Apsc Final
1/348
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
349 Terms
What is a breeding soundness exam (BSE)
a medical and reproductive assesment that evaluates a mares suitability for breeding
What are the purposes for a bse
find potential reproductive issues
assess fertility
optimize breeding efficiency
determine suitability for natural breeding, AI, or embryo transfer
minimize economic losses
What is the importance of a breeding soundness exam
ensures stallions and mares are capable of reproduction
identifies fertility issues early
enhances efficiency
evaluates reproductive anatomy and quality
crucial for breeding prgrams (preformance horse and genetic selection)
What is inculded in a breeding soundness exam
comprehensive history- estrous cycle, breeding history, pregnancy and foaling history, vaccine history, and more
physical examination
externam vulvar examination
rectal palpation
rectal ultrasound
vaginal speculum
uterine cytology
What does the vulva do
it is an external part that prevents foreign material entering
What does the rectal ultrasound help you see
allows the vet to see issues not spotted by hand, it can also determine the stage of a mares heat.
What is the point of a uterine cytology
used to asses the health of a mares uterus, by examining sample cells from the endometrium
it detects infectious diseases, inflammation, and other abnormalities
true or false if a mares results from a uterine cytology show inflammation her chances of [regnancy are lower.
true
What are some forms of restraints used for a breeding soundness exam
halter and lead rope
twitch
stocks
holding up a leg
chemical restraint
stall wall/doorway
What is a anaglesic
used to reduce pain ( painkiller)
what is a sedative
a drug, that slows down or depresses the central nervous system, resulting in a calming or drowsy effect.
What is an antispasmodic
An antispasmodic is a medication that relieves or prevents muscle spasms, particularly in smooth muscles like those in the digestive tract or urinary bladder. They work by relaxing these muscles, thus reducing spasms and related pain or discomfort.
What is an endometrial biopsy
An endometrial biopsy is a test performed that takes a sample of
the endometrium (the vagina's inner lining) and is examined under
a microscope in search of abnormal cells, cancer, or other
diseases.
What is the purpose of preforming an endometrial biopsy
to determine fertility
How is an endometrial biopsy preformed
clean perinium with povidone-iodine scrub
place a sterile covering on arm
insert arm with instrument into vulva, through vagina and cervix
then clamp a piece of uterus
remove arm
place tissue into bouins fixative to preserve
a uterine biopsy is graded based off of what
inflammation frequency, type, and degree
glandular nesting and periglandular fibrosis
describe the grading
Grade I: normal endometrium/mild focal inflammation or fibrosis
~80% chance of successful pregnancy
• Grade IIa: mild/moderate endometrial inflammation and/or multifocal periglandular
fibrosis
§ ~50 - 80% chance of successful pregnancy
§ 1-3 fibroblast layers
§ Average of 2+ fibrotic glandular nests per 5 mm
• Grade IIb: multifocal moderate endometrial inflammation and/or multifocal fibrosis
§ ~10 - 50% chance of successful pregnancy
§ 4+ fibroblast layers
§ Average of 2-4 fibrotic glandular nests per 5 mm
• Grade III: severe inflammation and/or diffuse fibrosis
§ <10% chance of successful pregnancy
§ Average of 5+ fibrotic glandular nests per 5 mm
describe a vaginal exam
clean perineum
separate the lips and insert speculum
shine light and examine vagina and cervix
remove speculum
then ensure vestibulovaginal fols obstruct the vagina
What is the vestibulovaginal fold
boundary between vestibule and vagina
in relation to the cervix more estrogen equals____ and more progesterone equals ____
more estrogen = looser cervix
more progesterone = tighter cervix
What are some reproductive issues found in bse
endometritis- inflammation of the uterine lining (endometrium)
Fibrosis- scarring and thickening of the uterine lining
uterine cyst
What are the causes of endometritis, fibrosis, and uterine cyst
endometritis- bacterial infections
fibrosis- chronic endometritis, previous infections, trauma, aging
uterine cyst- lymphatic blockages, scarring, and chronic uterine inflammation
what is one of the most common causes of infetility in mares
endometritis
