SFL 102 EXAM 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Art deco
Formal (symmetrical and vertical)
Flashy
Simple, but heavy scaled furniture
- a ton of motifs
- For the wealthy and elegant
- aztec/mayan symbolism
- Vertical design style
- Zeitgeist - ghost of time; compared to the skyscraper bookcase
- At Moderne: 1920s-1940s - "sleek vs chic" more horizontal
has intent
the difference between art and art design is that design
What can designers do to support sustainable and green design?
design around standard product sizes to reduce material waste
consider the recyclability of all materials
specify products free of urea formaldehyde
Correct!
Victorian
welcomed the new technology of the industrial revolution
Christian Style
Arts and Crafts
A rebellion against the machine or against the horrid things het were going on
Very structured and simple
Loosing crafts to machines
Handmade
Nature
Simple/ structural
Earth tones/ wood
joinery
Baroque
-overly decorated
-very fancy and ornate
-chinese-esque
DECORATION AND ORNAMENTATION
Ancient Egyptians
furniture was a sign of wealth
Bauhaus
-factory looking
-lots of big windows
-tubular steel
- Le Corbusier:
1. Roof space for use
2. Less walls; concrete slabs + curtain wall construction
3. Free facades - flood interior with light
4. Light
5. Raise buildings off the ground; people can use the space under
Rococo
came out from Baroque
not heavy
less serious and more lighter
represents exubarnece and happiness
more feminine (pastel colors)
how does historic style differ from historic period?
A style can transcend time.
A period can have many styles.
Historic periods are restricted to time, while style is not.
International
Radical simplification of form
Rejection of ornamentation
Large areas of glass (horizontal banding)
steel and concretes as preferred materials
Transparency of buildings
Honest expression of structure
Post modern
international style chairs because they are made of steel

Mid-century Modern
comes directly from Bauhaus
make US one of the most important design influences in the world
Charles and Ray Eames - influenced by modern designers; looking to the future = modernist; LCM = POTATO CHIP CHAIR
3 legs on the chair - it’ll be more stable on an uneven floor
Florence Knoll - she designed paces and couldn’t find furniture she wanted, so she designed her own furniture
