Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Large & diverse group of G + bacilli
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Aerobic, branched, & beaded – the branched filaments that extend along the agar are called substrate hyphae & into the agar are aerial hyphae
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Aerobic, branched, & beaded – the branched filaments that extend along the agar are called substrate hyphae & into the agar are aerial hyphae
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Aerobic, branched, & beaded – the branched filaments that extend along the agar are called - hyphae & into the agar are - hyphae
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Are found in the soil & organic material
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Some can grow at 50 °C
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Some can degrade AMYL ALCOHOL, PARAFFIN, & RUBBER
Culture of Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Cells elongate to form branching, filamentous forms
Culture of Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Cells elongate to form -, - forms
Culture of Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Some organisms form filaments or hyphae on the agar surface or into the agar
Culture of Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes
- Some organisms form - or - on the agar surface or into the agar
Nocardia spp
Nocardia asteroids complex
Nocardia brasilinesis
Nocardia farcinica
Nocardia nova
Rhodococcus equi
Gordonia spp.
Tsukamurella spp.
Streptomycess spp.
Actinomadura spp.
Aerobic Actinomyces / Branching Actinomycetes spp are
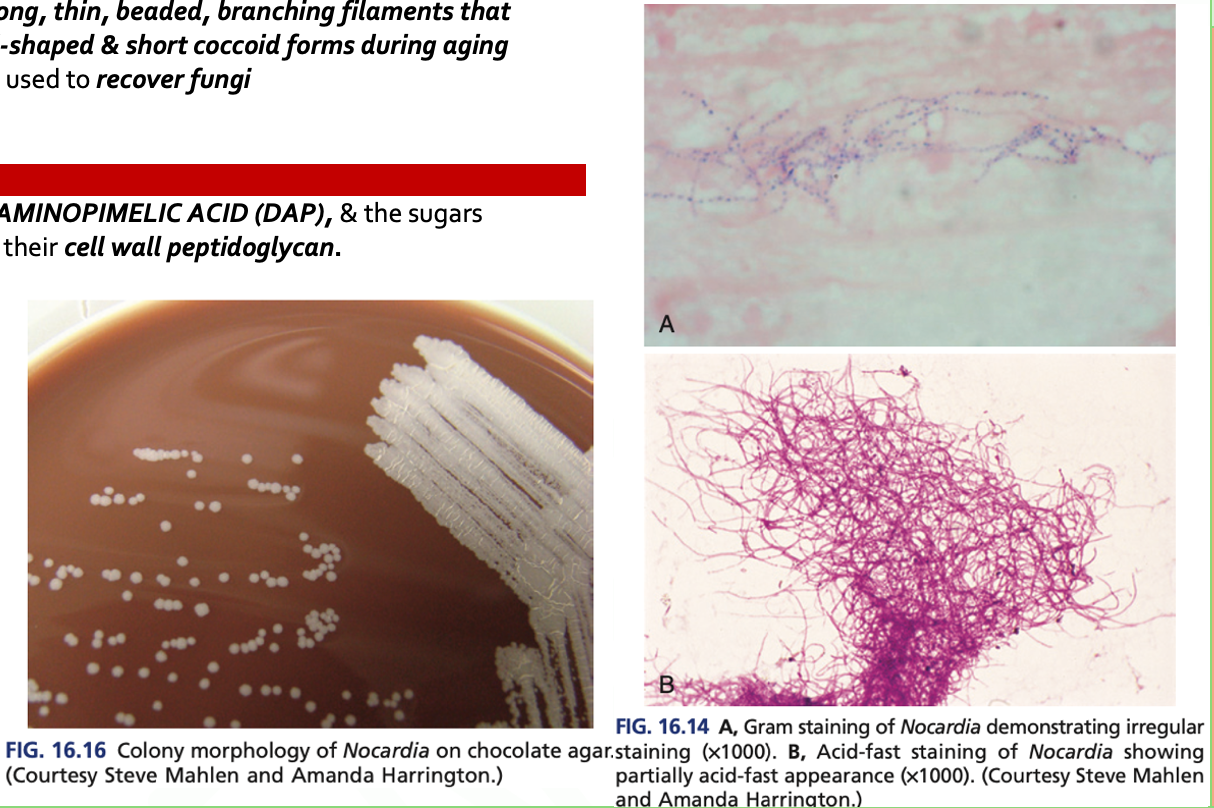
Nocardia spp.
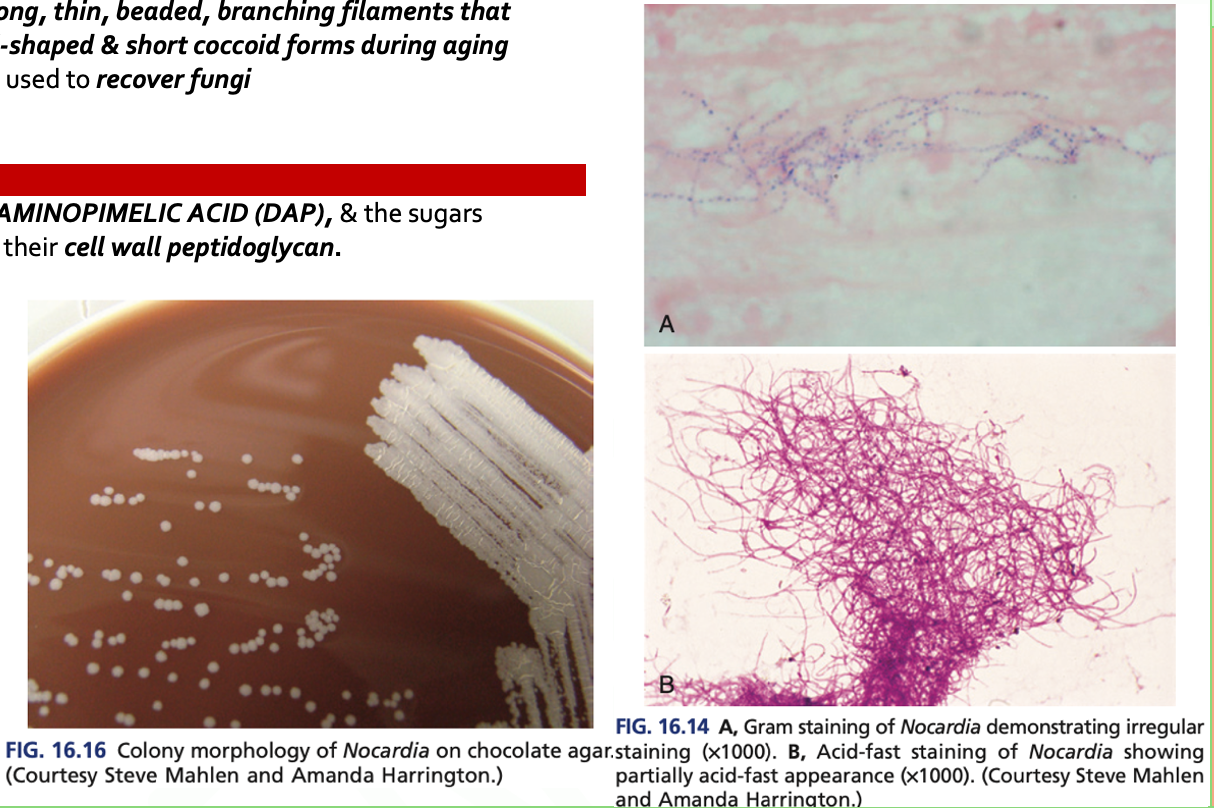
- Are AEROBIC, G+ bacilli with long, thin, beaded, branching filaments that occasionally fragment into rod-shaped & short coccoid forms during aging
Nocardia spp.
