Bio 225 Exam 1 - Epithelial Cells and Basic Biochemistry - Lloyd
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Epithelial Cells and Basic Biochemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Epithelial cells are important for
controlling transport
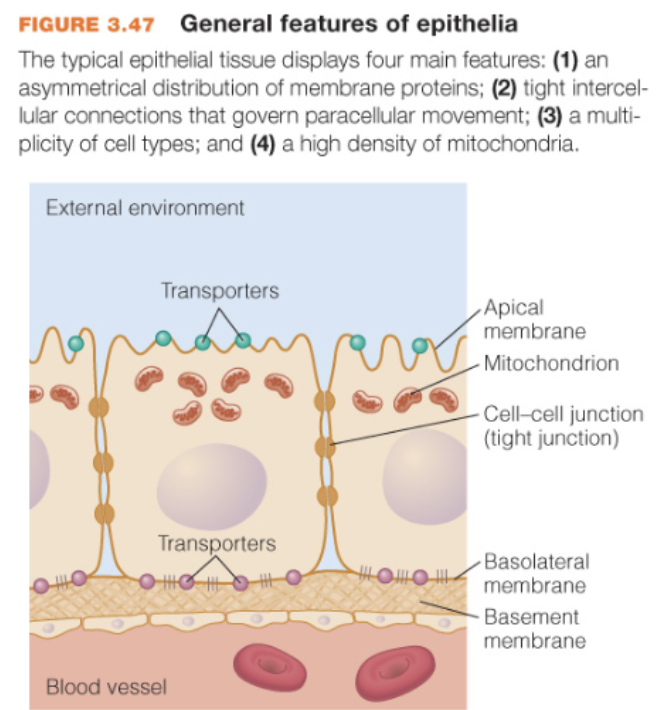
Epithelial cells general features
1) have asymmetrically distributed transporters (apical side and basolateral side)
2) are interconnected by protein linkages (tight junctions, leaky junctions, leaky tight junctions)
3) high lvl of cell type diversity — even w/in same tissue
4) abundant mitochondria
How are epithelium classified? (main classifications)
simple epithelium and stratified epithelium
simple epithelium
single layer of cells, indirect contact w/ basement membrane
stratified epithelium
multilayered, usually found where body linings are under mechanical pressure.
cells generally flatten as they are farther away from the basement membrane (more apical)
Classification of stratified epithelium
keratinized, parakeratinzed, transitional
keratinized stratified epithelium
mostly dead, lack nuclei and cytoplasm, contain tough resistant protein called keratin — found mostly in outer layers of skin
parakeratinized stratified epithelium
contains keratin, retain nuclei but it is reduced (pyknotic) — found in the esophagus and oral mucosa
transitional stratified epithelium
stretchy , appears to be stratified cuboidal — mostly in bladder, ureters, and urethra
All classifications of epithelium?
simple squamous epithelium, simple cuboidal epithelium, simple columnar epithelium, pseudostratified columnar epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, stratified cuboidal epithelium, stratified columnar epithelium, transitional epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium location and function
air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
