AP HUMAN EXAM UNIT 1
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
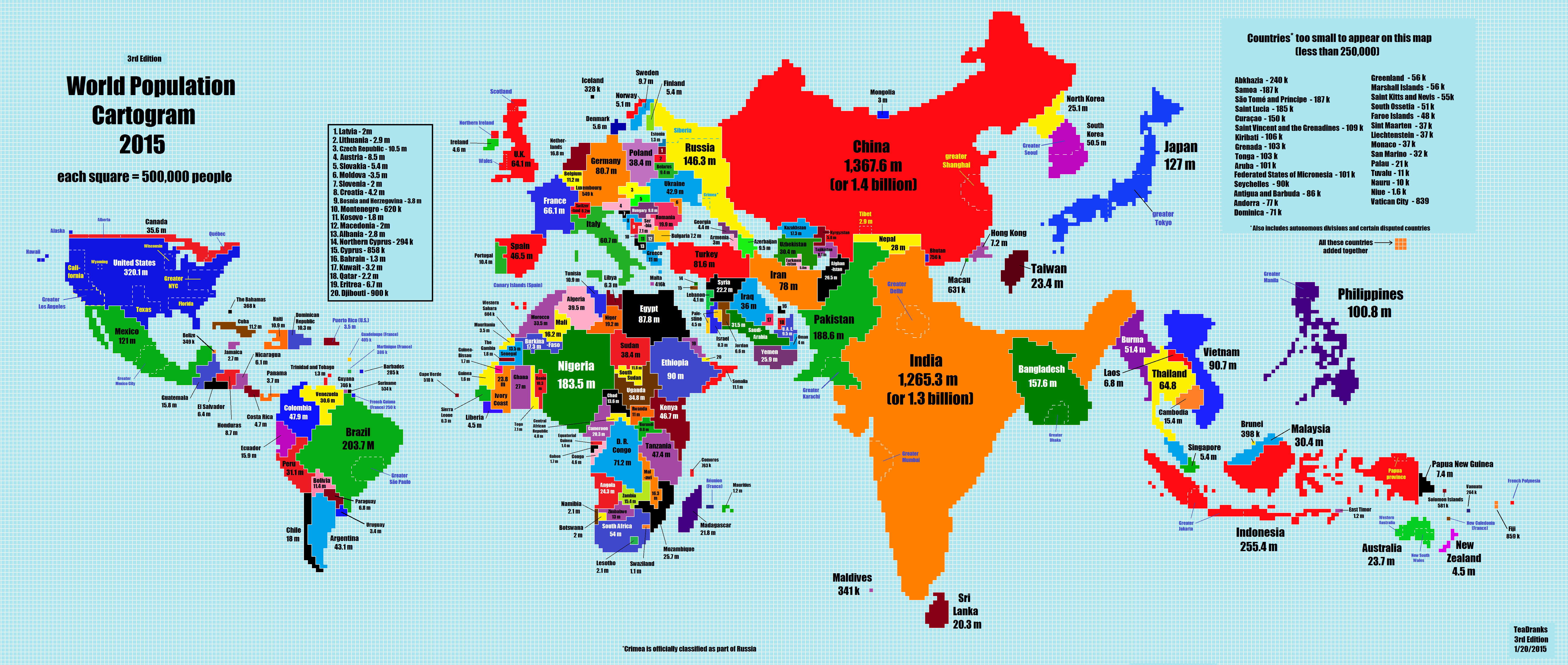
What type of map is this?
Cartogram
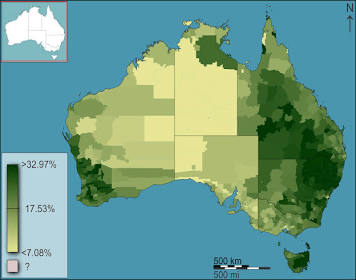
What type of map is this?
Chloropleth
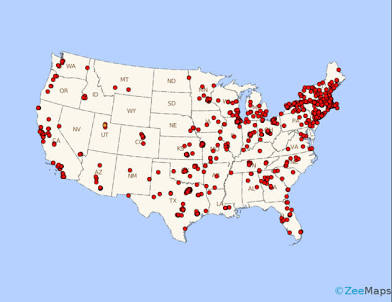
What type of map is this?
Dot density
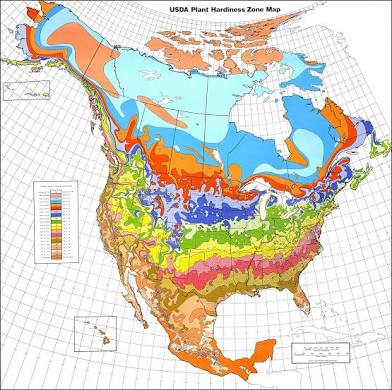
What type of map is this?
