Lecture 29: The endomembrane system: central to cell physiology
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Zheng 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
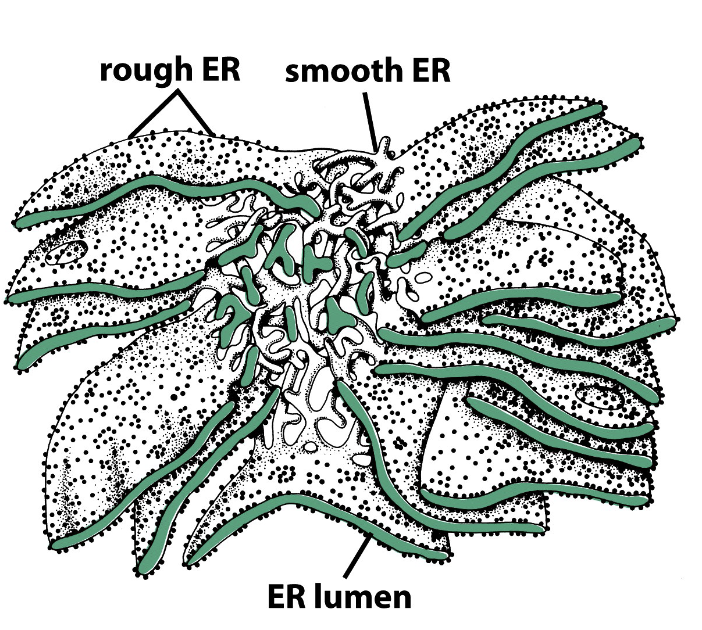
endoplasmic reticulum characteristics
sites for protein (rough) and lipid (smooth) synthesis
largest single-membrane bilayer organelle
exists as sheets (rough) and tubules (smooth) that are interconnected
enclose a space called ER lumen
rough ER
filled with ribosomes
used for protein synthesis
protein target and translocation into the ER
smooth ER
without ribosomes
used for lipid synthesis
have ER exit sites, involved with ER-Golgi trafficking
Which types of the ER are sheets and tubules?
rough ER is interconnected layers of flattened sheets, smooth ER is tubules
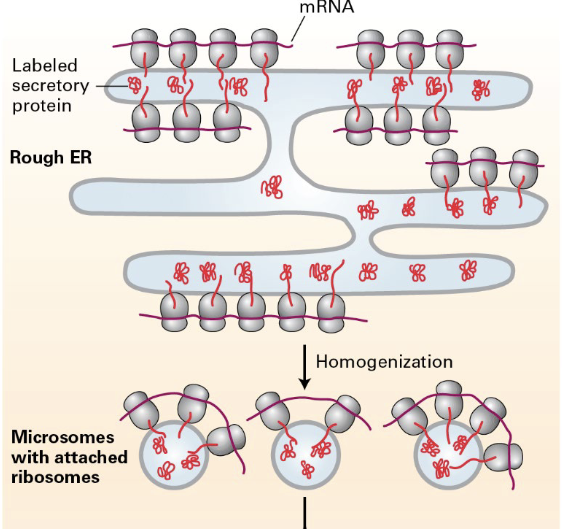
what happens when cells are homogenized?
the rough ER breaks into small microsomes, that are still functional (still have ribosomes) and can be easily purified
morphology of ER in animal and plant cells
very similar
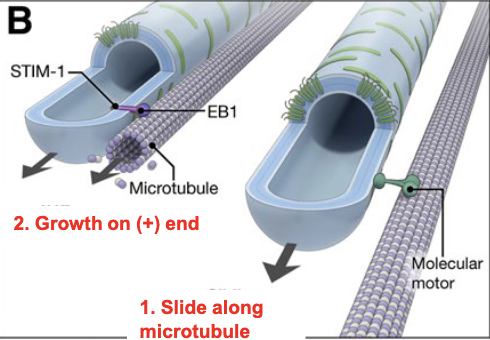
ER dynamics
consistently being reorganized (connections broken/formed)
ER tubules pulled out and moved on microtubules by motor proteins to make a network
ER tubule growth on microtubules
growing tubules slide along microtubules via motor proteins until the end, and grow with the growing (+) end of the microtubule
what gives the curvature for formation of tubules and edges of sheets?