What are some advancements in equine reproductive exams
Artificial Insemination (AI): Improved
semen preservation and transport
• Embryo Transfer (ET): Allows high-value
mares to produce multiple foals
• Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):
Fertilization enhancement for subfertile
stallions
• Genetic Testing & Hormonal Analysis:
Predicts fertility potential
• Advanced Imaging (Ultrasound &
Endoscopy): Detailed reproductive tract
assessments
STALLION BSE
What is a stallion
adult uncatrated male horse
Why do stallions get breeding soundness exams
to check the fertility
identify reproductive issues
see mating behaviors
semen quality
repro organs
and overall health
true or false a satifcactory breeder impregnates at least 85% of mares- 30-40 by live cover or 100-120 by AI
false,
A satisfactory breeder: impregnates at least 75% of mares ~
30 out of 40 by live cover or 90 out of 120 by artificial
insemination
When are good times for a stallion to get a bse
pre-purchase/recent purchase
pre breeding season (60-75 days prior)
when suspecting fertility issues
when considering a young stallion for breeding
BSE might be used to
estimate reproductive potential
provide routine evaluation prior to purchase
determine causes of poor reproductive preformance
What are te steps for preforming a bse
identifying stallion (age, breed, registered name, more)
health and breeding history (vaccines, number of mares bred)
venereal disease testing
general physical exam
external reproductive exam
internal reproductive exam
semen evaluation
What are some venereal diseases (Std)
Equine Viral Arteritis (EVA)
- Contagious Equine Metritis (CEM)
- Equine Herpesvirus (EHV)
- Equine Infectious Anemia (EIA)
- Dourine
What is included in a external exam of reproductive organs
● Evaluation conducted when penis is dropped
● Checks normal size, shape, or defects
Testes and epididymis
● evaluated after semen collection (more calm)
● Testes are palpated to see size, shape, symmetry, position,
smoothness, etc
true or false internal repro exam are typically done after semen collection
yes because they calmer
What is included in a internal reproductive exam
includes assessing the stallion’s reproductive health by
palpating and examining their internal genitalia, including the
inguinal rings and accessory sex glands.
true or false accessory glands are always easier to palpate after ejaculation
flase, the accessory sex glands may be more palpable
before ejaculation, so some practitioners may opt to palpate
before collection.
What is evaluated in semen collection
semen charcteristics, quality, ph, volume, concentration, motility, morphology, and daily output.
how is semen collected
with aid of a mare in heat
artificial vagina
semen collection allows for the assesment of what else
libido
Equine Dentistry
true or false dental disease is almost entirely preventable in every species
true
What are decidous teeth
baby teeth
true or false modified diet and eating patterns have resulted in some dental issues (domestication and confinement)
true
what are some importance of dental care
horse get old (teeth do not stop growing)
healthier horses live longer
utilize feed more efficiently
younger horses are being used in preformance more often and are asked to preform at higher levels
modified diet and eating patterns have caused dentaal issues
breding horse not chosen for dental issues
are younger horses being used in preformance and asked to preform at higher levels
yes
What does the amount of dental care a hors recieve depend on
age: younger and older horses require to be seen more (2-3 time a year)
lifestyle- ex. if a horse is on a grain diet. preformance horses generally require more dental care)
genetics- some have better teeth than others
mechanical changes- trauma or disease
What are other reasons dental care is important
dental and oral health
catching abnormalities/promblems early
ensures optimal nutrition (starts with mastication)
comfortability
enhance preformance
true or false a horses lips sort out and gather feed
true
describe a horse chewing
they chew in a circular motion using their cheeck teeth/molars with rough occlusal surface to grind.
true or false the upper and lower jaw are the same width
false they are different widths
What is anisognathism
a horse's lower jaw is set more narrow than their upper jaw. This uneven alignment is referred to as Anisognathism.
