Ch. 11: Common Equine Diseases
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
anthrax
A reportable bacterial disease caused by Bacillus anthracis
Gram + bacillus
Causes sudden death and septicemia
Can affect all warm-blooded animals (including humans)
Vaccine in presence of an outbreak
botulism
"Shaker foal syndrome"; Bacterial disease caused by Clostridium botulinum
Gram + rod, anaerobic, spore-forming
Ingestion through contaminated feed
Survives in soils and marine/freshwater sediments
Causes sudden death and muscle necrosis (prevents release of acetylcholine --> paralysis)
Types B, C, and D most common
High mortality from resp. paralysis
Vax: Series of 3, then consult vet
canker
Chronic hypertrophic, moist pododermatitis of the epidermal tissues of the foot
Caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum or Bacteroides spp.
Seen in South and Midwest
HX of housing in wet areas year round
Characteristic odor and lameness
TX: Superficial debridement and topical ABX
Lyme disease
Bacterial disease caused by B. burgdorferi
Gram - unicellular spirochete
Follows 2 yr enzootic life cycle
Primary vector= Deer tick (female) attaches for > 24 hrs
Common in humid areas w dense veg., May-
August
Signs: Low grade pyrexia, depression, stiffness, lameness, anorexia, joint swelling, eye problems
DX: ELISA
TX: Tetracycline, ORAL doxycycline
Potomac horse fever
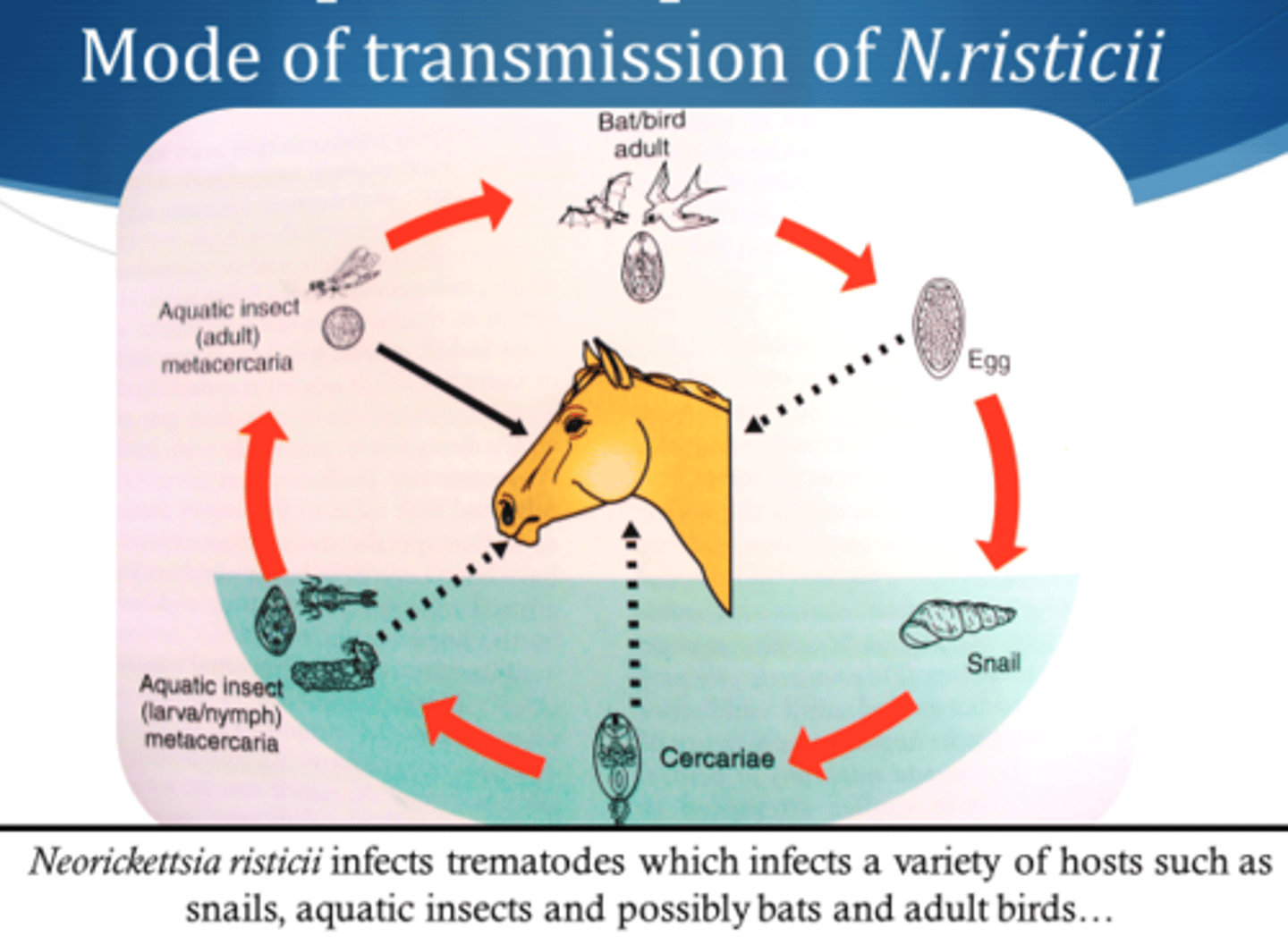
Bacterial disease caused by Neorickettsia risticii
Gram - cocci, obligate intercellular bacterium attracted to monocytes
Live inside flukes that infect snails --> larvae eaten by caddis/mayfly --> eaten by horse --> infection
Signs: Depression, D+, fever, toxemia, abortion, laminitis
DX: Feces/blood, PCR
TX: Oxytetracycline, fluids, NSAIDs
Vax: Series of 2, then semiannually
rain rot
Dermatophilus congolensis
Gram + actinomycete, facultative anaerobic
Also infects cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, cats, dogs
Found in high temp/humidity areas
Signs: Crusty scabs, matted hair tufts, yellow/green pus
DX: Culture
TX: ABX, soak/remove lesions, lime sulfur
Salmonella
Bacterial infection caused by Salmonella spp (esp. S. typhimurium)
Gram - rod
DX: Based on signs, neutropenia, and cultures; PCR
TX: IV fluids, electrolytes, plasma, NSAIDS
Zoonotic risk to staff --> quarantine!
carrier Salmonella
Subclinical carriers of Salmonella that intermittently shed the organism
May develop clinical signs if stressed
mild clinical Salmonella
Form of Salmonella infection involving pyrexia, anorexia, depression, and soft watery D+
Clinical signs for 4-5 days but shed organism for days to months after infection
acute clinical Salmonella
Form of Salmonella infection involving watery foul D+, abdominal pain, severe depression, anorexia, and pronounced neutropenia
Dehydrat equickly --> electrolyte imbalances
strangles
Caused by Streptococcus equi
Gram + cocci transmitted through nasal discharge (direct or indirect contact)
Signs: Sudden fever, mucopurulent discharge, abscess of submandibular/retropharyngeal lymph nodes, listlessness, anorexia
May be difficult for horse to swallow
DX: Culture (nasal swab, abscess pus, nasal wash), PCR, serology
TX: Penicillin, rest, palatable food, warm compress, flush (povidone-iodine), isolation, temp taken 2X daily
Prevention: Vax, quarantine new horses
Vax: Series of 4 (inj) or 2 (IN); booster semiannually

bastard strangles
Strangles that has metastasized throughout the body
Found in spleen, kidney, liver, mesentery, lung, brain
Tetanus
Clostridium tetani
Gram + bacillus, motile, anaerobic
Cause: Contaminated wounds (puncture involving rusty metal or manure) or surgical incisions
Incubation: 1-60 days (usually 7-10)
Signs: Generalized stiffness, dyspnea, "sawhorse appearance"
TX: Place horse in quiet dark area, raise food/water, body support, tetanus antitoxin, sedatives, muscle relaxants
Mortality: 50%
Vax: Series of 2 or 3 (depending on vax status of mare); annual boosters
sawhorse appearance
Characteristic stance seen with Tetanus infection caused by stiffness
Head, back, neck, and legs are stiff and tail head is elevated
thrush
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Gram - bacillus
Degenerative condition of the frog (central/lateral sulci)
Caused by unsanitary conditions
Signs: Odor, black discharge, lameness
DX: Clinical signs
TX: Cleaning affected area, antiseptic
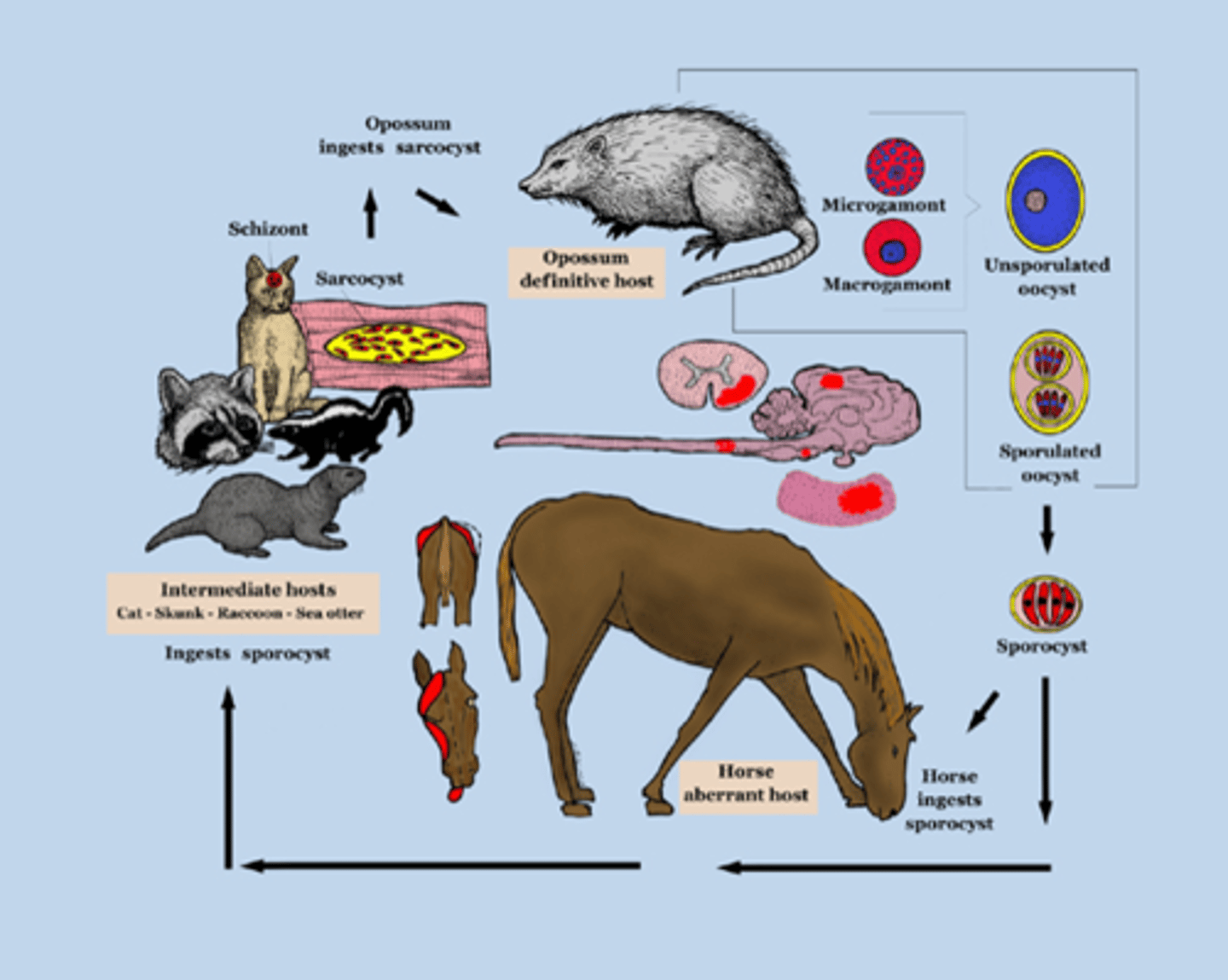
EPM
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis
Caused by Sarcocystis neuroma or Neospora hughesi
Carried by opposums; transmitted through consumed feces
Reportable
Signs: Muscle atrophy (quads/glutes), cranial nerve abnormalities (self-mutilation of tongue), recumbency
DX: ID of characteristic lesions, parasites on necropsy
Antemortem tests of serum/CS fluid
TX: Antiprotozoal drugs, NSAIDS, vitamin E, limit access to opossums
piroplasmosis
Babesia equi and B. caballi
Protozoans transmitted by ixodid ticks (Dermacentor nitens), esp. in tropical/subtropical and temperate regions
Protozoans invade RBCs
Signs: Pyrexia, depression, anemia, thirst, eye problems, yellow/red urine
Prevention: Tick control, sterilization of needles/instruments