Reticulons, that have a W-shaped structure
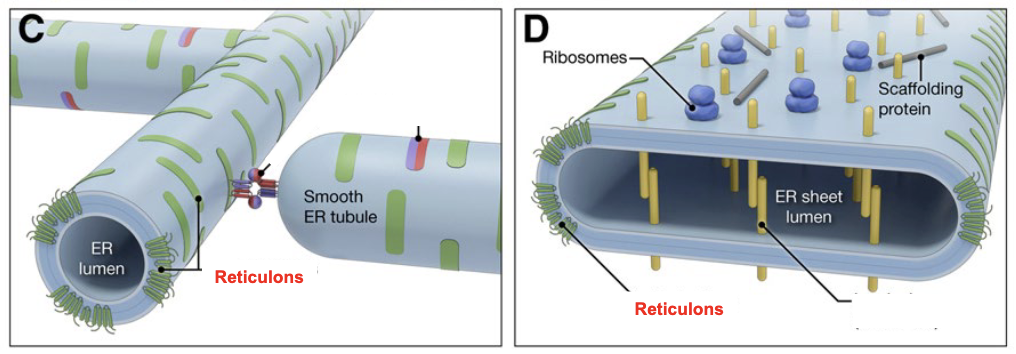
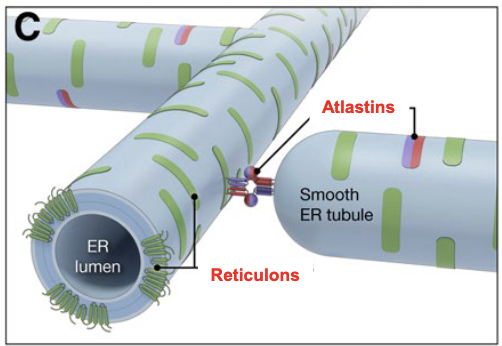
what fuses/connects different ER tubules?
Atlastins, which are a class of dynamin-like large GTPases that undergo oligomerization
what allows for spacing in sheet formation?
CLIMP63, ER luminal spacer

what are proteins targeted to the ER bound with?
ER-bound ribosomes
where do proteins made by ER-bound ribosomes end up?
within the ER lumen
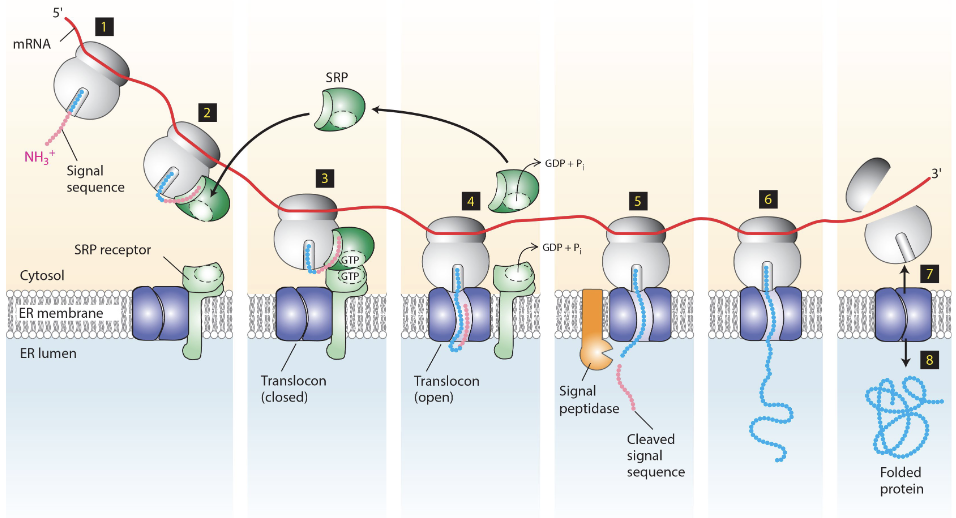
how are secretory proteins targeted to the ER?
