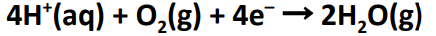GCSE Chemistry C5 - Energy Changes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Energy transfer during exothermic reactions
- transfers energy to surroundings so temp in surroundings increase
- product molecules have less energy than the reactants
- combustion, neutralisation, oxidation reaction
- coffee, hand warmers, self heating cans
Energy transfer during endothermic reactions
- takes in energy from surroundings so the temp of the surroundings decreases
- product molecules must have more energy than reactants
- thermal decomposition,
- sports injury packs
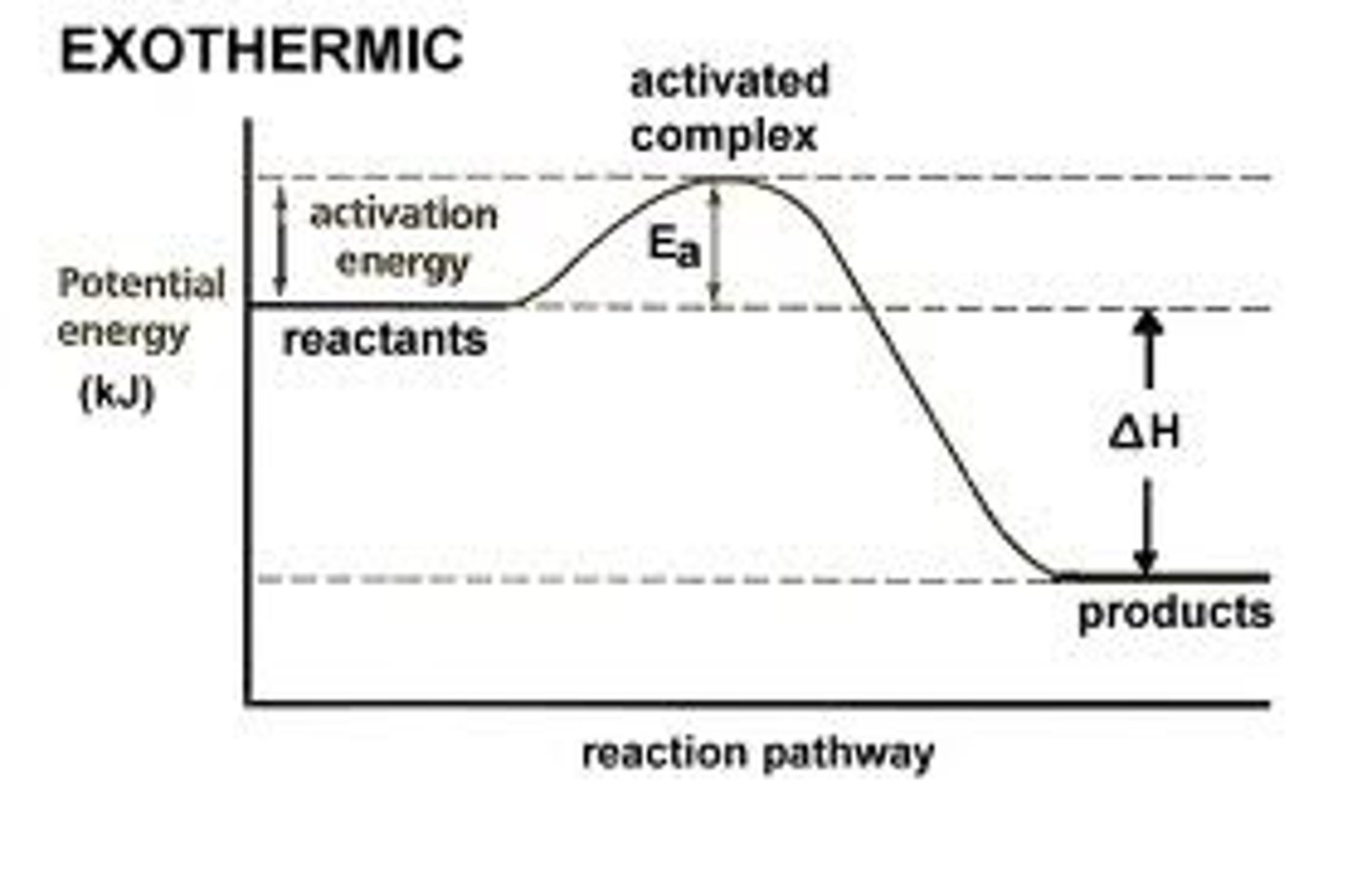
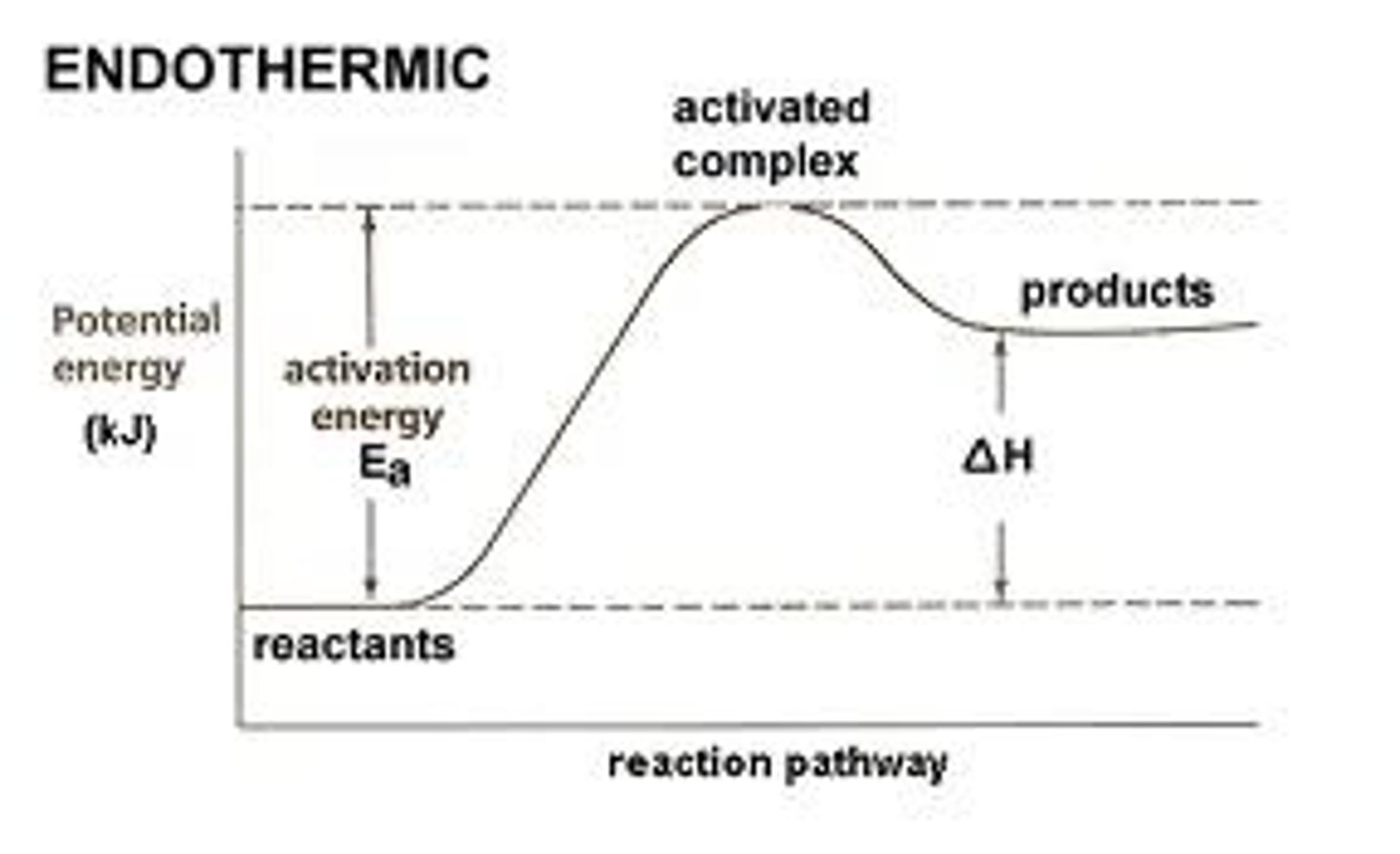
reaction profile
chemical reactions can only occur when reacting particles collide with each other ith sufficient energy
activation energy
minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react
exothermic graph
endothermic graph
endothermic energy change
energy taken in to break> energy released when formed
exothermic energy change
energy taken in to break < energy released when formed
how can a cell be made
by connecting two different metals in contact with electrolyte
non - rechargable cells and batteries
- chemical reactions stop when one of the reactants has been used up
- alkaline batteries are non - rechargeable
rechargeable cells and batteries
can be recharged becaue the chemical reactions are reversed when an external electrical current is supplied
fuel cells - the fuel
supplied by an external source of fuel (hydrogen) and oxygen or air. the fuel is oxidised electrochemically (hydrogen and oxygen) within the fuel cell to produce a potential difference
hydrogen fuel cell
- fuelc cells can be used constantly provided fuel keeps being put in
- hydrogen is a gas so needs to be stored at high pressure and so is harder to transport
- only produces water when burnt
rechargeable cells and batteries
- can be recharged by reversing reaction so fuel doesn't need to keep being supplied
- hard to dispose of (non - biodegradable)
- will stop working eventually
half equation at anode
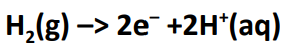
half equation at the cathode