Mortality: 10-15%
DX: Blood smears, complement fixation tests, ELISA, PCR
TX: Imidocarb dipropionate, tetracyclines, etc
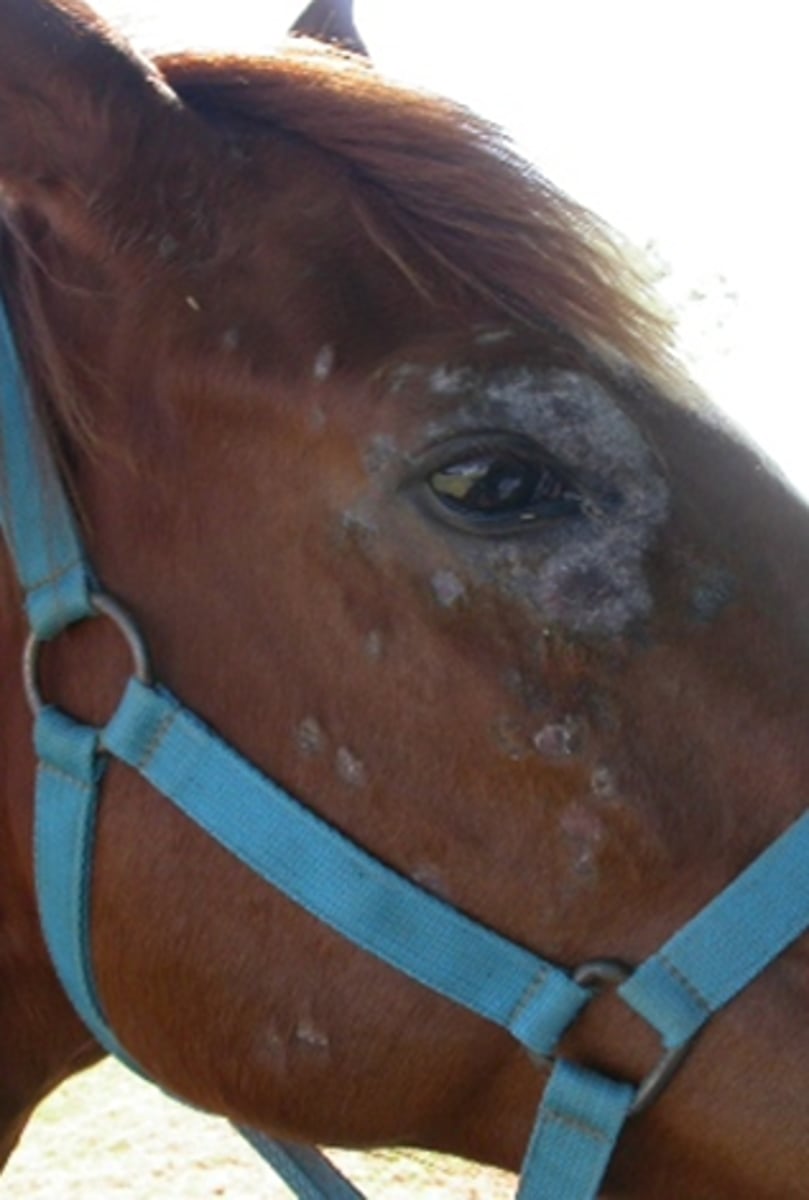
Dermatophytosis
Ringworm
Trichophyton and Microsporum spp. of fungi
Superficial cutaneous fungal infection (invasion of stratum corneum)
Highly contagious, direct/indirect contact
Can survive on equipment for 12 months
Signs: Small round lesions covered w small scales
DX: Wood lamp, culture, histologic exam
TX: Povidone-iodine, sulfur dip, antifungals, captan, thiabendazole ointment
Treat environment w dilute bleach
white line disease
Caused by bacterial, fungal, or yeast infection in the inner horn
Fungal = Onychomycosis
Signs: Hoof fills with cheesy material, lameness, warm soles, black foul-smelling substance
TX: Resection of underlying hoof wall, topical antiseptic
encephalomyelitis
Caused by equine alphaviruses
3 types: Eastern, Western, Venezuelan
Transmitted by mosquitoes
Neurologic disease
Signs: Fever, ataxia, anorexia, paralysis, circling, head pressing, hyperexcitability
No known TX; supportive therapy
Vax: Series of 3, 1 mo. apart; annual boosters in Spring
equine viral arteritis
Caused by equine arteritis virus (EAV)
Signs: Flulike symptoms, abortion, pneumonia in foals
Transmitted through resp. particles or venereally
Infected semen primary source
Stallion= natural reservoir
Incubation= 2-14 days
DX: Virus isolation, paired serum samples, viral antigen, viral nucleic acid detection
TX: NSAIDs, antipyretics, diuretics, rest
Castrate infected stallions
Vax: 1 dose after 6 mo. in intact breeding stallions; annually if still breeding
EIA
Equine infectious anemia (aka swamp fever)
Caused by equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), a lentivirus
Transmitted through blood-sucking insects
Signs: Fever, lethargy, anorexic, pale MMs, petechiae, icterus, neurologic signs, thrombocytopenia, anemia
No specific therapy
REPORTABLE
Quarantine or euthanasia
Coggins Test
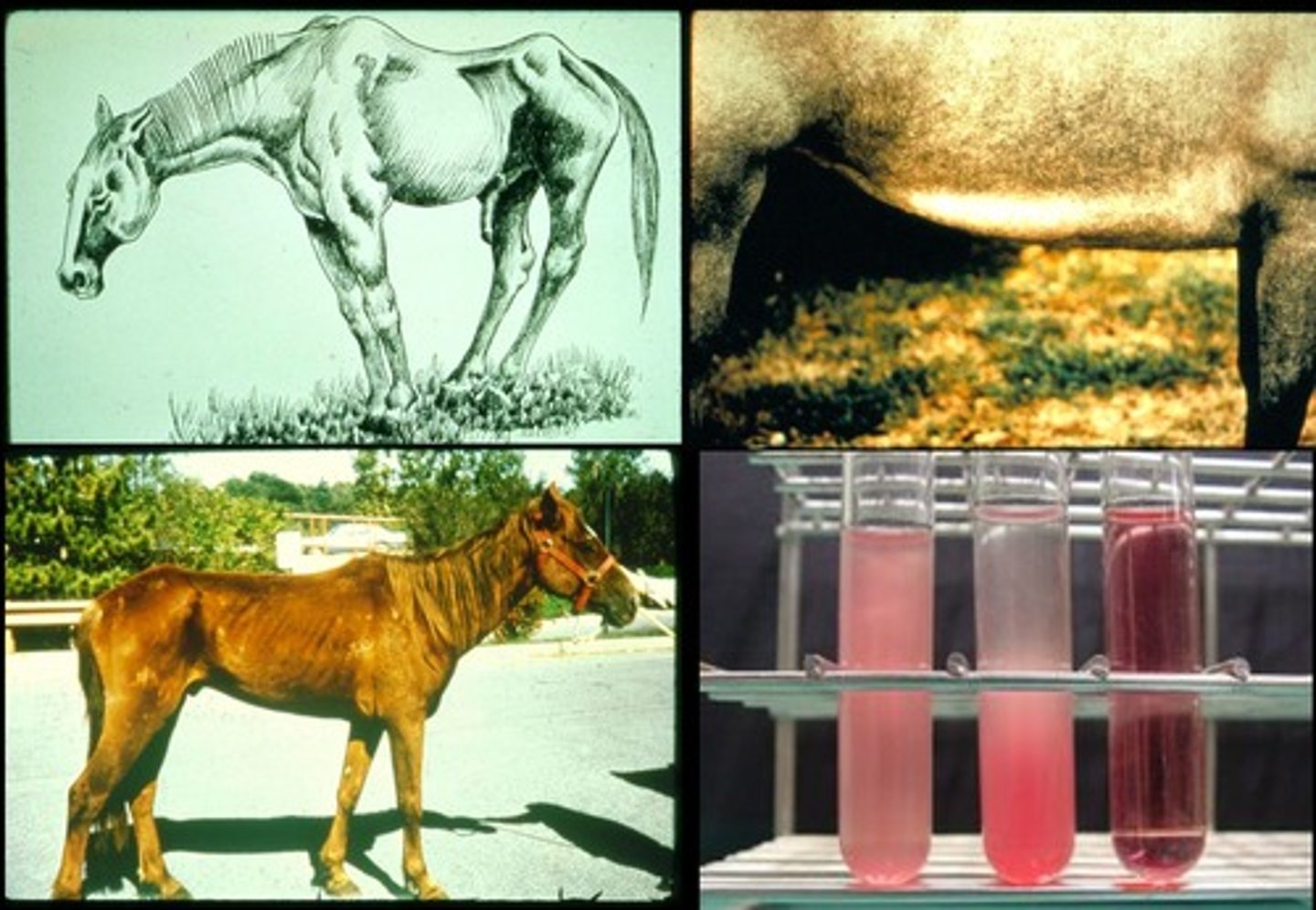
Coggins testing
Serologic testing performed for the diagnosis of Equine infectious anemia
equine influenza
Orthomyxoviridae
Often spread at rodeos and horse shows
High morbidity, low mortality
Incubation: 48 hrs
Targets lower resp. tract
Signs: Fever >106 F, anorexia, weight loss, mucopurulent nasal discharge, increased RR, retropharyngeal lymphadenopathy
DX: Virus isolation, immunoassay, PCR, antibody detection
TX: Supportive; rest, hydration, NSAIDs
Vax: Inactivated inj= series of 3, then every 3-4 months
MLV Intranasal= 1st at 11 mo, then q 6 months
Rabies
Infection caused by rhabdovirus (enveloped RNA virus)
Transmitted through bites for infected skunks, raccoons, foxes, bats (saliva)
Signs: Ataxia, lameness, loss of bladder control (GI/neuro signs)
No TX
DX postmortem (spinal cord and brain)
Vax: Series of 2 or 3; booster annually
rhinopneumonitis
Caused by equine herpesvirus type 1 and 4 (EHV-1 and EHV-4)
Signs: Mucopurulent nasal discharge, lymphadenopathy, coughing, abortion, scrotal edema, loss of libido in stallions, reduced sperm quality, ataxia, fever, loss of anal tone, tail paralysis, urinary incontinence, recumbency
DX: Postmortem PCR
TX: Isolation of horses w resp. form; all other cases treat w supportive care
Vax: Series of 3 (1 mo. apart), then q3-4 months or annually
vascular stomatitis
Rhabdoviridae familiy
Transmitted through insects (black fly, sand fly, mosquito, housefly)
Incubation= 3-7 days
Signs: Initially fever and excessive salivation --> white fluid-filled areas on oral mucosa --> ulceration
Vesicles and lesions form on other areas (coronary band, belly, muzzle, prepuce, udder)
DX: Antibody detection, viral isolation
TX: Limited b/c horses recover usually within 7-14 days; supportive care in severe cases
West Nile virus
Caused by virus in Flaviviridae family
Spread by mosquitoes after biting infected birds
Signs: Low grade fever, inappetence, depression, colic, personality changes, unresponsiveness, coma
Many show signs of recovery in 3-7 days and fully recover in 1-6 months
DX: IgM ELISA of CS fluid, plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) of serum, PCR of brain tissue
TX: Supportive
Reportable disease if neurologic
Remove stagnant water to keep mosquito pop. low
Vax: 1st at 3-4 mo, 2nd 1 mo. later, 3rd dose at 6 mo; annual booster
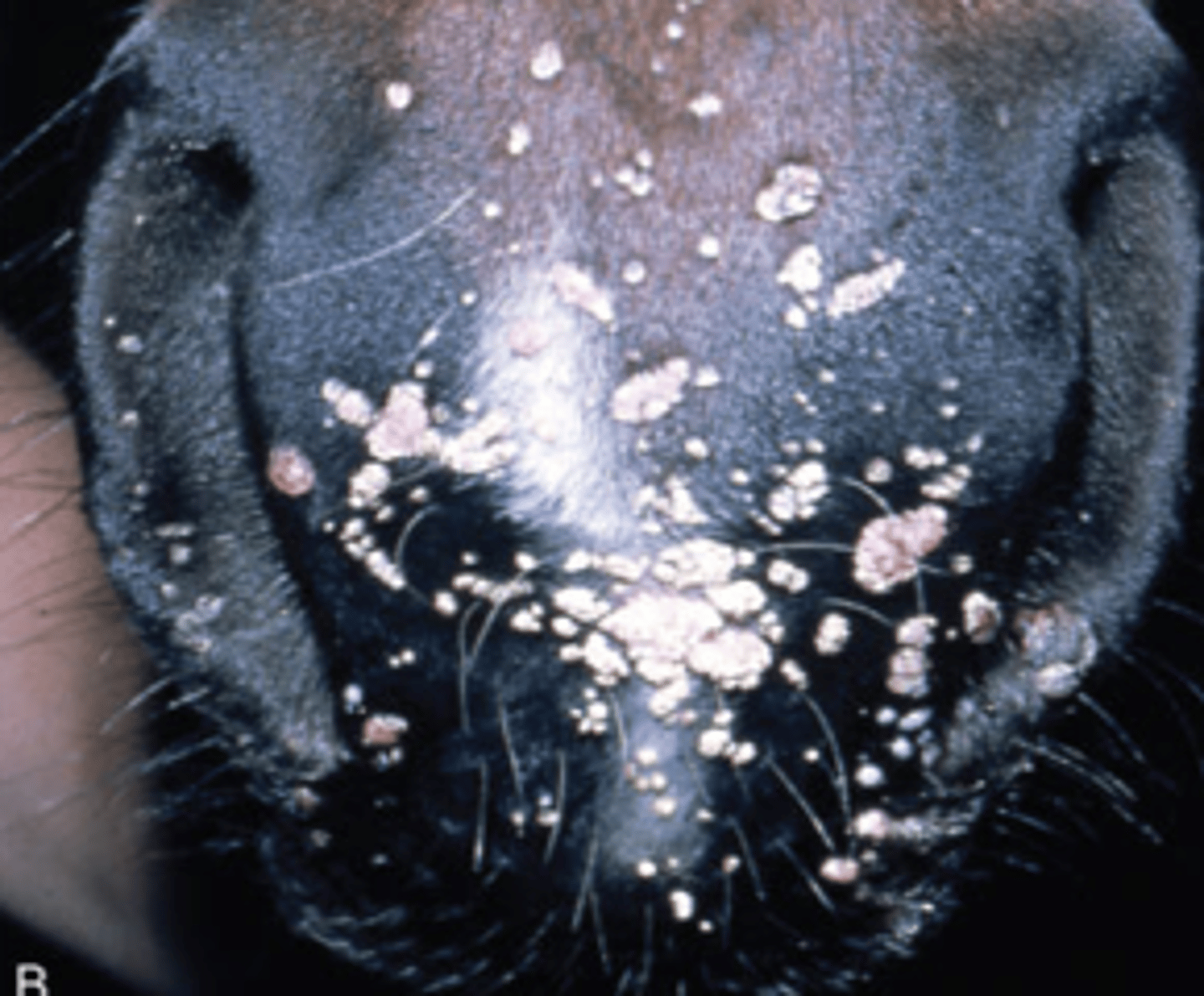
cutaneous papillomas
Equus caballus papillomavirus type 1
Warts that appear around the lips and muzzle, but also the eyelids, prepuce, inner thighs, and distal limbs
Spread by direct contact (horse shows, sales, breeding) or fomites
Usually harmless until irritated by tack
Usually resolve in 3-4 months
If not gone in 6-9 months, indicates autoimmune deficiency
Can be removed by cautery or cryosurgery
choke
Noninfectious
Occurs when feedstuffs become lodged in the esophagus
Causes: Inadequate water intake, large particles, quick eating, dry food
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or "heaves"
Noninfectious resp. disease
Cause: Air pollutants (dust, mold), diet, genetic linkage, HX of resp. tract infection
Mor common in horses >6 y.o.
