lecture 1, cardiovascular I
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
the cardiovascular system functions in
transport and exchange
what does the cardiovascular system transport and exchange of?
materials
nutrients
serve as building blocks/energy for the cells of the body
gases
oxygen needed for cell respiration (ATP production, oxygen needed for ETC)
hormones (endocrine system)
immune system components
antibodies, white blood cells (blood is a distribution medium, vasodilation and vasoconstriction)
platelets (fragments, blood clotting)
water
blood is mainly water H-bonds
hold polar things in solution
heat
blood temp. is higher than core because outside is always moving
waste produced by the cell
carbon dioxide produced from cell respiration
breakdown of sugar, fat, AA
CO2 + H2O = carbonic acid
heat (too much, too little, not good)
urea, creatinine (breakdown of creatinine in muscle), bilirubin (come from heme)
the cardiovascular system is composed of
blood
heart
blood vessels
blood
transport medium
load things in → nutrients or waste
heart
produces force to move blood through the circuit
centralized pump to pressurize blood
blood vessels
arteries (very strong to withstand high pressure), arterioles (branched off arteries), capillaries, venules veins
complete the closed circuit → lungs and heart
pulmonary circuit → lungs and heart
systemic circuit → delivery to tissues around the body (left side is more muscle because has to send blood everywhere)
artery away, vein in
friction gets more and more because of SA of all the arterioles
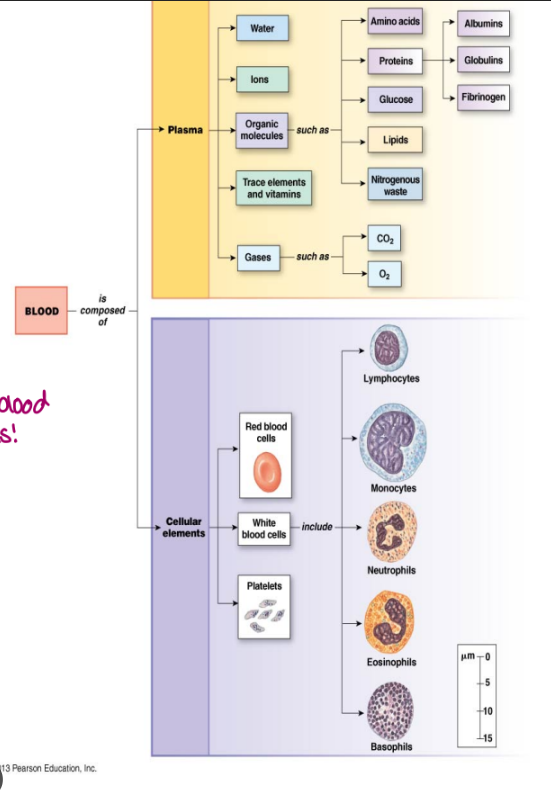
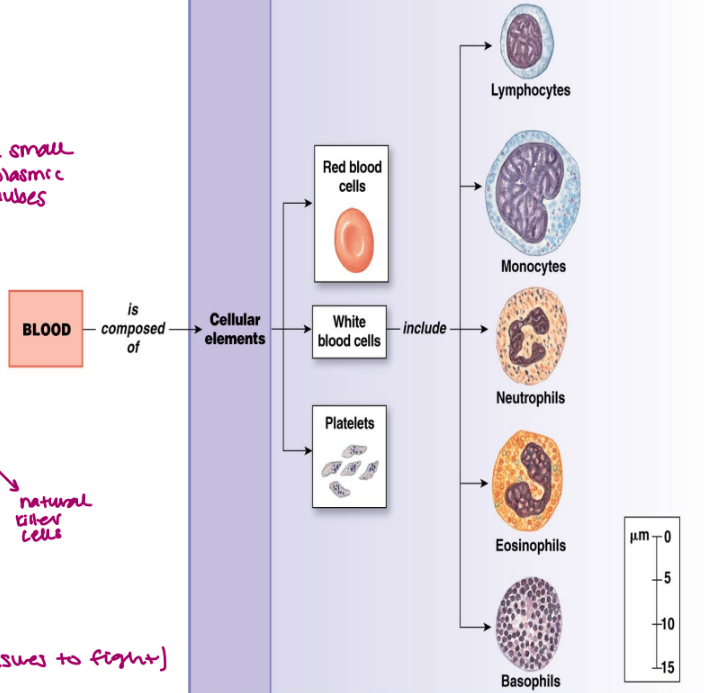
blood consists of
plasma: solutes, water
formed elements
erythrocytes cells
leukocytes cells
platelets
plasma
main component is water (<90%)
dissolved components include:
proteins (7%)
albumins (protein that pH buffer), globulins (antibodies), fibrinogen (starting materials), hormones (use blood as transport medium) → make blood viscous
electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium)
nutrients (amino acids, glucose, lipids)
gases (O2, CO2) binds to hemoglobin to transport, can’t do straight in blood do to polarity)