Isoline

What type of map is this?
Graduated (proportional) symbol
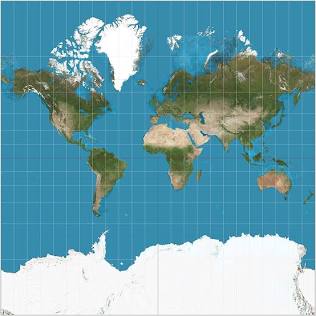
What are the pros and cons of a mercator map?
Shape and direction are accurate but the sizes are distorted, especially near the poles
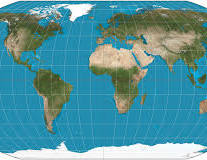
What are the pros and cons of a robinson map?
Everything is distorted, but distortion is spread evenly
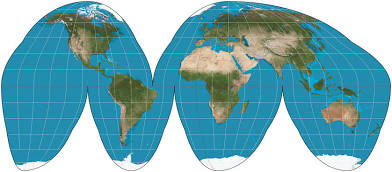
What are the pros and cons of a goode-homosline map?
Continent sizes are accurate, but directions and distance aren’t
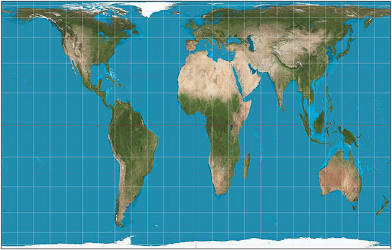
What are the pros and cons of a gall peters map?
The area is accurate, but it’s distorted, especially near the equator
Geospatial Data
All information including physical features and human activities
GIS
A system for capturing, storing, and displaying data
GPS
System that uses satellite data to pin point a specific location on earth
Remote Sensing
Process of taking pictures of earth from satellites
Absolute location
Precise spot where something is located
Relative Location
Location in compared to other things
Space
Extent of an area in either absolute or relative
Place
Specific human and physical characteristics of a location
Distance Decay
Interaction decreases as distance increases
Time-space Compression
Increasing connectivity between distant places
Pattern
Geometric or regular arrangement of something in an area
Sustainability
Taking enough resources for the current population while leaving enough for future generations
Natural Resources
Physical material from Earth people need and value
Environmental Determinism
Theory that the physical environment causes social development
Possibilism
Physical environment limits some human actions, but people can adjust to their environment
Scale
Relationship between distance on ground and the distance on map
Scale of Analysis
How zoomed in or out you are when looking at geographic data
Region
Place larger than a point and smaller than a planet grouped together because of a common feature
Formal Region
Based on quantitative data, includes all government areas
Functional Region
Based around a node or focal point such as radio broadcasts
Vernacular (perceptual) Region
A common qualitative characteristic, such as South or Midwest
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Township and Range
Clustered Settlement Pattern
Grid Street Pattern
Clustered Settlement Pattern (T&R is a type of grid)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Site
Situation
Relative Location
Site (site is an absolute location; situation is relative)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Absolute Location
Reference Map
Thematic Map
Thematic maps (reference maps use absolute location)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Globalization
Nationalism
Foreign Investment
Multinational Corporations
Nationalism (All other terms have to do with multiple countries)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Westernization
Uniform Consumption Preferences
Enhanced Communications
Local Traditions
Local Traditions (associated with folk culture; everything else is associated with popular culture)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Latitude and Longitude
Site
Situation
Absolute Location
Site (describes a physical place, everything else describes location)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Major airport
Grid street pattern
Major Central Park
Natural Harbor
Public Sports Facility
Natural harbor (it’s not part of the cultural landscape)
Pick the one that doesn’t belong:
Time Zones
China
US railroads
15 degrees
China (there’s only one timezone)
The “why of where” (refers to human-environment interaction)
Idea that explanation of a spatial pattern is crucial
Opposite of distance decay is…
Time-space compression
What map is drawn at the largest scale?