Signs: Dyspnea, abd. breathing, nasal discharge, cough, lack of stamina, hyperpnea at rest
Some have summer-pasture associated
DX: HX, clinical signs, endoscopy, trach wash (neutrophils), culture
TX: Remove resp. irritants from environment
heave line
A ridge along the costal arch that may develop in horses with COPD due to chronic abdominal breathing
colic
Abdominal pain
4 Causes:
1) Gut distention (fluid, sand, gas, ingesta)
2) Pulling at root of mesenteric artery (torsion, hernia, tumor)
3) Ischemia/infarction (torsion, thrombus)
4) Enteritis/ulcers (inflammation of GI tract from stress, disease, parasites)
Signs: Repeating standing/lying down, rolling, kicking @ abd., pawing, looking at abd., grunting, sweating, distention, positioning to urinate, tenesmus, decreased BMs, tachypnea, flared nostrils, abnormal behavior, inappetence
DX: Exam, HX
TX: Place NG tube to administer mineral oil/pain meds, hand walking, continued monitoring, IV fludis, abd SX
Prevention: Establish and adhere to set routine, high quality forage, small freq. meals, deworming, daily exercise, avoid meds, inspect feeds, reduce stress, elevate feed
Cushings syndrome
Hyperadrenocorticism
Usually secondary to adenoma or hyperplasia
Signs: PU/PD, long/thick/curly coats, failure to shed in spring, dull coats, sway back, pot belly, laminitis, fat deposition in supraorbital fossae, weight loss, polyphagia, depresison, increased sweating, loss of back muscle tone
May be diabetic
DX: ACTH test, insulin/BG test
TX: Cyproheptadine, pergolide mesylate
EIPH
Exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage ("bleeders")
Hemorrhage that originates from small pulmonary vessels associated with strenuous exercise
DX: Endoscopy
TX: Rest to allow lesions to heal, furosemide, nasal strips, nitric oxide, bronchodilators, procoagulants, antiinflammatories, omega 3 FAs
exertional rhabdomyolysis
Necrosis of the striated skeletal muscle associated with exercise
"Cording up/Tying up"
Can be sporadic or chronic
sporadic exertional rhabdomyolysis
"Cording up" that occurs when a horse is asked to perform for long periods or perform heavy exercise when not in condition to do so
Other causes: Deficiencies of vit. E, selenium, Na or Ca
Signs: Muscle cramps, refusal to move, increased RR/HR, excessive sweating
DX: Increased serum creatine kinase and aspartase aminotransferase (AST)
TX: Stall rest, fresh water, hay diet, correct fluid balance + diuretics
Prevention: Proper conditioning and balanced diet
EPSM
Equine polysaccharide storage myopathy
Form of chronic exertional rhabdomyolysis
Seen in draft horses, Quarter Horses, warm bloods
INHERITED
Signs: Camped-out stance, sweating, hindlimb stiffness, abnormal gait, reluctance to move, loss of muscle mass, weakness
DX: Increase CK and AST, signs, muscle biopsy, CBC, UA, exercise testing
TX: Forage diet at 1.5-2% of BW, limit starch to <10%, increased fat (horse is more sensitive to insulin)
