bacterial conjunctivitis
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
conjunctival anatomy
thin and clear mucus membrane that covers posteirior portion of eyelid
lubricate
protect
provide nutrition
prevents friction btw eye and lids
brief blood supply review
anterior ciliary artery —> posterior conjunctival artery —>peripheral and marginal tarsal arcades
whats the venous drainge
inferior and posterior ophthalmic veins
where does lateral canthus drain
superficial parotid lymph nodes
where does medial canthus drain
submandibular lymph nodes
bacterial conjunctivitis risk factors
generally develop from exogenous contaminatino or from the bodys ocular surface flora
mostly seen as acute but can be present as hyperacute or chronic
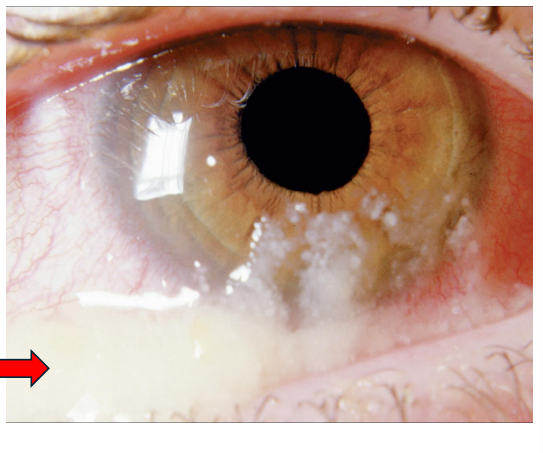
whats this
mucopurulent discharge
whats pathoneumonic for bacterial conjunctivitis
mucopurulent discharge
what is mucopurulent discharge
A collection of tears and immune cells that are over expressed
whats the most common cause of acute bacterial conjunctivitis in ADULTS
-Staphylococcus Aureus-
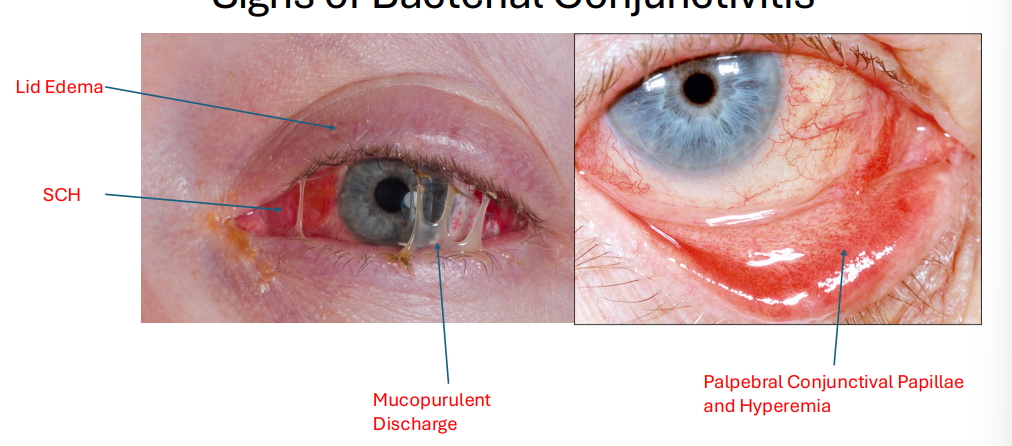
what are signs of bacterial conjunctivitis
lid edema
sub conjunctival hyperemia
chemosis
foreign body sensation
mucopurulent discharge 2 most defining things
palpebral conjunctival papillae and hyperemia
classication of staph auereus
gram + bacteria w spherical/cocci shape
asymmetric onset but can become bilateral
MOST COMMON IN ADULTS
diagnosis w staph aureus
blood agar plate or mannitol salt agar plate
streptococcus pyogenes conjunctivitis
• Mucopurulent discharge
• Conjunctival papillae
• Conjunctival hyperemia
• Chemosis
• Foreign body sensation
• Lid Edema •
Pseudo-membranes
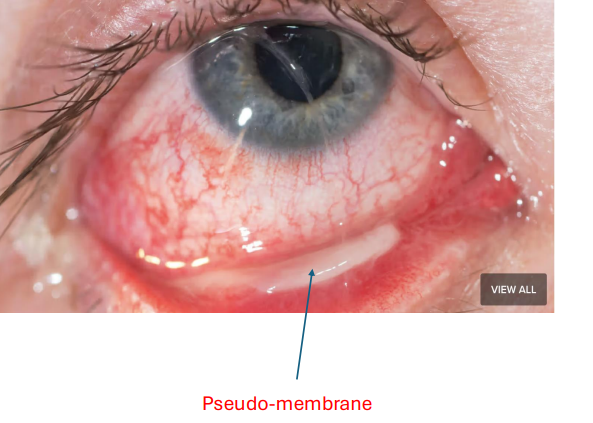
whats a pseudomembrane
EASILY peeled off
NO bleeding
Corynebacterium Diphtheriae Conjunctivitis signs and symptoms
• Mucopurulent discharge
• Conjunctival papillae
• Conjunctival hyperemia •
Chemosis
• Foreign body sensation
• Lid Edema
• Membranes
