B4. 2 - Ecological Niche
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Ecological niche
Role an organism plays in its community, (what it does, where it lives, and impact) affected by abiotic and biotic factors

Biotic factors impacting niche (4)
Predation, parasites, disease, resource/food competition

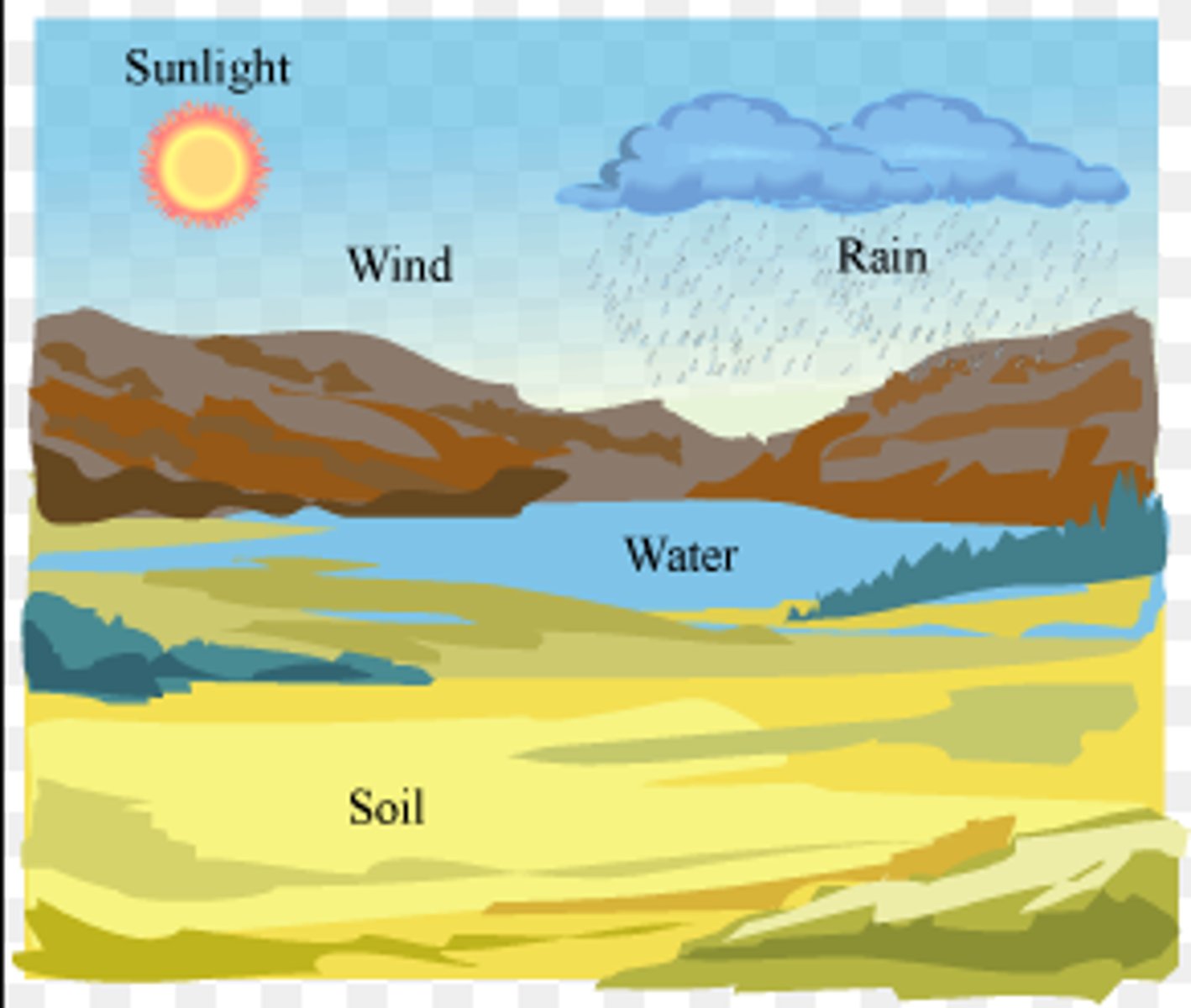
Abiotic factors impacting niche (5)
Temperature, soil pH, precipitation, natural disaster, amount of sunlight
List the 3 modes of respiration
Obligate anaerobes, facultative anaerobes, obligate aerobes
Obligate anaerobes
Poisoned by oxygen (do not have enzymes to digest it) use anaerobic respiration via nutrients like iron, sulfur, and methane, sink to the bottom of a culture tube
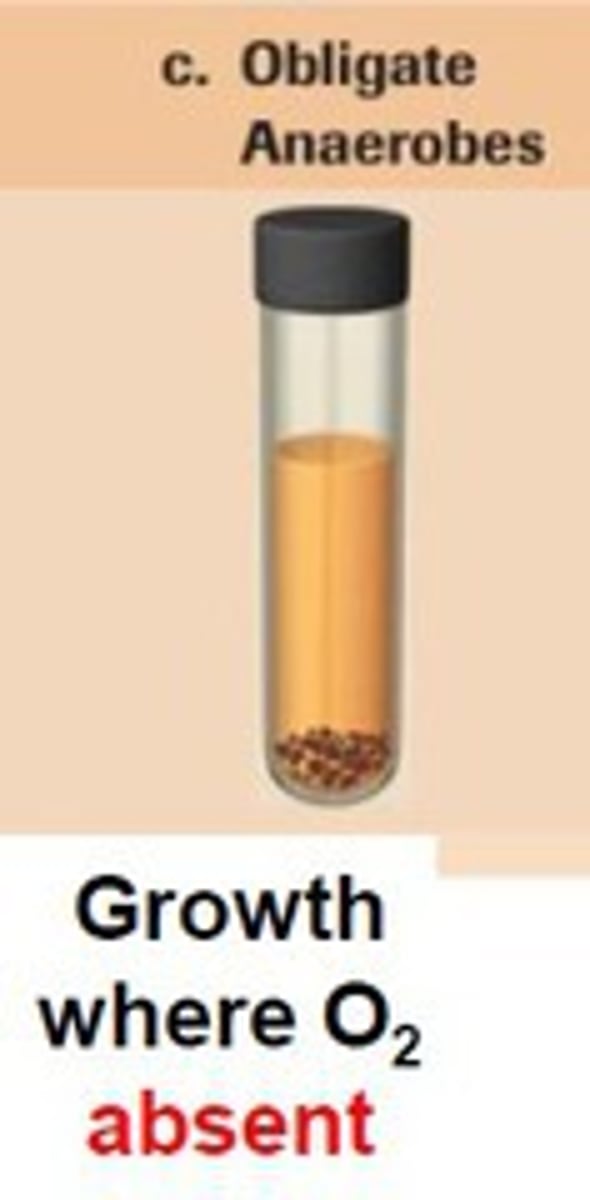

Example of obligate anaerobe
Methanogenic archaea
Facultative anaerobes
Use fermentation and cellular respiration to respirate, not poisoned by oxygen, dispersed throughout the culture tube
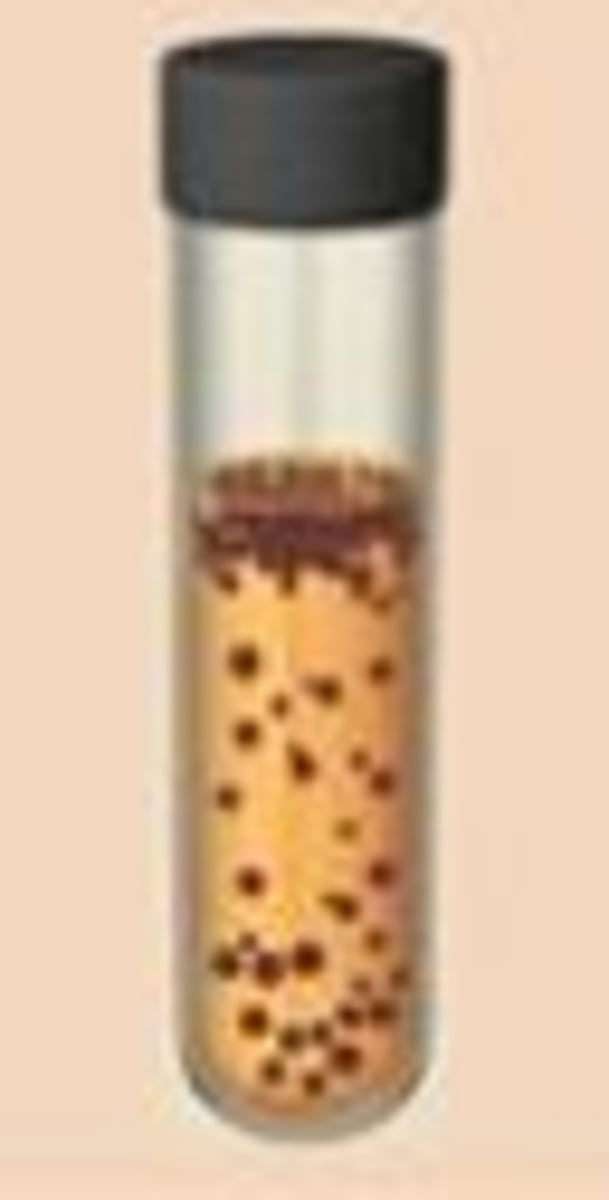