Gradually introduce exercise
recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis
Form of exertional rhabdomyolysis seen in Thoroughbreds, Arabians, and Standardbreds
Caused by autosomal dominant trait (TBs) or improper reg. of intracellular Ca in skeletal muscle
Signs: Muscle stiffness, sweating, refusal to move
DX: CBC/chem, UA, exercise testing, blood vit. C/selenium levels, muscle biopsy
TX: Reduce anxiety, high caloric intake, dantrolene, phenytoin
HYPP
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
Form of recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis
Autosomal dominant trait associated with Quarter horses + their crosses, Appaloosas, and American Paints
Diagnosed between birth and 3 y.o.
Signs: Not always shown; may include muscle weakness, twitching, dog sitting, staggering, periodic URI obstruction, recumbency
TX: Light exercise, corn syrup, grain, calcium gluconate, sodium bicarbonate, trach tube (if URI obstruction)
Prevention: Decrease dietary K (avoid beets/molasses, alfalfa, brome hay, soybean oil/meal, canola oil); feed beet pulp, corn, oats, barley, late cut Timothy hay/Bermuda grass
Feed several small meals
Meds: Acetazolamide, hydrochlorothiazide
habronemiasis
Summer sores; characterized by granulomatous lesions caused by larvae of Habronema spp or Draschia megastoma
Seasonal with fly pops.
Common with high heat/humidity areas, or poor sanitation
DX: Location and characteristics of lesions (found on glans penis or urethral process), time of yr, histopathology
TX: Kill parasites (ivermectin, others), decrease inflammation, ABX
hernia
Protrusion of internal organ through the wall of its containing cavity
Intestines, umbilical, scrotal, inguinal
Usually self-correcting, but may perform surgery after foal is weaned
hypothyroidism
underactivity of the thyroid gland
Causes: Low T3/T4
Signs: Slow shed or absence, long rough hair coat, cold intolerance, depression, weakness, lack of muscle tone, tying up, laminitis, infertility, irregular heat cycles, lack of milk production, goiter
Can be congenital in foals (caused by low iodine diet by mare during pregnancy)
DX: CBC, serum chem, TSH stim test
TX: Supplemental T3/T4 through feed additives
lameness
incapable of normal locomotion; failure to travel in regular and sound manner
Causes: Structural or functional disorder of one or more limbs or of the trunk
Can be associated w pain
Weight-bearing, non weight-bearing, mixed, compensatory/complementary
DX: HX and exam, local anesthesia, rads, ultrasound, scintigraphy, MRI, arthroscopy, synovial fluid analysis, electromyography, muscle biopsy
Watch head (will rise when lame forelimb is bearing weight) or croup (raise on lame hindlimb side)
weight bearing lameness
Animal tries to decease weight placed on affected leg by taking shorter steps, leaving leg on ground for shorter time, and elevating body
Often associated w injuries to motor nerves, ligaments, tendons, bones, and feet