what is the maxilla
the upper jaw
maxillary teeth are slightly wider t or f
t
how much wider is the maxilla in comparison to the mandible
30%
the occlusal surface of the upper and lower cheek teeth has an inclination of__ to __ degrees
10-15
What are 8 clinical signs of dental issues
dropping feed
difficulty chewing
weight loss
excessive salvation
bad breath
resisting the bit
head tossing
adverse effects of bad teeth/confromation (weight loss, colic, interfere with preformance, painfulness)
What is dental flotation
the process of filing down a horses teeth (filing down sharp points)
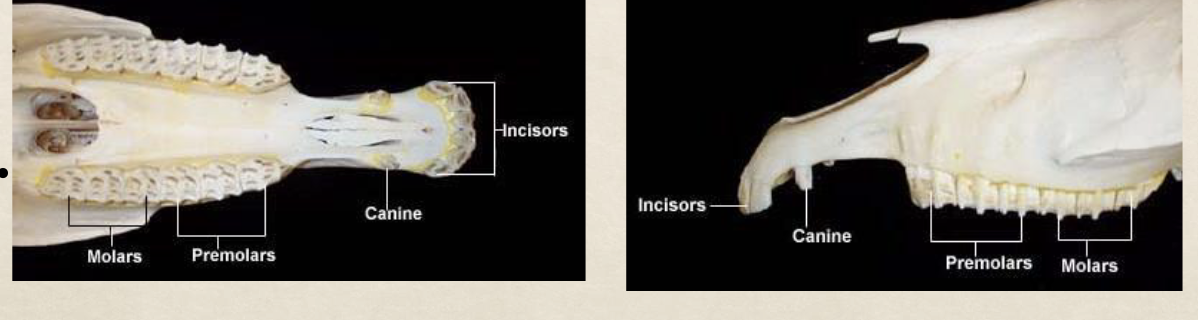
What are incisors used for
grasp and cut food, and grooming
How many incisors do horses have
6 on top 6 on bottom
true or false horse incisors errupt as decidous then become permanent
true
what are canines used for
fighting
what are premolars and molars used for
grinding
describe the position/confromation of the premolars and molars
tightly wedged with a wide surface
true or false wolf teeth are classfied as premolars, but are vestigal
true
What is the function of wolf teeth
no function
wolf teeth are similar to..
wisdom teeth
What issues can wolf teeth impose
they can interfere with the bit
What are the deciduous teeth and their erruption time

true or false a foal is normally born with atleast one errupted tooth
