US History: Unit 3 - The New Nation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
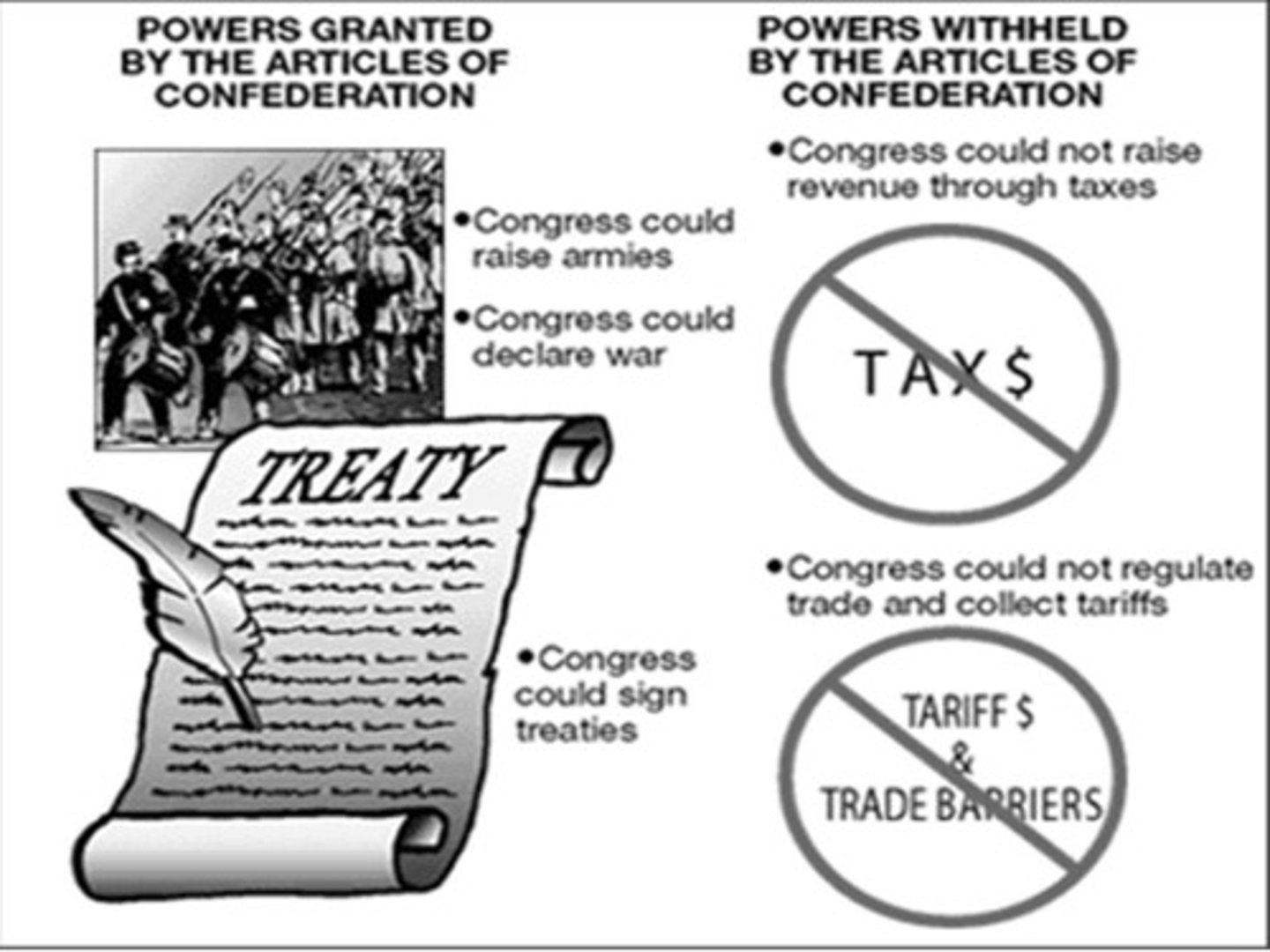
Articles of Confederation
* America's first government
* Weak national government with no president and lacks ability to taxes
* Power was with individual states, weak national/central government
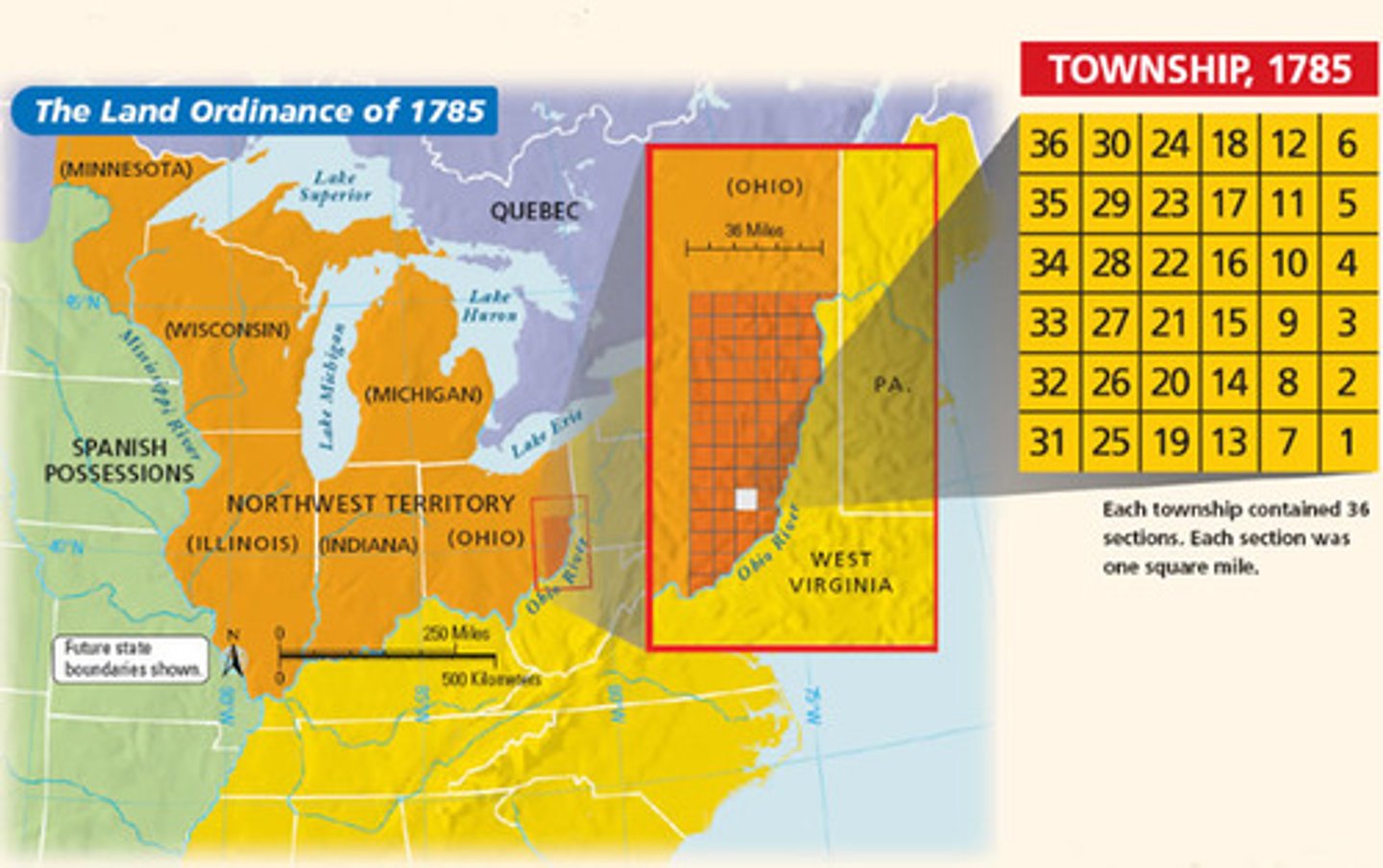
Land Ordinance of 1785
Created a plan for selling off federal land west of the Appalachian mountains for towns and farms