non weight bearing lamenss
Swinging leg disorder
Seen as animal brings leg forward
Associated w joints, muscles, extensor tendons, bursasa, and tendon sheaths
mixed lameness
Lameness that affects both weight-bearing phase of gait and the swinging phase
complementary lameness
Aka compensatory lameness
Develops as compensation for originally affected limb
predisposing lameness
Lameness that results from a factor that predisposed the horse to lameness
Includes poor shoeing, systemic disease, faulty conformation, poor condition, immaturity, and poor hoof care
inciting lameness
Lameness as a result of trauma
Trailer accidents, kicked by another horse, incoordination
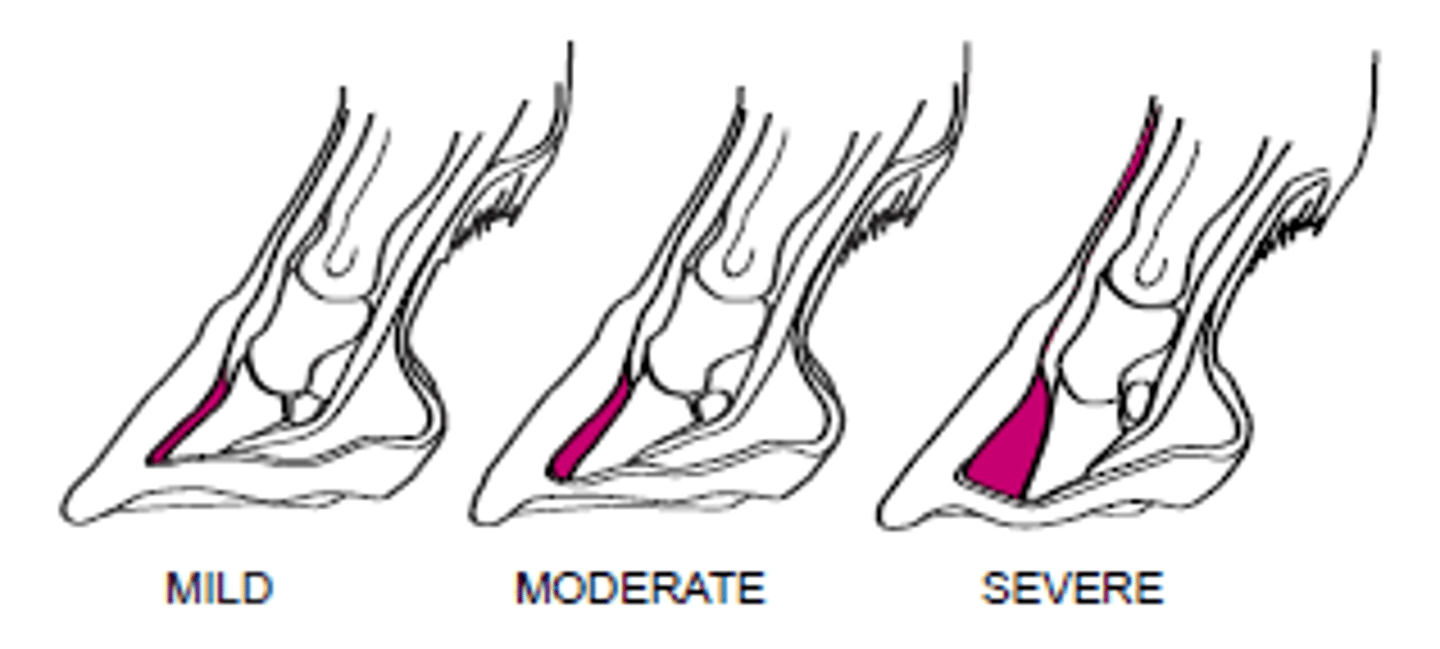
laminitis
Inflammation of the sensitive laminae of the foot
Causes: Endotoxin-induced microthrombosis, altered vascular flow, vasoconstriction, enzyme destruction, grazing during certain months, grain overload, GI inflammation, metritis, retained placenta, endotoxemia, sepsis, pleuropneumonia, Cushing's, prolonged weight bearing, black walnut exposure
subacute laminitis
Mild form of laminitis
Causes: Riding on hard surfaces, hooves trimmed too short, black walnut
Signs resolve quickly without permanent damage
Usually no coffin bone rotation
acute laminitis
More severe laminitis
Disease does not respond rapidly to TX
Likely coffin bone rotation
TX: To prevent chronic form of disease; includes antiendotoxin therapy, vasodilators, anticoagulants, corrective trimming, SX
refractory laminitis
Form of acute laminitis that doesn't respond within 7-10 days of TX
Signs: Increased digital pulse, lifting feet every few sec, lameness, camped-out stance, pain
chronic laminitis
Continuation of acute stage of laminitis
First signs of coffin rotation
Early= begins with rotation of coffin (days to months)
Chronic active= Coffin is rotated but unstable and could penetrate sole
corns
Bruises of the soft tissue underlying the sole that cause development of reddish discoloration
Causes: Work on hard surfaces, flat soles, stepping on small objects
TX: Rest, drying of abscess, soaking in Epsom salts, prevent infection
navicular syndrome
Syndrome that causes signs associated w navicular region
Predisposing conditions= Hard work, small feet, heels trimmed too low, upright pasterns
Signs: Intermittent lameness in horses between 4-15 y.o., shor choppy stride, pointing of affected toe
TX: Special shoeing, cutting of navicular nerve
nerved
A horse that has had its navicular nerve cut to treat navicular syndrome
These horses can't be used for hard work and can be dangerous to ride (can't feel ground)
1/2-1 inch scars above bulbs of front feet
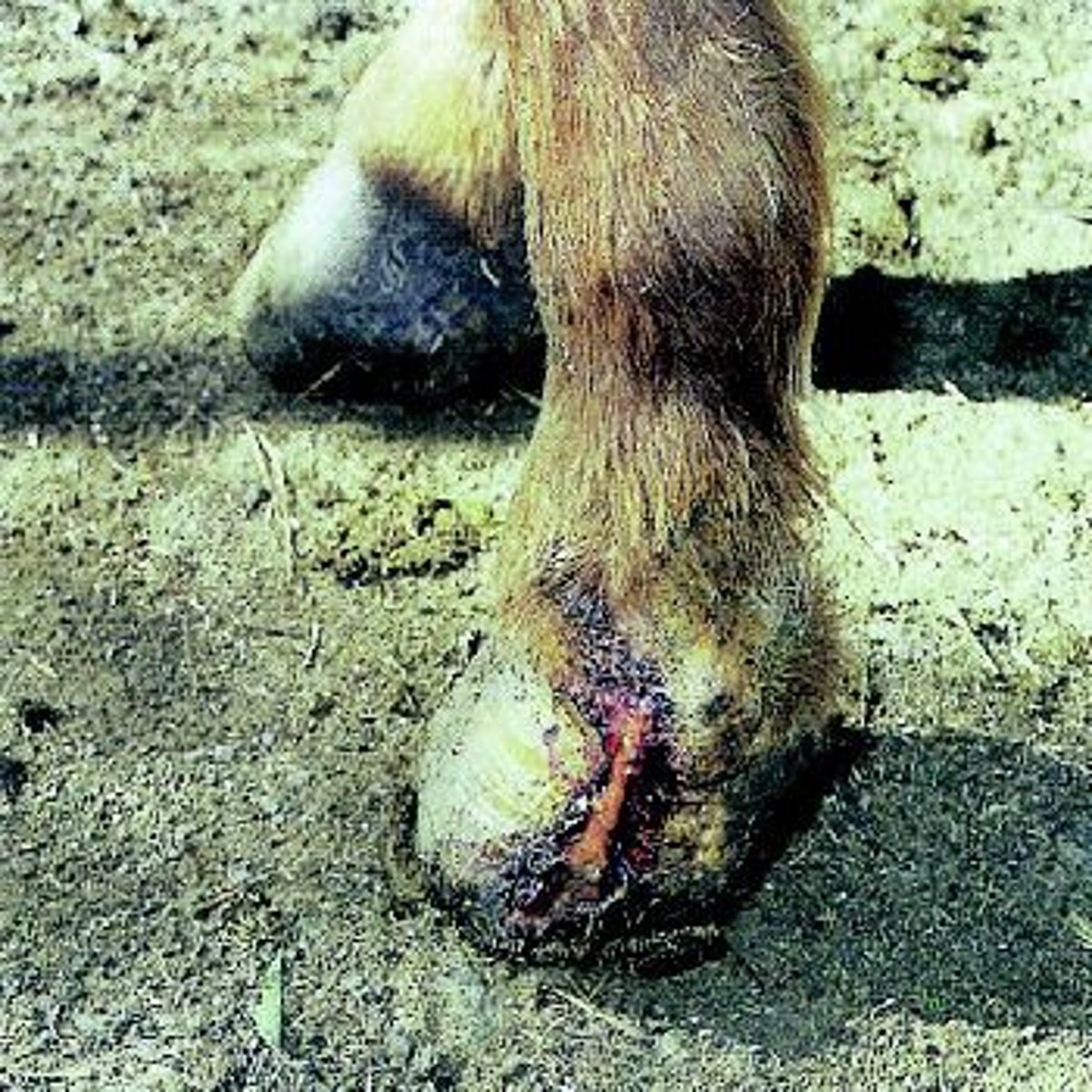
quittor
A deep-seated sore that drains at the coronet
Causes: Corns, puncture wounds, chronic inflammation of collateral cartilage of distal phalanx
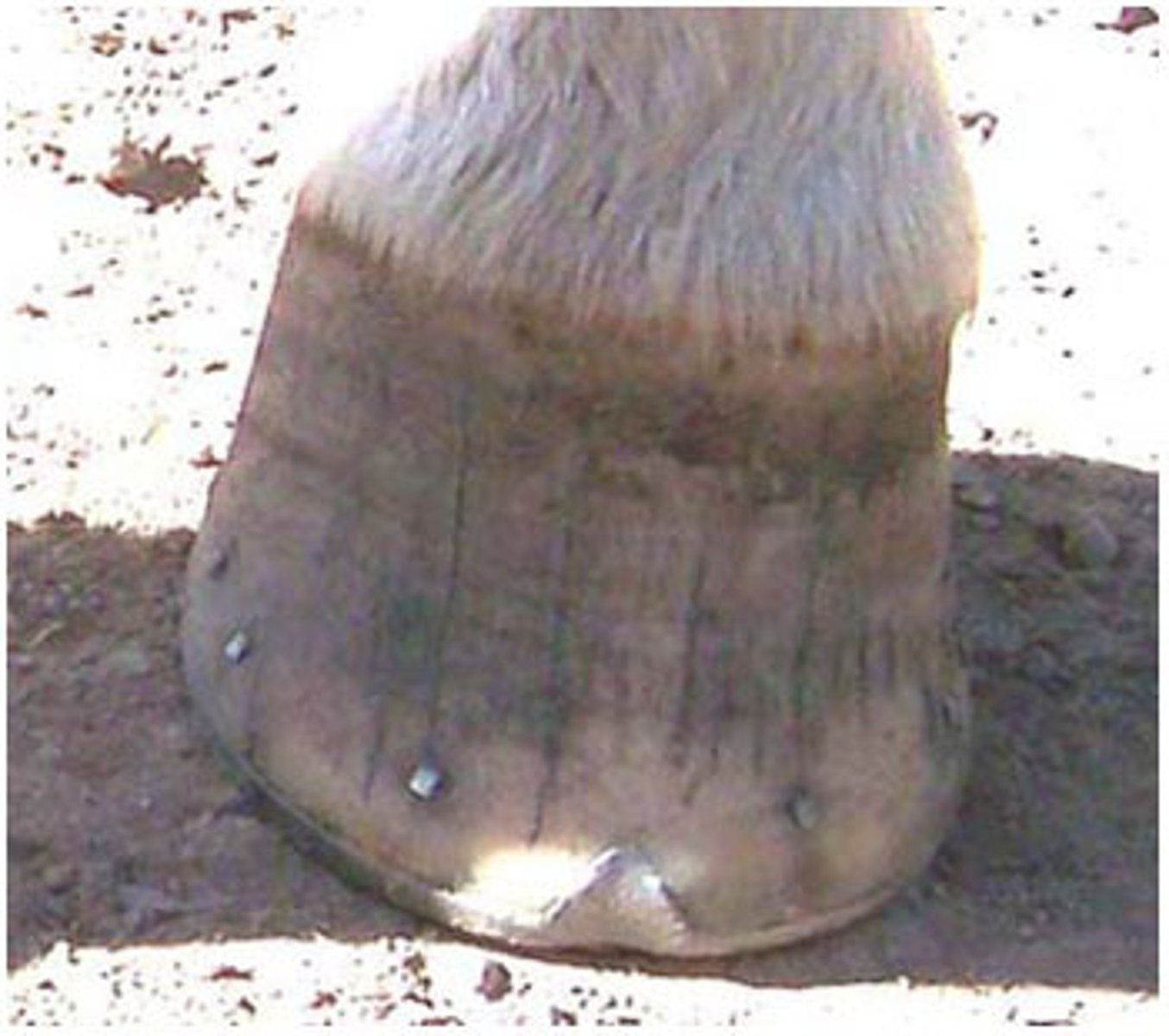
sand cracks