false usually born with no errupted teeth
1rst deciduous incisors and
PM erupt within first week of
age.
yes
if a horse has no teeth you can assume
it is less than a week old
how many deciduous does a young horse have
24: 12 incisors and 12 premolars
when do permenant teeth begin to errupt
2.5 years of age
When do permanent teeth begin to errupt
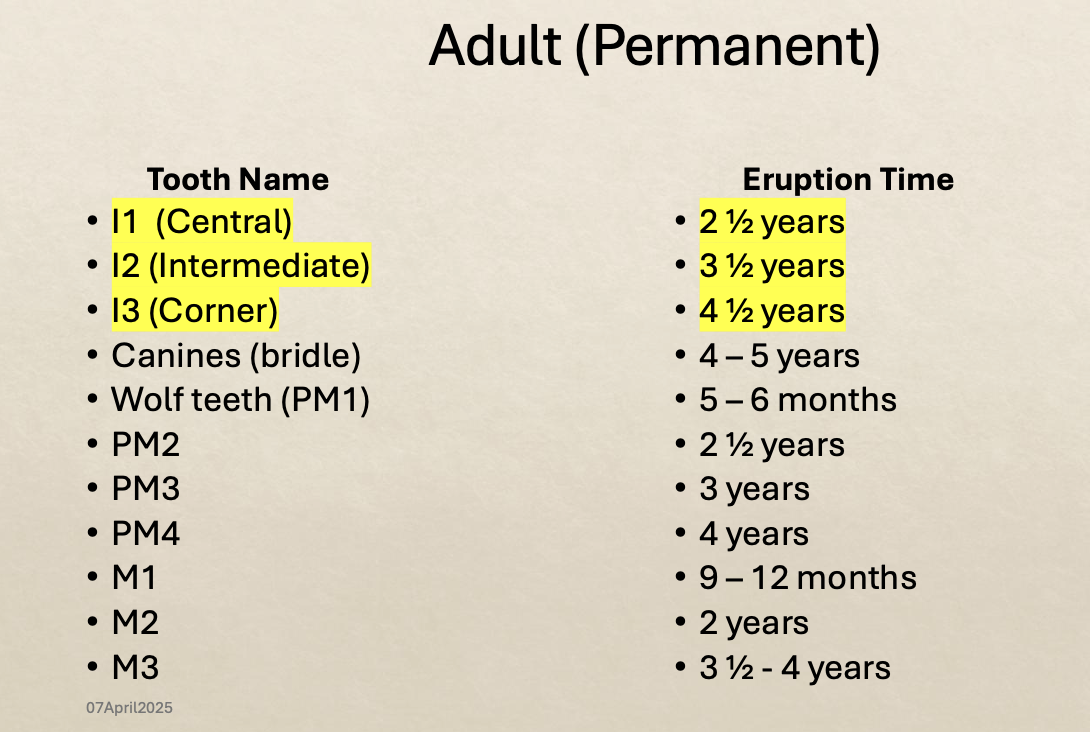
Which teeth ar which
Why are horses jaws deep
to accommodate long teeth
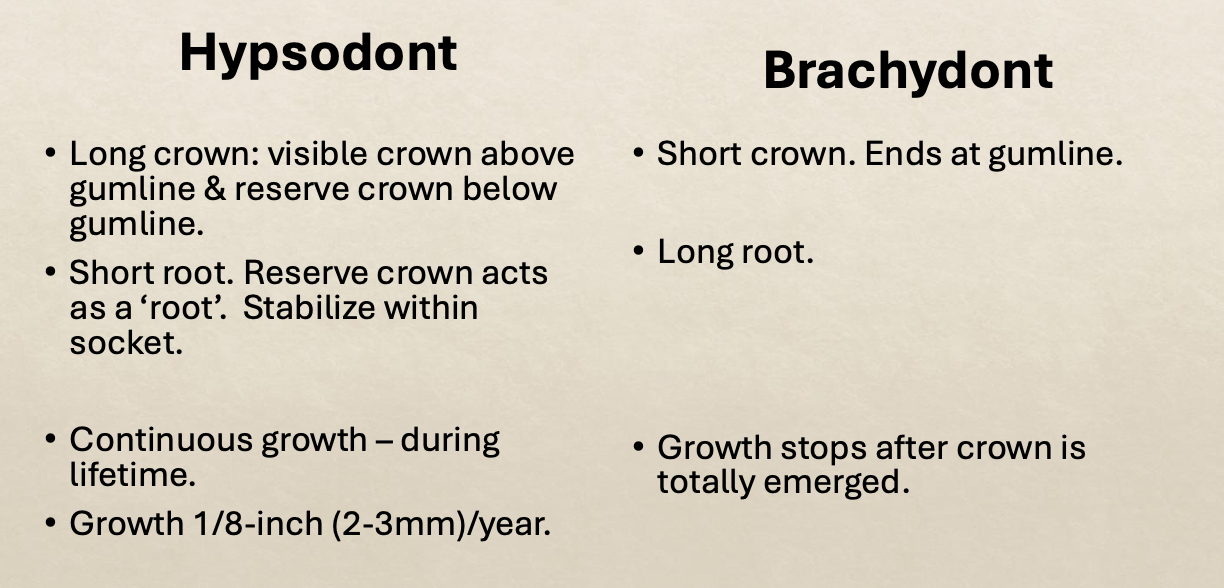
What is hypsodont and its importance
dentition pattern characterized by teeth with high crowns.
• Allows for more wear and tear
how fast is tooth eruption for horses
slow 2-3 mm per year to componsate for wear
how many teeth do horses have
males have 40-42 permanent teeth
females have 36-40 teeth
what is the difference between male and femal horse dental confromation
males have canine teeth
what does it mean to have hypsodont teeth
are high crowned and keep growing
true or false cheek teeth continually erupt
true
can horses grow new teeth
no
what is the normal pace for teeth growth
hypsodont have 3 primary tissues + rough oclussal surface what are they
enamel
detin
cementum
pulp
describe enamel, detin, cemntum, and pulp
1. Enamel: hardest tissue in the body. Grinding fibrous feeds.
2. Dentin: Softer calcified tissue. Wears faster >> enamel. Acts as
a cushion for brittle enamel.