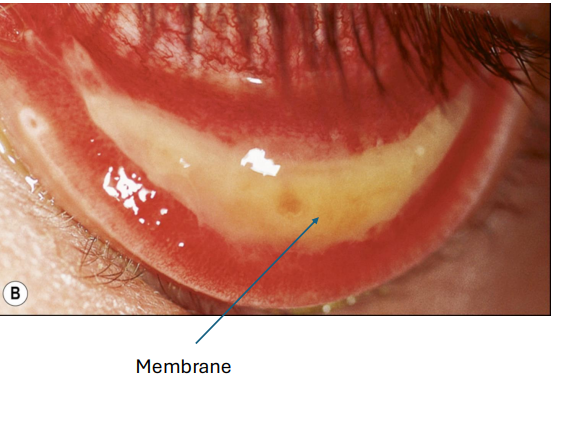
Corynebacterium Diphtheriae
can penetrate cornea
Gram Positive (+) that is clubbed shaped
membrane
DIFFICULT to peel off
will cause conjunctival bleeding
why should we worry about membranes
palpebral conj can stick to bulbar —→ symblepharon
can cause scarring
can possibly speed up healing if removed
can use cotton tip applicator/jewlers forceps
how do you treat acute bacterial conjunctivitis
4th generation Fluoroquinolone - 1 gtt TID for 5-7 days
-Besifloxacin 0.6%
-Gatifloxacin 0.5%
-Moxifloxacin 0.5%
pregnancy category C
whats the MOA of 4th gen Fluoroquinolone-
MOA- inhibits DNA replication of bacteria by targeting enzymes DNA Gyrase and Topoisomerase IV
Good broad spectrum coverage
whats the contraindication for 4th gen Fluoroquinolone-
-Damage to growing cartilage in children
-Tendonitis and tendon rupture
what other than 4th gen fluorofquinolones can be used for acute bacterial conjunctivitis
Polymyxin B/Trimethoprim 1 gtt QID for 5-7 Days
Pregnancy Category C
MOA of Polymyxin B/Trimethoprim
Polymyxin B- binds to phospholipids in gram-NEGATIVE bacteria Trimethoprim- inhibits tetrahydropholic acid (THF) by binding to dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) –effective with mostly grampositive bacteria and some gram NEGATIVE bacteria
if he gives an allergy give a back up
who is Polymyxin B/Trimethoprim for acute bacterial conjunctivitis good for
kids
whats the f/u for Acute Bacterial Conjunctivitis
every 2-3 days initially
then 5-7 days until resolved
once we see that it is working
hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis cause
Neisseria Gonorrhea
CULTURE W CHOCOLATE AGAR
Neisseria Gonorrhea classification
gram - that is diplococcus/kidney bean shaped
acquired by sex
what does hyperacute mean
you wipe away the discharge and it comes back instantly
signs/symptoms of Hyperacute Bacterial ConjunctivitisNeisseria Gonorrhea
• Hyperacute mucopurulent discharge
• ****When you remove, it reappears almost instantly**** •