ER-signal sequence on the n-terminal of the protein, once emerged, will guide the ribosome-mRNA-nascent peptide complex to the ER
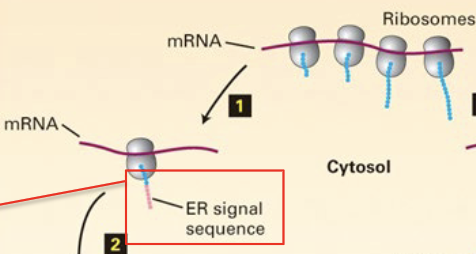
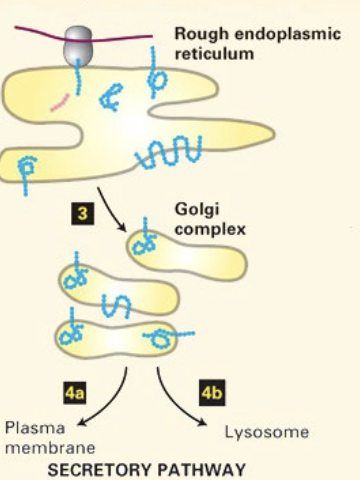
what happens when the ribosome-mRNA-nascent peptide complex is attached to the ER?
the peptide is translated and translocated to the lumen of the ER (co-translational)
what is the ER signal sequence?
~25 amino acid long sequence, with a stretch of ~ 10 hydrophobic amino acids in the centre
what happens when there is no signal sequence on the end of the peptide and what does it mean?
the protein is not incorporated to ER/microsomes. This means that the sequence is necessary for ER import
what happens when imported proteins have the N-terminus removed and what does it mean?
No effect on growing protein, meaning that cleavage of signal sequence once incorporated has no effect on protein synthesis
what happens when proteins that have completed synthesis want to be added to ER/microsomes and what does it mean?
there is no import of proteins. This means that import must occur DURING synthesis (co-translational
What is SRP and what does it do?
Signal Recognition Particle, contains a hydrophobic binding groove (in P54 subunit) that binds the signal sequence
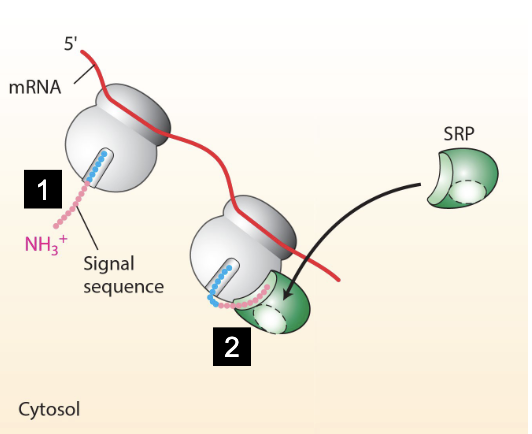
what happens when SRP docks the nascent-polypeptide-ribosome-mRNA?
SRP binds to the alpha subunit of SRP receptor (both in GTP-bound state)
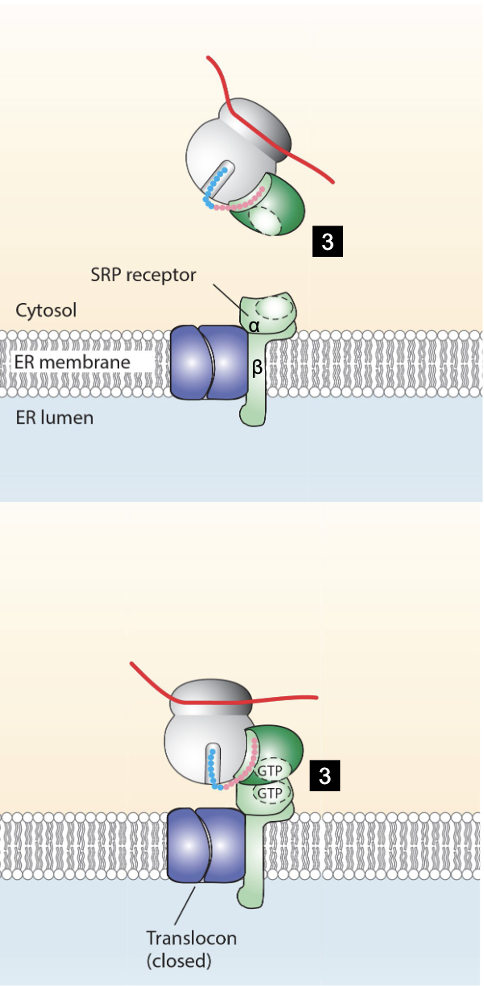
what happens once the nascent polypeptide-mRNA-ribosome is properly docked?
