Reliability and Validity ONE
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Reliability
the consistency or stability of the measure
Method Error
error from the experimenter and testing situation (ex. poor instructions, if research wants study to go certain way)
Error
the difference of the score the participant gave us and where they should actually fall on the regression line
Observed score =
true score + measurement error (O = T + E)
Where do you find each letter (O, T, E) on the scatterplot
O: the dot(s) on the graph
T: where the person should fall on the regression line
E: the difference between their true score and observed score
What is the reliability formula?
reliability = true score / (true score + error score)
Reliability is how much ______ there is in your measure
ERROR
Perfect Reliability
Score of 1.00
Scores range from 0-1
As the error increases, the reliabliity coefficient _____
decreases
How do we actually measure reliability?
Correlation coefficients!
Correlation coefficients
value that indicates the strength of the relationship between two variables
What are the vales of r that represent the strength of relationships?
± 0.70 - 1.00 = strong
± 0.30 - 0.69 = moderate
± 0.00 - 0.29 = none to weak
What are the different types of reliability?
Test/Retest, Alternate Forms, Split-Half, Cronbach’s Alpha, Interrater
Test Retest Reliability
Measuring consistency across TIME
If the measure is reliable, people should score the same way EACH time they are measured
Two Problems with Test Retest Reliability
Practice Effects: people get better at answering questions the second time around
Short Interval: if the time between completing the measure is short, people might remember how they responded to the question
Alternate Forms Reliability
to control for test/retest problems, you can use different versions of the SAME measure
tests take at Time 1 and Time 2 are equivalent
to be equivalent, scales must have the same number of items, difficulty level, instructions, time limits, examples, and format
This is VERY DIFFICULT to ensure
examples: MCAS
Split-Half Reliability
split items on a measure in half and correlate the two halves
Consistency across ITEMS
Cronbach’s Alpha (α)
overall internal consistency of a measure
basically saying “what’s the consistency between item 1 and item 2, what’s the correlation between item 1 and item 3 and so on…”
across all items, that’s the global measure for the tool
scores range from 0-1, where higher scores means greater consistency between items
consistency across ITEMS
Interrater Reliability
to test for reliability of observational methods
interrater reliability = (number of agreements / number of possible agreements) x 100
Kappa coefficient - better than % agreement above
Validity
degree to which a measure assesses what it it supposed to assess
What are the different types of validity?
Content, criterion, construct
Content validity
the measure contains a good sample of items that are relevant and representative of the construct
Criterion Validity
the psychological measure is capable of predicting actual behavior
Formula for criterion validity
y = bx + a
use unstandardized scores
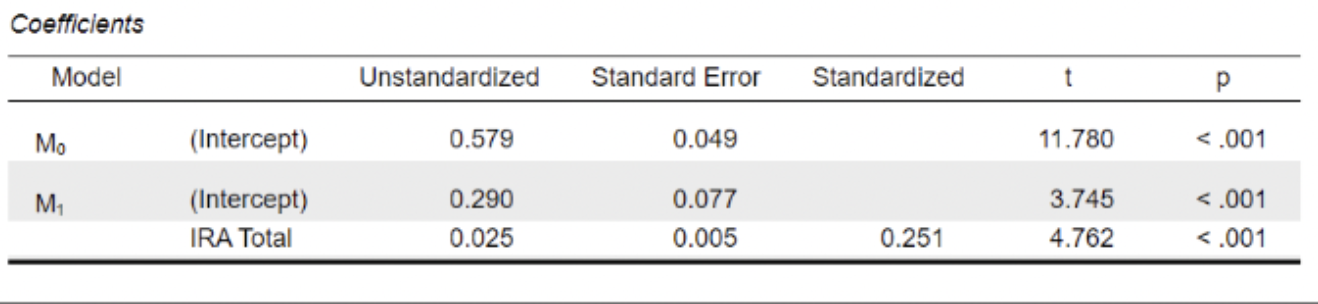
What would the formula be given this table - we are measuring risk score for violence
Violence = 0.025 (risk score) + 0.29
Construct validity
the degree to which the measure assesses the psychological construct
considered the most important type of validity
to test for construct validity, researchers correlate the measure with other measures of the construct, and with measure of other constructs
What two validities fall under construct validity?