Example of facultative anaerobes
E. coli and yeasts

Obligate aerobes
Need oxygen, use cellular respiration to make ATP, float to the top of the culture tube

Example of obligate aerobes
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
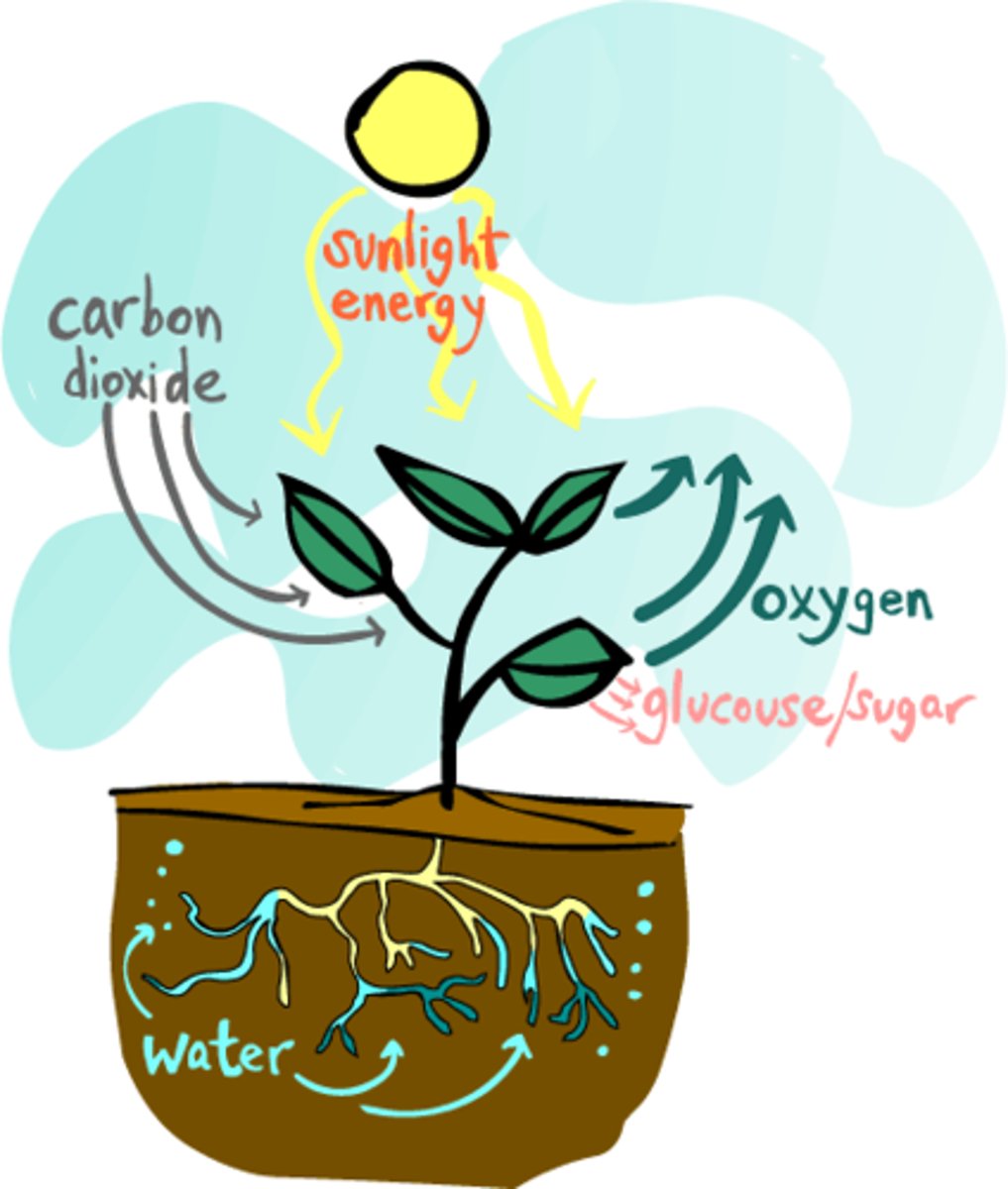
Photosynthesis
Process by which organisms convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy as glucose
Holozoic nutrition (4)
In which food is ingested, digested, absorbed, and assimilated.
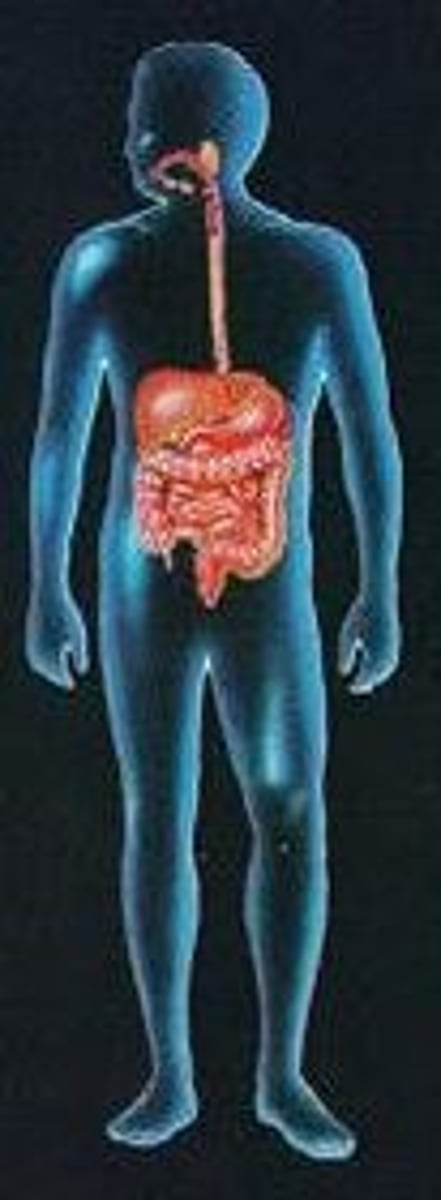
Are all animals holozoic? (True or False)
False. All animals are heterotrophic, but holozoic nutrition also includes protozoa and bacteria, but not saprotrophs
Mixotrophy
A form of nutriton in which both autotrophy and heterotrophy may be utilized, depending on the avalibility of resources
Obligate mixotrophy
Both hetero- and autotrophic methods of nutrition are used always (eg Euglena , sea slugs)
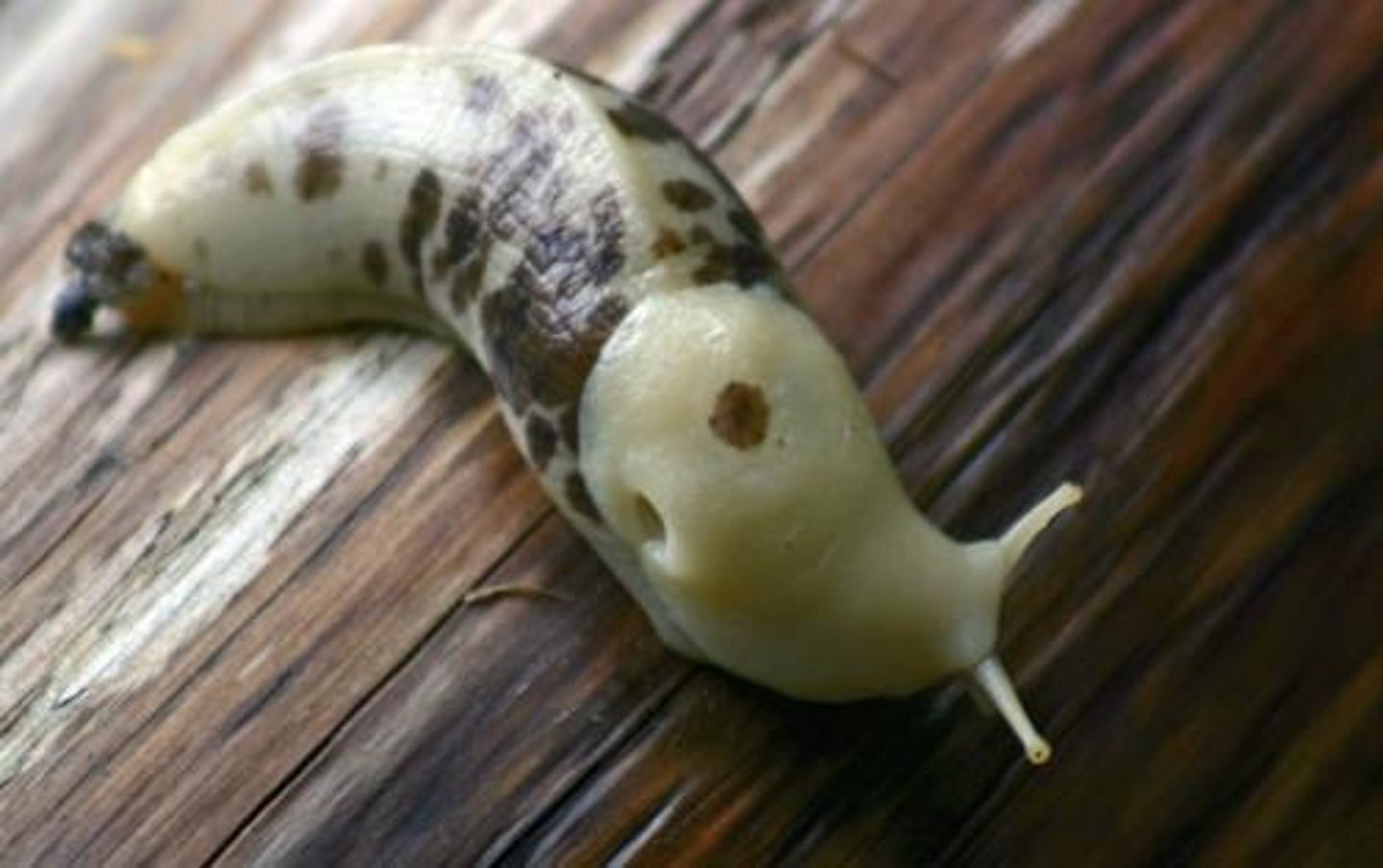