P54 of SRP and alpha subunit of SRP receptor hydrolyze their bound GTP, destabilizing the interaction interface and dissociating them from each other
ER signal sequence opens the translocator and enters the channel
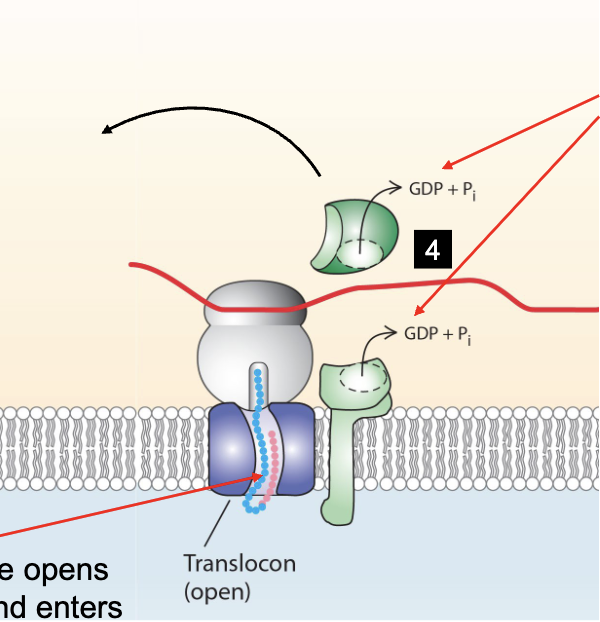
what happens as the polypeptide translocates into the ER and mRNA is translated?
ER signal sequence gets cut off by signal polypeptidase and is degraded
translocator closes, ribosome is released, translocated protein is folded in lumen of ER
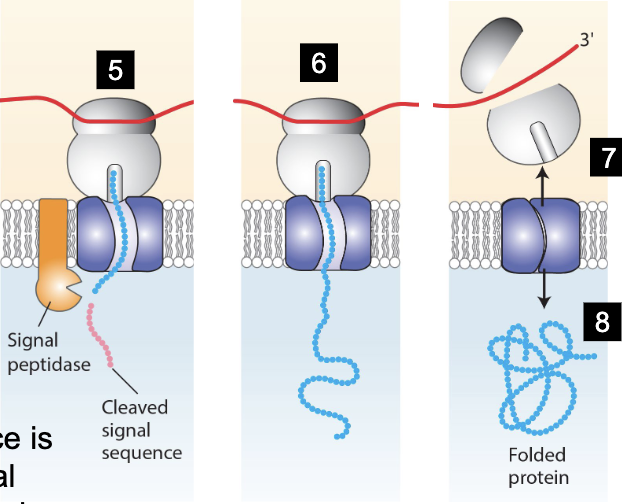
entire process of targeting secretory proteins to ER lumen
Signal sequence formed from nascent polypeptide-mRNA-ribosome complex
signal sequence recognized by P54 of the SRP to form SRP-nascent-polypeptide-mRNA-ribosome complex
P54 interacts with alpha subunit of SRP receptor, bringing the complex to the ER
complex is docked to the ER translocator, opens it and enters. P54 and alpha subunit of SRP hydrolyze GTP to GDP
Signal polypeptides cleaves the signal sequence
mRNA translation within ER lumen
translocator closes, ribosome is released
protein folding begins