Convergent Validity: scale correlates with other measures of the same thing
Divergent Validity (discriminent validity): scale does not correlate with different constructs
Method Bias
Correlations between measures of different traits using the same method
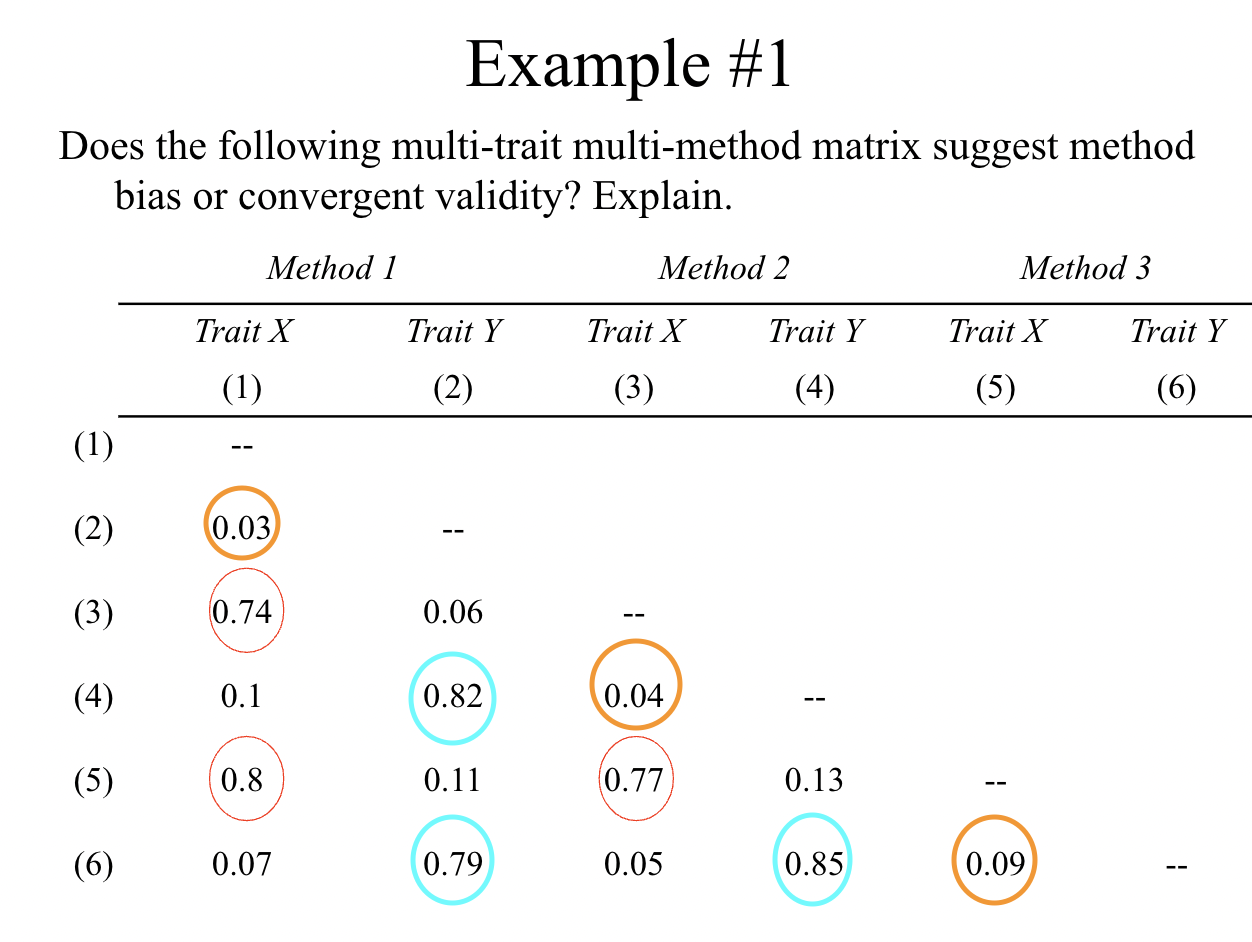
What do each color represent?
red: convergent validity
blue: divergent validity
orange: method bias