World map (global scale)
Name an example of how scale of inquiry affects the truth
Maps of crime rates in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and the US
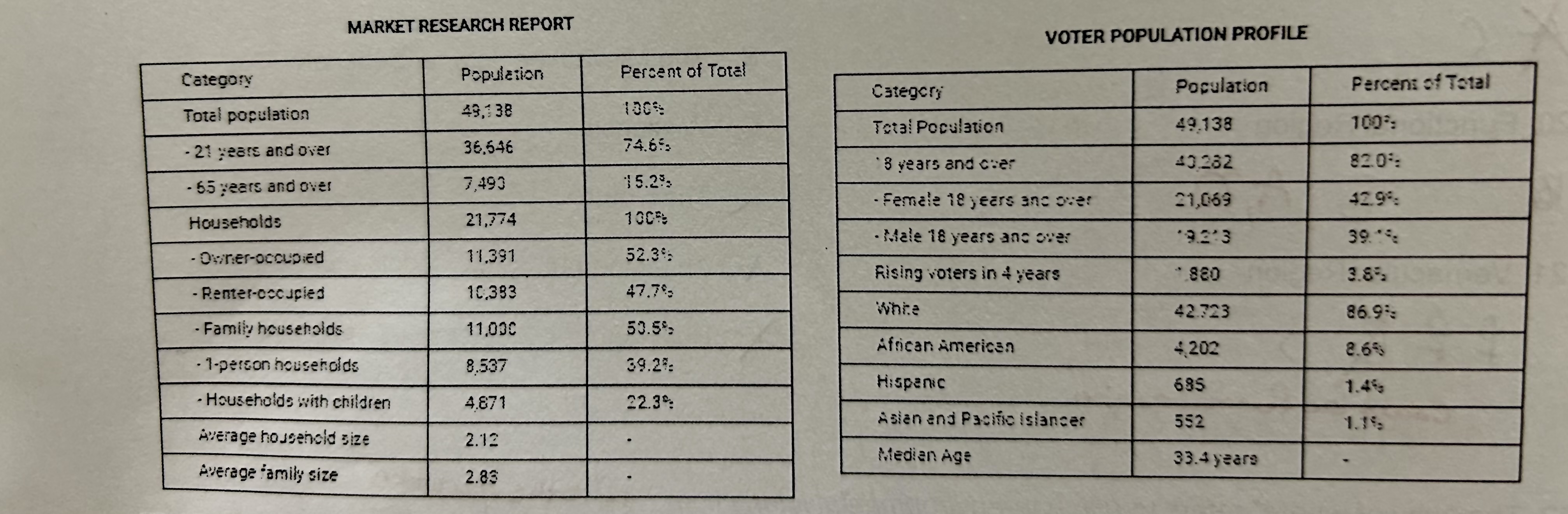
Where is this data from?
The Census Survey
Why are maps always distorted?
It’s impossible to represent the three dimensions of Earth on a two dimensional surface