3. Cementum: Similar to dentin, being softer than enamel.
Cushions enamel. Helps anchor tooth to the periodontal ligament.
4. Pulp: Nerve and blood supply
Describe the difference between the human and horse molar (crown, root, growth)
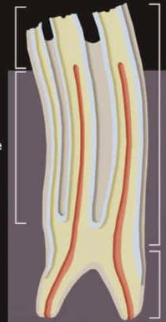
list the parts of the tooth
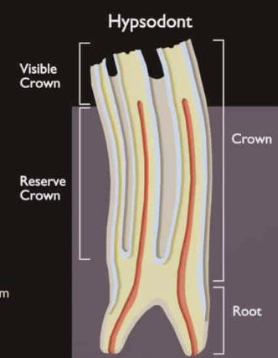
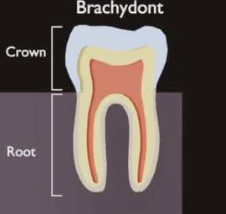
list the parts of the tooth
What is a dental infundibulum
The infundibulum of a tooth, also known as a dental cup, is a funnel-shaped invagination or cavity found in the enamel of the tooth's crown. It is lined with enamel and filled with cementum, a specialized tissue that covers the tooth's roots.
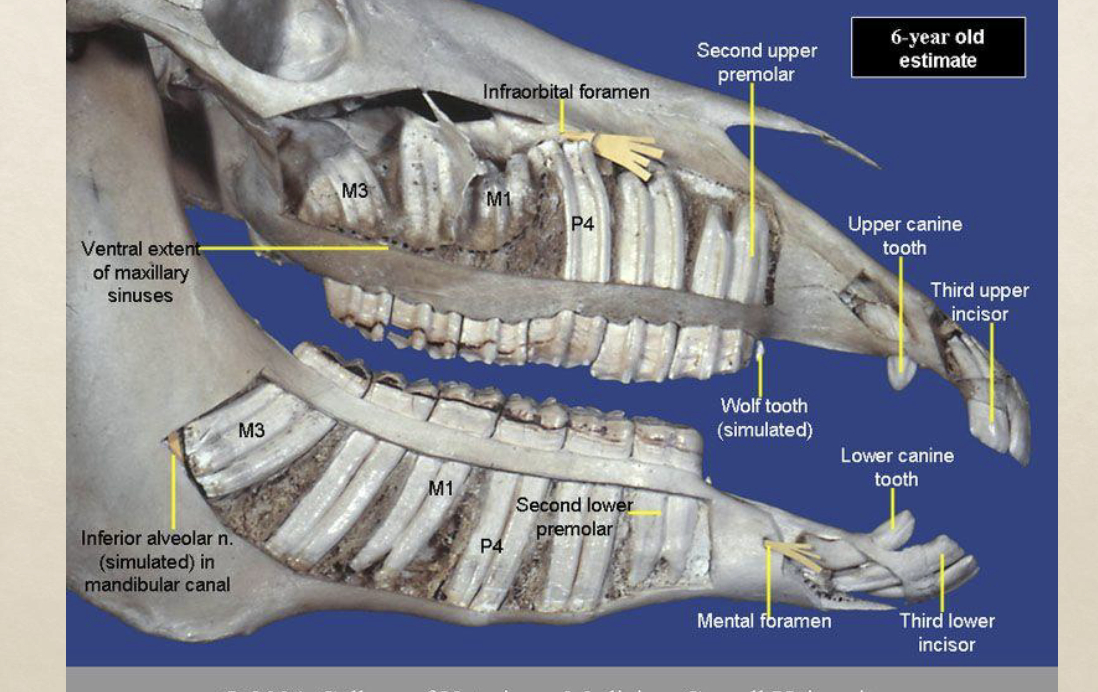
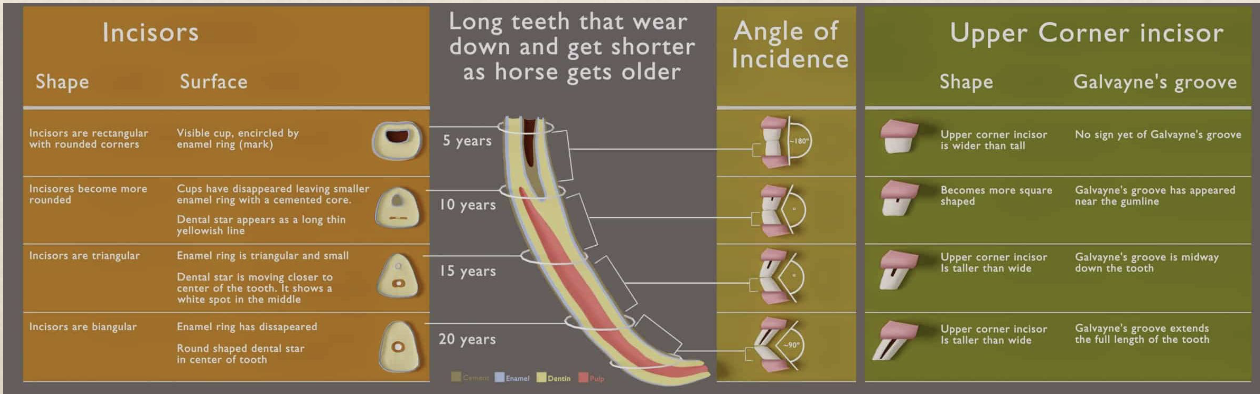
aging horses is based on what
disappearance of cups
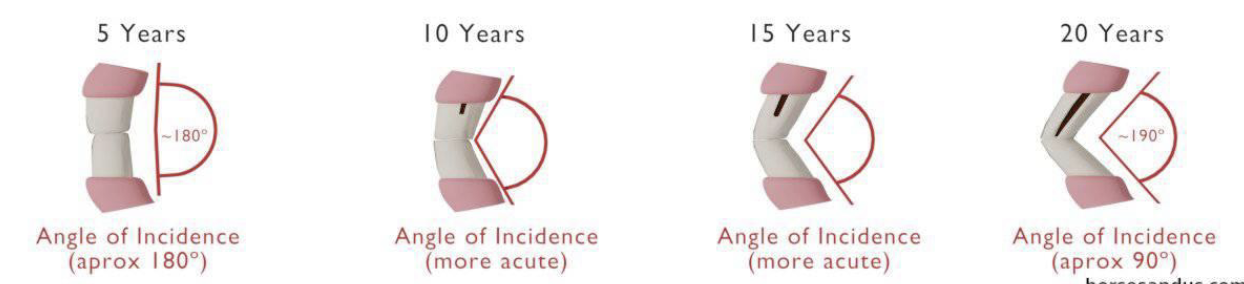
angle of incidence (angle formed by the meeting of lower and upper incisor teeth ( young: 160-180 adult: angle will slant forward and outward)