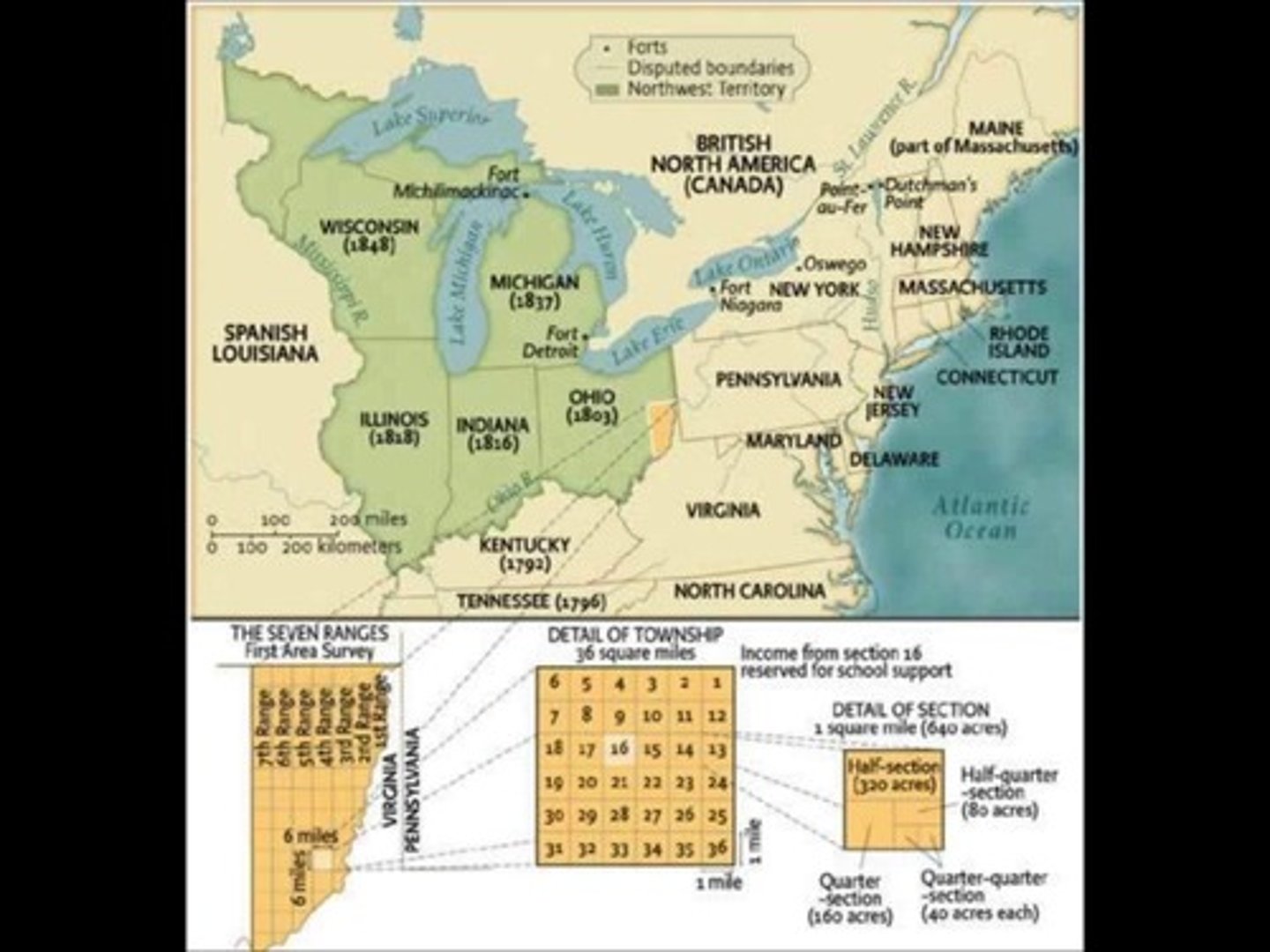
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
* Process for states in Northwest Territory to be admitted to the US: Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota
* 60,000 people were needed to become a state
* Section 16 of every town had to be a public school
* No slavery allowed
Shays' Rebellion
* Farmers in Massachusetts revolted due to increased state taxes
* There was no national military to stop the rebellion