Toe cracks/quarter cracks/heel cracks
Vertical cracks in the hoof wall
Causes: Dryness/brittleness of the hoof, injury to coronet, long hoof walls
TX: Burning crescent at tip of crack, filing groove across the tip, corrective shoeing, commercial sealants
Prevention: Keep hooves moist with hoof dressing and regular trimming
grease heel
Dermatitis verrucosa
Chronic seborrheic dermatitis of the plantar surface of the fetlock or pastern
Usually found on hindlimbs; can also affect palmar surface of fetlock on forelimb
Greasy, foul-smelling lesions
May have lameness
Prevention: Good housing conditions
TX: Clipping hair and cleaning with soap/water, topical antiseptic
TBX, tetanus prophylaxis (if cellulitis develops)
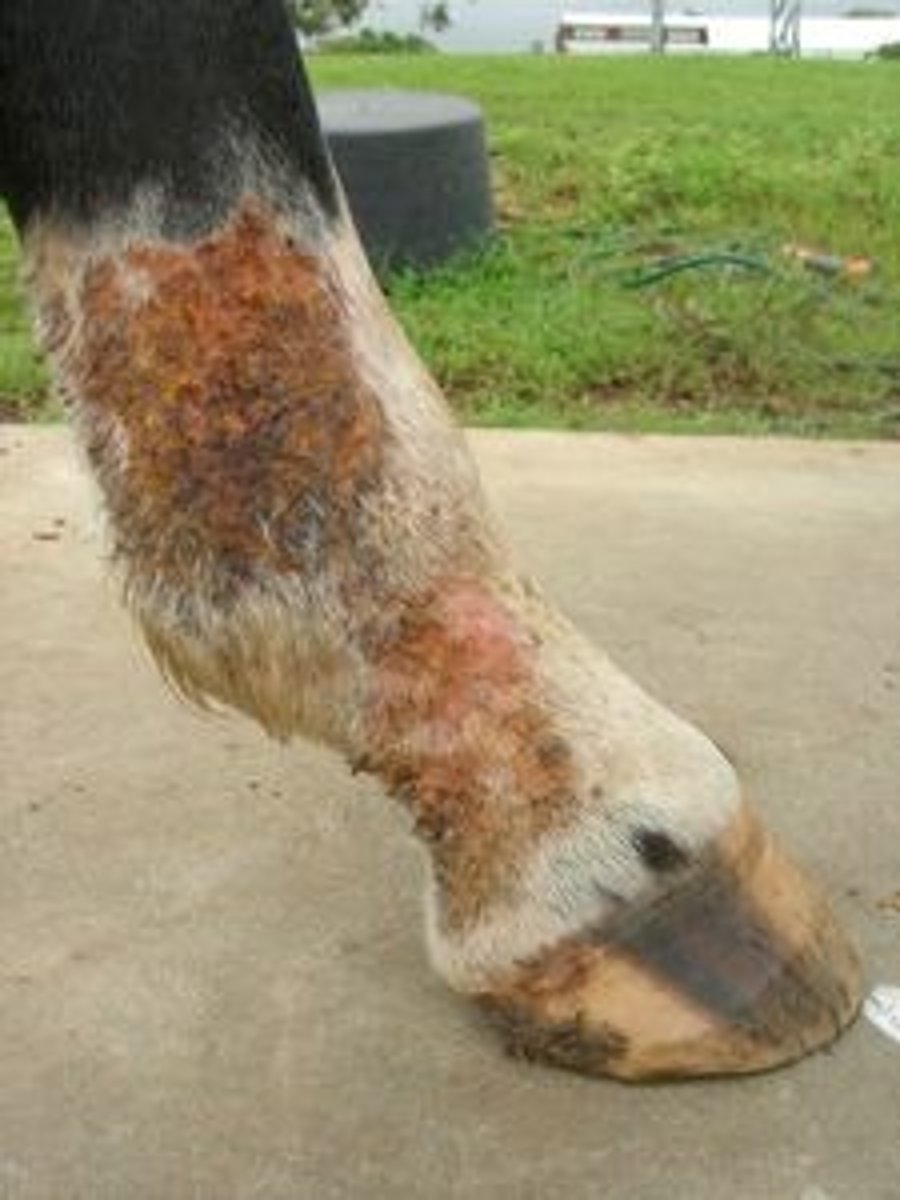
seedy toe
"Hollow wall" or dystrophia ungulae
Condition that occurs secondary to laminitis
Palmar hoof surface contains hollow space that varies in size
Mealy substance found inside hollow space
TX: Clean area and pack with juniper tar and oakum
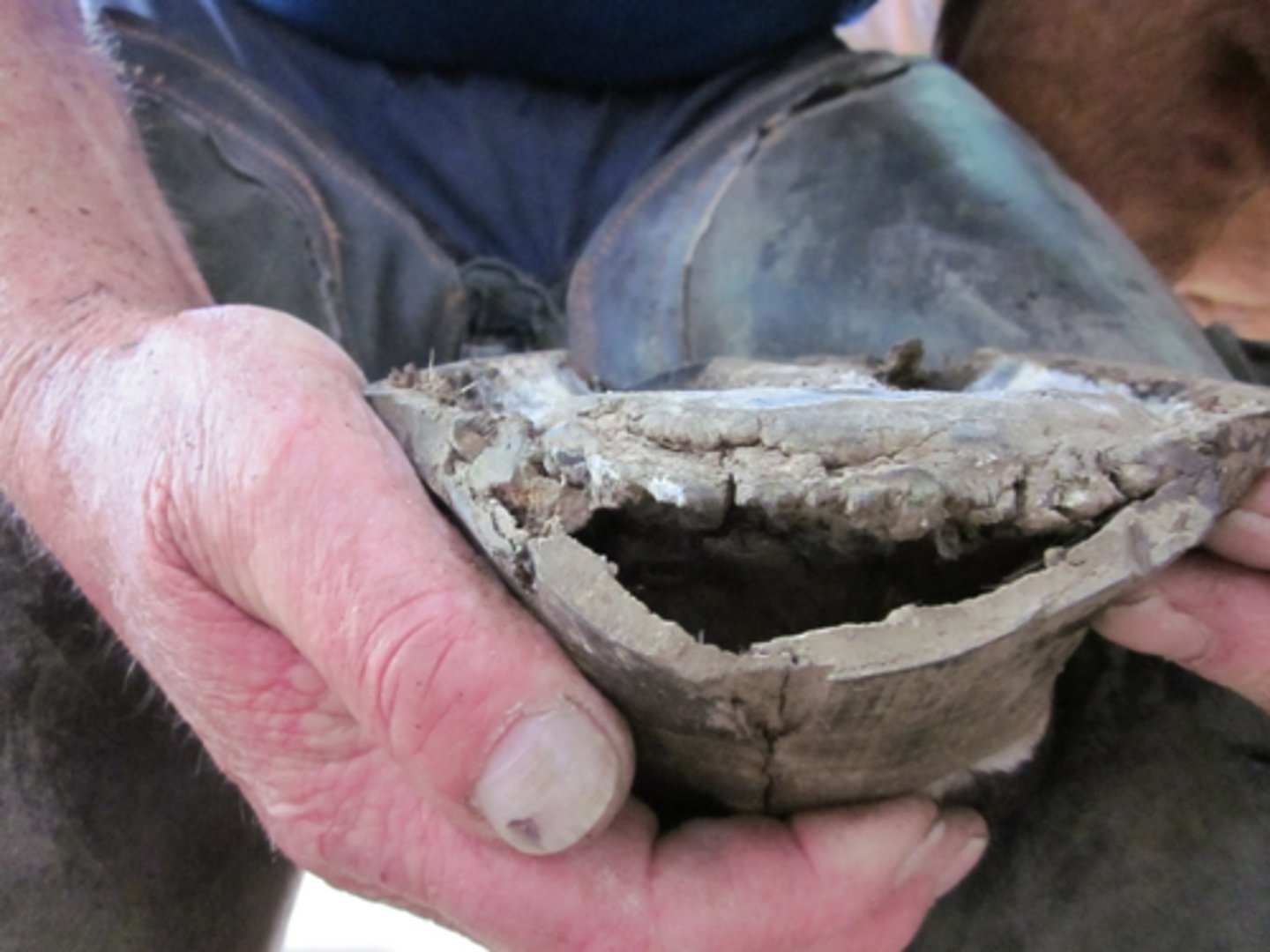

side bone
Ossified lateral cartilages located proximal to the rear quarter of the hoof head
Often on forelimbs, on one or both legs, and on either or both sides of the hoof
Unknown cause
Horse may become lame
TX: Rest, NSAIDs
bucked shins
Found in horses 2-3 y.o. that are involved in intense training
Temporary unsoundness originating at dorsal surface of the cannon bone --> inflamed periosteum
Pain and lameness
TX: Rest for 30-60 days
Prevention: Gradual increase in exercise
splints
Abnormal or new bone growth that occurs on the splint bones or cannon
Causes: Strain/trauma to the interosseus ligament between splint bones and cannon, conformation faults
Influs of blood supply
Signs: Subtle lameness, pain, heat at palmar cannon surface, lump on cannon
Sweeney
Any group of atrophied muscles
No known TX
In shoulder muscles, associated with nerve over the shoulder crossing the spinal cord
shoe boil
"Capped elbow"
Soft swelling at the elbow caused by irritation
Causes: Injury from long heel on a front shoe, or from contact with surface horse is laying on
TX: Tincture of iodine, shoe boil boot/roll
Prevention: Don't leave long heels on front shoes
bone spavin
Distal tarsal osteoarthritis
New bone growth on the medial/proximal end of the 3rd metatarsal/tarsal and central tarsal bones
Causes: Faulty conformation
Signs: Pain on hock flexion, rolled hip during mvmt, toe dragging
TX: SX; full recovery not always possible
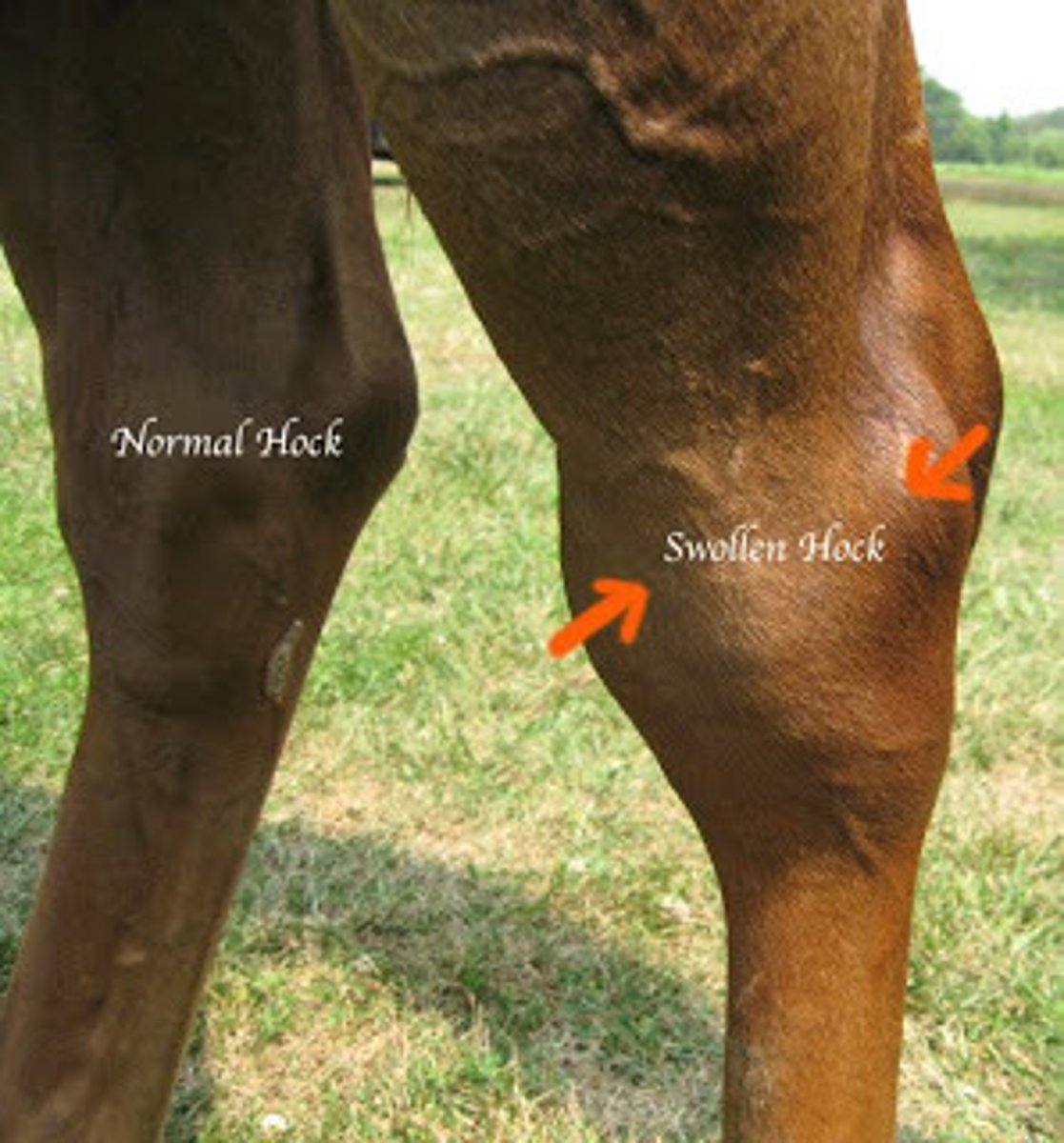
curb
Fullness of the plantar surface distal to the hock
Causes: Enlarged plantar ligament due to poor conformation, hard stops, or long sliding stops
stringhalt
Involuntary flexion of the hock during forward mvmt
May affect one or both hindlimbs
Cause: Nerve degeneration
Signs: Jerking of leg toward abdomen w mvmt
TX: SX to remove part of lat. digital extensor tendon

ringbone
