotation, extension, restitution, external rotation, expulsion
B. Descent, flexion, internal rotation, restitution, extension, external rotation, expulsion
C. Descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation, restitution, expulsion
D. Descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, restitution, external rotation, expulsion
D. Descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, restitution, external rotation, expulsion
The nurse knows that effacement refers to
A. The softening of the cervix in preparation for labor and delivery
B. The discomfort that begins in the back and radiates around to the abdomen
C. Thinning of the cervix as it is drawn upward from the uterine side walls
D. Dilatation of the cervical opening as the uterus contracts and retracts pulling on the cervix
C. Thinning of the cervix as it is drawn upward from the uterine side walls
The nurse is performing a Leopold's maneuver and pelvic assessment. The figure below indicates the findings. What is the position and presentation of the fetus?
A. Cephalic presentation, Left Occiput anterior (LOA)
B. Cephalic presentation, Right Occiput Anterior (ROA)
C. Brow Presentation, Left Occiput anterior (LOA)
D. Face Presentation, Right Occiput Anterior (ROA)
A. Cephalic presentation, Left Occiput anterior (LOA)
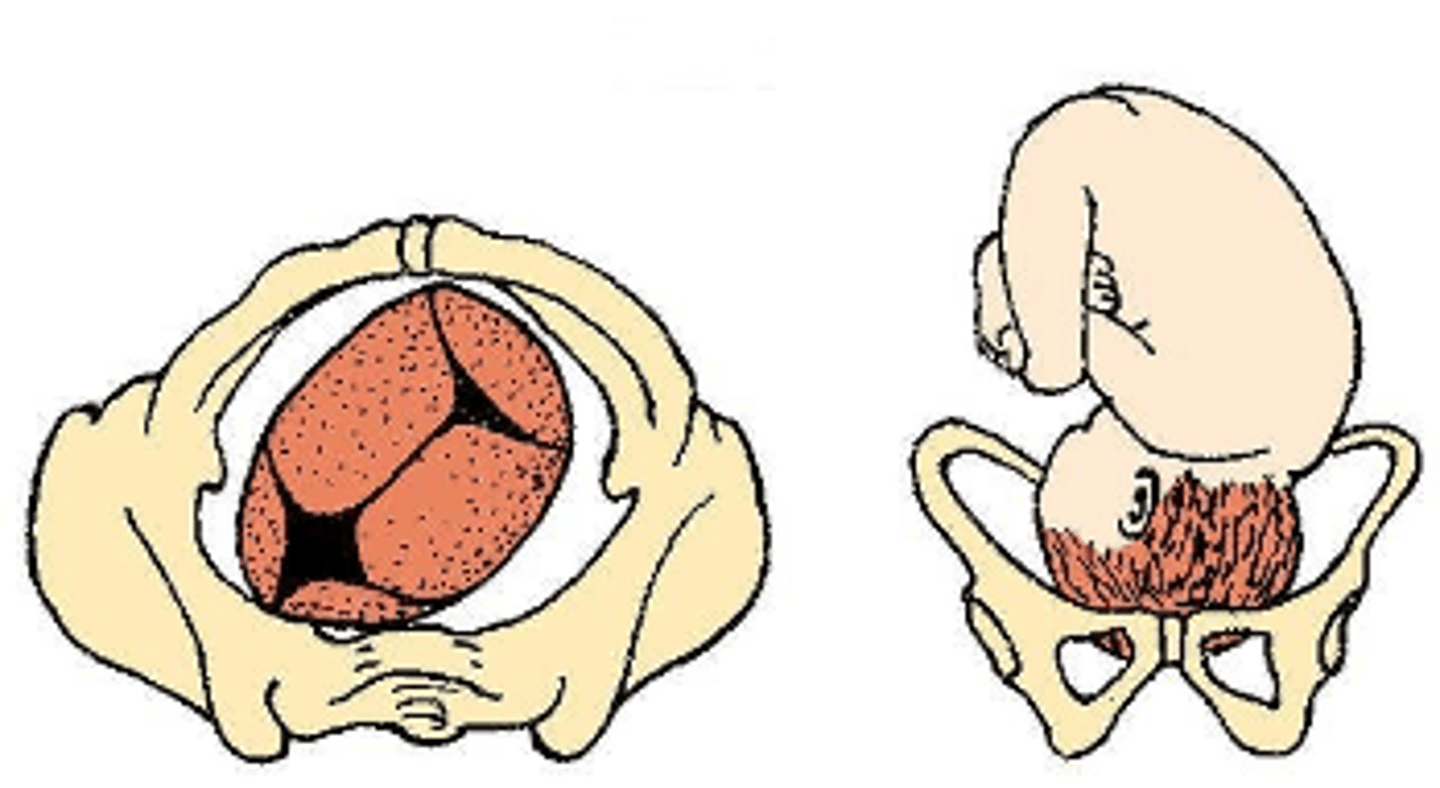
The resident has just told your patient that her baby's head is at zero station - she asks what that means so you will tell her that:
A. The baby's head is at the ischial spines - this is the smallest part of the pelvis
B. The baby's head is below the ischial spines - this is the smallest part of the pelvis
C. The baby's head is ready to be born - as the head is now engaged
D. The baby's head is above the ischial spines - this is the largest part of the pelvis
A. The baby's head is at the ischial spines - this is the smallest part of the pelvis
Your patient is 39 weeks pregnant and has called the clinic to ask if she might be in labor.
The following signs indicate that she is likely in true labor:
A. Bloody show
B. Cervical effacement
C. Contractions that get stronger or less strong depending on maternal movement
D. Regular contractions that have been getting stronger and closer together
D. Regular contractions that have been getting stronger and closer together