Constitution
* Fundamental laws and rights that drive US government
* "Supreme Law of the Land"

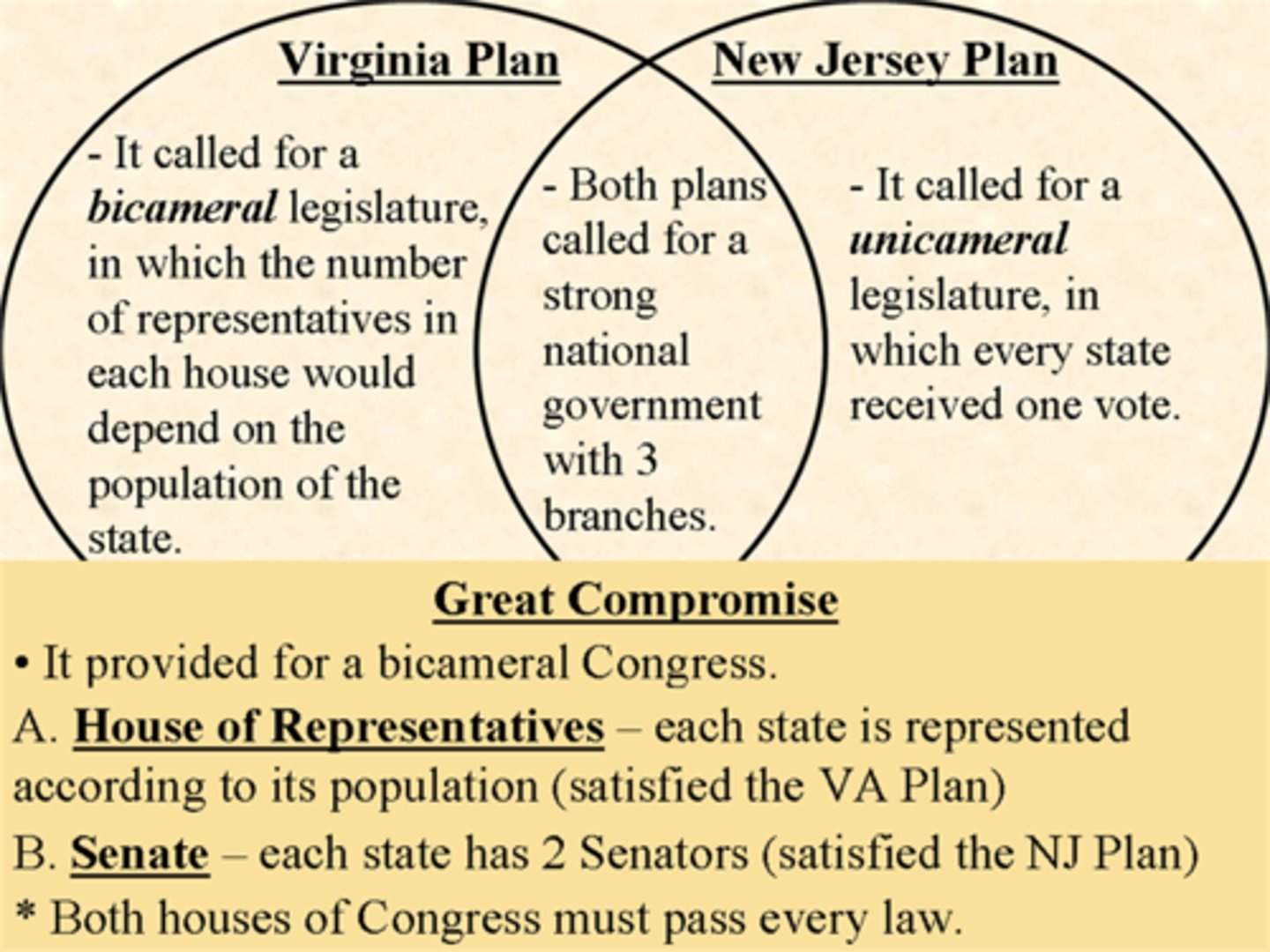
Great Compromise
* Virginia Plan wanted representation based on population
* New Jersey Plan wanted equal representation
* The Great Compromise established a Senate (equal representation) and a House of Representatives (based on population)
Separation of Powers
Power is divided between legislative, executive, and judicial branches
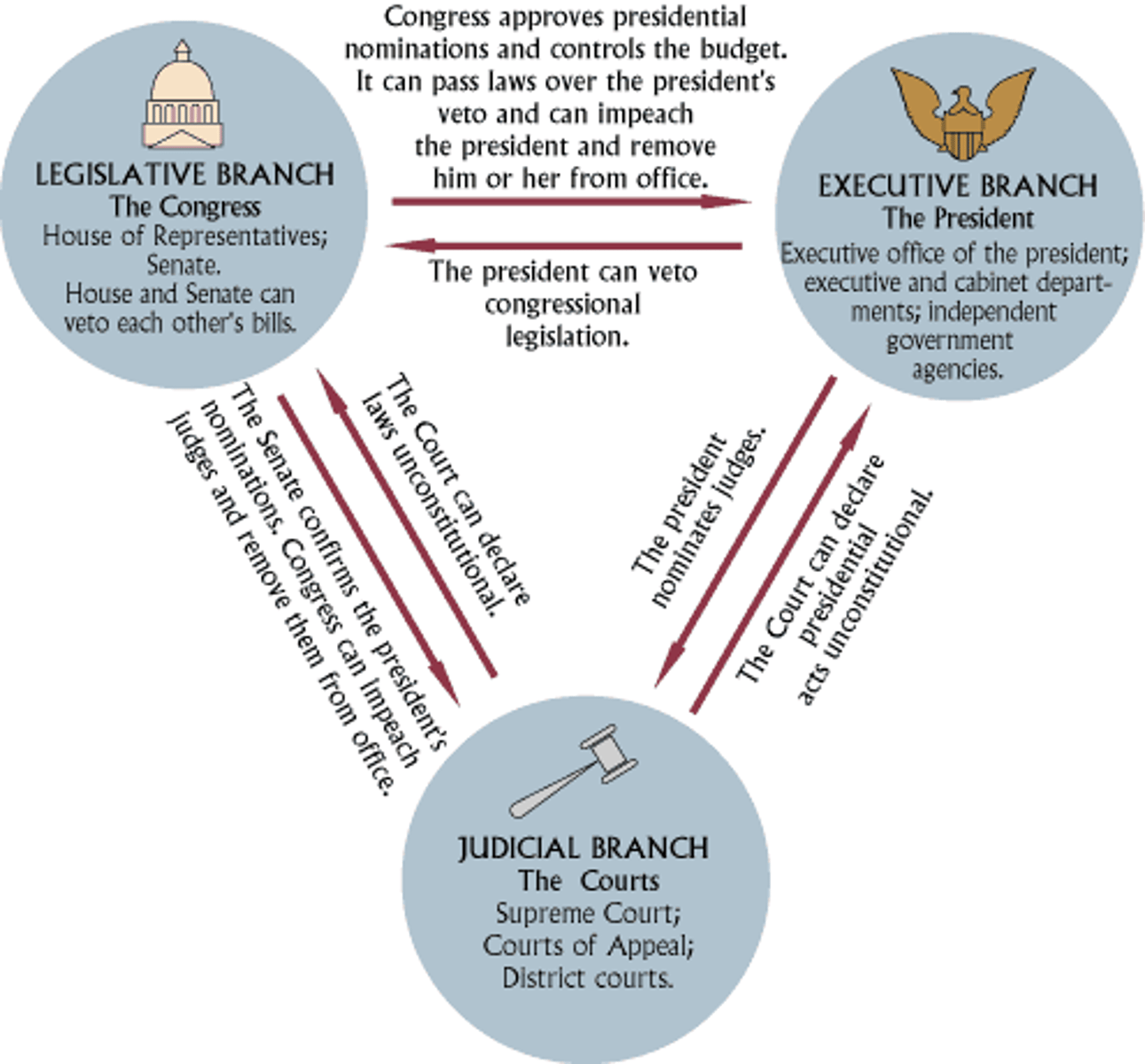
Checks & Balances
* Branches of government have certain powers to keep them from getting too much control
* Branches of government are able to check the other branches to balance power
Limited Government
* The government must follow the powers granted by the constitution
* Citizens' rights are protected
* States have rights not given to the federal government (10th amendment)
3/5s Compromise
* Slaves will count for 3/5 of the population for representation
* Slave trade made illegal after 1808