Conjunctival papillae
• Pre-Auricular Adenopathy
• Severe conjunctival hyperemia
• Chemosis
• Corneal ulceration and possible perforation •
Foreign body sensation •
Severe Lid Edema
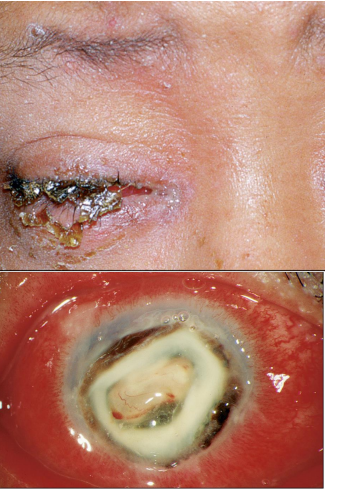
chemosis
swelling of conj
looks bubbly
how do you diagnose hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis - neisseria gonorrhea
chocolage agar
thayer martin agar
what are the bacteria that can penetrate the cornea
Neisseria Gonorrhea
Neisseria Meningitidis
listeria species
Haemophilus influenza
corynebacterium diphtheriae
diagnosis of Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
• Confirmed by microbiology- Gram stains, PCR and culturing media including blood agar, chocolate agar and Thayer-Martin agar
how do you treat Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
• Would recommend consultation with infectious disease specialist
• Treatment would include single dose 1g of cephtriaxone IM and azithromycin 1g P.O
• If severe with corneal involvementtopical gtts include Fortified antibiotics(Tobramycin and cephazolin) and 4th generation FQ q1-2 hours
in reality we are probably not treating this - get them out adn report to department of public health
Follow Up Schedule for Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
wo/ corneal involvement —> every 2 days
serious corneal involvement —> every day
Hyperacute Conjunctivitis - Haemophilus Aegyptus
does the same thing just very aggressive
not as much as neiserria gonnorhea
hes not really focusin gon it = many types of bacterial cause many things
when does acute bacterial conjunctivitis go away
1-2 weeks
hyperacute too (about)
chornic bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized by
injection
discharge,
swelling
foreign body sensation
and papillae of the tarsal conjunctiva
persisting 2-3 weeks or longer
chlamidyal trachomatis
GRAM NEG
subtypes
subtypes A-C = trachoma
subtypes D-K = inclusion conjunctivitis
trachoma
superior palpebral conjunctivitis
vector is a fly