Milo Baughman - taught at BYU; known for creating furniture; closed his interior design form to become a presbyterian minister, but remarried an LDS lady and became baptized
Christian Style
victorian, fancy
Decoration
Ornamentation
boulle work
patterned inlays of brass and tortoiseshell
cabriole leg
stylized animal leg (probably derived from oriental influences)
ormolu
addition of mercury brass and gold amalgam
bubble diagram
prototypical lay out
what needs to be next to what
make bubbles relative to size
loose design, so can easily alter
design process
Phase 1: ID project, determine scope of services, consider schedule and budget
Phase 2: programming - gather date, identify primary issues, document existing state
Phase 3: schematic design; bubble and block
Dome
romans created it
Roman Column
tuscan, doric, corinthian
more simple becasue they were in a rush to buld tnem
Greek Column
(doric)
all shafts are fluted
start wide (at the bottom) and get smaller (at the top)
capital
top
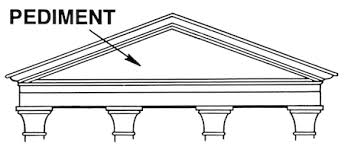
pediment
triangle that sits on top
volute
curled end of a column
ionic
has a smooth shaft instead of fluted shaft
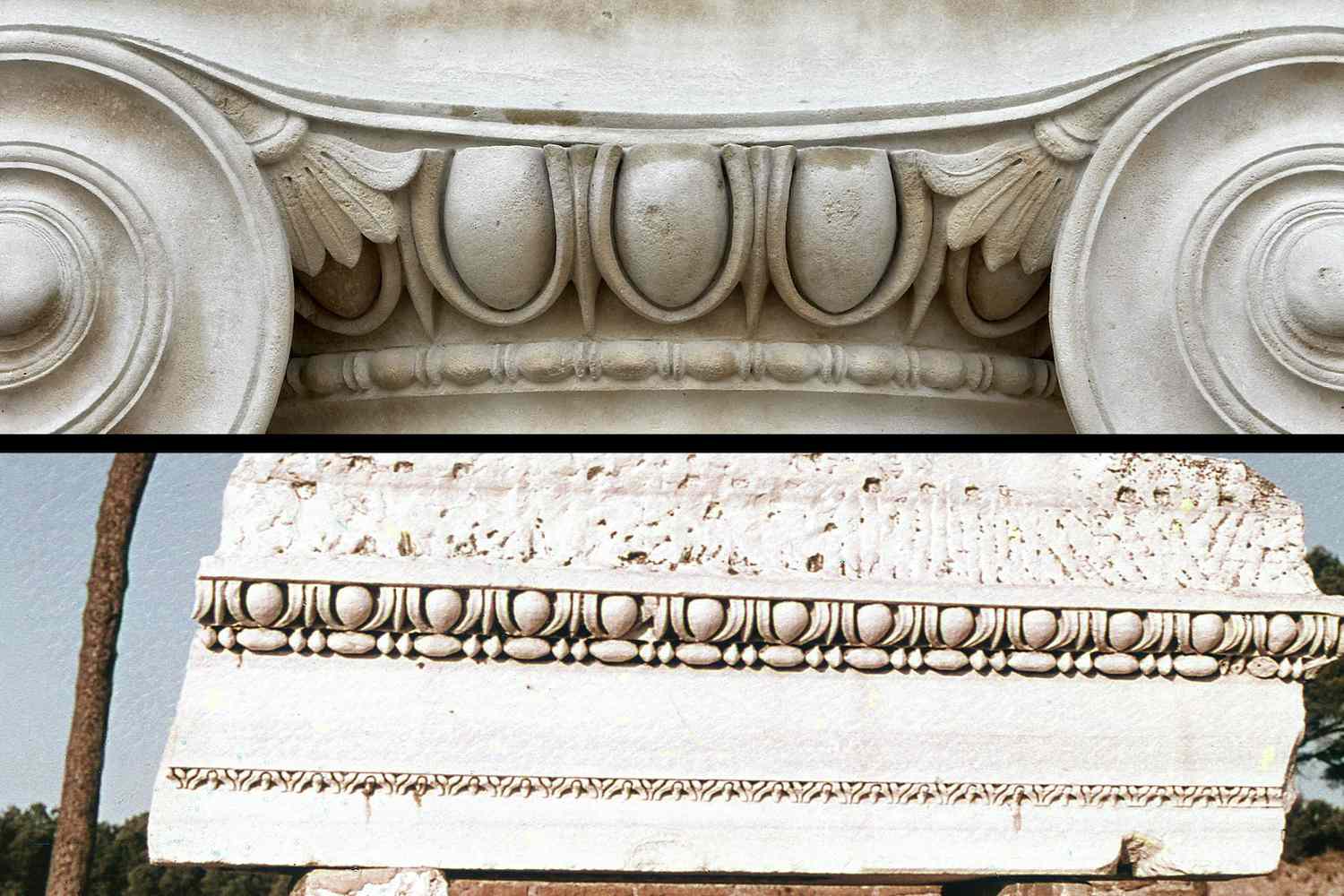
dentil
little designs that look like teeth
egg and dart
something round separated by something sharp

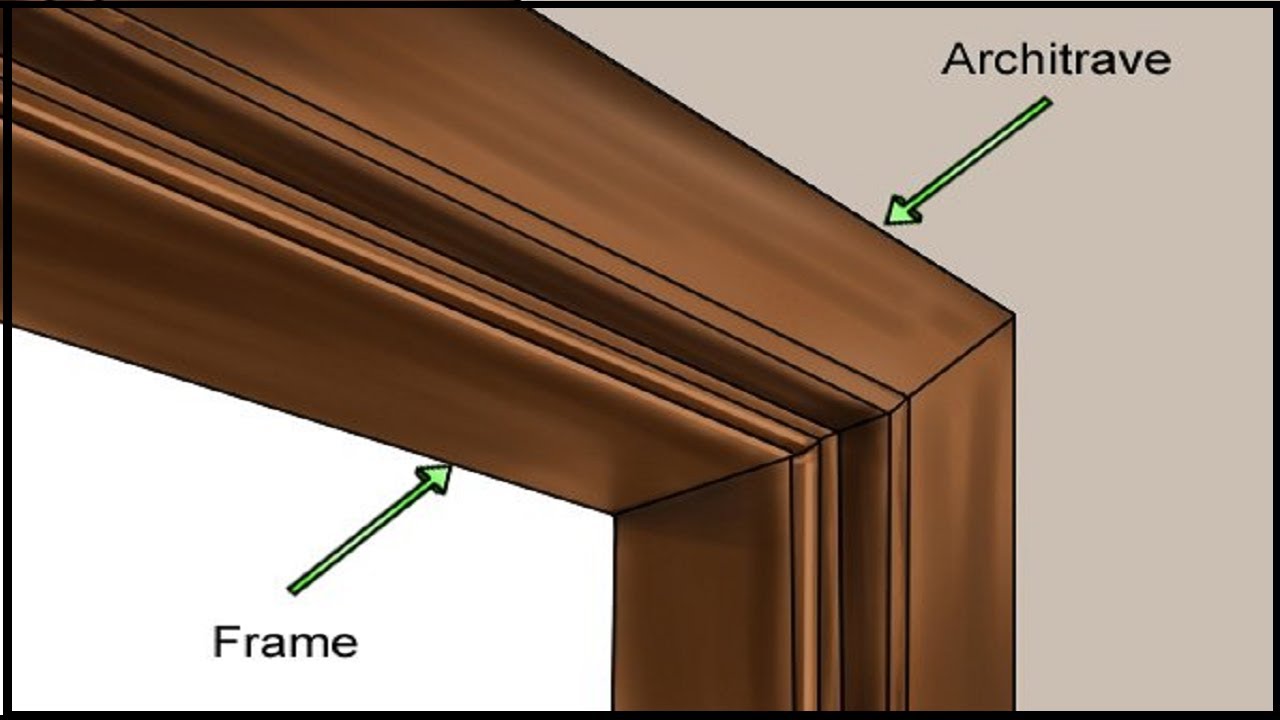
architrave
"main beam:, sits horizontally
the horizontal beam that rests directly on top of the columns, forming the lowest part of the entablature
doorways
compliant
toilet to wall
15 inches
general conversations distance
8 feet
public proxemic
13 feet away
shallow conversation
dining table to wall for traffic clearance
3 feet
8 feet between people
ideal distance for conversation
bedside to wall distance
18 inches
ADA
forces designers to design for all people
American Disabilities Act of 1990
Prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities in several areas, including employment, transportation, public accommodation, communications and access to state and local government programs and services
why is access important?
universal design
"...design of products and environments to be usable by all people to the greatest extent possible without adaptation or specialized design"
EXAMPLE: both increasing the width of doorways/hallways AND providing high-contrast signs
aging in place
living longer and independently in their homes rather than moving to retirement facilities