- It grows on nonselective media used to recover fungi
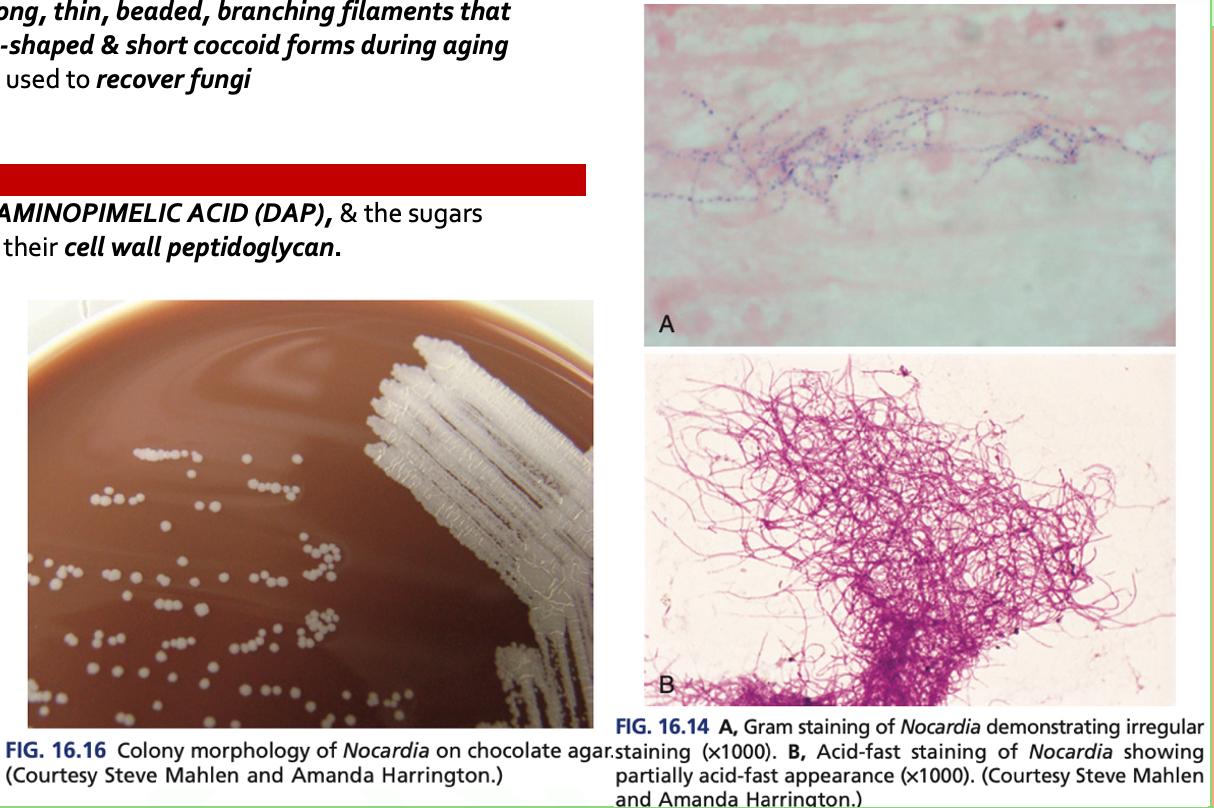
Nocardia spp.
- There is a presence of MESODIAMINOPIMELIC ACID (DAP), & the sugars ARABINOSE & GALACTOSE in their cell wall peptidoglycan.
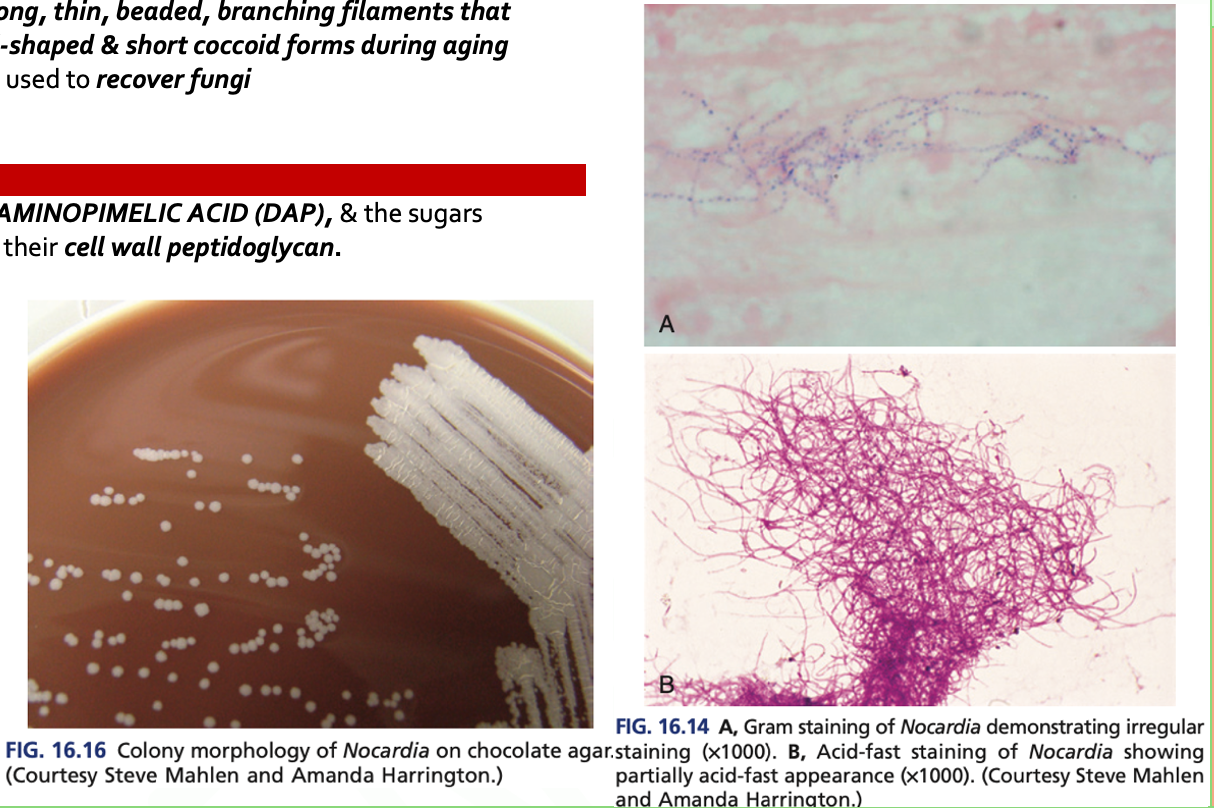
T
Nocardia spp. are PARTIALLY ACID FAST (t/f)
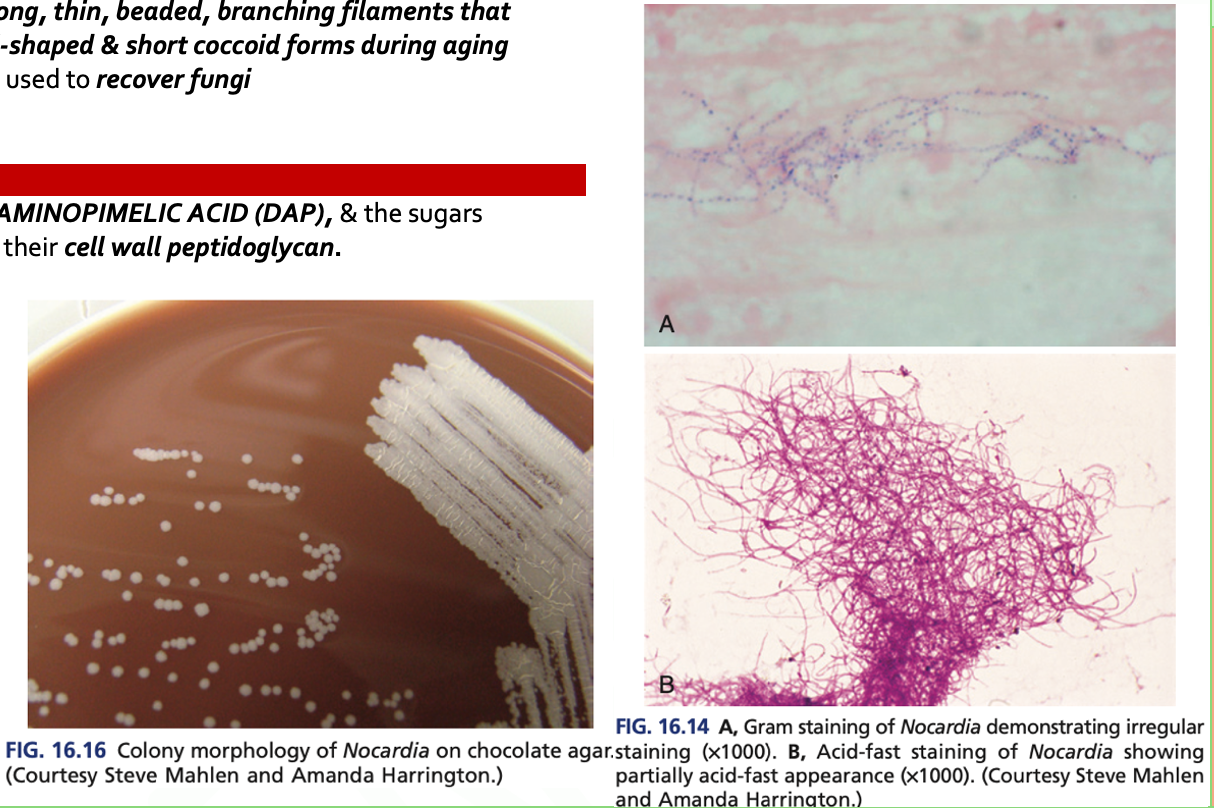
F
Nocardia spp. are STRICTLY AEROBE
Nocardia spp. are STRICTLY ANAEROBE (t/f)
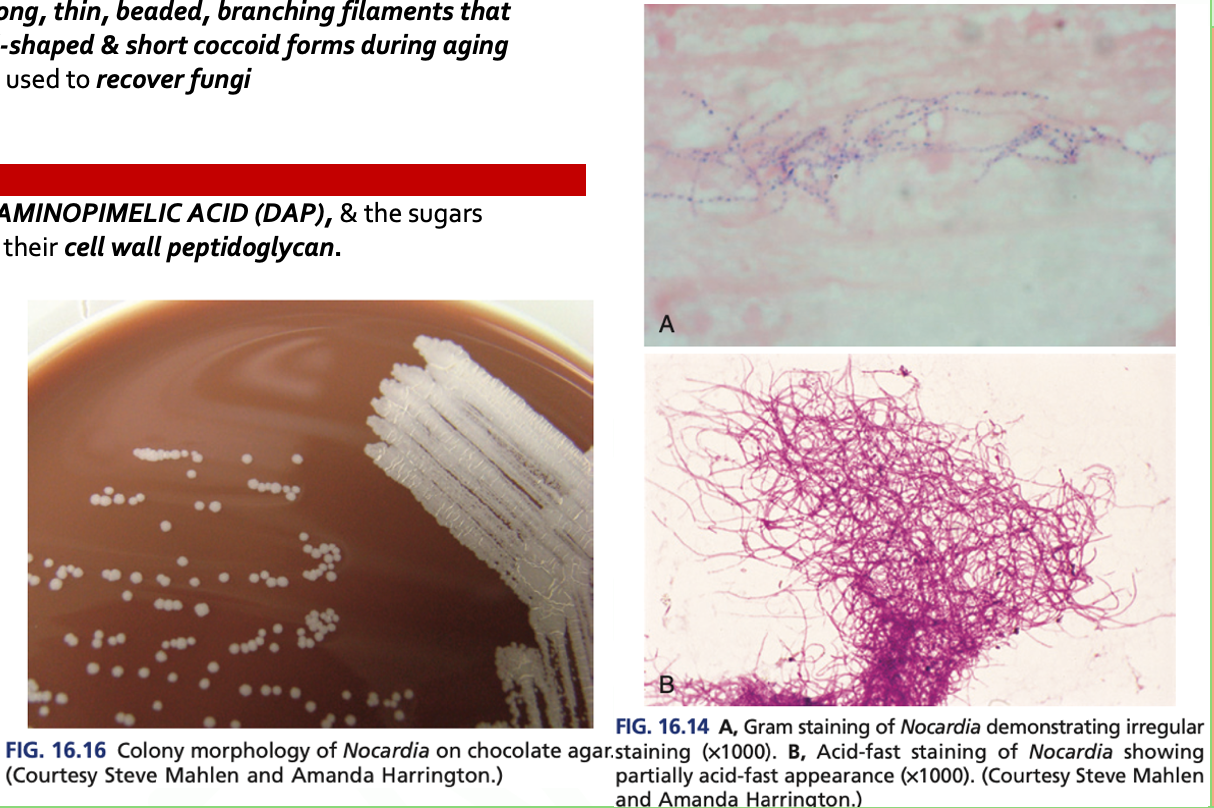
T
Nocardia spp. are CATALASE + (t/f)
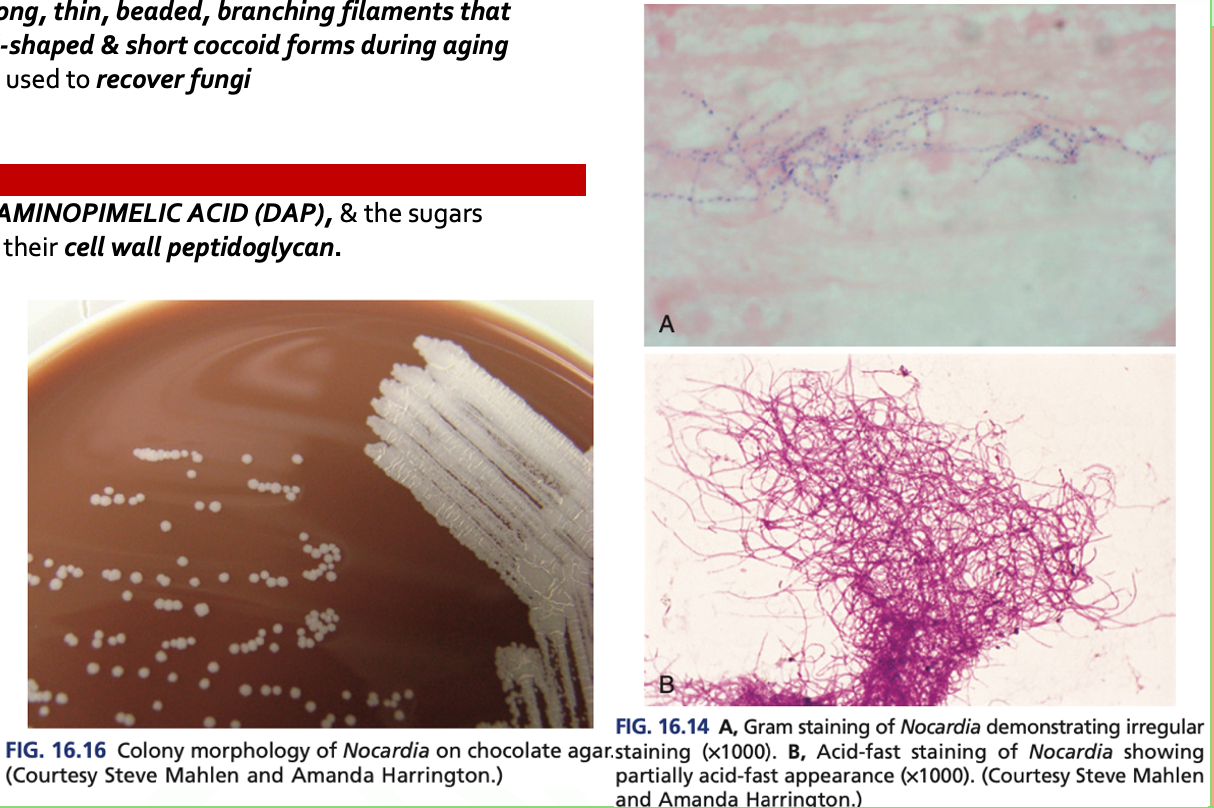
• Nocardia asteroides
• Nocardia brasilinesis
• Nocardia farcinica
• Nocardia nova
Nocardia species are
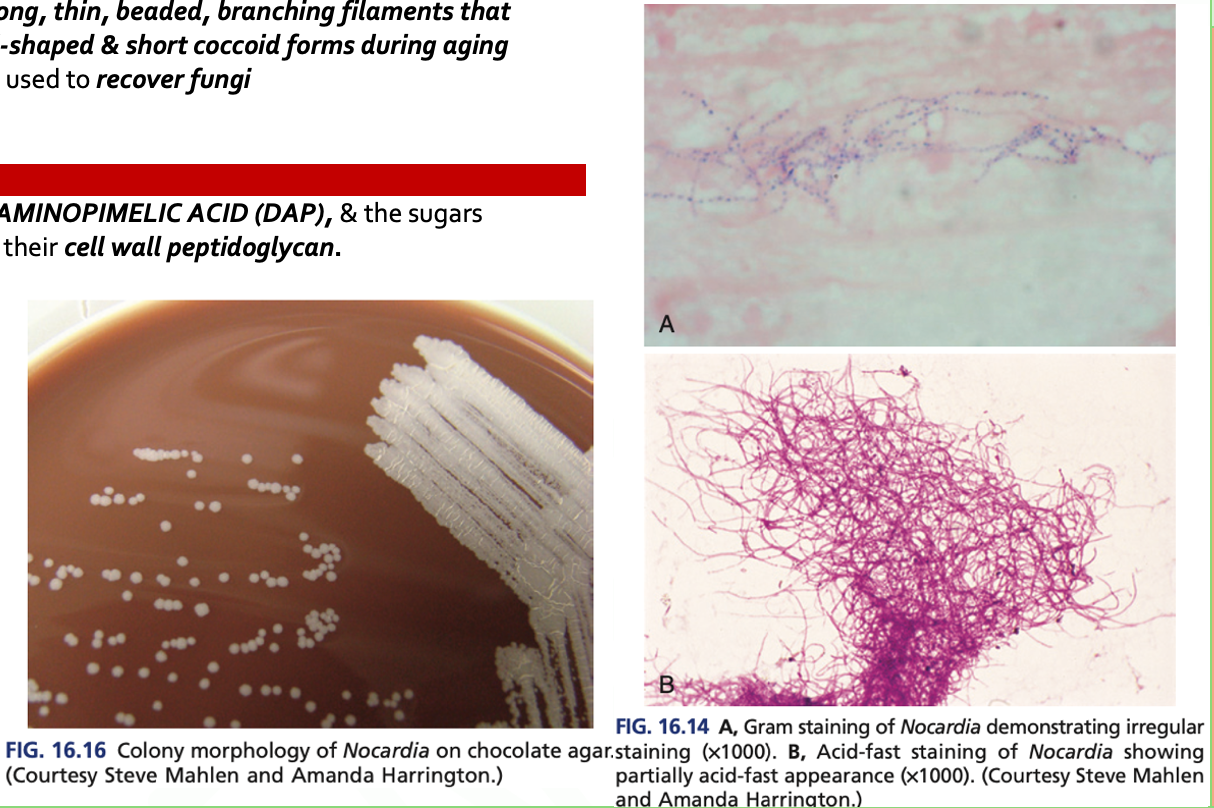
RESISTANCE TO LYSOZYME
Differential test of Nocardia spp. (t/f)
Susceptible to Lysozyme
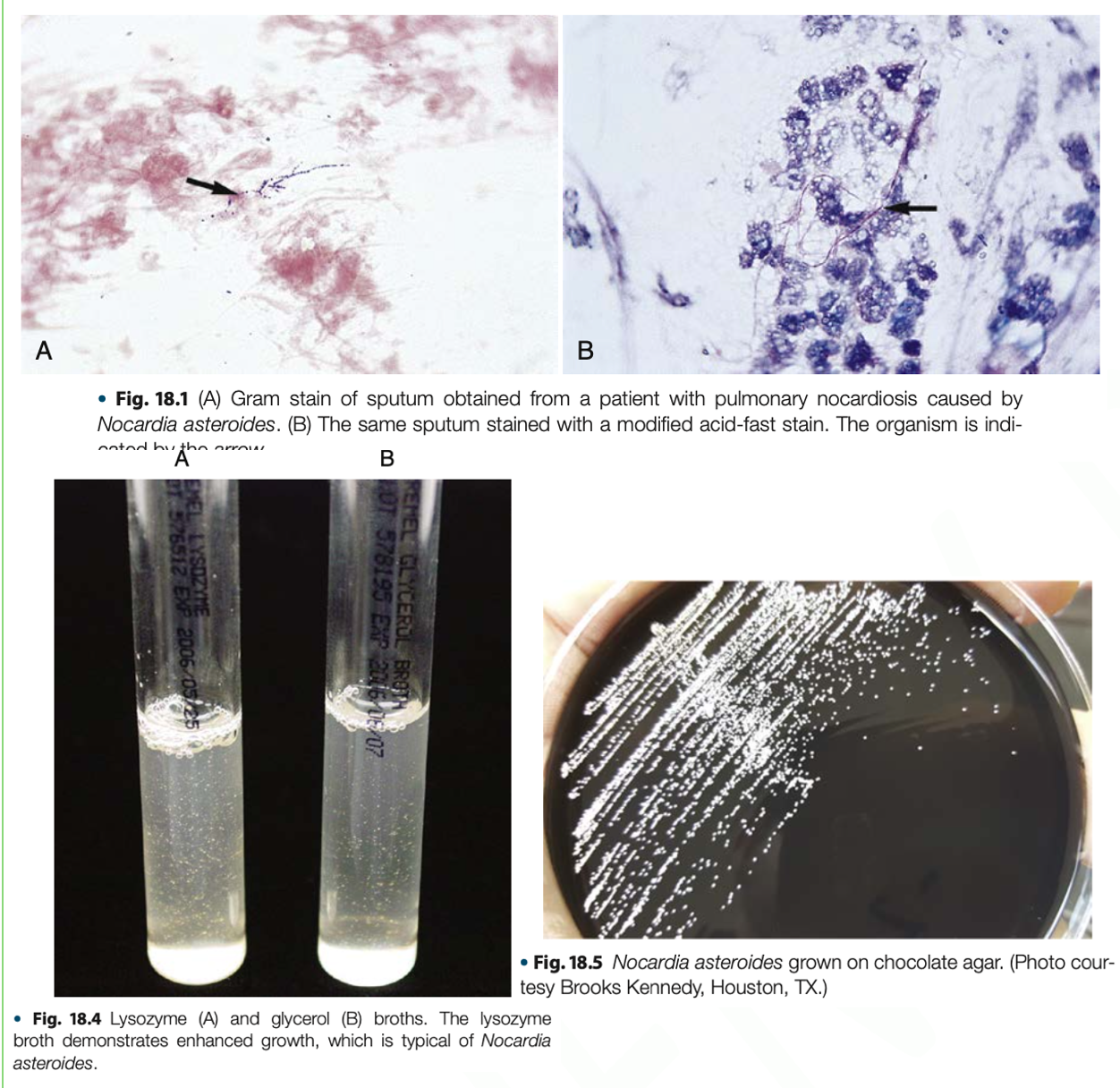
Nocardia asteroides complex
- Are responsible for 80-90% of human infection
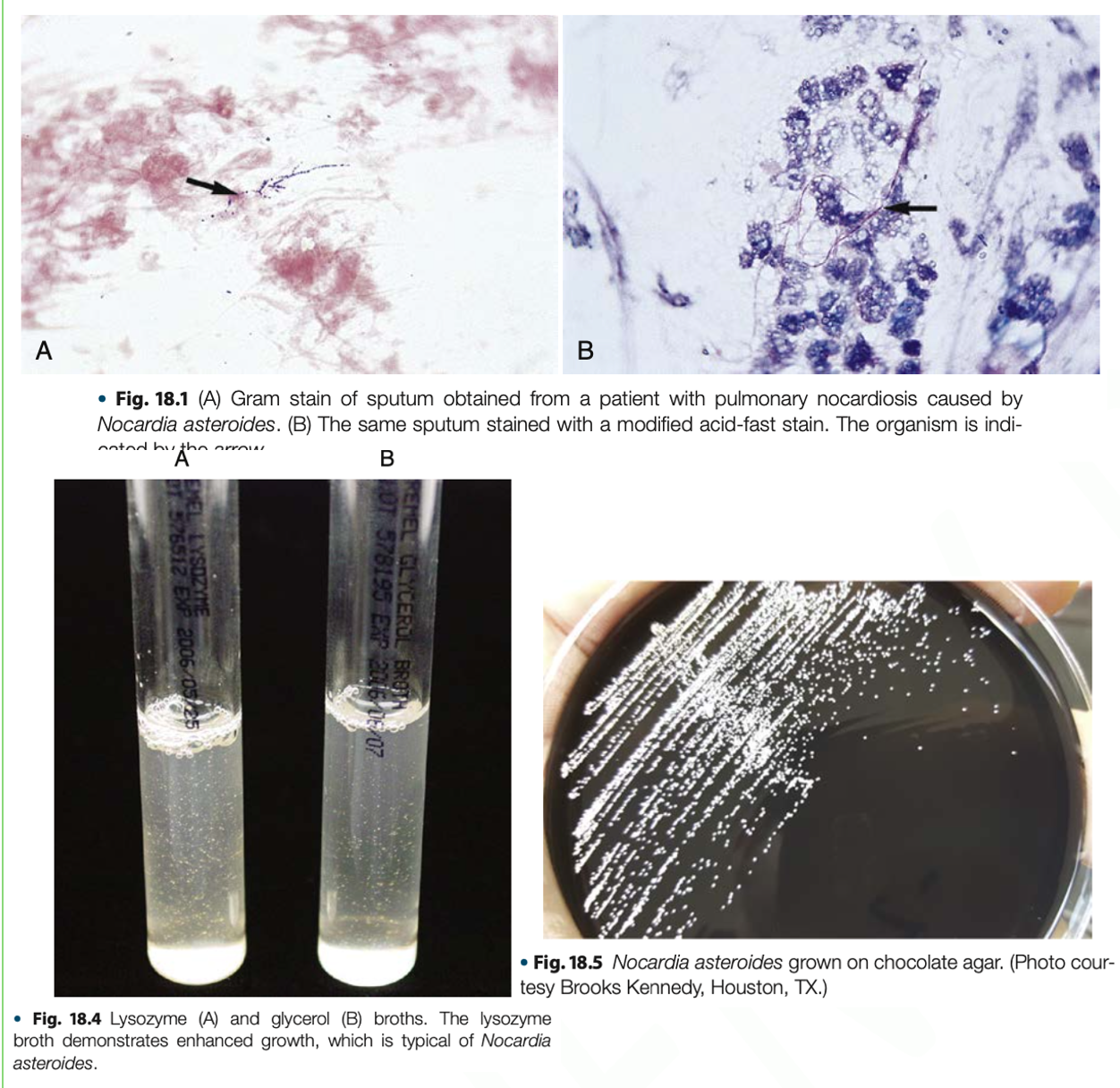
Nocardia asteroides complex