New bone growth that occurs on the proximal, middle, or distal phalanx
Most commonly on forelimbs, but can occur on hindlimbs
Causes: Poor conformation, heavy work for years, excessive pulling on ligaments --> disruption of periosteum
Classified by location on bone or by joints involved (high, low, periarticular, or articular)
Articular always causes lameness (involves joint surface)
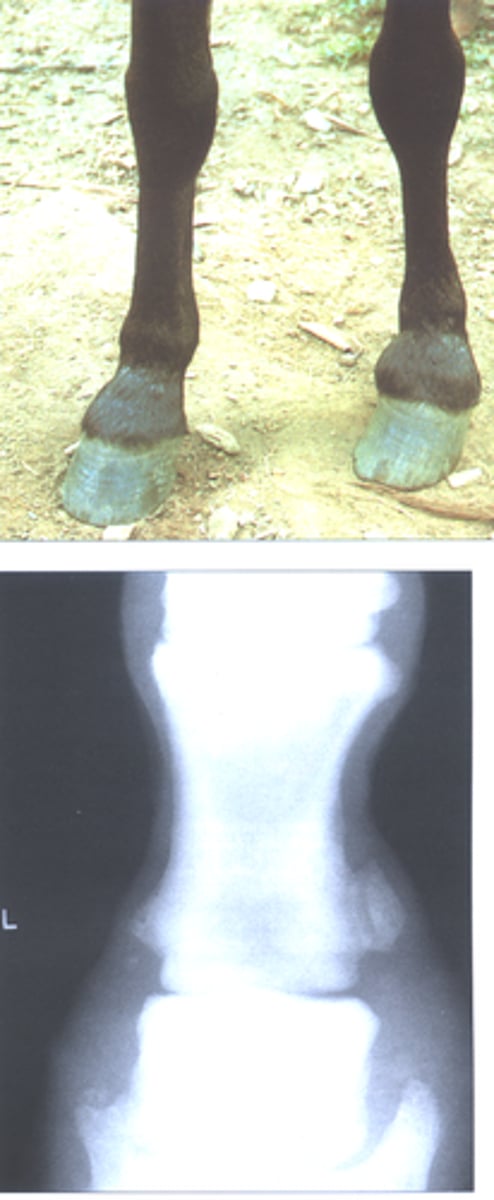
sesamoiditis
Inflammation of proximal sesamoid bones
Horse doesn't extend fetlock to normal level
Inflammation and pain of fetlock
May involve periosteum damage and new bone growth
osselets
Inflammation around fetlock joint
Causes: Strain or concussion on immature bones
Upright pasterns can predispose
Inflamed area feels like putty (hemorrhage/fluid)
Short, choppy stride
Arthritic condition
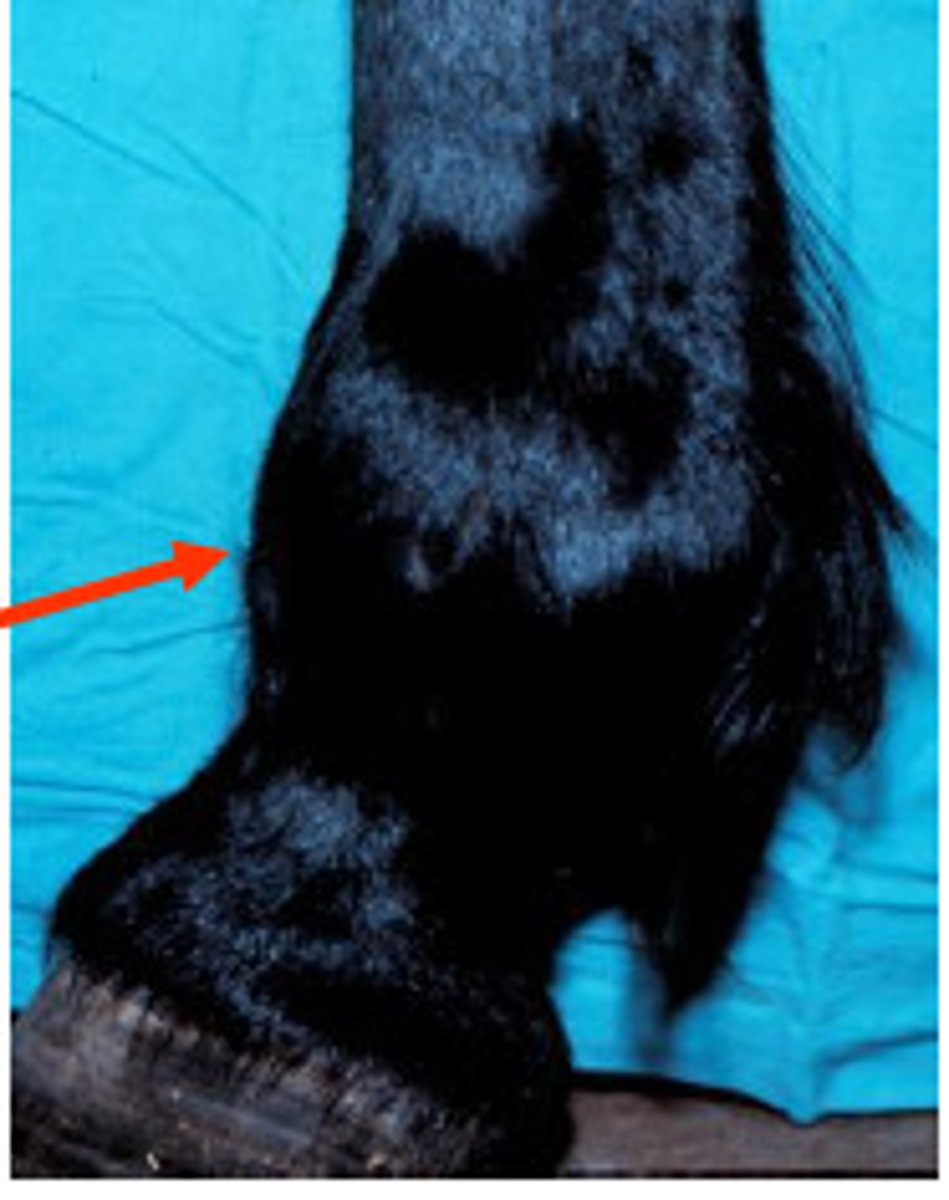
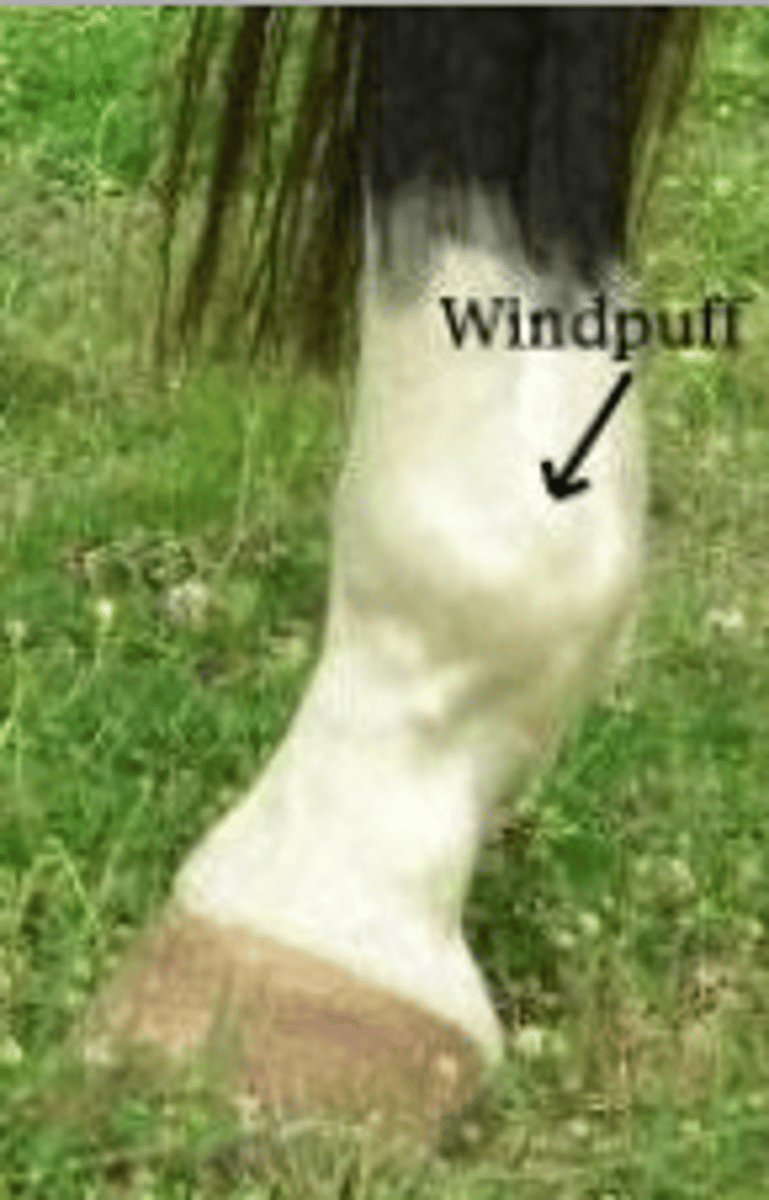
windpuffs
"Wind galls"
Enlargement of the fluid sacs around the pastern or fetlock
Can occur on any limb
Causes: Hard work or work on hard surfaces
TX: Cold packs over "puff", topical liniment
Reappears when horse is exercised
Not serious

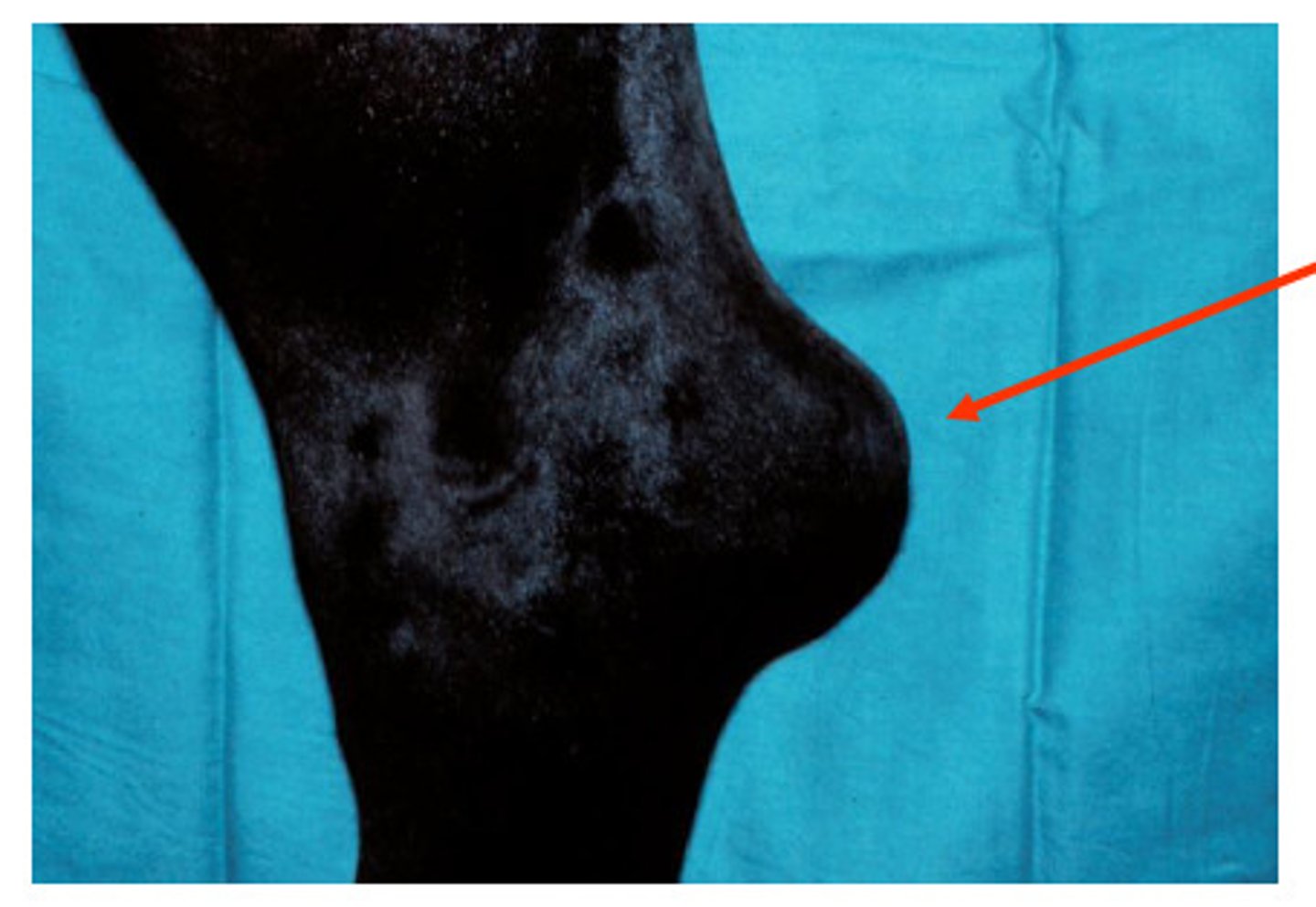
bog spavin
Filling of the natural depression of the dorsal surface of the hock; chronic distention of the jiont capsule
Causes: Faulty conformation (too straight in hock joint), trauma
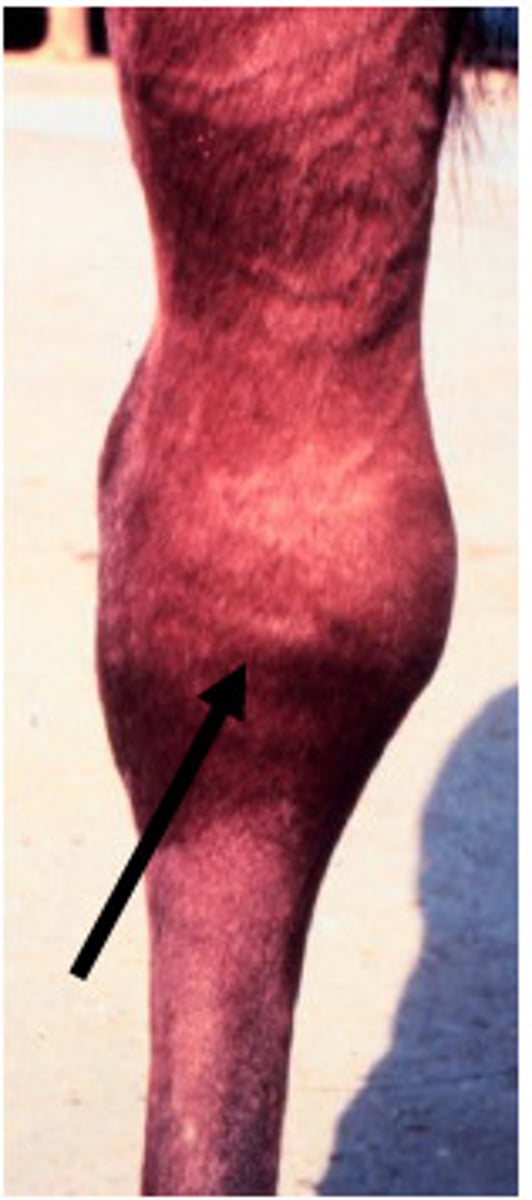
carpal hygroma
"Popped knees"
Traumatic bursitis of the carpus
Sudden onset due to strain/sprain on ligaments that hold carpal bones of knee in place
Damage to joint capsule --> fluid fills area
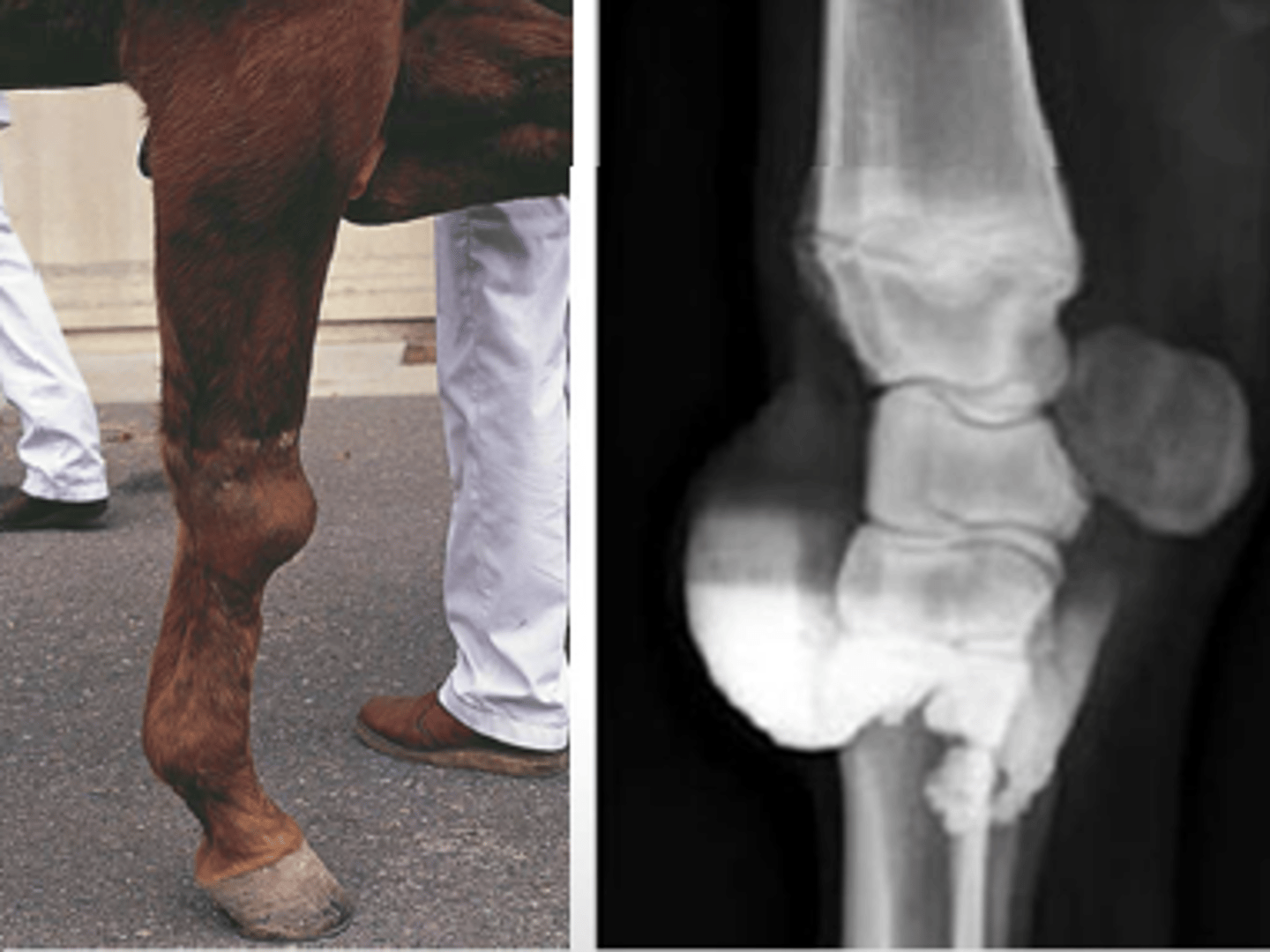
capped hock
Traumatic bursitis of the hock --> enlargement
Caused by bruising
TX: Tincture of iodine to reduce size
bowed tendon
Hemorrhage inside tendon sheath due to severe strain (superficial or deep flexor tendon)
Occurs in fatigued horses, usually on forelimbs
Thickened palmar surface of cannon
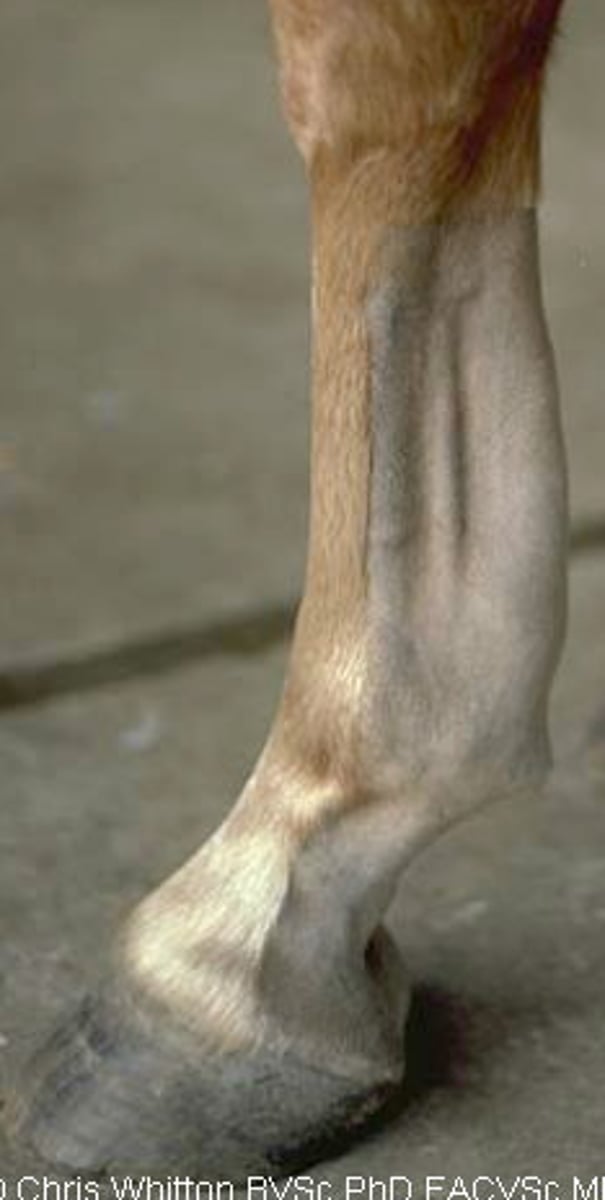
thoroughpin
Tenosynovitis of the tarsal sheath
Soft, puffy area of hock caused by trauma or tendon strain
Excess buildup of synovial fluid
TX: Pressure and massage of area
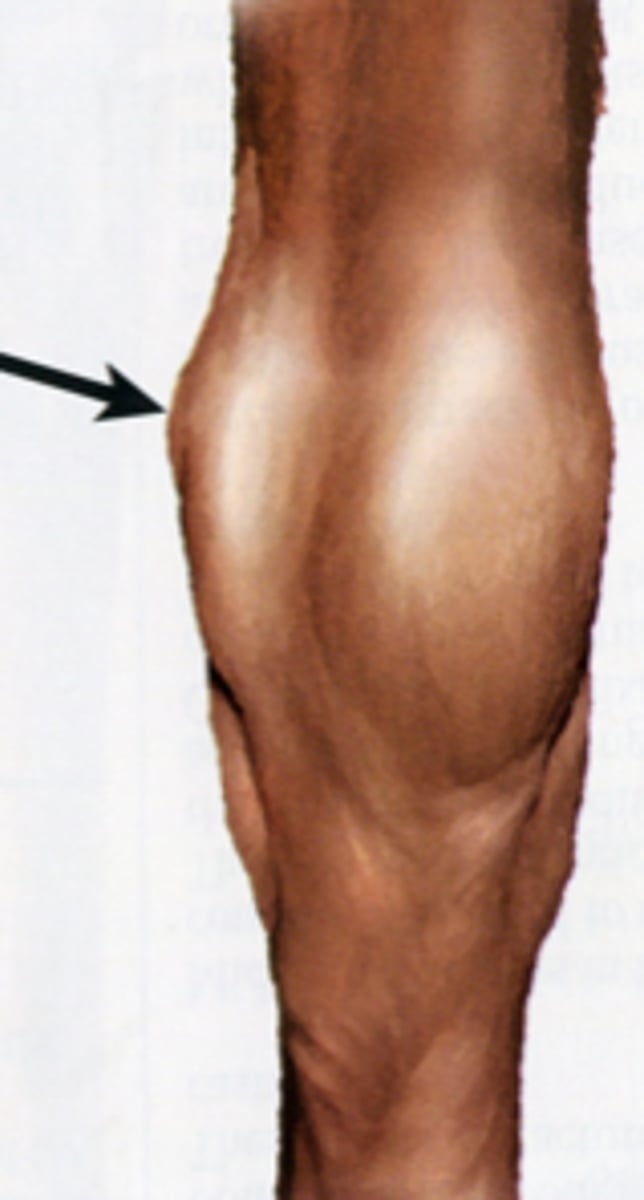
patellar luxation
Displacement of the stifle
Usually moves upward and to inside
Can be replaced
Recovery more likely if young
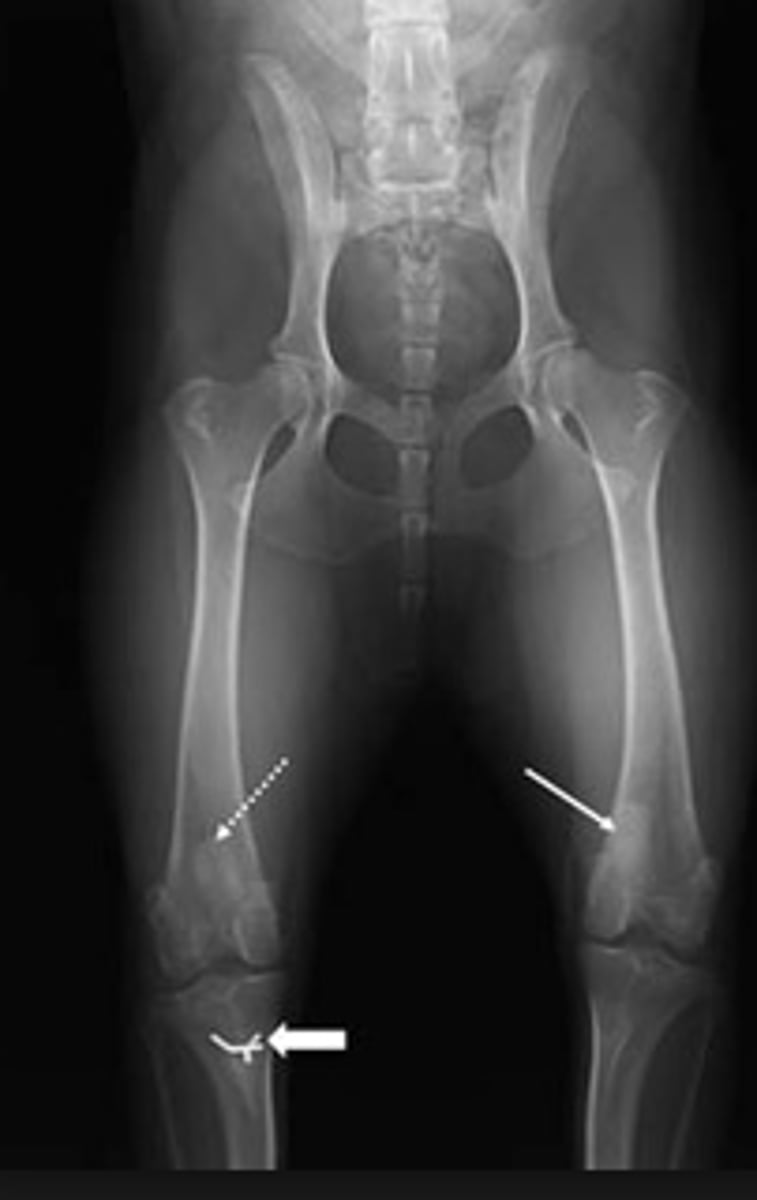
physitis
Enlargement of the growth plates of certain long bones
Affects young, rapidly growing foals (4-8 mo. old)
Unknown cause
Signs: Enlargement of distal radius, tibia, and 3rd metacarpal/tarsal
TX: Change foal's ration, limit exercise, NSAIDs
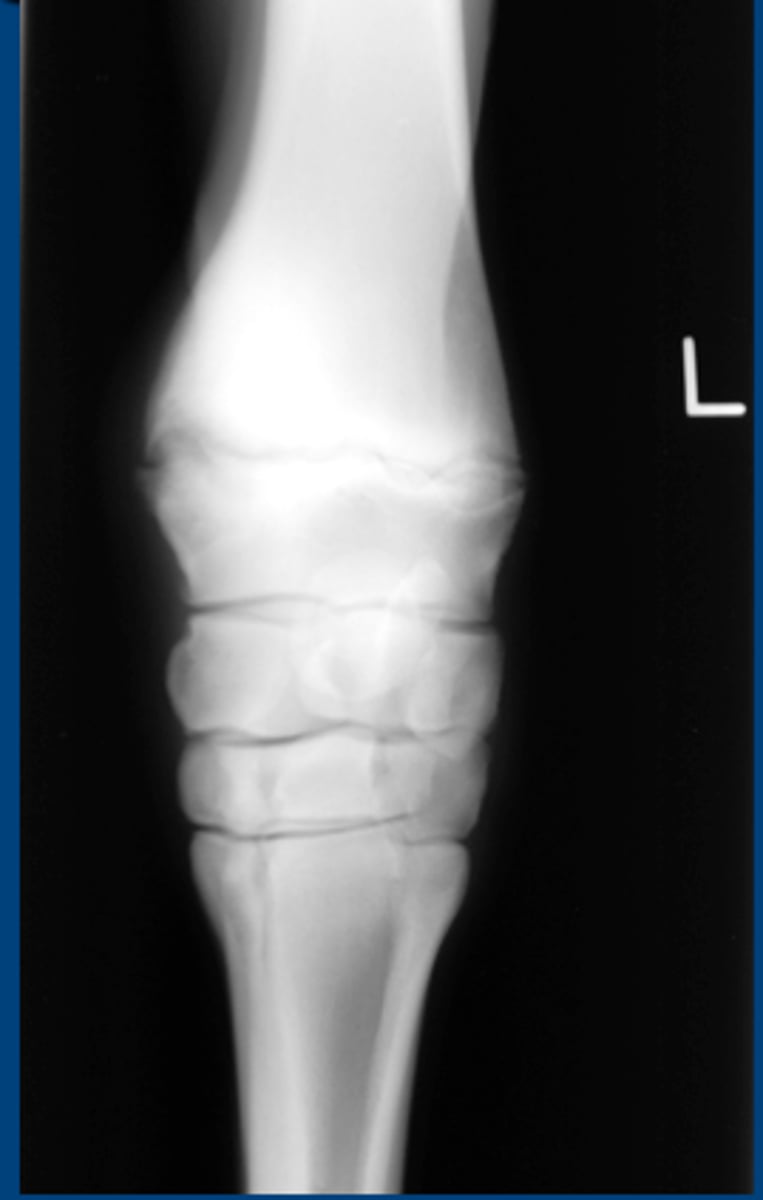
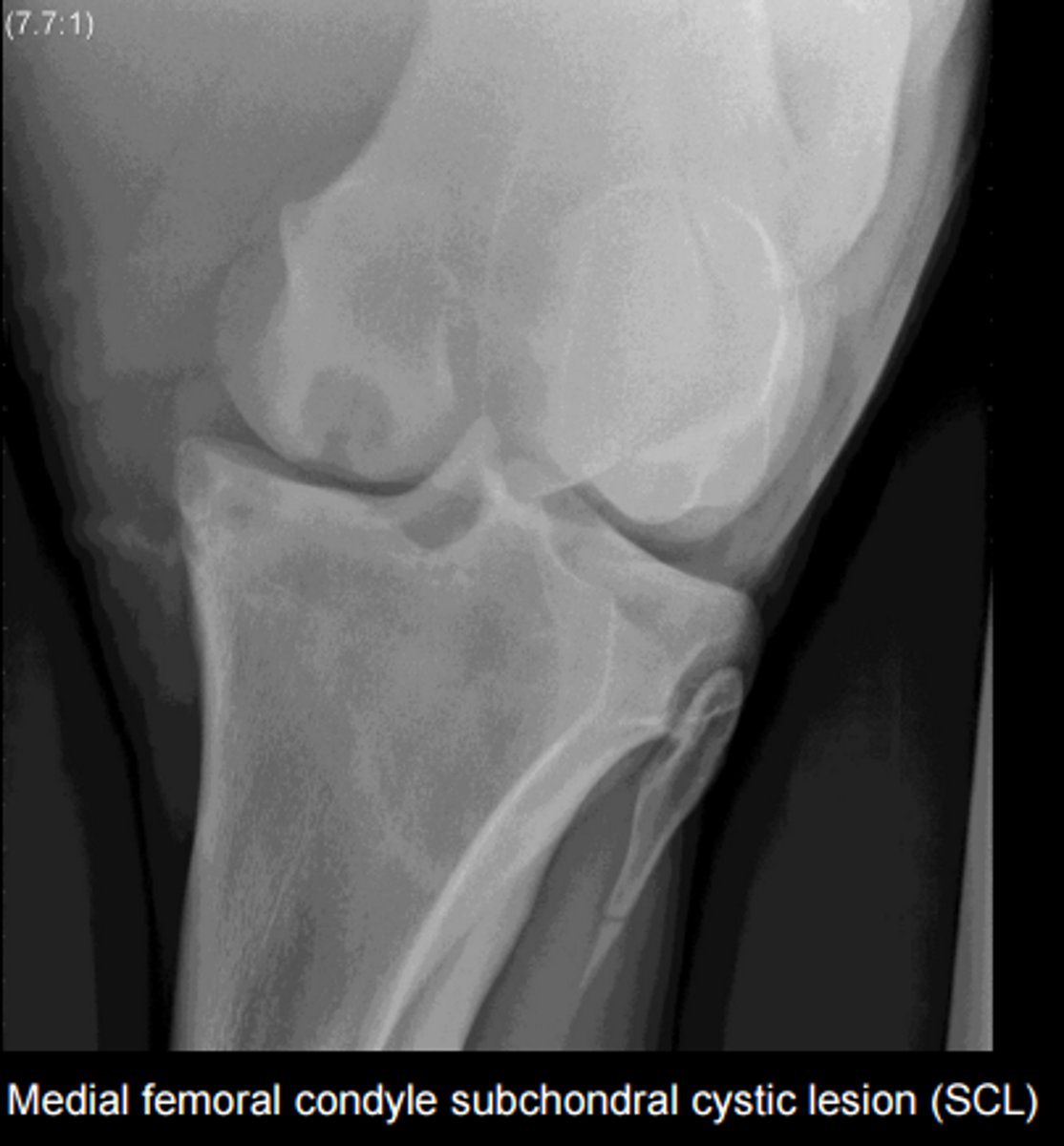
subchondral cystic lesions
Bone cysts
Articular or nonarticular
May not always produce lameness
TX: Normal bone remodeling, intraarticular meds
Usually in horses <3 y.o.
Most common sites= stifle, pastern, coffin, elbow
melanomas
Benign growths of the tail and anus, and the head of gray horses