metabolic wastes (nitrogenous waste-urea, creatine) plasma components
“-ogen”
inactive something
formed elements
erythrocytes (RBC)
leukocytes (WBC)
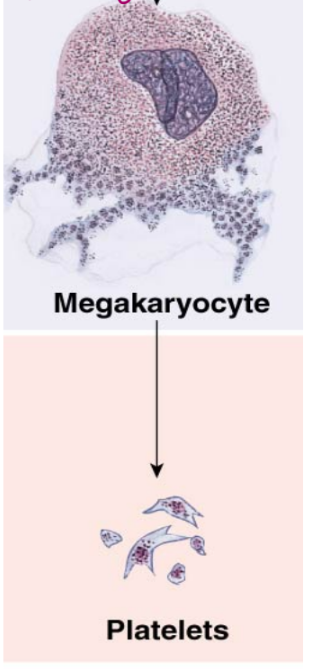
platelets (not a cell! megakaryocyte fragments, have granules)
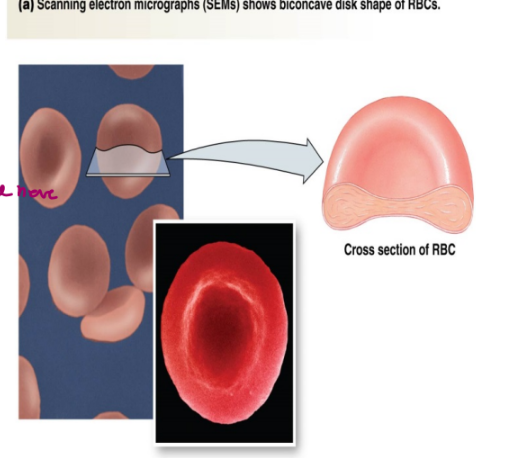
erythrocytes
5 million per microliter of blood (4-6)
live 120 days (turned over by spleen)
reproduced in bone marrow (stem cells located here)
anuclear upon maturity
do not have organelles
specialized for O2 transport
responsible for a small quantity of CO2 transport
no MHC1 so we cab do blood transfusions
erythrocytes (continued)
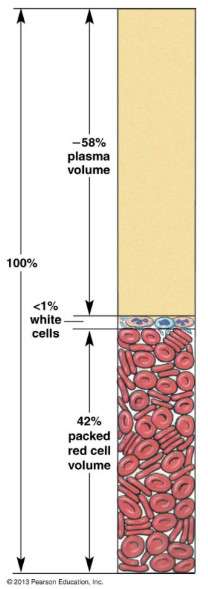
hematocrit (Hct)
ratio of red blood cells to plasma
expressed as a percentage
37-47% red blood cells in women and 40-54% red blood cells in mean (higher in males)
increased red blood cell production in response to erythropoietin → allows to make more RBC
produced from the kidney in response to low blood oxygen
kidney senses state of affair
kidney is endocrine tissue
cab turn up RBC
leukocytes
important immune system components
escape from blood into tissues
granulocytes and agranulocytes (very small cytoplasmic granules)
not always well balanced
long lived
infection fighting - police department
WBC
granulocytes (mast cells)
basophils
eosinophils
neutrophils
agranulocytes
monocytes (macrophages)
lymphocytes
t cells
b cells
natural killer cells
originate in blood but can transport anywhere
platelets
megakaryocytes are fragmented to produce platelets (have granules on inside of structure and can de-granulate)
live ∼10 days (really short live because not a cell)
primary function is to prevent blood loss in damage blood vessels (trying to maintain pressure)
hemostasis (HEMA-blood, STASIS-static/constant)
blood vessels vasoconstrict to slow pressure into affected area (increase resistance, decrease flow)
platelets bind to exposed collagen of damaged vessels
activated platelets release cytokines (they are sticky)
activate more platelets
positive feed back (dangerous because activate more and more platelets which causes blood clots, need localized activation, trigger a damage blood vessel)
FLOW