seen more in regions w limited acess to water and sanitation
affects children more
signs of trachoma
chronic inflammation w large follicles/papillae on superior palpebral conj and scarring
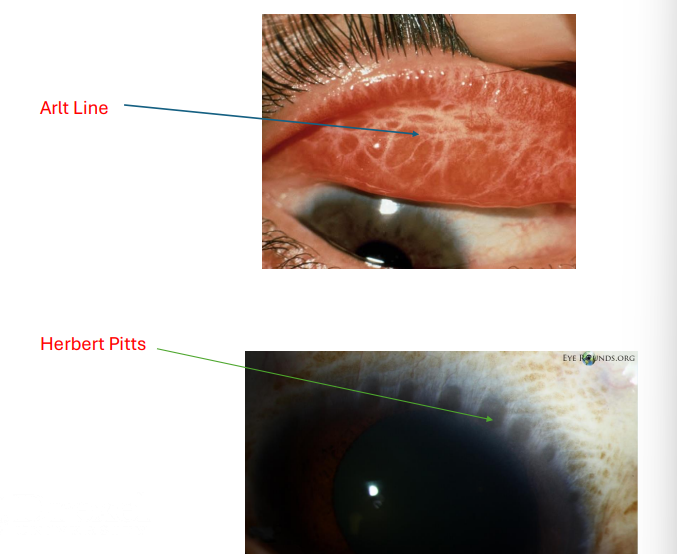
Arlt Line = horizontal scaring in conj ***************
herberts pits = scarred limbal follicles **************
PATHONEUMONIC
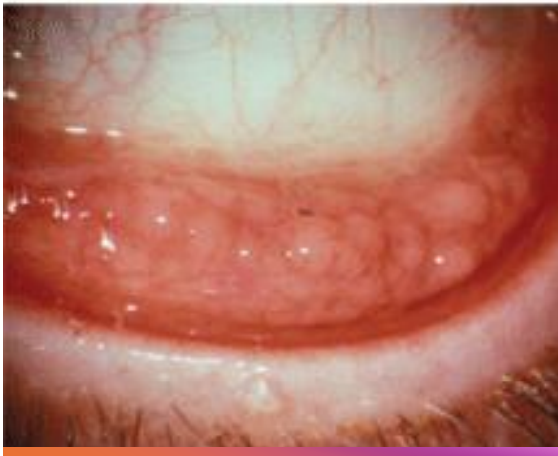
inclusion conjunctivitis
oculo genital transmitted condition (HENCE subtypes D-K)
more typically unilateral
follicles/papillae on INFERIOR PALP CONJ
can exhibit keratitis w SEI
can confirm w nucleic acid amplification test
how do you treat trachoma
doxycycline 100mg BID PO for 2 weeks,
or
Azithromycin 20mg/kg PO single dose
how do you treat inclusion conjuctivitis
Treat with doxycycline 100mg bid x 7-10 days
or
single dose of 1g azithromycin PO,
contraindications of doxycycline
Avoid in children, liver and kidney problems
teeth discoloration/enamel defect
– -Pregnancy Category D
-Side effects could include nausea/vomiting,
photosensitivity
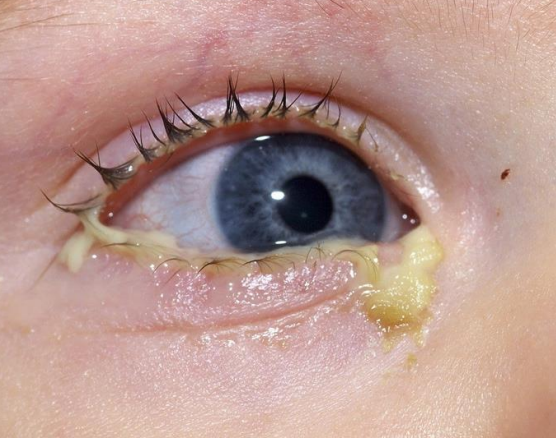
pediatric bacterial conjunctivitis - MOST is caused by
H. influenza - bacteria
similiar signs and symptoms as previous conjunctivitis
papillary
follicles vs papillae
follicles are big and mounded
single feeder blood vessels
papillae are velvety
bunch together
is pediatric bacterial conjunctivitis contagious
HIGHLY
how do you treat pediatric conjunctivitis
Polymyxin B/Trimethoprim 1 gtt 4-6 times per day (depending on severity) for 7-10 days
Great safety profile in children
Follow up every 2-3 days- must avoid interaction as it can be highly contagious
whats another pediatric bacterial conjunctivitis causer
streptococcus pneumoniae
category A
No evidence to fetus in 1st trimester or later
category X
Fetal abnormalities or toxicity in animal studies or human studies, and risk outweighs the benefits
what bacteria are acute, hyper acute, and chronic
acute = staph auerues (around eye)
hyperacute - gonnorrhea
chronic = chlamydia