Facultative mixotropohy
Hetero- or auto trophy is only used when nutrients are lacking (eg phytoplankton)
Saprotrophs
heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by external digestion. release inorganic nutrients as part of nutrient cycles.

What are the 3 Domains of life?
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
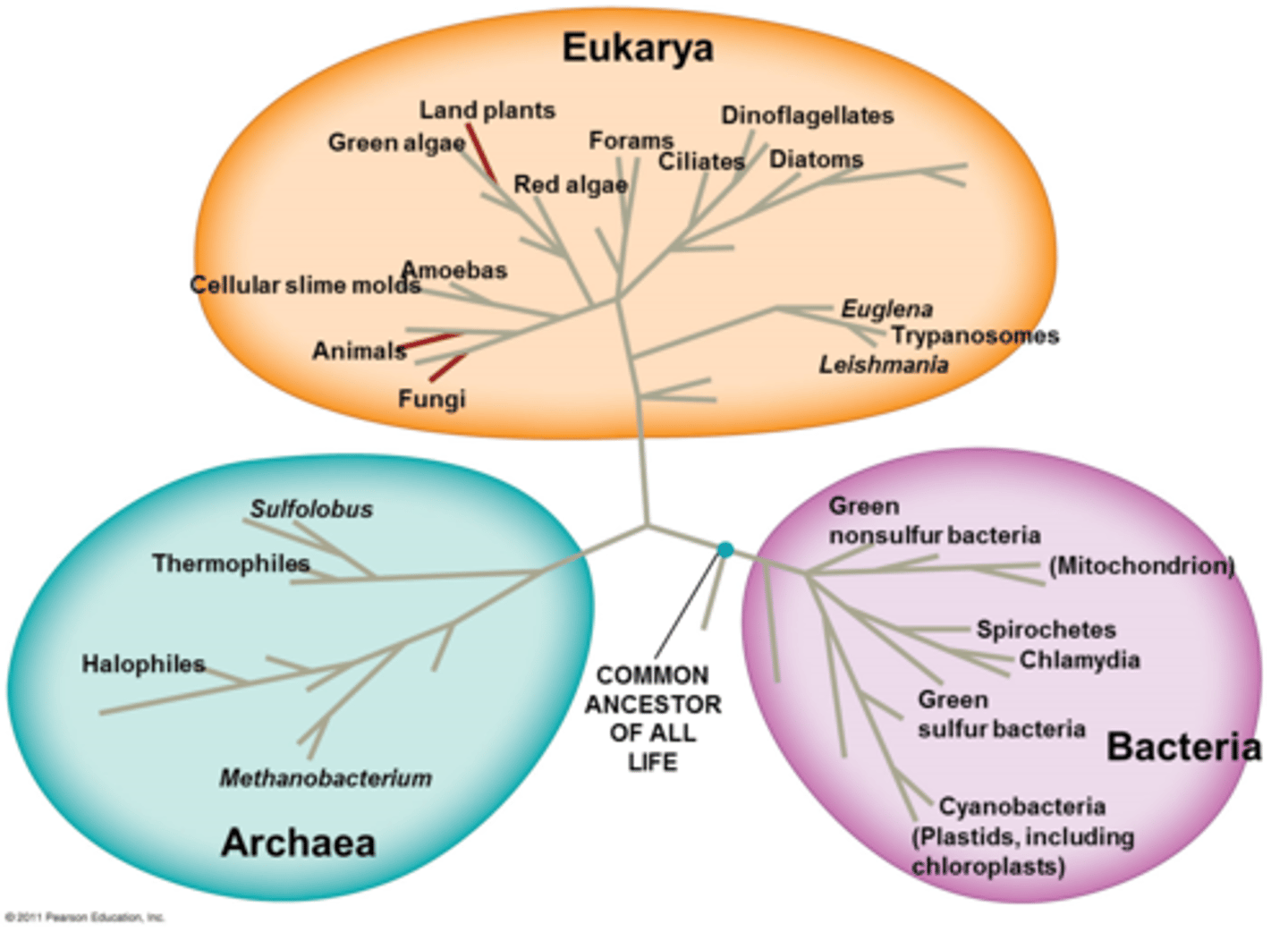
Archaea
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan (contain polysaccharides)
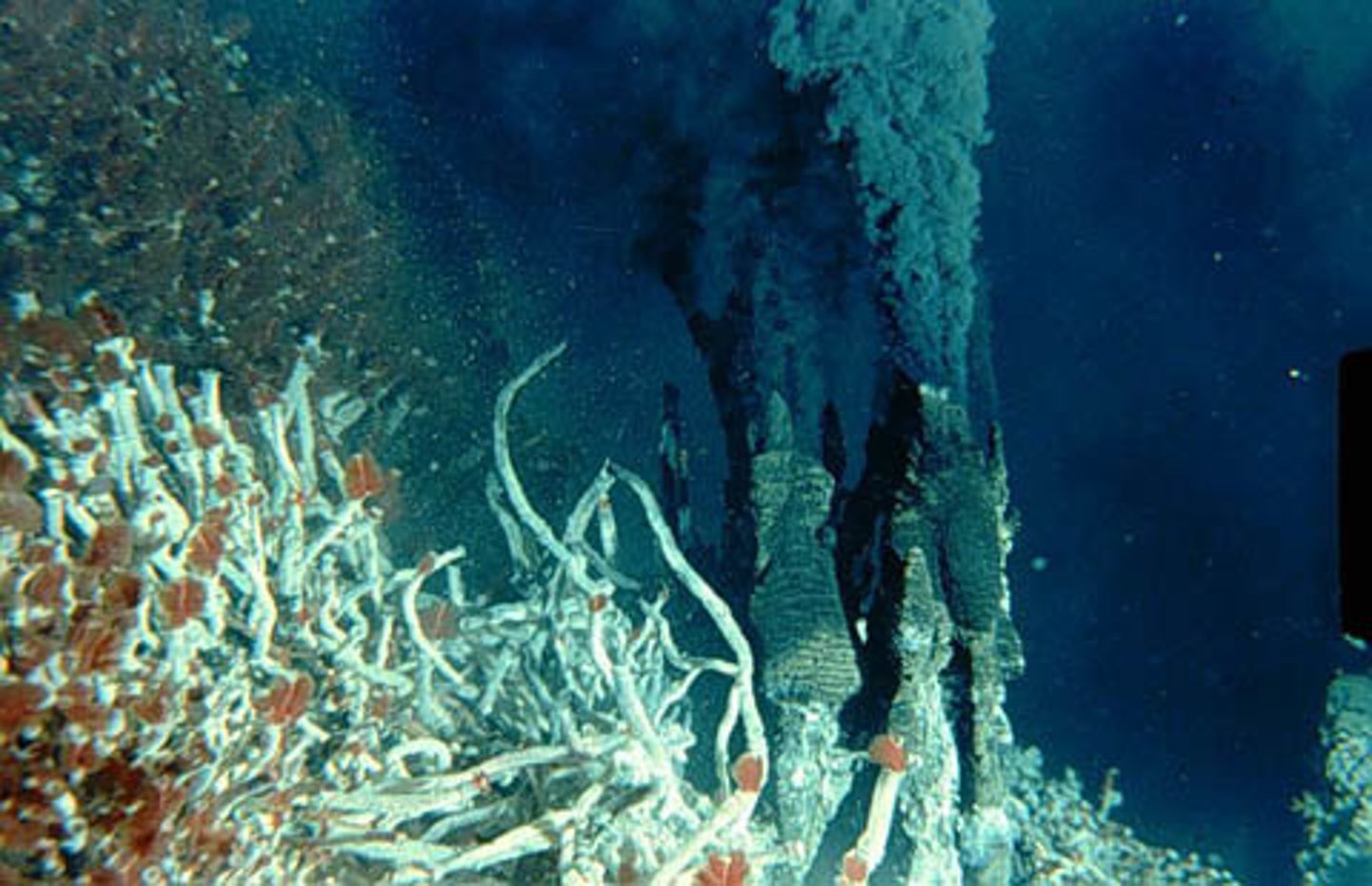
Chemoautotrophic archaea
Rely on the oxidation of inorganic compounds (like methane for methanogens in the stomach/ocean) to synthesize energy

