Fluorescence spectroscopy
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
What is Fluorescence
is when emitted light is at a higher wavelength than excitation light.
2
New cards
Thermal relaxation?
when the excited electron is set to the lowest excitation level S1.
3
New cards
Kasha’s rule?
Photemission happens during transition of the lowest vibrational level (S1) of first excited state, this is Kashas rule.
4
New cards
What is Phosphorescence?
spin turns from singlet (S1) to triplet (T1) which is intersystem crossing then energy returns from lowest excited state (T1) to ground state.
5
New cards
How can you explain Luminescence lifetime
It is the time elapsed between excitation and emission.
6
New cards
What is the idea of a Spectrum
It is the dependence of intensity on wavelength.
7
New cards
Stokes shift?
The excitation and emission spectrums are mirror images of each other and the gap between the difference in their wavelengths is called the stokes shift.
8
New cards
What is a Fluorimeter
It is used to measure fluorescence.
9
New cards
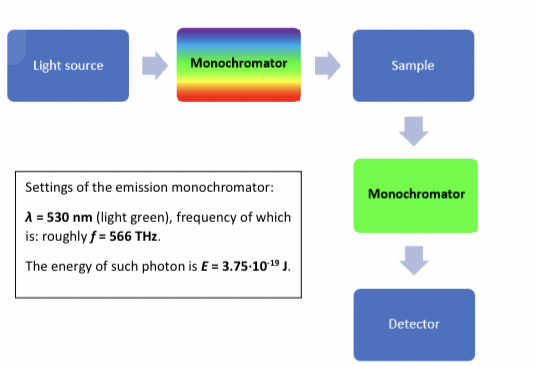
Which Monochromator is the emission side.
The light green Monochromator is the emission side.
10
New cards
cold emission phenomenon?
Light is not generated by high temperatures so molecules can be excited in different ways.
11
New cards
Interpretation of excitation spectrum?
If excitation wavelength is constant as a function of emission wavelength. Represents vibrational levels from the ground
12
New cards
What happens to the emission spectra shape due to change in excitation wavelength
If change is made to the excitation wavelength in the excitation range the emission spectra shape will not change.
13
New cards
Conditions for
Multiplicity (M) is the number of possible orientation states of the magnetic moment assigned to the spin state (S) relative to the directions of the magnetic field, M= 2S+1
14
New cards
Singlet state
This confirms the Pauli exclusion principle by permitting transition, S = 0 and M = 1
15
New cards
Triplet state
This denies Pauli exclusion principle by forbidding transition, S = 1 and M = 3
16
New cards
Reason for the arrangement of Fluorimeter
the arrangement of the second perpendicular to to sample solution is because excitation light reaching the sample can reach the detector and affect results if in linear arrangement but in the perpendicular arrangement we can exclude the light.
17
New cards
Types of luminescence?
Radiative and non radiative(excitation energy to heat energy)
18
New cards
Examples of radiative luminescence
Fluorescence and phosphorescence
19
New cards
What is Luminescence?
Excitation by stimulation and emission energy to the environment in form of EM waves
20
New cards
Quantum yield range?
0 to 1
21
New cards
Quantum yield formula
N(emis)/N(absor) = K(fluor)/K(sum)
N is number of particles and K is probability of transition
N is number of particles and K is probability of transition
22
New cards
Difference between fluorescence and phosphorescence?
Fluorescence is shorter than phosphorescence