- Are facultatively intracellular parasites – resistant to intracellular killing & cause tropism for neuronal tissue
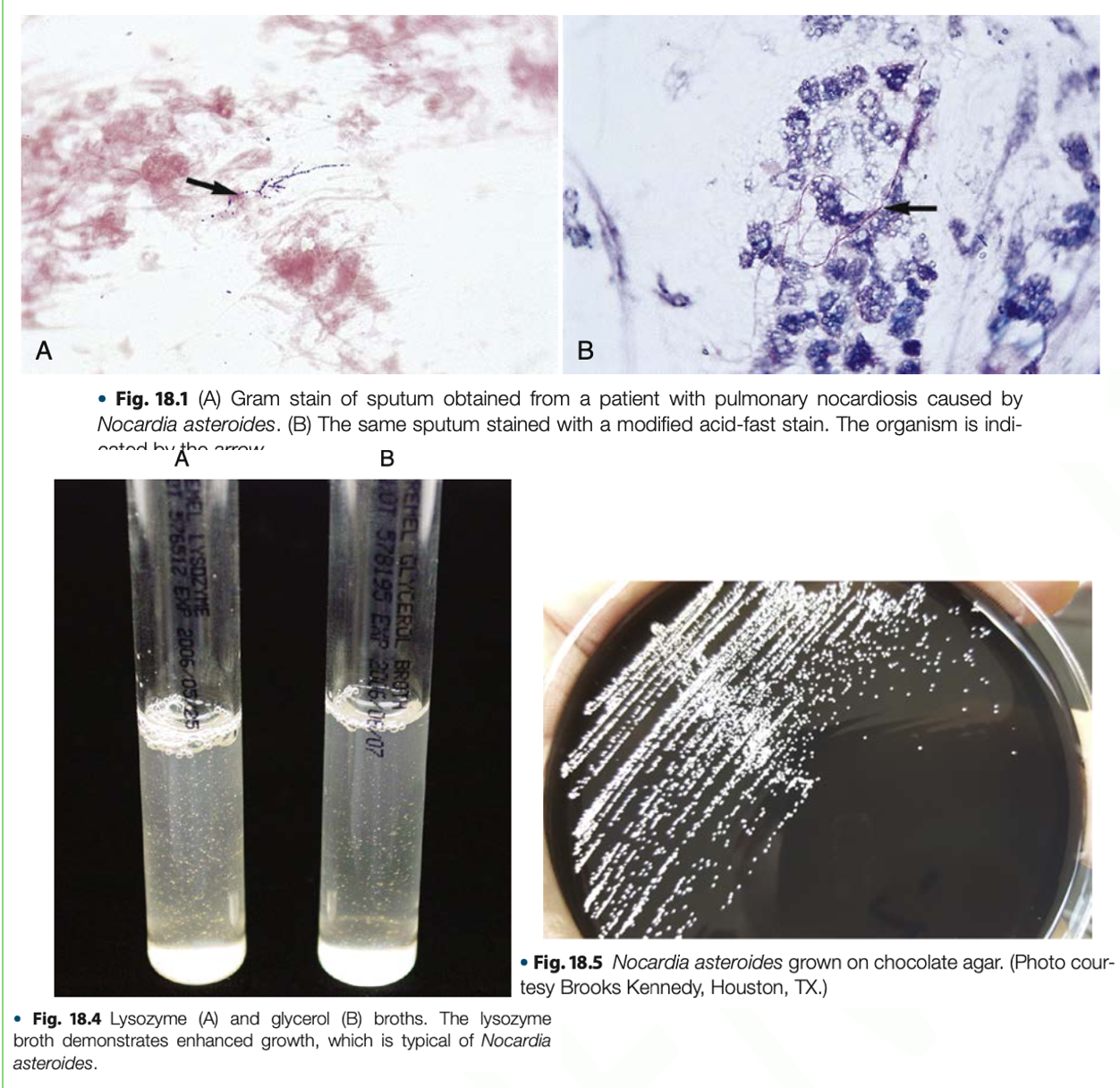
Nocardia asteroides complex
- They have the ability to inhibit phagosome – lysosome fusion
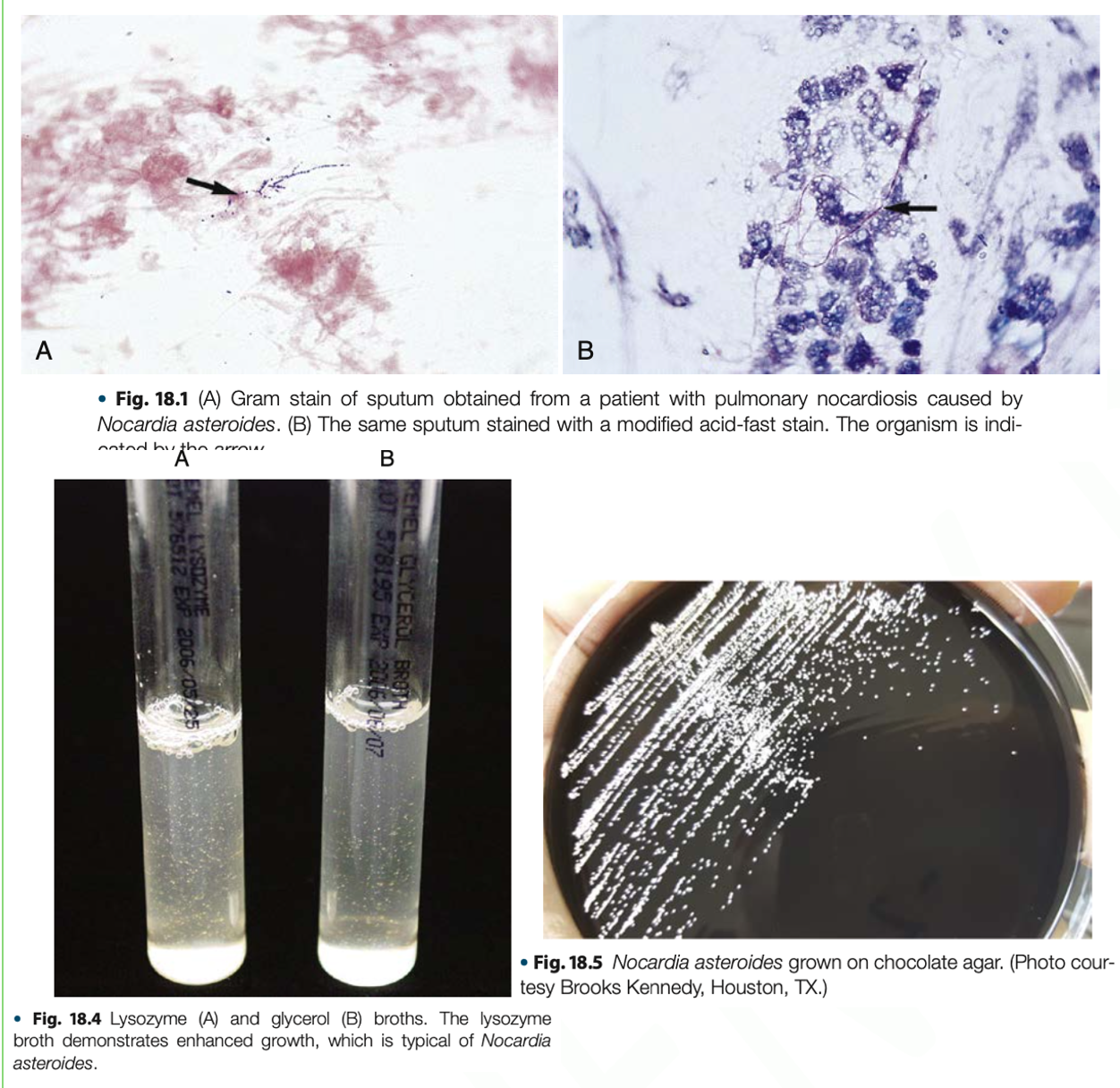
Nocardia asteroides complex
- They produce large amounts of catalase & hemolysin
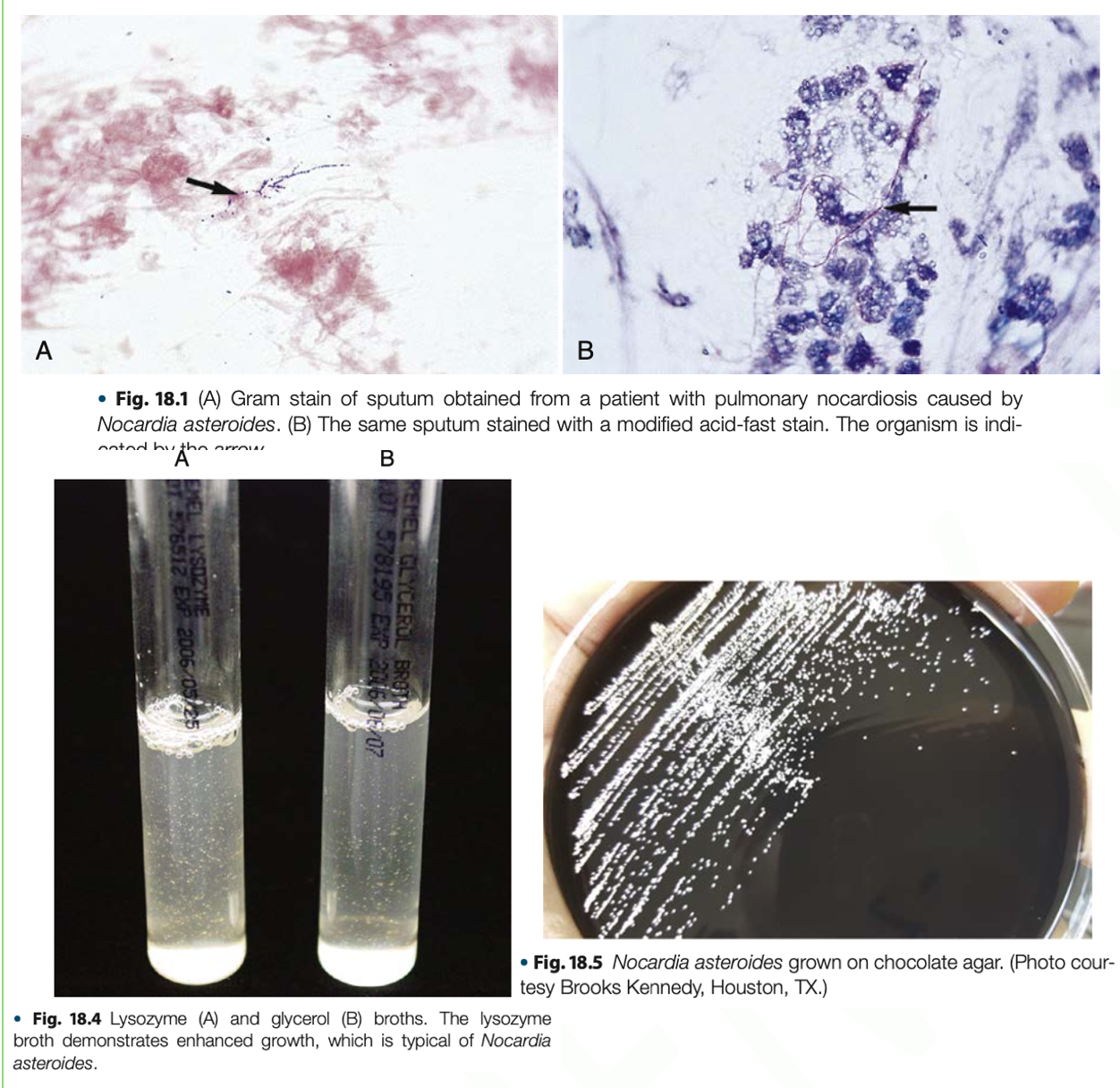
Nocardia cyriageorgica
Nocardia brasilinesis
Nocardia otitidis cavarium
COB
- Infection is acquired through INHALATION
Nocardia cyriageorgica
Nocardia brasilinesis
Nocardia otitidis cavarium
COB
- It can cause INVASIVE PULMONARY INFECTION
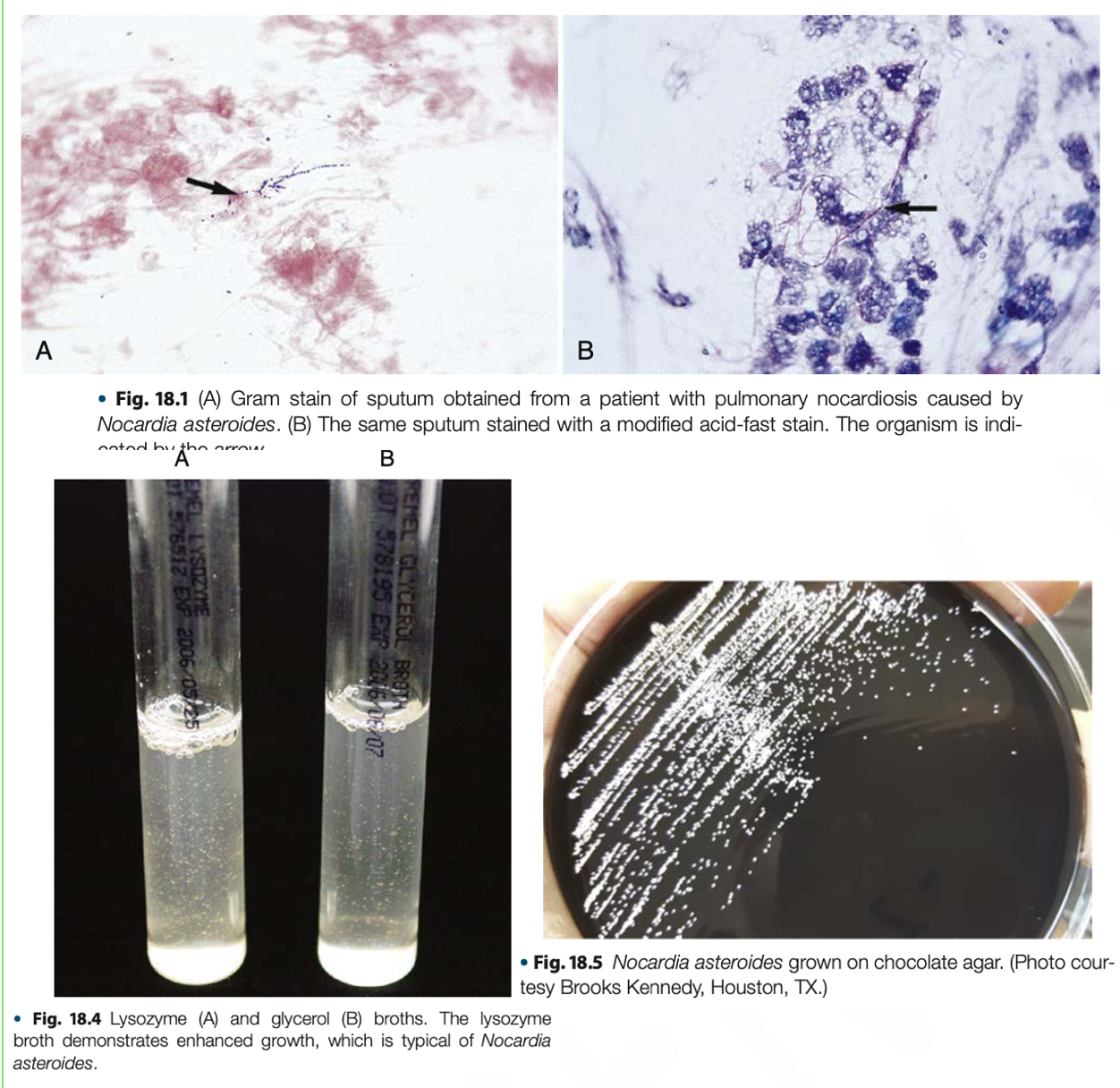
Nocardia asteroides
Nocardia brasiliensis
AB
MAJOR CAUSE of SKIN INFECTION
• Actinomycetoma / Madura’s Foot
• Lymphocutaneous Infection
• Pulmonary Diseases – CONFLUENT BRONCHOPNEUMONIA; sputum is thick & purulent; NO ENCAPSULATION OF THE ABSCESS & SULFUR GRANULES
Types of Skin Infection of Nocardia asteroides
Actinomycetes / Madura’s foot
chronic, localized, painless subcutaneous infection; presence of SULFUR GRANULES