Photosynthetic archaea
Use photosynthesis to obtain nutrients. Examples include H. salindrum, which does not use chlorophyll to photosynthesis but other nutrients
Heterotrophic archaea
Marine species that feed on lignin (complex carbohydrates that protect plants from pathogens, similar to bark)
What is the relationship between dentition and diet?
The diet of an organism impacts in dentition, For example, herbivores tend to have stronger jaw muscles and blunter teeth, while carnivores have sharper teeth. The diet of an organism shapes its dentition and mouth shape— a deduction made from a theory.
What is the relationship between dentition and diet in H. sapiens?
The increase in omnivoric tendencies in Homindae result in less stronger jaw muscles and smaller, less sharp teeth.
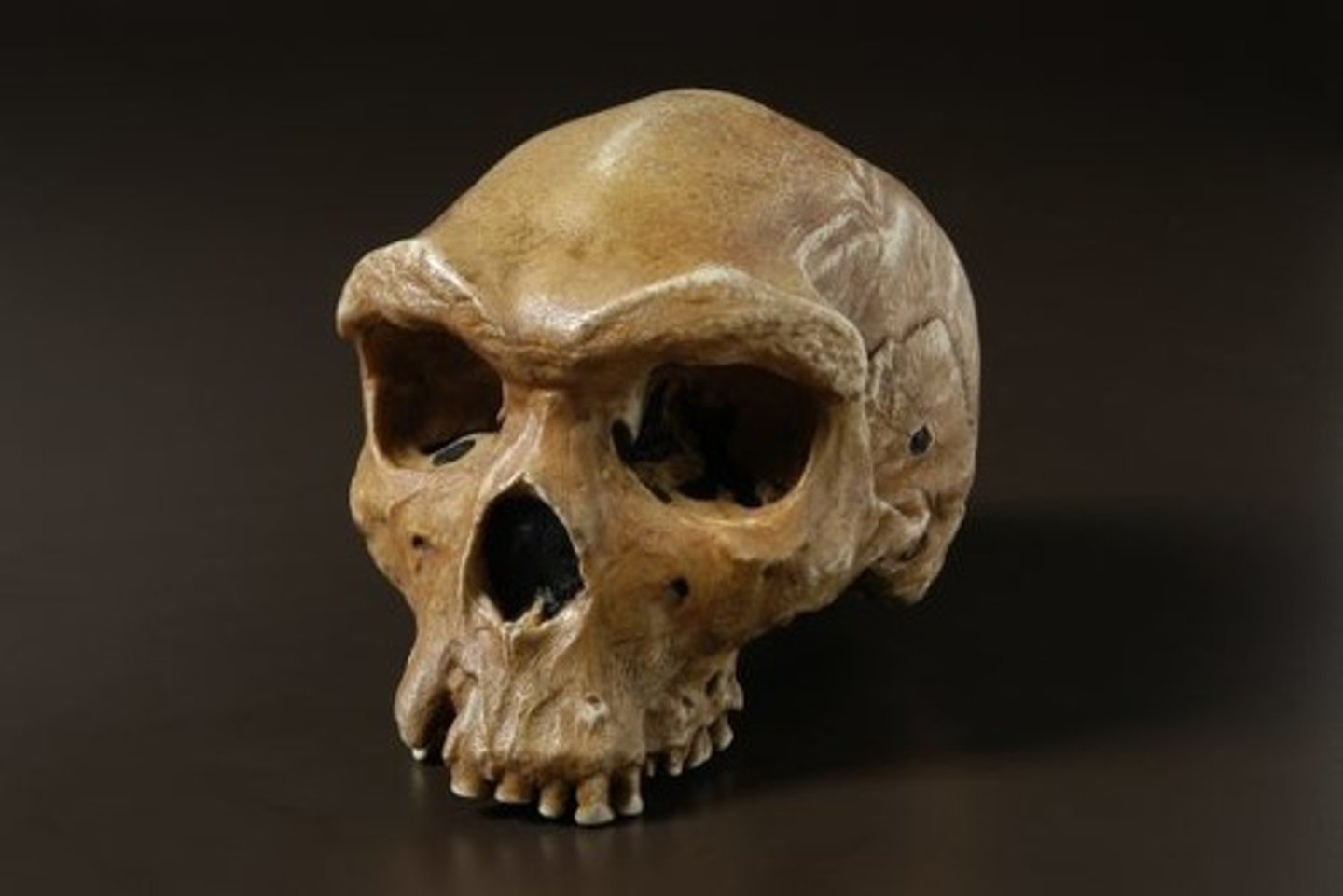