allows materials to pass thru by diffusion and filtration and secretes lubricating substance

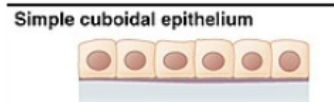
Simple cuboidal epithelium
in ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules
secretes and absorbs
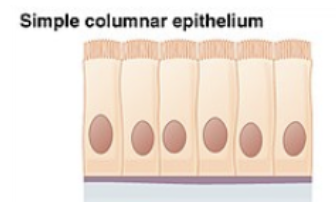
simple columnar epithelium
ciliated tissues are in bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus; smooth (nonciliated tissues) are in the digestive tract, bladder
absorbs; also secretes mucous and enzymes
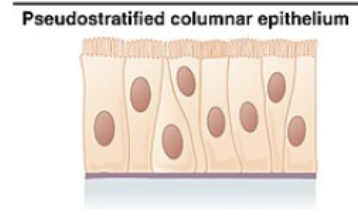
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
ciliated tissue lines trachea and much of upper respiratory tract
secretes mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus
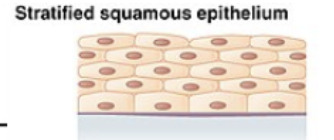
Stratfied squamous epithelium
lines esophagus, mouth, and vagina
protects against abrasion
stratified cuboidal epithelium
sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands
protective tissue
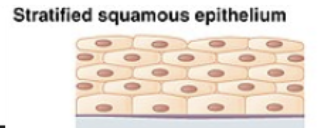
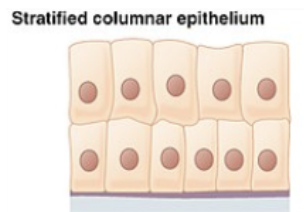
stratifed columnar epithelium
male urethra and the ducts of some glands
secrets and protects
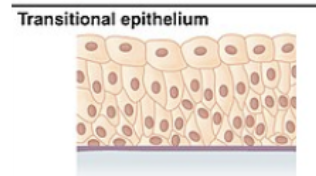
Transitional epithelium
lines bladder, urethra, and ureters
allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch
Transit around or thru cells
transcellular transport and paracellular transport
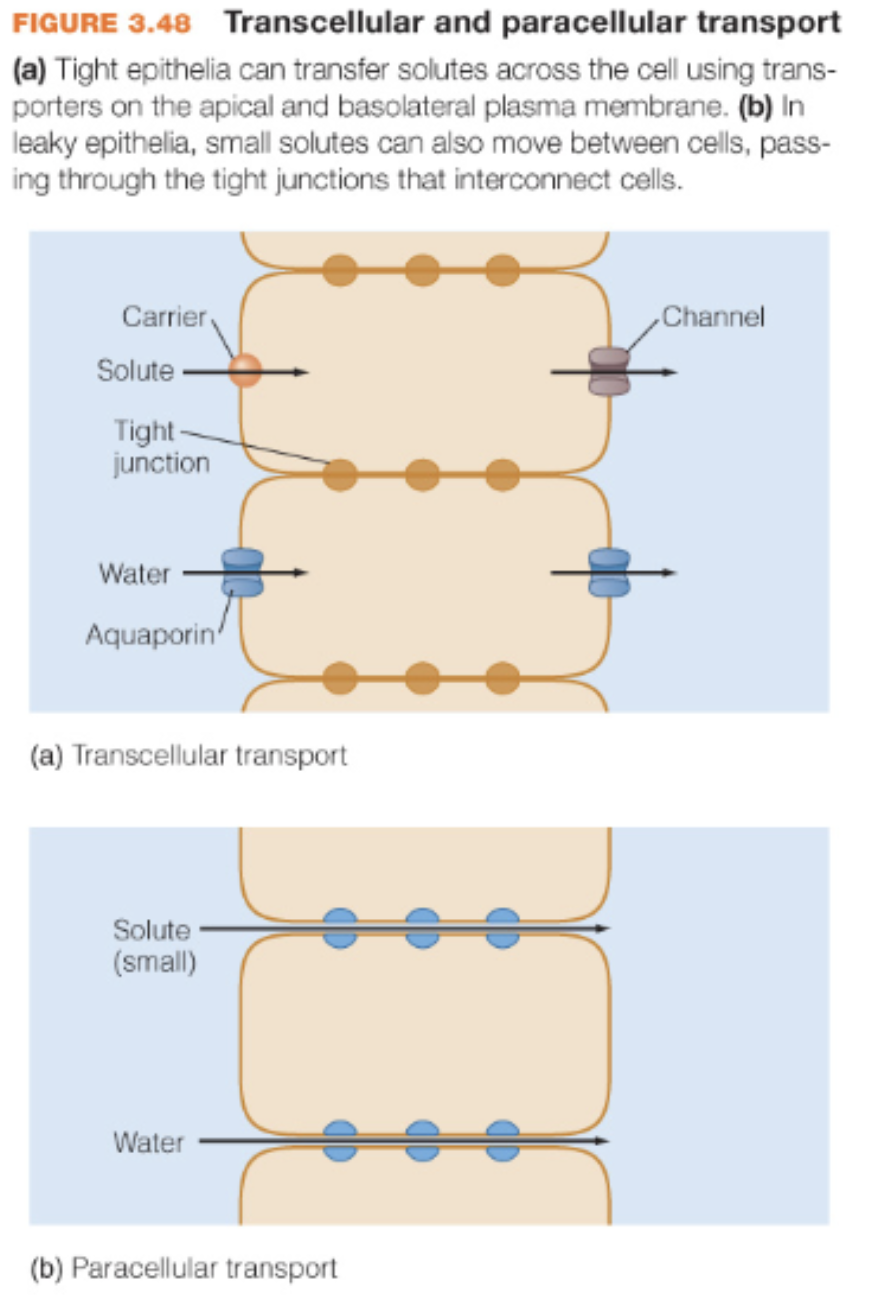
Transcellular transport
tight epithelia can transfer solutes across cell using transporters on the apical and basolateral plasma membrane
paracellular transport
in leaky epithelia, small solutes can move b/w cells, passing thru tight junctions that interconnect cells
energy units
4184 J = 1 cal
1 kCal = 1000 calories
1 kCal = 4.184 J
Types of energy
radiant energu, mechanical energy (potential energy, kinetic energy), electrical energy, thermal energy, chemical energy