You are admitting a patient to L&D and she tells you that she thinks that her "water broke."
Which of the following findings would indicate that the fluid is amniotic fluid?
A. The fluid is clear, pale yellow and has an alkaline pH of 7.0
B. The fluid is clear, pale yellow and has an acidic pH of 5.0
C. The fluid is blood tinged and has an acidic pH of 6.0
D. The patient reports that she has been "leaking" fluid for the past 8 hours
A. The fluid is clear, pale yellow and has an alkaline pH of 7.0
As a nursing student you know that signs of placental separation include: (select two that apply)
A. Mothers has the urge to push
B. Umbilical cord shortens
C. Gush of blood
D. Uterus contract and descend into the pelvis
E. Uterus becomes more globular and firm
C. Gush of blood
E. Uterus becomes more globular and firm
Which of the following pharmacological measures for pain management in labor has the minimal risk for newborn respiratory depression
A. Butorphanol
B. Nitrous oxide
C. Hydromorphone / Dilaudid
D. Nubain/Nalbuphine
B. Nitrous oxide
You are caring for a newly admitted patient with a diagnosis of hyperemesis gravidarum. Which finding is a clinical manifestation of this diagnosis?
A. Ketones present in urine sample
B. Platelets of 100,000
C. Fasting serum glucose of 100
D. Hemoglobin of 10.8
A. Ketones present in urine sample
You are caring for a patient who is 37 weeks pregnant. You are concerned about the risk of preeclampsia when the patient tells you she is having:
A. A history of headaches at 14-18 weeks gestation
B. Scotoma (blind spots in her vision)
C. Edema in her feet and ankles
D. Fatigue
B. Scotoma (blind spots in her vision)
The goal of glycemic control in a pregnancy complicated by diabetes is:
A. Avoiding maternal hypoglycemia
B. Maintaining a Hemoglobin A1C of below 8.0
C. Maintaining maternal fasting blood sugar at 120mg/dl or less
D. Maintaining maternal fasting blood sugar at 65-95mg/dl
D. Maintaining maternal fasting blood sugar at 65-95mg/dl
You are caring for a patient who has just been diagnosed with HELLP syndrome. You would expect to see the following findings in her lab results:
A. Low platelets (<100,000)
B. Decreased liver enzymes (AST and ALT)
C. Elevated WBCs
D. Elevated hemoglobin level (>12.0)
A. Low platelets (<100,000)
You are providing care to a client with pre-eclampsia on Magnesium sulfate. Which on the following finding would cause concern?