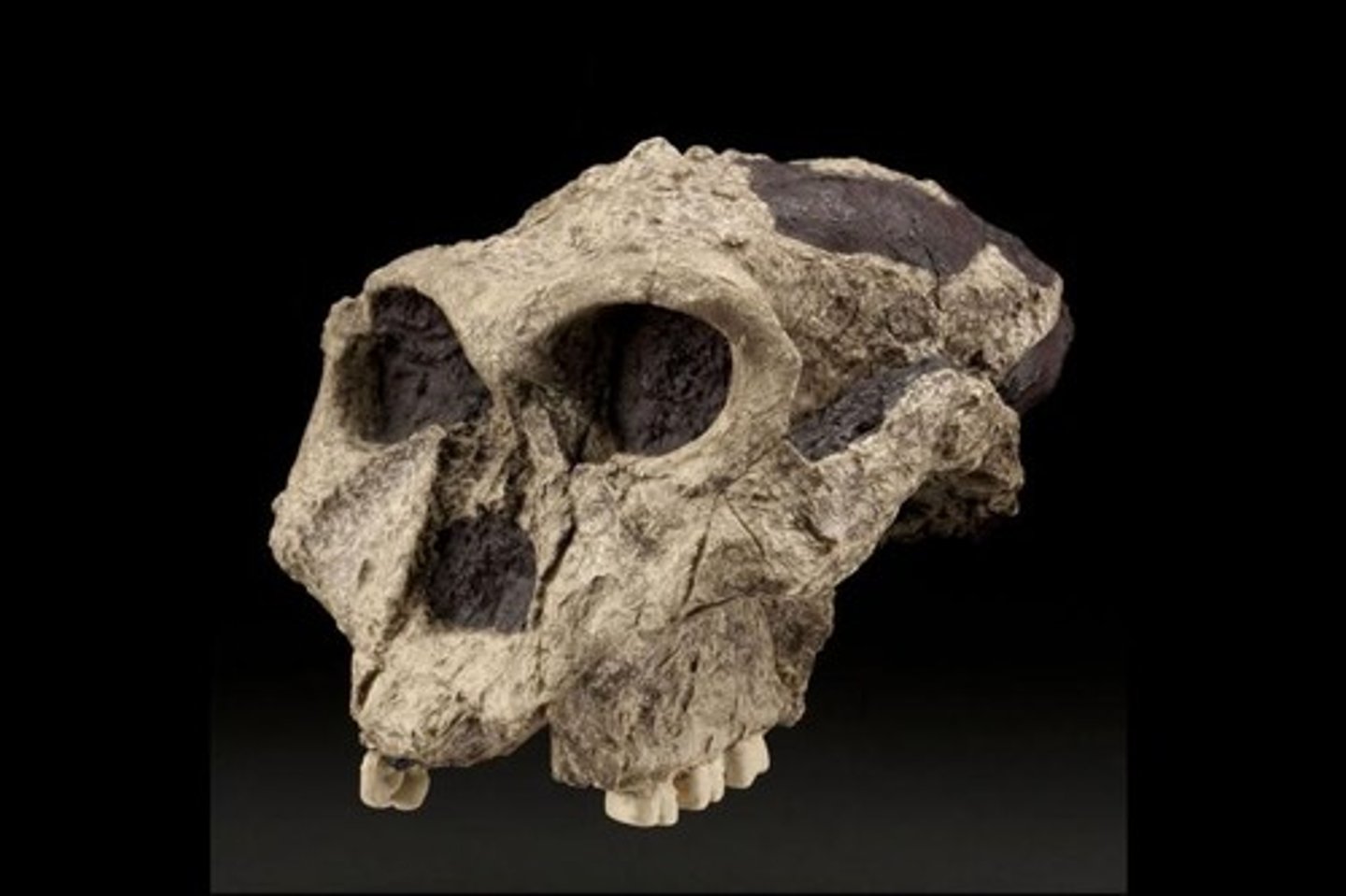
What is the relationship between dentition and diet in P. robustus?
P. robustus has larger teeth and chewing muscles, as well as a sagittal crest, which suggested stronger jaw muscles to chew tough leaves and nuts easily.

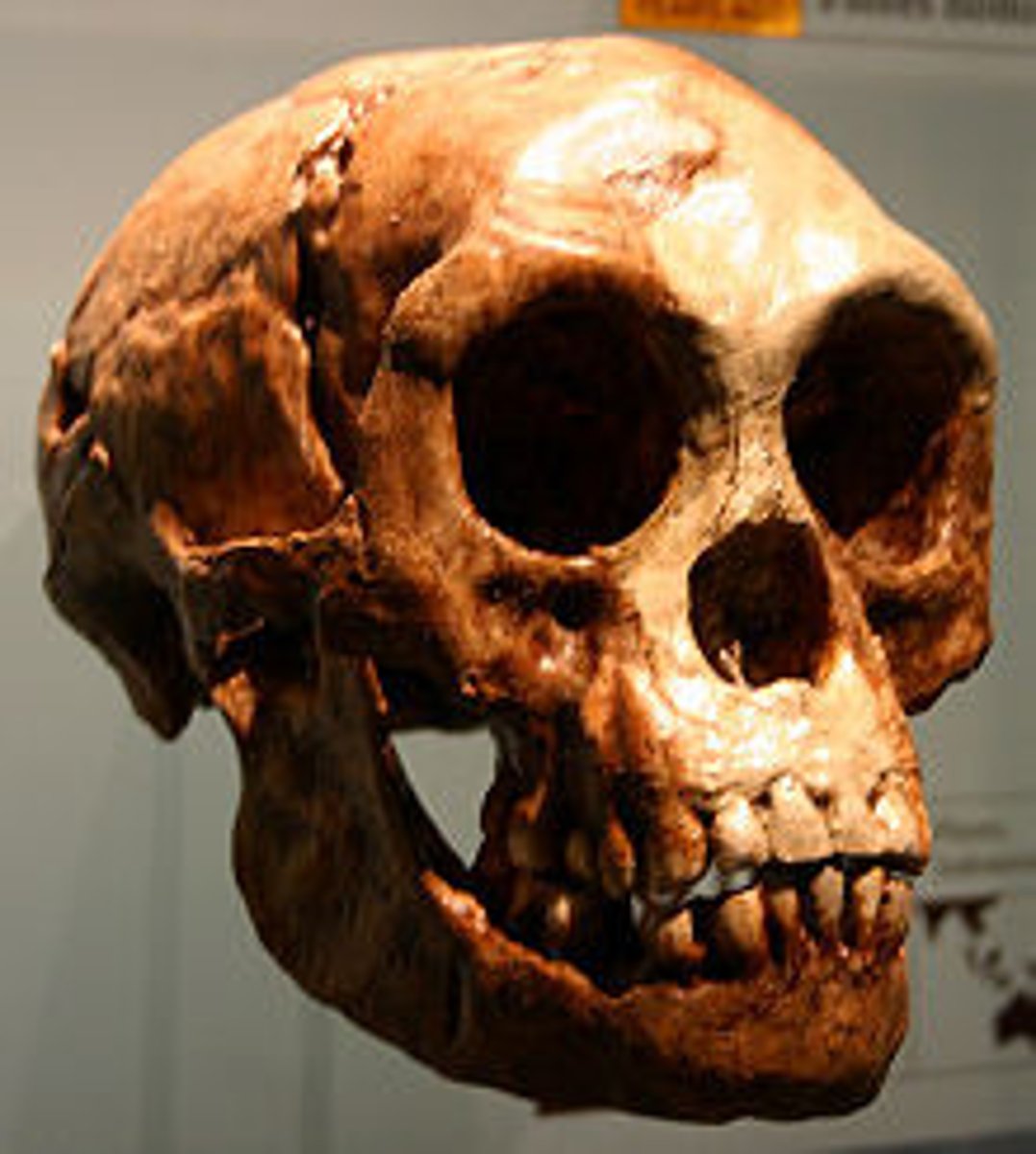
H. florensiensis?
H. florensiensis had large teeth for a small head size, and teeth markings that indicated it being an omnivore.

Include an example of plants for resisting herbivory
Plants also produce toxic secondary compounds (phytochemicals) in seeds and leaves (eg stinging nettles, nightshade, cactus), thorns (pineapples), mimicry

Chemical, physical and behavioural adaptations in predators with examples
Physical - speed, agility, dentition, sensory systems (eg lions)
Chemical - poison in cone snail (Conus geographus)
Behavioural - stealth (eg cats), mimicry, dolphin hunting

List chemical, physical and behavioural adaptations in prey with examples
Physical - Camouflage (zebras), hedgehogs' spikes
Chemical - poisonous frogs, skunks w/ chemical warfare
Behavioural - mimicry, "super organism" in schools of fish

List examples of adaptations of plant form for harvesting light
Trees that reach the canopy, lianas, epiphytes growing on branches of trees, strangler epiphytes, shade-tolerant shrubs and herbs growing on the forest floor.
Lianas
These are thick parasitic vines that use tree trunks to reach the sunlight, getting nutrients from the tree and the air. (roots on the ground, flowers & leaves on canopy)