1 J is
the amount of energy used when 1 watt of power (W) is expended for 1 sec
1 W = 1 J/s
Most biological processes involve the
transfer of energy from one form to another
(touch) mechanical E —> chemical E —> electrical E
Energy can be stored in/as
electrochemical gradients
chemical energy
How energy is stored in electrochemical gradients
biological systems can use energy to move molecules out of random distribution (molecules w/in a system tend to diffuse randomly w/in open space) —> this leads to diffusion gradients (a form of energy storage) which are either chemical, electrical, or electrochemical
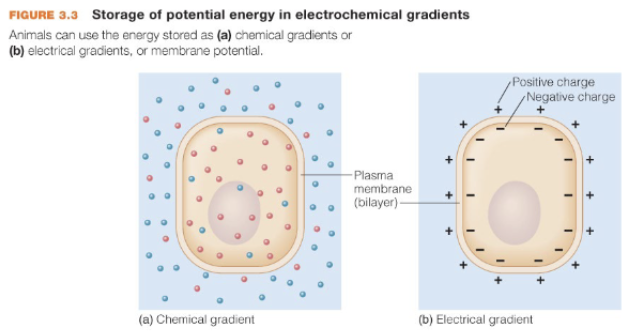
movement of what controls relative charges
ions
Hyperpolarization and depolarization example of elctrochemical gradient
gradients of Na+ and K+ across cell membrane largely determine resting membrane potential. when specific ion channels open, movement of ions changes the membrane potential. depolarization and hyperpolarization
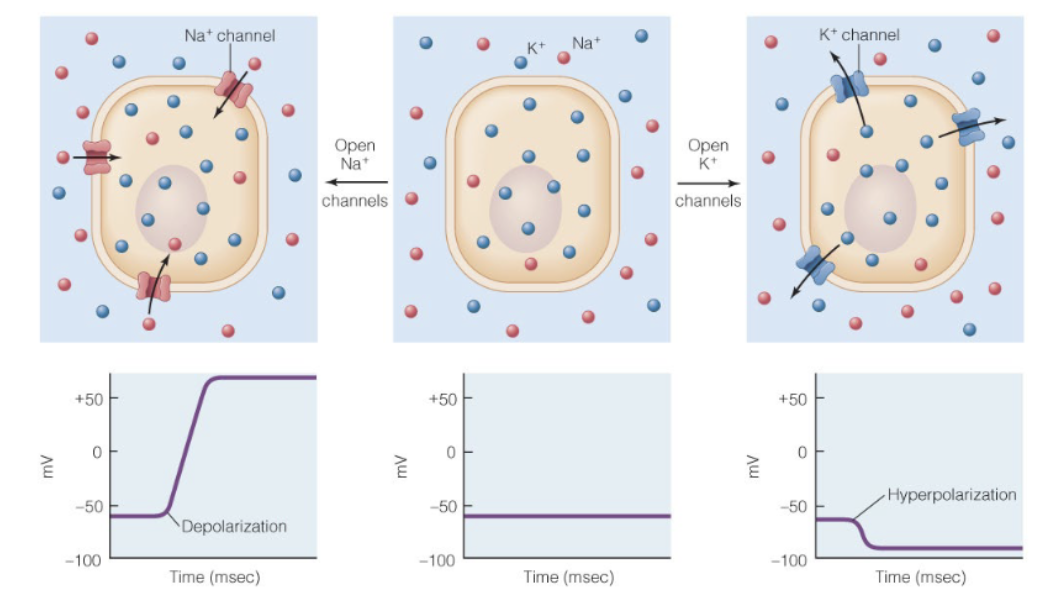
hyperpolarization
If K+ moves out of cell, magnitude of membrane potential inc.s
depolarization
If Na+ moves into cell, magnitude of membrane potential dec.s
Every chemical has
a characteristic energy associated with it; this energy is associated with the bonds b/w atoms
Most chemical rxns involve
changes in chemical energy
transition of substrate to product requires
certain lvl of activation energy
enzyme catalysts function
reduce activation energy of a reaction (make S—>P more likely to occur) increasing the rate of the reaction
S+E ←→ES←→ES*←→EP*←→EP←→E+P
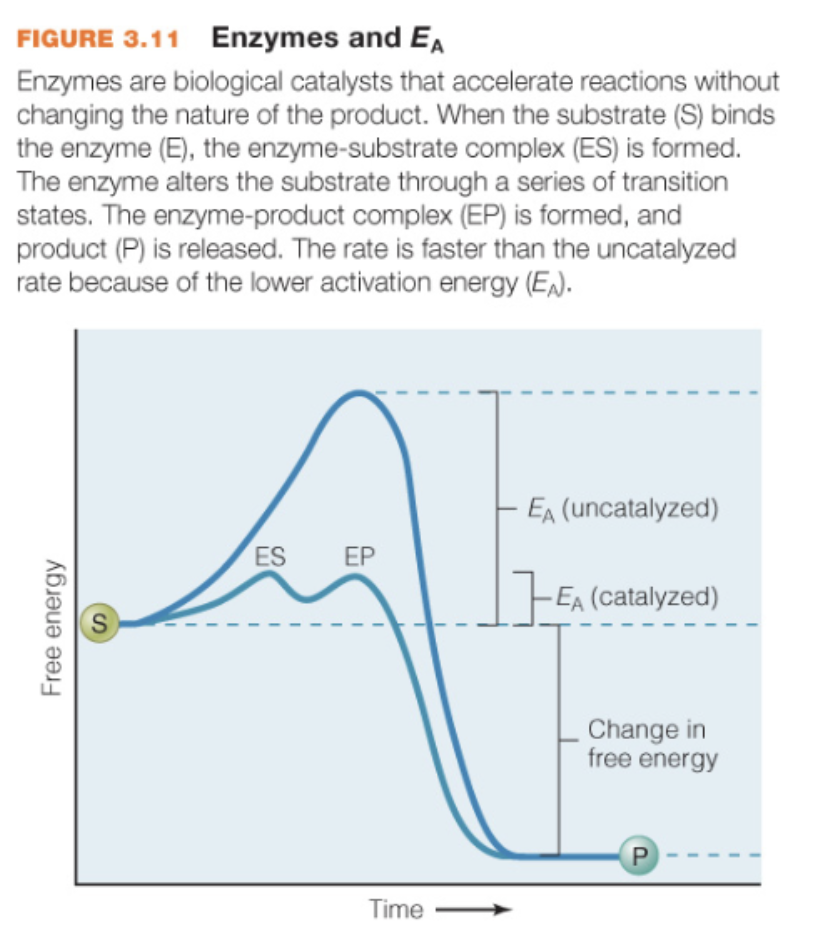
Enzyme catalysts important info
they aren’t consumed during this process (they are recycled: broken down and then translated again when needed)
don’t change the nature of the substrate or product
