CPI Review SP25
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
tachycardia
greater than 100 bpm
bradycardia
less than 60 bpm
normal heart rate
60-100 bpm
Hypotension
systolic arterial pressure less than 90 mmhg, MAP less than 65mmHg, decrease in systolic pressure greater than 40mmHg from baseline
Hypertension
blood pressure consistently greater than 140/90 mmHg
Fluid Overload due to CHF
CVP greater than 6mmHg, PCWP greater than 18mmHg
Normal Blood Pressure
120/80
The types of lung diseases or conditions that can be associated with wheezing
Asthma, CHF (COPD), bronchitis, & emphysema
Cardiac Angina (pain)
pain in the chest, neck, back, or arms, lightheadedness, abnormal heartbeat, anxiety
Capillary refill
pressing firmly on the patient’s fingernail until the nail bed is blanched and then releasing the pressure
Peripheral Skin Temperature
causes extremities to be cool to touch
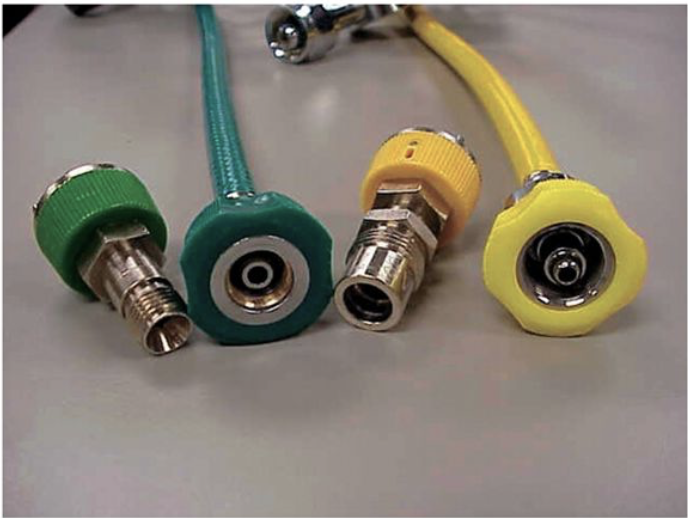
DISS
inlets of blenders, flowmeters, ventilators, and other pneumatic equipment

What safety system is this?
Diameter Index Safety System
PISS
Applies only to the valve outlets of small cylinders including size E

What safety system is this?
Pin Index Safety System
American Standard Safety System
standards for threaded high-pressure connections between large compressed gas cylinders (sizes through H/K)

What is this flowmeter called?
Bourdon Gauge
Fixed Orifice
operate under variable pressures as the pressure reducing valve adjust
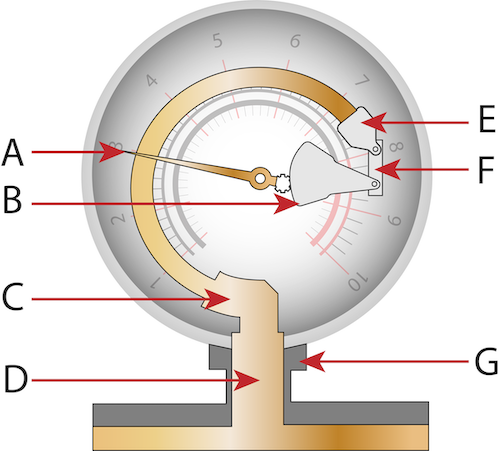
What is G?
Gas Inlet Connector
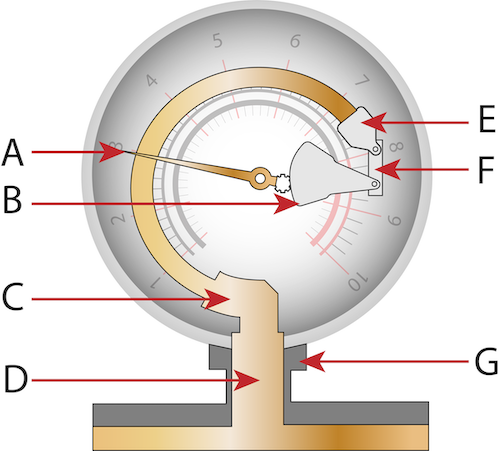
What is A?
pressure indicator gear
Overall Goal of Oxygen Therapy
maintain adequate tissue oxygenation while minimizinf cardiopulmonary work
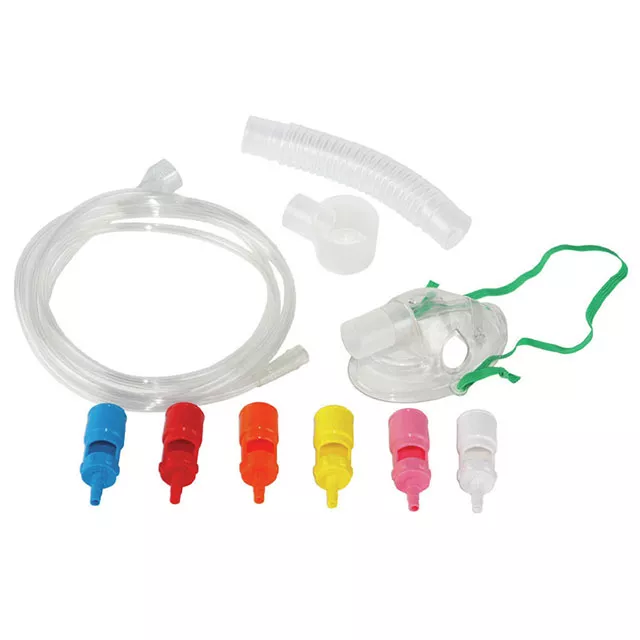
What kind of mask is this?