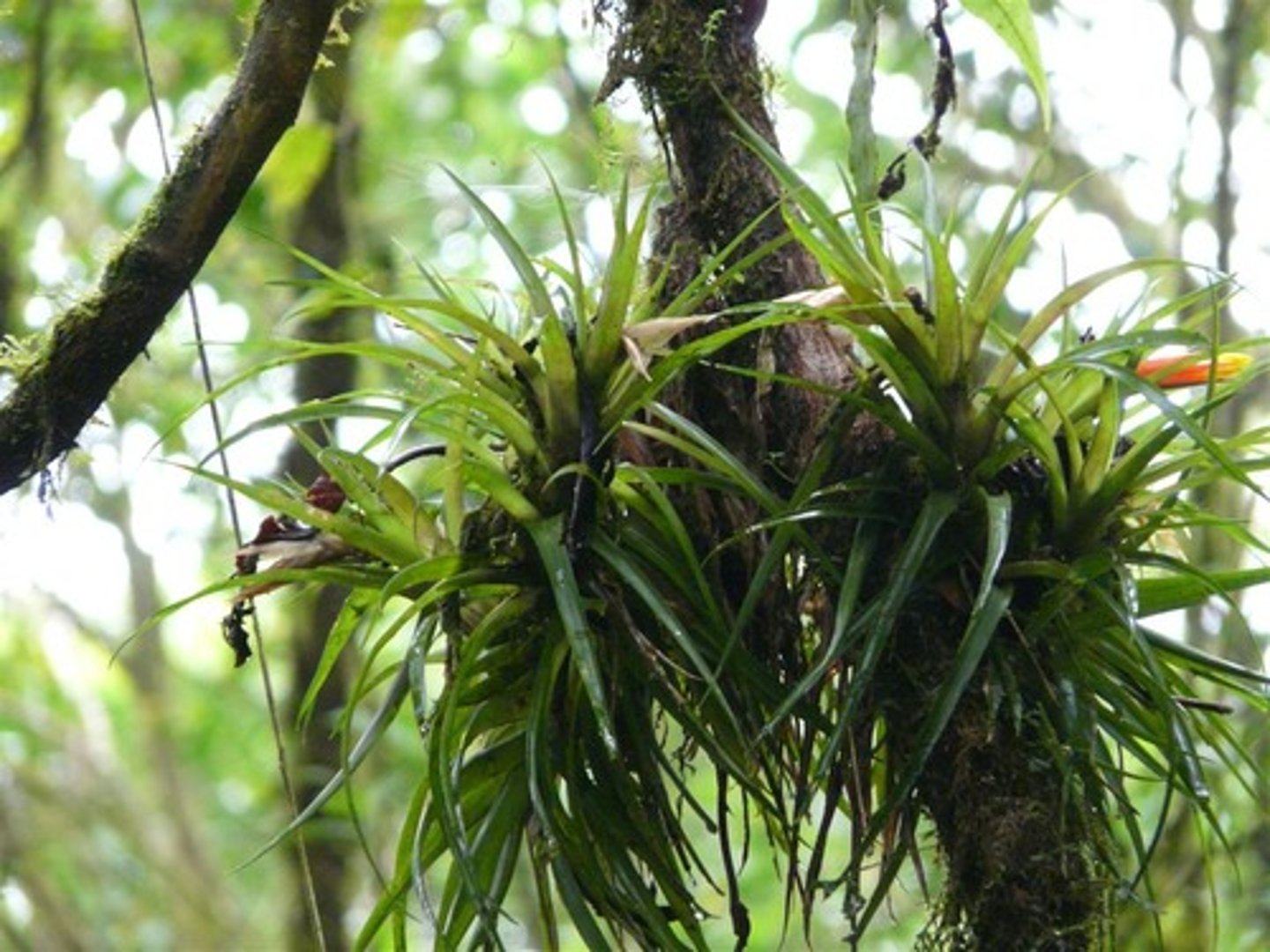
Epiphytes
plants such as mosses, lichens, and orchids, that grow on other plants but do not take nutrients from them

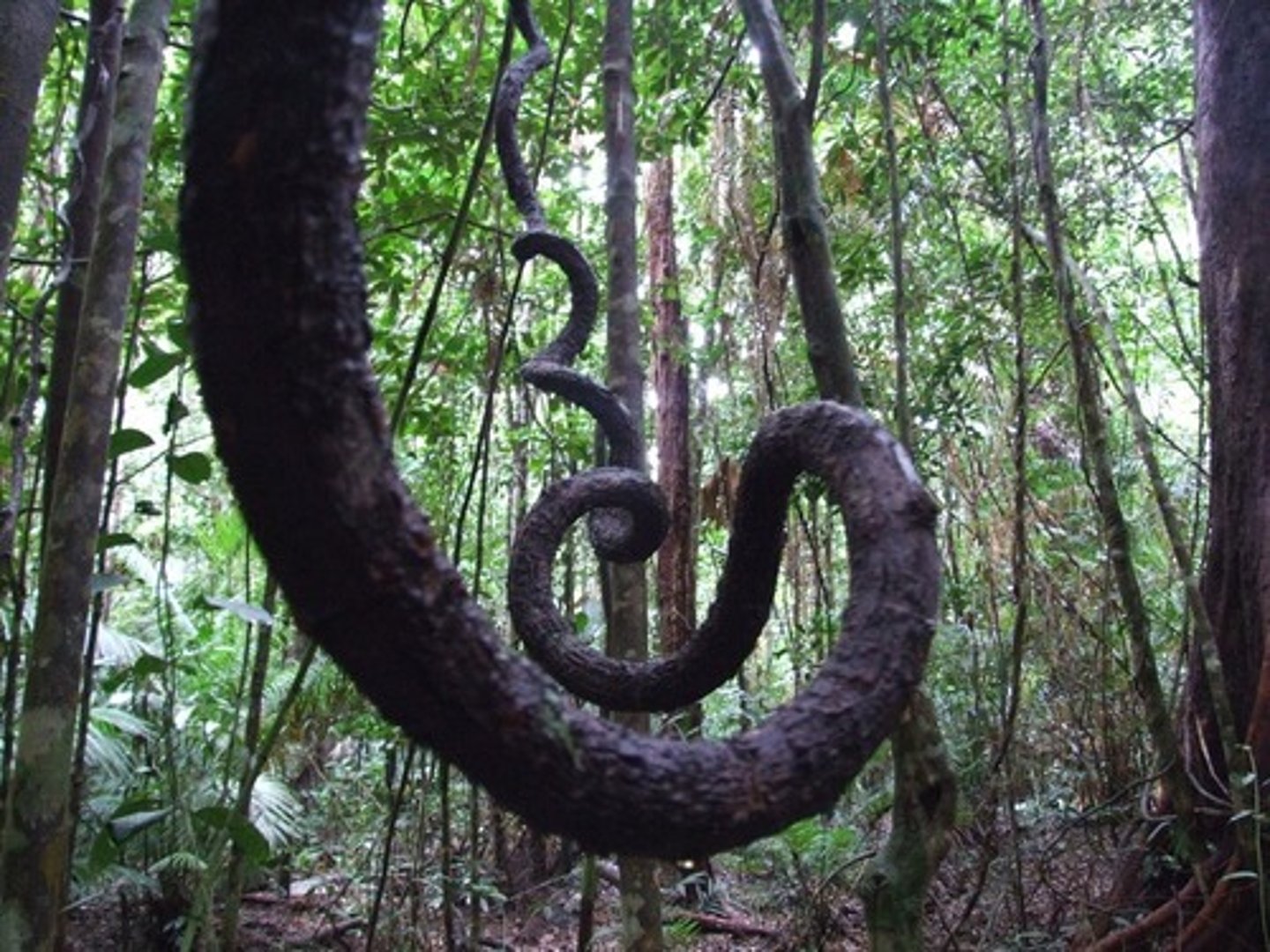
Strangling epiphytes
kill the supporting trees by compressing their trunks within a complete or partial network of roots (eg strangling figs, malapota)