energy carrying molecules often involve
a phosphate bond (not always)
common energy carrying molecules
ATP, ADP, GTP, PCr (phosphocreatine)
ACetyl-CoA uses ___ instead of _____
CoA, phsophate

Protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
proteins are made up of
20 different amino acids
LAMPVIG, WFY, STCNQ, DEKHR
Primary structure main features
peptide bonds (covalent bonds) —> polypeptide chains
Secondary structure main features
polypeptide backbone exists as alpha-helices or beta-pleated sheets
hydrogen bonding is the main form of stabilization for this structure
Tertiary structure
secondary structures are folded into globular protein structures
disulfide bonds (disulfide bridges) and noncovalent bonds (hydrogen bonds, ionic bonding, LDFs/Van Der Waals) with some salt bridges (combination of hydrogen bond and ionic bond) and hydrophobic interactions are the primary bonds involved in tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
proteins that contain more than one polypeptide chain
Bonding: Van der Waals, H-bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, occasional disulfide bonds (covalent bonds)
What can denature proteins
heat/pH changes
Denaturation refers to
the loss of any aspect of 3D quaternary, tertiary, or even secondary structure sufficient to cause protein loss of function
What are chaperones
molecules that hep to fold proteins correctly
Hsp
Heat shock proteins
Help to maintain or refold proteins
Not all chaperones are _____ __ ____, but all are referred to as ____
responsive to heat; Hsp
Carbohydrates are
polymers made of monosaccharides which are joined by glycosidic bonds
monosaccharides—>disaccharides—>polysaccharides
polysaccharides
polymers of monosaccharides combined in linear or branched fashion (amylose, amylopectin, glycogen)
may contain amino sugars
polysaccharides may
may contain additional amino sugars (chitin)