Air Entrainment Mask
Three Objectives of Oxygen Therapy
Correct documented or suspected acute hypoxemia, decrease symptoms associated with chronic hypoxemia, decrease the workload hypoxemia imposes on the cardiopulmonary system
When would you use a nasal cannula?
Patient in stable conditions who needs low FiO2
When would you use a nasal cannula?
home care patient who needs long-term therapy
When would you use a nasal cannula?
low to moderate FiO2 while eating
When would you use an air entrainment mask?
patients in unstable contion who needs precise low FiO2
When would you use a facemask?
emergencies, short-term therapy requiring moderate FiO2
When would you use a facemask?
mouth-breathing patients requiring moderate FiO2
Which oxygen device uses precise FiO2?
Air Entrainment Mask
Describe how to measure BP & determine the sound heard when ausculataing a BP.
Simple mechanical manometers
List the criteria (sputum) for diagnosis of chronic bronchitis.
mucoid — clear, thin, frothy
mucopurulent — (yellow, green, viscid, smelly thick — both mucoid & purulent [pus])
Describe the conditions that respond well to low-to-moderate O2 concentrations.
acute exacerbation of COPD, Emphysema, Chronic Bronchitis, Drug OD w/o aspiration, Neuromuscular disease, & Post-op patients w/ normal lungs
Determine which oxygen device is least affected by RR, VT, or ventilatory pattern.
any high flow device
AEM (venturi mask)
air-entrainment nebs
HFNC
AirVO2, Precision flow, Max Venturi.
Describe x-ray changes that are consistent with various disease states. For example what will cause an increase in A-P diameter on the chest.
Identify & explain the stages in a regulator & describe or identify a pressure relief valve & safety systems of a regulator.
Identify the early signs of hypoxia.
The initial symptoms of hypoxia may include shortness of breath, confusion, rapid heart rate, and cyanosis. These signs indicate inadequate oxygen delivery to tissues.
Describe how to choose an oxygen delivery device to deliver pre-mixed heliox
Clark’s oxygen analyzer
measure oxygen levels in liquids (%O2)
Galvanic’s oxygen analyzer
oxidation occurs in the anode & electrode where reduction occurs in the cathode (electrical energy)
Calculate & describe relative humidity of a gas.
(content / capacity) x 100
Calculate & describe absolute humidity of a gas.
(temperature) x (% saturation) or (mass of water vapor / volume of air)
Respiratory Acidosis / Alkalosis
Acidosis: pH < 7.35, PaCO2 > 45
Alkalosis: pH > 7.45, PaCO2 < 35
Metabolic Acidosis / Alkalosis
Acidosis: pH < 7.35, HCO3 < 22
Alkalosis: pH > 7.45, HCO3 > 26
Combined Acidosis / Alkalosis
Acidosis: pH < 7.35, HCO3 < 22, PaCO2 > 45
Alkalosis: pH > 7.45, HCO3 > 26, PaCO2 < 35
Hyperoxemia
Adults > 100
Newborn > 90
Mild hypoxemia
Adults 60 - 79
Newborn 50 - 59
Moderate hypoxemia
Adults 45 - 59
Newborn 40 - 49
Severe hypoxemia
Adults < 45 Newborn < 40
Troubleshoot a bubble-diffusion humidifier.
Troubleshoot a non-rebreather
increase the flow if the bag begins to deflate
Troubleshoot a partial rebreather mask
Troubleshoot a T-piece specifically when the mist disappears.
Explain the difference between a compensated and uncompensated flow meter (Thorpe tube)
A compensated flow meter’s density remains constant regardless of any backpressure after the needle valve, while an uncompensated flow meter’s accuracy is affected by changes in backpressure invalidating flow scale making readings less than the actual flow.
Determine the indication for using a bourdon gauge.
Determine what oxygen device to use for a COPD patient.
Describe the indications & functions of a bubble humidifier.
Explain all principles of aerosol particle generation.
Describe the indication, contraindication, hazards associated with the ultrasonic nebulizer.
Demonstrate & troubleshoot an ultrasonic nebulizer.
Explain & troubleshoot the use of a LVN to medicate & mobilize secretions.
Explain & troubleshoot the use of a SVN to medicate & mobilize secretions.
State the indications & contraindications of aerosol therapy.