CONFLUENT BRONCHOPNEUMONIA
Pulmonary Diseases of Nocardia asteroides
Confluent Bronchopneumonia
sputum is thick & purulent
F
CONFLUENT BRONCHOPNEUMONIA HAS NO ENCAPSULATION OF THE ABSCESS & SULFUR GRANULES
CONFLUENT BRONCHOPNEUMONIA HAS ENCAPSULATION OF THE ABSCESS & SULFUR GRANULES (t/f)
T
Rhodococcus, Gordonia & Tsukamurella is G +, Catalase +, branching, filamentous bacteria that can fragment into rods & cocci (t/f)
Rhodococcus, Gordonia & Tsukamurella
- They can be isolated from soil, fresh, marine water, & organic matter
T
Rhodococcus, Gordonia & Tsukamurella is primarily acquired by inhalation (t/f)
Rhodococcus, Gordonia & Tsukamurella
- They can grow on most of the nonselective beaded, branching filaments that occasionally fragment into rod-shaped & short coccoid forms during aging
Rhodococcus, Gordonia & Tsukamurella
- It grows on nonselective media used to recover media for bacterial, mycobacterial, & fungi isolation
• Skin Infections
• Pneumonia
• Peritonitis
• Catheter-Associated Sepsis
SPPC
Types ok Skin Infections of Rhodococcus, Gordonia & Tsukamurella
Rhodococcus equi
- Found in soil & causes respiratory tract infection in animals
Rhodococcus equi
- It is PARTIALLY ACID FAST – has mycolic acid with LONGER carbon chains
Rhodococcus equi
- It can persist & replicate within MACROPHAGES
Rhodococcus equi
- It can infect IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PX (HIV)
Rhodococcus equi
- Causing SLOWLY PROGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS PNEUMONIA
Coccobacilli in “zigzag” pattern
Diphtheroid G + rods
Microscopy of Rhodococcus equi
SUSCPETIBLE TO LYSOZYME
Differential test of Rhodococcus equi
SUSCPETIBLE TO LYSOZYME
Differential test of Rhodococcus equi
SUSCPETIBLE TO LYSOZYME
Differential test of Gordonia spp.
• Smooth
• Slimy colonies
• Glossy to irregular edges
microscopy of Gordonia spp.
F
Gordonia spp. is G + to gram variable
Gordonia spp. is G – to gram variable (t/f)
T
Gordonia spp. is Partially acid-fast (t/f)
T
Gordonia spp. is NON-MOTILE (t/f)