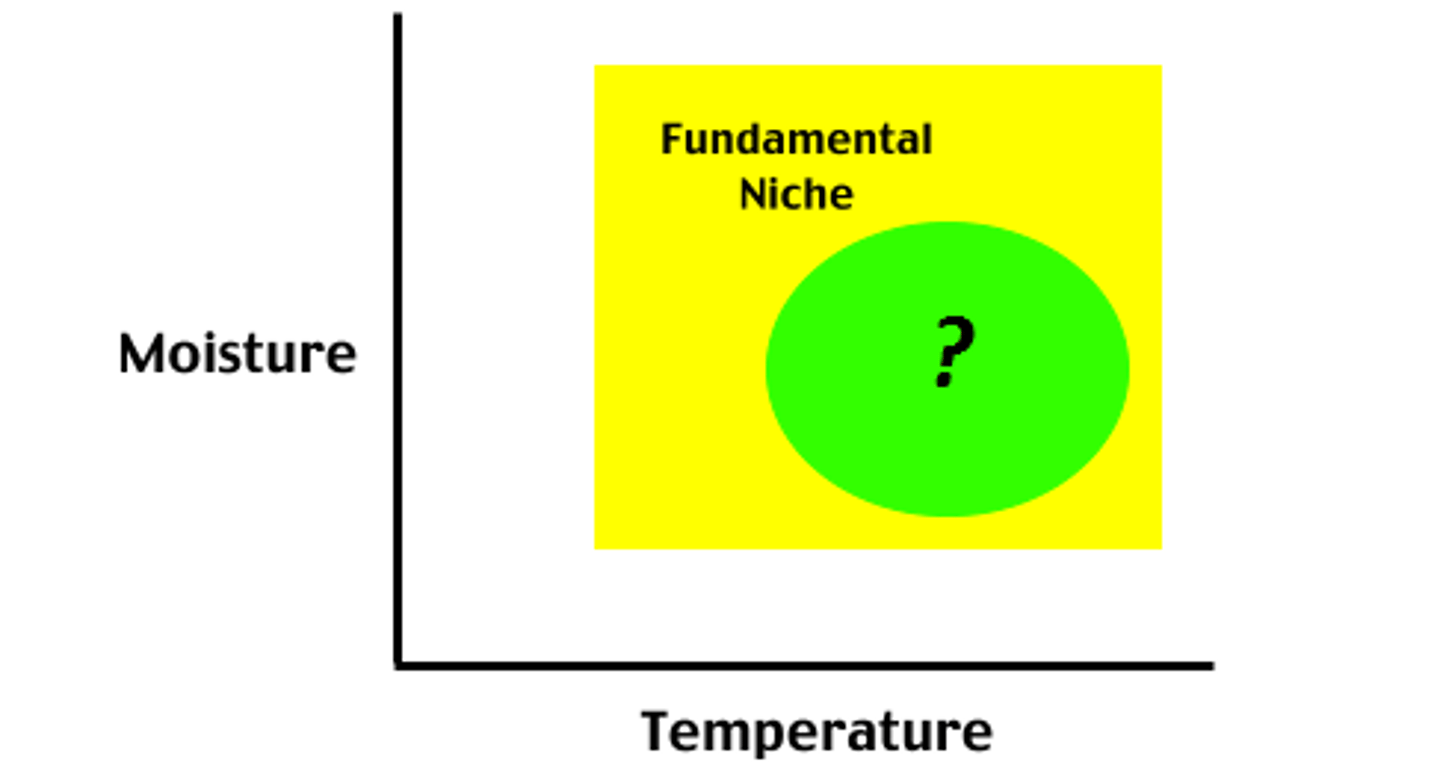
Fundamental niche
The full potential range of the physical, chemical, and biological factors a species can use if there is no competition from other species.
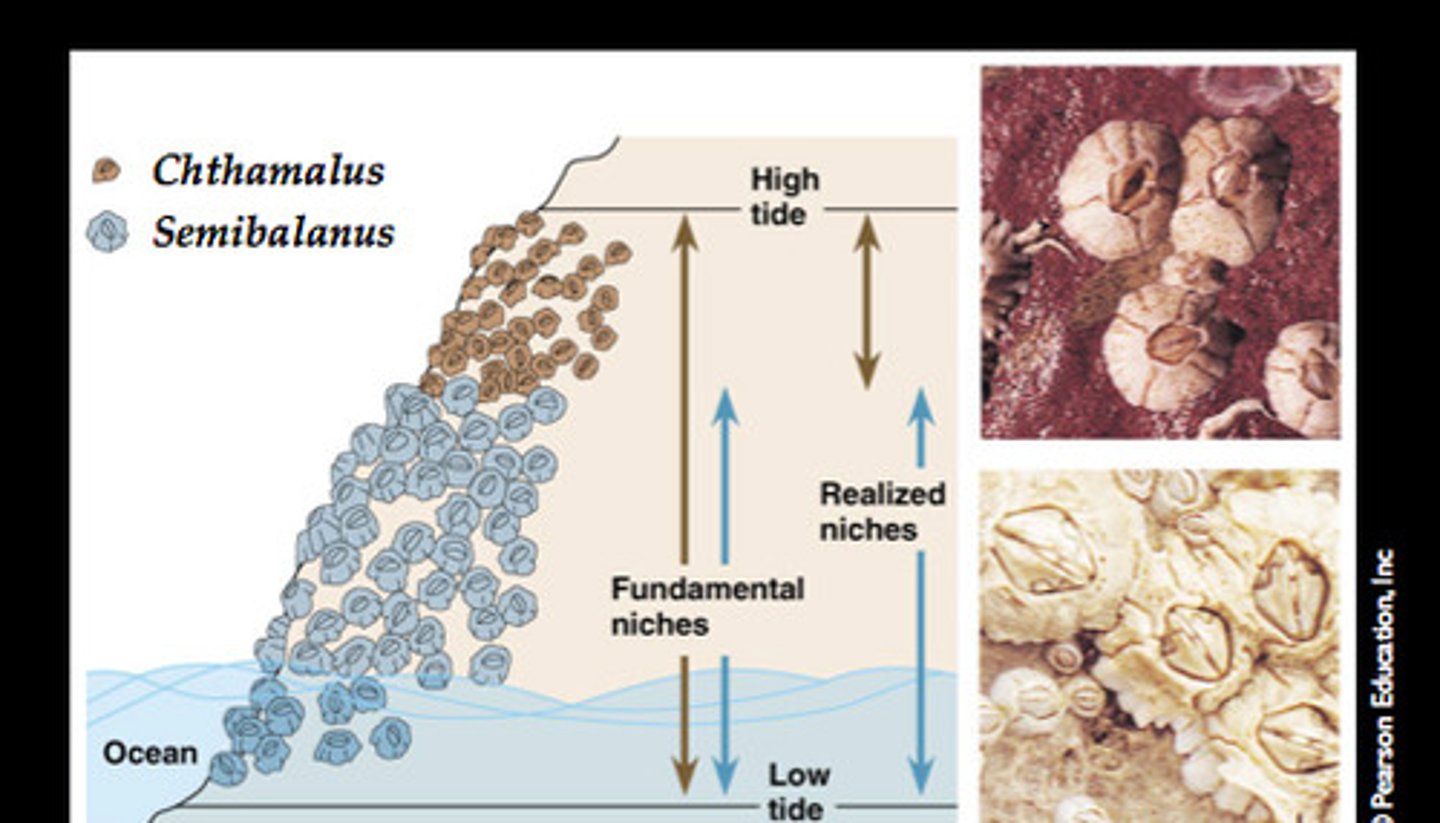
realized niche
the range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives, limited by competition and other limiting factors of population size
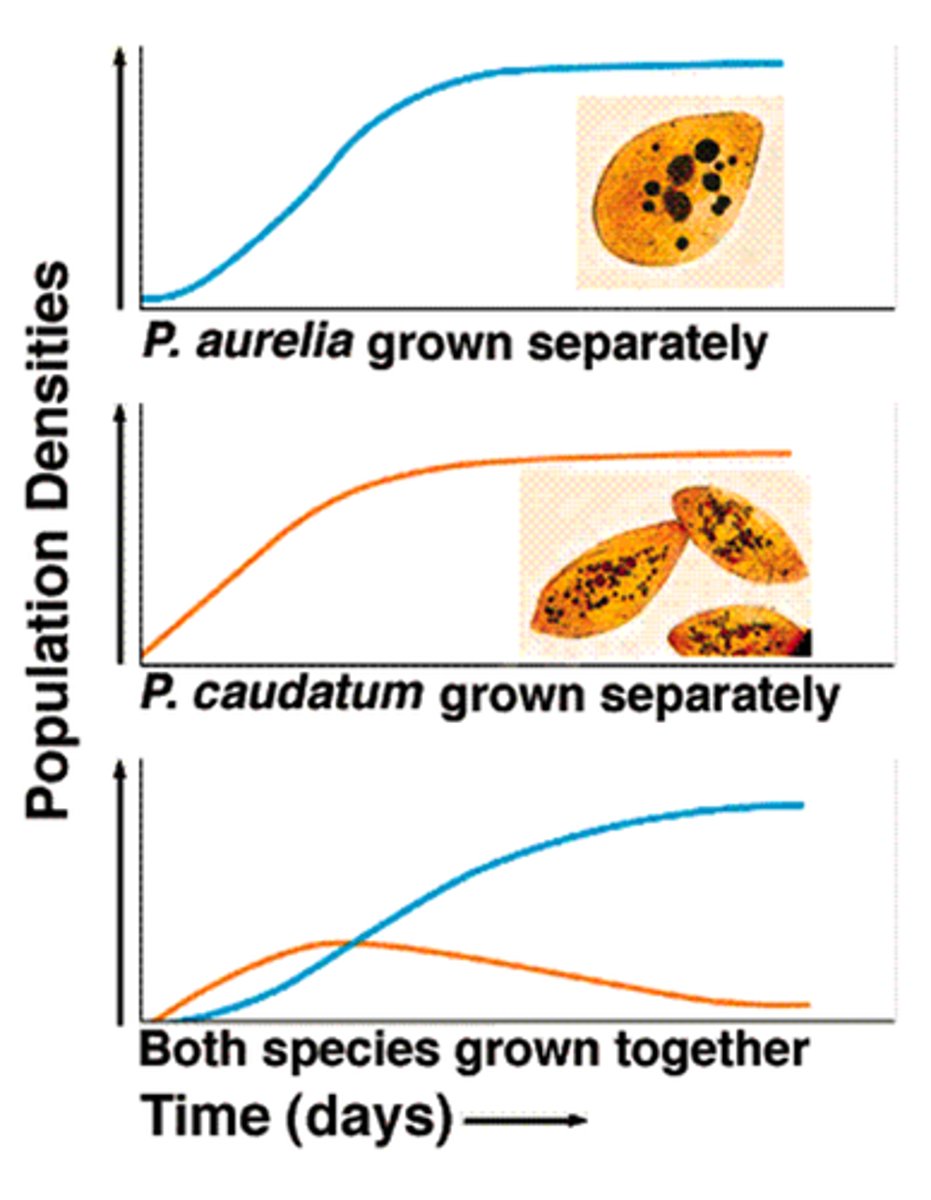
competitive exclusion principle
Ecological rule that states that no two species can occupy the same exact niche in the same habitat at the same time (Gause's experiment)
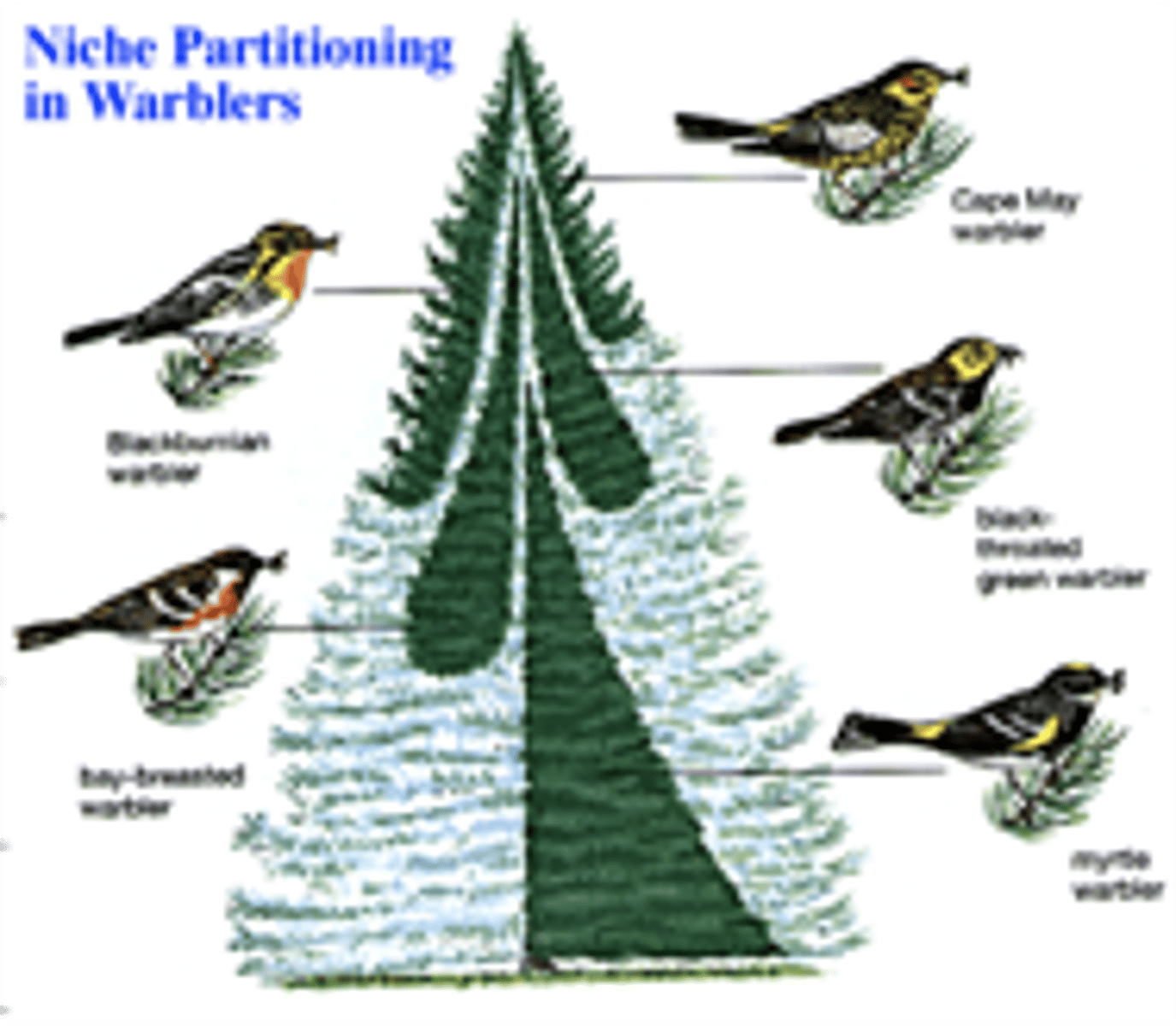
Niche partitioning -- temporal and spatial
the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist (temporal for detritivore invertebrates like bears and crows, spatial for warber birds)
What is an outcome of interspecific competition?
elimination of one of the competing species or the restriction of both to a part of their fundamental niche
What are the relative advantages of specificity and versatility?
- Encourage stability, reduce competitive exclusion, uphold symbiotic relationships, encourage biodiversity, help all members to have unique niches and thus contribute to the ecosystem different :)
For each form of nutrition, what are the unique inputs, processes and outputs?
Holozoic nutrition -- ingested, digested, absorbed, assimilated