Aerosol therapy hazards
Devices used for aerosol therapy
Calculate drug dilutions, e.g. translate 1:500 to mg/cc, understand % solutions, translate from medication dosage (2.5 mg albuterol in 3 ml diluent to 1:100 or other ratio)
1000g/ 500mL = 2mg
Calculate absolute humidity of a gas at 37 degrees and fully saturated with water vapor, and a gas that is 60% saturated with water vapor.
(Temperature) x (% Saturation)
37 × 0.60 = 22.2 mg/L
Calculate the humidity deficit given the absolute humidity.
BH (%)= (content [mg/L] / 43.8) x 100
Content (mg/L)= absolute humidity
Calculate cylinder duration for E and H cylinders.
H= 3.14 E= 0.28
Cylinder duration (min)= [(cylinder pressure (psig) x (conversion factor)] / flow (L/min)
Full = 2200
Half = 1100
Take down to 500 = cylinder pressure - 500
Dilute a solution for example dilute 4 cc of an 8% mucomyst to a 4% solution. How ml of mucomyst would you need and how many ml of saline would you need?
% strength (decimals)= [(dilute solute) x (% strength of solution)] / total amt (solution)
Raul’s Way= x (0.08) = (4cc) (0.04) = 2ml
Recognize the body humidity a bubble humidifier will produce.
Identify the doses of all respiratory medications, the classification of the medications drug & explain how each classification of medication works.
IS indications
atelectasis, secretions, presence of conditions disposing to atelectasis, patients who can follow instructions & repeat demonstrations to the RT.
IS contraindications
untreated pneumothorax, elevated ICP, hemodynamic instability, patient inability to take a deep breath or cooperate, active hemoptysis
Goal for IS
patient must be achieving 1/3 of predicted volume (based on age, height, & gender)
ONLY hyperinflation
Indication for a USN
Conditions or procedures that may be associated with development of micro-atelectasis
Identify the different type of oxygen flowmeters & explain when you would use them under various circumstances (such as horizontally placed E-cylinder)
Cold & heated aerosol delivery by mask indications
Post extubation edema: Tx with cool air LVN
Croup baby: Tx with cool air
Post-op management of upper airway
Upper airway edema
Mobilizations of secretions
Cold & heated aerosol delivery by mask contraindications
Untreated pneumothorax causing a stop in Tx
Thick, copious or bloody secretions
VE > 10 L/m
Expired VT < 70% of delivered VT
Body temp < 89.6 F (32 C)
NO ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cold & heated aerosol delivery by mask hazards
Nosocomial infections
Elevated airway pressures
Pooled condensation in patient circuit
Hyperthermia
Tubing meltdown
Electrical shock
Recognize condensation in the corrugated tubing when setting up an aerosol device & what occurs in regards to the FiO2.
increase FiO2 decrease in total flow caused by back pressure
Describe the relationship between a patient’s hydration level and delivery of aerosol or ultrasonic nebulizer therapy.
Indications of all types of aerosol therapy.
induce cough, inflammation, infection, oxygen therapy w NC @ least 4 LPM
Contraindications of all types of aerosol therapy.
no relative or absolute contraindications
Hazards of all types of aerosol therapy.
bronchospasm, overhydration, aspiration of condensation, infection/contamination due to water especially with trach
IPPB Indications
presence of atelectasis or secretion retention, if 1/3 of IS is not reached or EzPAP/AccuPAP not successful, pneumonia, COPD, bronchiectasis
IPPB absolute contraindication
untreated tension pneumothorax
IPPB relative contraindications
ICP > 20, hemoptysis, Active TB, vomiting/nausea, hemodynamically instability, flail chest, spinal cord injury, facial trauma
Determine the role for each knob on the IPPB such as terminal flow, flowrate, pressure, sensitivity.
Determine hyperventilation with IPPB.
Troubleshoot the IPPB machine. For example a patient is not able to trigger the machine on, cycle the machine off, inspiratory time is very long.
Given a patient scenario and various volumes achieved by a patient using an IS, determine the effectiveness.
Evaluate the patient's lung expansion and inspiratory efforts to ascertain the effectiveness of the Incentive Spirometry (IS) based on achieved volumes.
IS indications
presence of atelectasis, restrictive lung diseases, pre/post abdominal/thoracic surgery, & neuromuscular patients
IS contraindications
untreated tension pneumothorax, unable to take instructions, obtunded/unconscious, uncoordinated, & cannot pull 1/3 of predicted value
IS hazards
hyperventilation & respiratory alkalosis, discomfort, pulmonary barotrauma, bronchospasm, & fatigue
Characteristics of IPPB
intermittent positive pressure breathing
specialized form of NIV used in short treatment periods (ab. 15 mins) to achieve deep breath through positive pressure assisted breaths
Setting when using wall vacuum for suctioning adults & children
adults < 200 mmHg
children & infants < 120 mmHg
Indications of NT suctioning
to clear secretions, relieve airway obstruction, or obtain a specimen for diagnostic purposes
NT suctioning contraindications