Gordonia spp. has an absence of Mycelia
Gordonia spp. has a presence of Mycelia (t/f)
F
Gordonia spp. is Catalase +
Gordonia spp. is Catalase - (t/f)
Gordonia spp. is considered as “Nocarioform” – fragment into rods/cocci
Gordonia spp. is considered as “-” – fragment into rods/cocci
rods/cocci
Gordonia spp. is considered as “Nocarioform” – fragment into -
F
Tsukamurella spp. are G + long rods (t/f)
Tsukamurella spp. are G – long rods (t/f)
F
Tsukamurella spp. Fragments to 3 parts (t/f)
Tsukamurella spp. Fragments to 5 parts (t/f)
Tsukamurella spp. HAS NO AERIAL HYPHAE (t/f)
Tsukamurella spp. HAS AERIAL HYPHAE (t/f)
F
Tsukamurella spp. is Slightly acid-fast by Kinyoun staining method
Tsukamurella spp. is Partially acid-fast by Kinyoun staining method (t/f)
Kinyoun staining method
Tsukamurella spp. is Slightly acid-fast by -
Circular colonies with RHIZOID EDGES & white / orange pigment
Microscopy Tsukamurella spp.
Streptomycess spp.
Are found in soil & primarily saprophytes
Dry to chalky heaped colonies
Culture of Streptomycess spp.