How do you explain the changes in land acreage here?
The acreage increased through use of polders and dikes
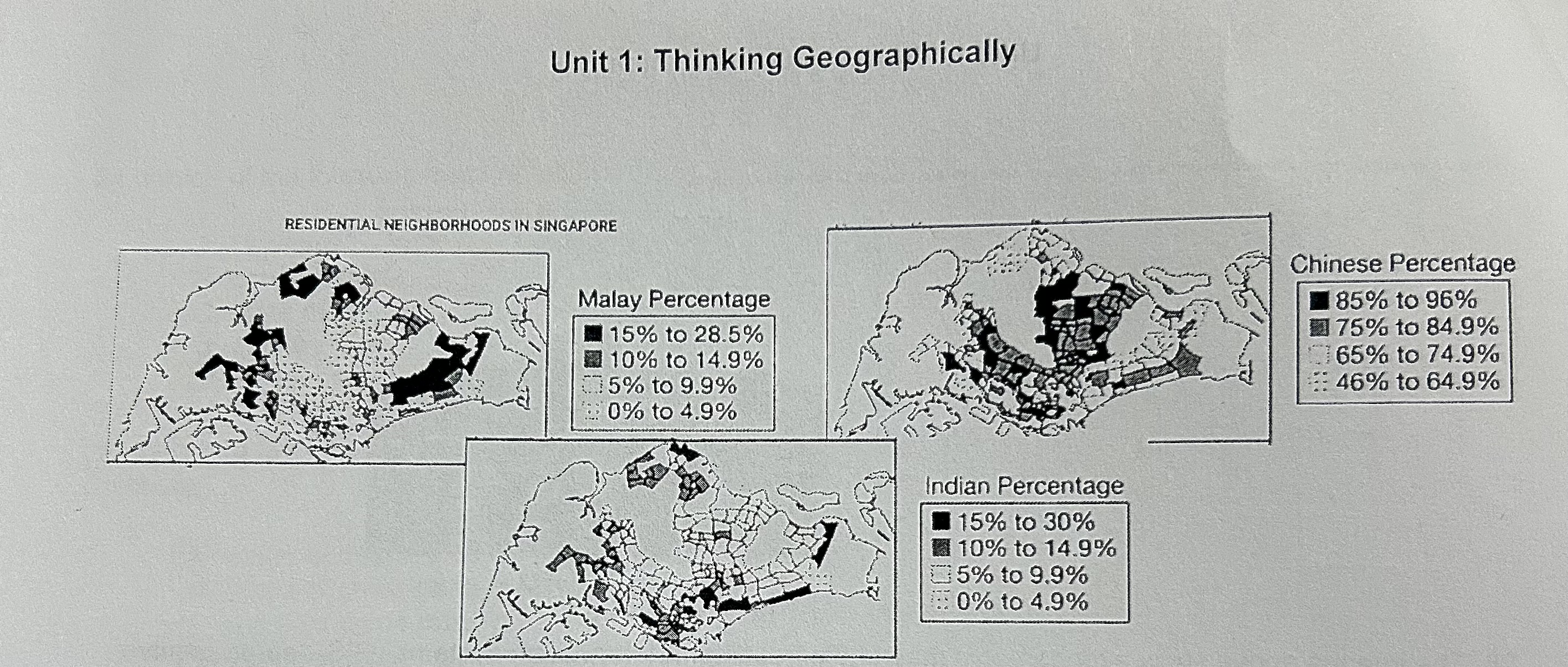
Describe the spatial pattern of ethnicity in this map
Ethnic Chinese are the majority across most the city; Ethnic Malay and Indian residents are concentrated in peripheral neighborhoods.
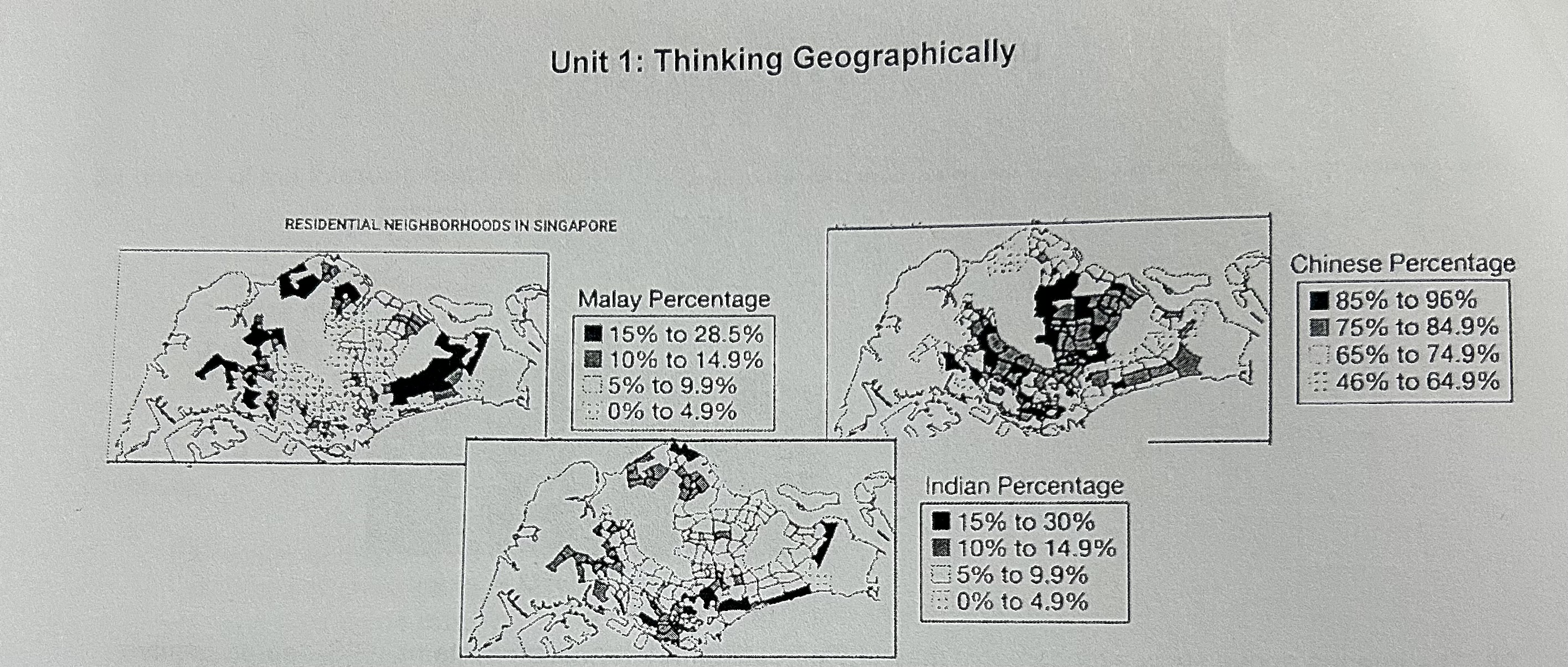
Who would use data from this map?