8-% of gray horses >15 y.o.
TX: SX removal
Can become malignant and invade vital organs
recurrent uveitis
aka periodic ophthalmia, or moon blindness
Recurrent inflammation of uveal tact in one/both eyes (iris, ciliary body, choroid)
Causes: Bacterial/viral infection, parasites, trauma; LEPTOSPIROSIS
Appaloosas predisposed, Standardbreds at reduced risk
Signs: Blepharospasm, conjunctival/ciliary injection, lacrimation, vascularization, hypopyon, swollen dull iris, vitreal inflammation,
Can cause secondary conditions of eye
Common cause of cataracts
DX: Clinical signs, serum for lepto. titration, conjunctival biopsy
TX: Reduce inflammation (corticosteroids), ABX
Prognosis variable

roaring
Laryngeal hemiplegia
Whistling/wheezing when respiration is increased
Usually associated with inspiration
Causes: Broken rings in trachea, paralysis of muscles controlling vocal cord tension
Can usually be surgically corrected
wobbler syndrome
Compression of spinal cord in neck region
Identified between birth and 4 y.o
Incoordination begins in hindlimbs and becomes worse
True wobblers will not improve
May be genetic
Can be caused by equine degenerative myeloencephalopathy or deficiency of vitamin E during rapid growth phase
sarcoids
cutaneous tumors of fibroblastic origin
Linked to bovine papillomavirus type 1/2
Can develop anywhere; appearance varies with type
6 recognized types
DX: Histopathology
TX: SX excision (recurrence likely), chemo, imiquimod, irradiation
toxins
Ionophores, Yew poisoning, poison hemlock, red maple leaf, oleander toxicosis, blister beetles, Bracken fern, yellow star thistle, tansy ragwort
Signs vary, but usually include neuro, CV, MS, colic
parasites
Includes large/small stongyle, pinworm, bot flies, ascarid/roundworm, stomach worm, threadworm, tapeworm, apicomplexa, lice, flies, mites, ticks
persistent patent urachus
Urine passes through urachus after 48 hrs of age
TX: Keep umbilicus clean and dry, antiseptics, monitor rectal temp, ABX, closure of urachus
septic foal
Neonatal bacterial septicemia
Most common cause of morbidity in foals from birth to 7 d.o.
Mortality- 75%
Cause: Failure of passive transfer of antibodies
Can be acquired before or after birth
Usually gram - (E. coli) or Strep/Staph
May be multisystemic
DX: Blood culture, aerobic/anaerobic culture
TX: Systemic ABX (after C/S results), antiulcer meds
premature foals
Delivery before gestational age of 320 days
Signs; Small size/BW, weakness, delayed time to stand, poor suckling reflex, silky hair coat, floppy ears, prominent forehead, hyperextension in fetlocks
No specific therapy
dummy foals
Neonatal maladjustment syndrome, or asphyxia
Foals lose suckling reflex by 24 hrs old
Causes: Low O2 levels during birth (cerebral edema and hemorrhage)
Signs: Neuro
TX: Supportive care
Anaplasma
Tick borne bacterial disease similar to Lyme, but causes higher grade fever
Clear leg edema present