A residential design approach that considers the needs of clients throughout their life
Americans with disabiities
ADA: handrails, braille, handicapped door openers - for people with disabilities
universal: equitable use, perceptible information, simple and intuitive use
design theory
"a coherent description, explanation, and representation of observed or experience phenomena"
purpose: helps us predict the future
- Framework for Analysis
- Facilitates the development of the field
- Application to practical real-world problems
- Provides evaluative criterion for judging real-world problems (in past, present and future).
- Critical component that forms the foundation of any body of knowledge
arousal
Some spaces or more interesting to us (different to each person)
Explains how we get to peak excitement (some spaces do or do not overwhelm us
sense of place
Describes your relationship, which you can express through feelings or perceptions, to a particular place or setting. Sence of belonging or attachment.
mystery/ complexity
Some spaces are boring and don't pull our attention, while other do that are stimulating because of layers or lighting
place attachment
a place that has meaning and attachment to you personally
visual journey
How you go through a space starting with the sense of arrival and sight lines. Also zones play a factor
third place
involves creating spaces that are neither home nor work, fostering informal social interaction and community
local cafe
privacy regulation theory
explains why people prefer staying alone sometimes and at other times appreciate the opportunity for social interactions
control theory
the sense of control a person desires over one’s own physcial environment
controls included are decisional, behavioral, and cognitive
sense of self theory
expression of one’s identity
stimulation theory
explains environment as a source of information gathered through the senses
explains why intense, bright colors within confined spaces casue adverse reactions
could be employed in places where a jumpstart into increased activity is desired
analysis of space
part of phase 2
come up with all the soaces and minimum requirments for each space
phase 1
identify project
determine scope of services
consider schedule and budget
phase 2
programming
analysis of space
phase 3
schematic design
(bubble or block)