A. Urine output of 50ml/hr
B. Protein is urine of 2g/24hr
C. Respiratory rate of 11/min
D. Serum levels of Mag Sulfate of 6mEq/L
C. Respiratory rate of 11/min
A 25-year-old gravida 1 para 0 reports for prenatal care. She is at 5-weeks gestation and her medical history shows that she has Type 1 diabetes. Which of the following would indicate understanding of her medical therapy?
A. "My current insulin needs have not changed and I don't need dose adjustment from my pre-pregnancy insulin regimen"
B. "My current insulin needs have greatly increased, and they need to double my dose to prevent severe hyperglycemia"
C. "My current insulin needs have decreased, and I need dose adjustment because I am at risk of developing hypoglycemia"
D. "My current insulin needs have increased, and I need dose adjustment because I am at risk of developing hyperglycemia"
C. "My current insulin needs have decreased, and I need dose adjustment because I am at risk of developing hypoglycemia"
A client with type 2 diabetes at 20 weeks gestation complains that they feel nauseous and and excessive thirst. On assessment the client is confused and respirations are shallow at rapid at 35 breaths per minute with a sweet fruity scented breath. The nurse identifies that these signs and symptoms are indicative of?
A. Diabetic ketoacidosis
B. Urinary tract infection
C. Hyperemesis gravidarum
D. Hypoglycemia
A. Diabetic ketoacidosis
A client reports for an initial prenatal visit at 14 weeks gestation. On assessment her Blood pressure is 180/100mhHg with protein in urine of 300mg. The nurse understand that that this is indicative of:
A. Gestational hypertension
B. Pre-eclampsia
C. Eclampsia
D. Chronic hypertension
D. Chronic hypertension
You are caring for a mother who reports to the emergency room at 26 weeks gestation with history of vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain. On examination you observe dark red blood and clots, and her abdomen feels tense. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ectopic pregnancy
B. Placenta Previa
C. Miscarriage
D. Placental abruption
D. Placental abruption
A primary risk of Pitocin (oxytocin) is:
A. Tachysystole
B. Early decelerations
C. An increased rate of c-section
D. Prolonged labor
A. Tachysystole
A client comes in with irregular uterine contractions and drainage of amniotic fluid at 32 weeks gestation. Which of the following medications is recommended for this situation?
A. NSAIDs
B. Gabapentin
C. Clonidine
D. Betamethasone
D. Betamethasone
As a nursing student you understand the consequence of persistent posterior positions in labor include?
A. Labor dystocia
B. Reduced pain sensation
C. Precipitate labor
D. Shorter second stage of labor
A. Labor dystocia
You are caring for a client with cord prolapse. Which of the following interventions would he suitable for this case? (select three that apply)
A. Try and see if the cord can be replaced back into the cervix gently
B. Administer oxygen 10L via mask
C. Position the client in extreme Trendelenburg
D. Position the client in supine position for adequate gaseous exchange
E. Glove examining hand and quickly insert two finger in vagina and push presenting part upward
B. Administer oxygen 10L via mask
C. Position the client in extreme Trendelenburg
E. Glove examining hand and quickly insert two finger in vagina and push presenting part upward
A 33-year-old client with a history of one cesarean section would like to know if she is a candidate for Vaginal Birth after Cesarean Section (VBAC). Which of the following would be a contraindication for this? (select two that apply)
A. First c-section involved classical incision
B. Uterine trauma and perforation that was successfully repaired
C. Maternal Age
D. Preterm labor
E. First c-section involved pfannenstiel incision
A. First c-section involved classical incision
B. Uterine trauma and perforation that was successfully repaired
Which of the following would be a contraindication for a vacuum extraction?
