A1.2 Nucleic acids
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid that carries all the genetic material for living organisms
What is the macromolecule, polymer and monomer of DNA?
Macromolecule → deoxyribonucleic acid
Polymer → polynucleic acid
Monomer → nucleotides
Where is DNA found?
Mainly found in the nucleus (chromosomes)
Also in chloroplast and mitochondria of eukaryotes
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (type of DNA) is used in protein synthesis and can be found in cytoplasm and nucleus
Used as genetic material for some viruses (Covid or HIV)
Components of a nucleotide
Pentose sugar (five carbon atoms)
Phosphate group (acidic and negatively charged)
Nitrogenous base (has 1 or 2 rings in structure)
The nitrogenous base and the phosphate bond to the sugar by covalent bonds
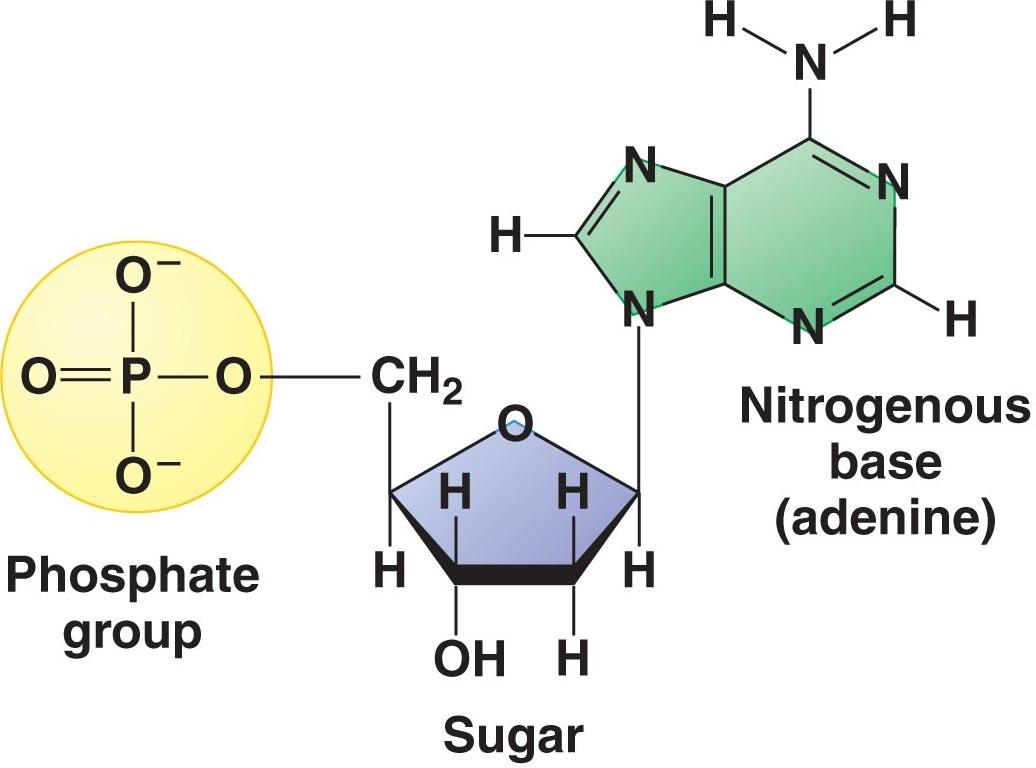
How is the sugar-phosphate backbone linked to form a polymer?
The phosphate of one nucleotide links to the pentose of another through covalent bonds
What are the four nitrogenous bases?
Adenine
Thymine (Uracil)
Cytosine
Guanine
The sequence of these bases is how information is stored
RNA form
RNA is a polymer
The nucleotides are always linked by a condensation reaction
The hydroxyl group (OH) of one phosphate is combined with the OH of a pentose
OH + H → H2O (water as waste product)
The remaining oxygen atom forms covalent bond between the two nucleotides
DNA structure
Composed of strands/polymers of nucleotides
Double helix shape
Has bases A,T,C,G
Two antiparallel strands
The pentose sugar is deoxyribose
Has constant diameter of 2 nanometers
Complementary base pairs
Adenine and thymine pair together (form 2 hydrogen bonds)
Cytosine and guanine pair together (form 3 hydrogen bonds)
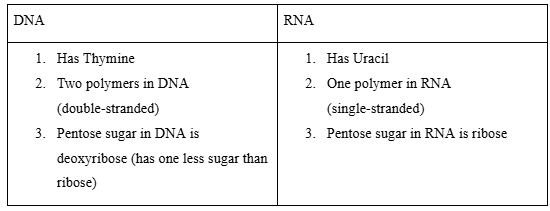
Differences between DNA and RNA
DNA replication
Semi-conservative (produces two identical new molecules, containing 1 original and 1 new strand)
Replicated by complementary base pairing
Gene
Specific section of DNA that genetic information consists of
Gene expression
When a gene has an effect on a cell
How is the information stored in DNA limitless?
Genetic information is stored in base sequence of one of two strands
4 possibilities for each base
4² possibilities for a sequence of two bases
4^n possibilities for a sequence with n bases
DNA molecules can be any length
Stored in very small size, thus making it efficient storage
Codon
Made of 3 bases
there are 64 codons
Most codons specify one amino acid
One codon signals start of protein synthesis
3 codons signal stop
Universal genetic code
All living organisms and viruses use the same genetic code, all codons code for the same amino acids (few minor exceptions)