Federalists
Politicians who wanted a strong national government in the Constitution

Anti-Federalists
Politicians who wanted to protect individual rights and power of the states in the Constitution

Federalist Papers
* Written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay
* Encouraged people to ratify (approve) the Constitution

Bill of Rights
* 1st 10 amendments of the US Constitution
* Guarantees rights to US citizens
George Washington
* First president of the US
* Established the cabinet (advisers to president)

John Adams
* Vice President under Washington
* He was the second President of the U.S
* Last Federalists president

James Madison
* Took detailed notes at the Constitutional Convention
* Often called "The Father of the Constitution"
* One of the authors of the Federalist Papers

Alexander Hamilton
* Secretary of the Treasury during Washington's Presidency
* One of the authors of the Federalist Papers

Hamilton's Financial Plan
* Create a national bank
* National government would take over all debts from states and nation
* Protective Tariff
* Hamilton wanted to stabilize US economy

Whiskey Rebellion
* Small farmers of western Pennsylvania rose up in rebellion against a tax on whiskey
* President Washington sent 13000 and the rebels' protest quickly ended
* First time federal government exercises its power over the states
Washington's Precedents
* Serving two terms as President
* Established the Cabinet
* Advocated for American neutrality
* Farewell Address

Sedition Acts
* Illegal to protest against the government
* Freedom of the Press was restricted
* Passed during John Adams' presidency and cost him re-election

XYZ Affair
* France began to seize goods from neutral American cargo ships
* John Marshall, Elbridge Gerry, and C.C. Pinckney, U.S. representatives, attempted to meet with French Foreign Minister Talleyrand to settle the dispute
* Anonymous French ministers X, Y, and Z required a loan of 32 million florins and $250,000 in cash to even consider negotiations

Judicial Review
Gives the courts power to decide if laws are fair based on the constitution

Marbury v. Madison
Court case that established judicial review