Saprotrophy -- externally digested detritus, assimilated, given back to plants/soil
Detritivory -- internally ingested detritus, assimilated, excreted
Autotrophy -- input: sunlight/oxidation reactions, process: photosynthesis/oxidation reactions, output: carbon compounds
Mixotrophy -- input: sunlight/oxidation/heterotrophy, process: assimilated, ouput: carbon compounds
Obligate anaerobes -- input: minerals (eg iron sulfur) process: assimilation output: ?
Facultative anaerobes -- input: fermentation/respiration process: assimilation output: ?
Obligate aerobes -- respiration

What are the advantages of specialized modes of nutrition to living organisms?
Help obtain nutrients easier for energy transfer & nutrient cycling (eg stylets in aphids, sagittal crest in Homindae) helps limit competitive exclusion and interspecific competition by promoting biodiversity
How are the adaptations of a species related to its niche in an ecosystem?
-- include example of dentition and diet, adaptations of herbivores and plants to resist herbivory, the chemical, physical and behavioural adaptations of predator and prey, etc
Include an example of adaptations of herbivores for feeding on plants
Metabolic adaptations to digest plant toxins (monarch butterflies), piercing and chewing mouthparts of leaf-eating insects (eg modified stylets in aphids that use pectinase to digest pectin and access glucose in phloem, incisors in goats)