A. Pre-eclampsia
B. Head at station 0
C. Breech presentation
D. Cervix at 10cm dilatation
C. Breech presentation
You are working as an RN in a labor and delivery unit. Which of the following clients would you see first?
A. A primigravida at 5cm dilatation with a report of vaginal bleeding with clots and a tense abdomen
B. A multigravida in fourth stage of labor with mild bleeding and complaining of difficulties attaching infant to breast
C. A primigravida at full dilatation and head at station -1 complaining about urge to push
D. A multigravida at 8cm dilatation complaining about painful uterine contractions
A. A primigravida at 5cm dilatation with a report of vaginal bleeding with clots and a tense abdomen
You are caring for a mother 14 hours after birth. The nurse understands that the uterus should be:
A. Midline, firm, and halfway between the symphysis pubis and umbilicus
B. Midline, firm, and at the level of the symphysis pubis
C. Midline, firm, and at the level of the umbilicus
D. Slightly pushed to the side, boggy, and halfway between the symphysis pubis and umbilicus
C. Midline, firm, and at the level of the umbilicus
The day after birth of her baby, a mother tells the nurse that she has been urinating excessively. What is the nurse's response?
A. You probably have a UTI, I will obtain a urine sample
B. This is a normal response to eliminate extra extracellular fluid from the pregnancy
C. This may be an early sign of postpartum pre-eclampsia
D. You will need to cut back on your fluid intake
B. This is a normal response to eliminate extra extracellular fluid from the pregnancy
A nurse is preparing to perform a fundal assessment on a postpartum client. The initial nursing action in performing this assessment is which of the following?
A. Ask the mother to urinate and empty her bladder
B. Ask the client to turn on her side
C. Massage the fundus gently before determining the level of the fundus.
D. Ask the client to lie flat on her back with the knees and legs flat and straight.
A. Ask the mother to urinate and empty her bladder
The nurse is assessing the lochia on a 1-day PP patient. The nurse notes that the lochia is red and has a foul-smelling odor. The nurse determines that this assessment finding is:
A. Indicates the need for increasing ambulation
B. Document this as a normal finding
C. Indicates the need for increasing oral fluids
D. Indicates the presence of infection
D. Indicates the presence of infection
Which of the following psychological responses would be a characteristic of puerperal psychosis?
A. Excessive weepiness and feeling of inadequacy on day 1 postpartum
B. Fatigue after birth
C. Mother is restless and say that she sees ghosts trying to steal her baby
D. Mood swings, anxiety, and insomnia on day 7 postpartum
C. Mother is restless and say that she sees ghosts trying to steal her baby
You are caring for a client in immediate postpartum period with heavy bright vaginal bleeding and clots. On abdominal assessment the bladder is empty and uterus in firm, midline, and halfway between symphysis pubis and umbilicus. What should the nurse consider the most likely cause of this hemorrhage?
A. Normal bleeding associated with birth
B. Cervical tear or deep lacerations
C. Uterine atony
D. Superficial lacerations
B. Cervical tear or deep lacerations
You are caring for a client with postpartum hemorrhage from uterine atony. Which of the following would be a priority nursing diagnosis?
A. Start an IV infusion of 1L Ringers lactate with 10-40 units of Oxytocin
B. Administer oxygen 10L via mask
C. Notify their provider
D. Massage the uterine fundus and express clots
D. Massage the uterine fundus and express clots
As a nursing student you understand the following intervention would be contraindicated in a client with severe pain of left leg and Deep Vein Thrombosis:
A. Encouraging bed rest
B. Massage the affected area to promote muscle relaxation
C. Elevation of the affected leg and use of compression stocking
D. Administer prescribed anticoagulant therapy and analgesics
B. Massage the affected area to promote muscle relaxation