tooth surface (young: broad and flat adult: surface becomes oval 8-12 years old triangle >15
estimation
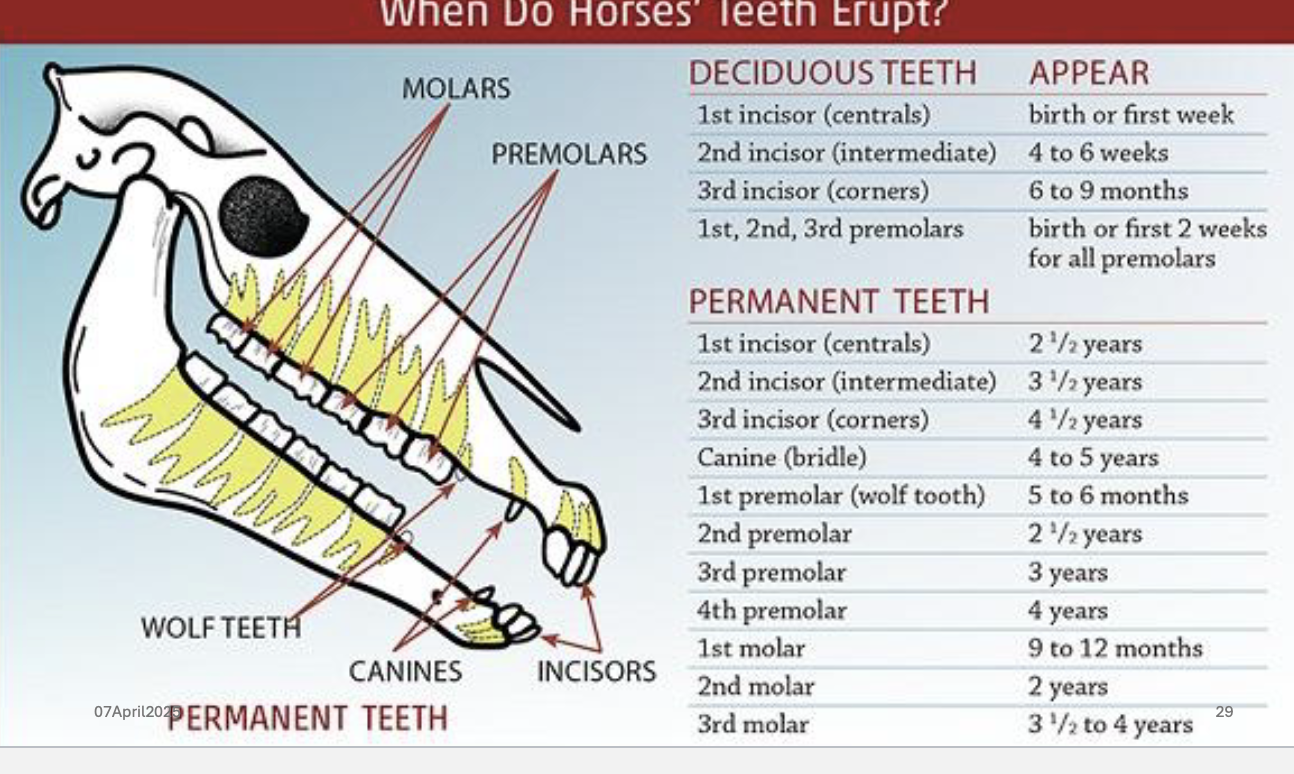
for deciduous teeth
central incisors erupt by___
intermediate incisors erupt by ___
corner incisors erupt by ___
Newborns: born without
teeth [or with 4 central
incisors (2 top, 2 bottom)].
• Central incisors erupt by 8
days.
• Intermediate incisors by 8
weeks.
• Corner incisors by 8
months.
• ~ 8 days, 8 weeks, 8 months
What is the difference between deciduous and permanent teeth
The deciduous teeth can be distinguished from permanent teeth because they are wider than they are tall and they have shallow roots.
while permanent teeth are taller than they are wide with long roots
What is the eruption time for central, intermediate, and corner incisors
I-/central incisors 2.5 years
I-2 intermediate incisors erupt at 3.5 years
I-3/corner incisors 4.5 years
• In wear
• Shape of the tooth
• Surface: Presence or absence of Cups, stars and spots on the
occlusal surface of the tooth.
• Cups: Center of the infundibulum. Gets smaller and disappears ~
8 years-old.
• Enamel spot: what’s left of the center of the cup.
• Angle of incidence
how do you determine a horses age by its teeth
incisor eruption
angle of incidence
the disappearance of cups with age ( The central incisors' cups disappear at 6 years, the intermediates at 7, and the corners at 8 on the bottom jaw)
grinding surface shape (young rectangle, old oval and triangle)
The dental star, a yellowish spot on the grinding surface, appears after the cup disappears.
Dental stars appear in the central incisors at 8 years, intermediates at 9, and corners at 10.
Galvayne's Groove:
A groove on the lateral surface of the upper corner incisor, starting to appear at about 10 years of age.
It extends halfway down the tooth by 15 years and reaches the full length by 20 years.