A government agency seeking to promote equal opportunities across ethnicities
An example of possiblism
Modification of landscapes by human cultures
Why would a planner use a map at 1:24,000 scale instead of 1:250,000?
A map at 1:24,000 scale shows the town closer and in more detail
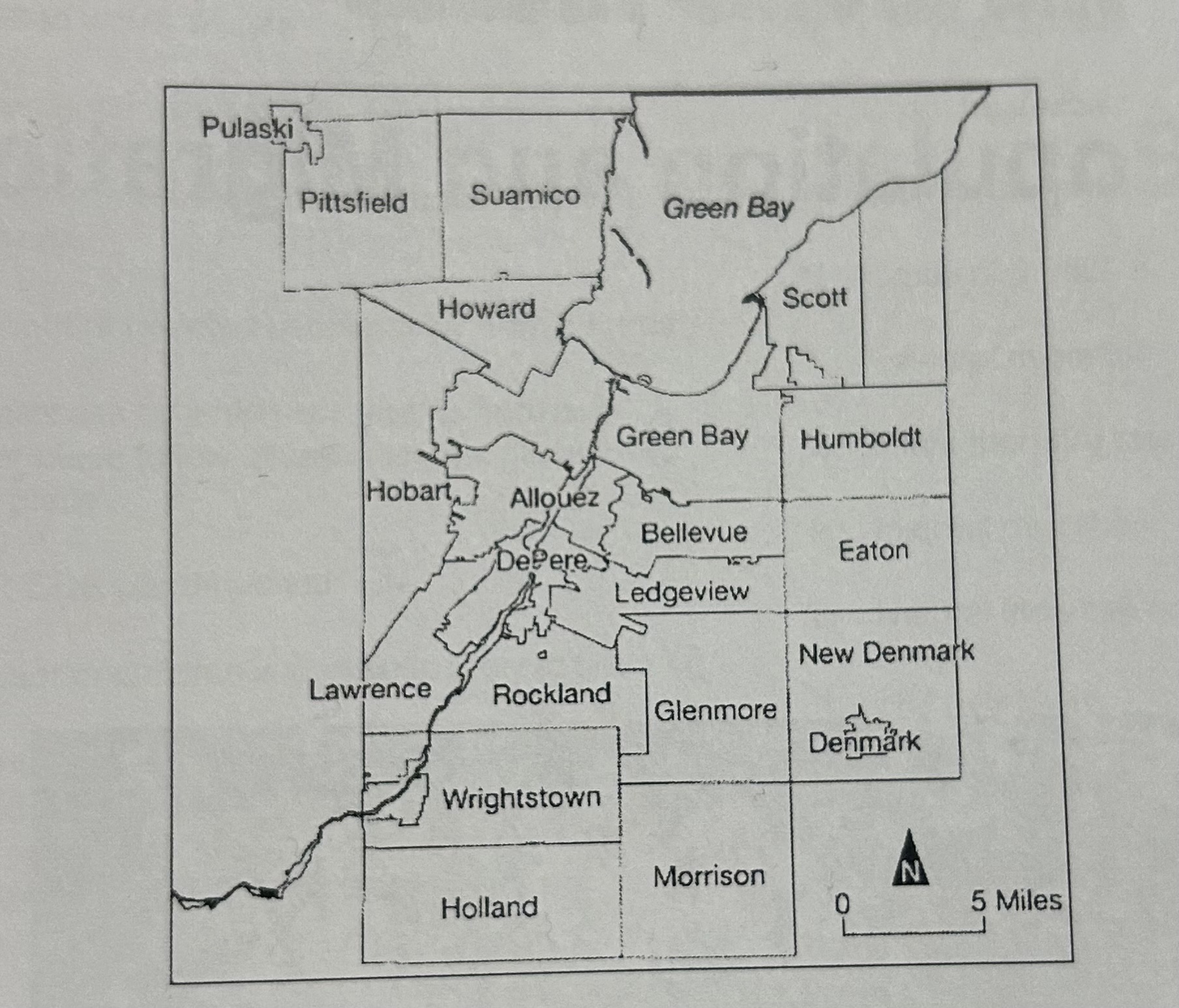
Identify the scale of this map
Local, showing the towns and townships in a county

Watersheds and milkshed are defined as what type of region?
Functional/Nodal