have - heaped colonies
Gray-white colonies
Culture of Streptomycess spp.
color or the colonies
Have MUSTY BASEMENT ODOR
Culture of Streptomycess spp.
Have what kind of ODOR
T
Culture of Streptomycess spp.
• Hyphae are characterized by variable pigmentation (t/f)
Actinomadura spp.
- It causes wound infection for persons walking barefoot especially in tropical countries – MYCETOMAS
MYCETOMAS
Actinomadura spp. causes wound infection for persons walking barefoot especially in tropical countries –
Actinomadura spp.
- The microscopic & colony morphology are very similar to Nocardia spp.
Nocardia spp.
Actinomadura spp.’s microscopic & colony morphology are very similar to -
• Waxy
• Cerebriform
• Colored colonies with “MOLAR TOOTH” (routine agar)
Culture of Actinomadura spp.
• Actinomadura madurae
• Actinomadura pelletieri
Species of Actinomadura spp.
Nocardia
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: +
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : EXTENSIVE
Lysozyme : R
Rhodococcus
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: + / –
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : minimal
Lysozyme : V
Gordonia
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: + / –
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : minimal
Lysozyme : S
Tsukamurella
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: + / –
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : minimal
Lysozyme : R
Streptomyces
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: ––
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : EXTENSIVE
Lysozyme : S
Actinomadura
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: ––
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : Variable / Sparse
Lysozyme : S
Dermatophilus
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: ––
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : Branching
Lysozyme : S
Nocardiopsis
Differential Test on Gram + Branching Bacilli
PARTIALLY Acid Fast: ––
Appearance on Tap H2O Agar / Branching Aerial Hyphae : EXTENSIVE
Lysozyme : S