BMS 124: Enzymes
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
20 AA
how many amino acids are in the universe
Amino acids that we cannot produce ourselves and must get from environment
What are essential amino acids
Amino acids that we produce ourselves
What are non essential amino acids
Amino acid
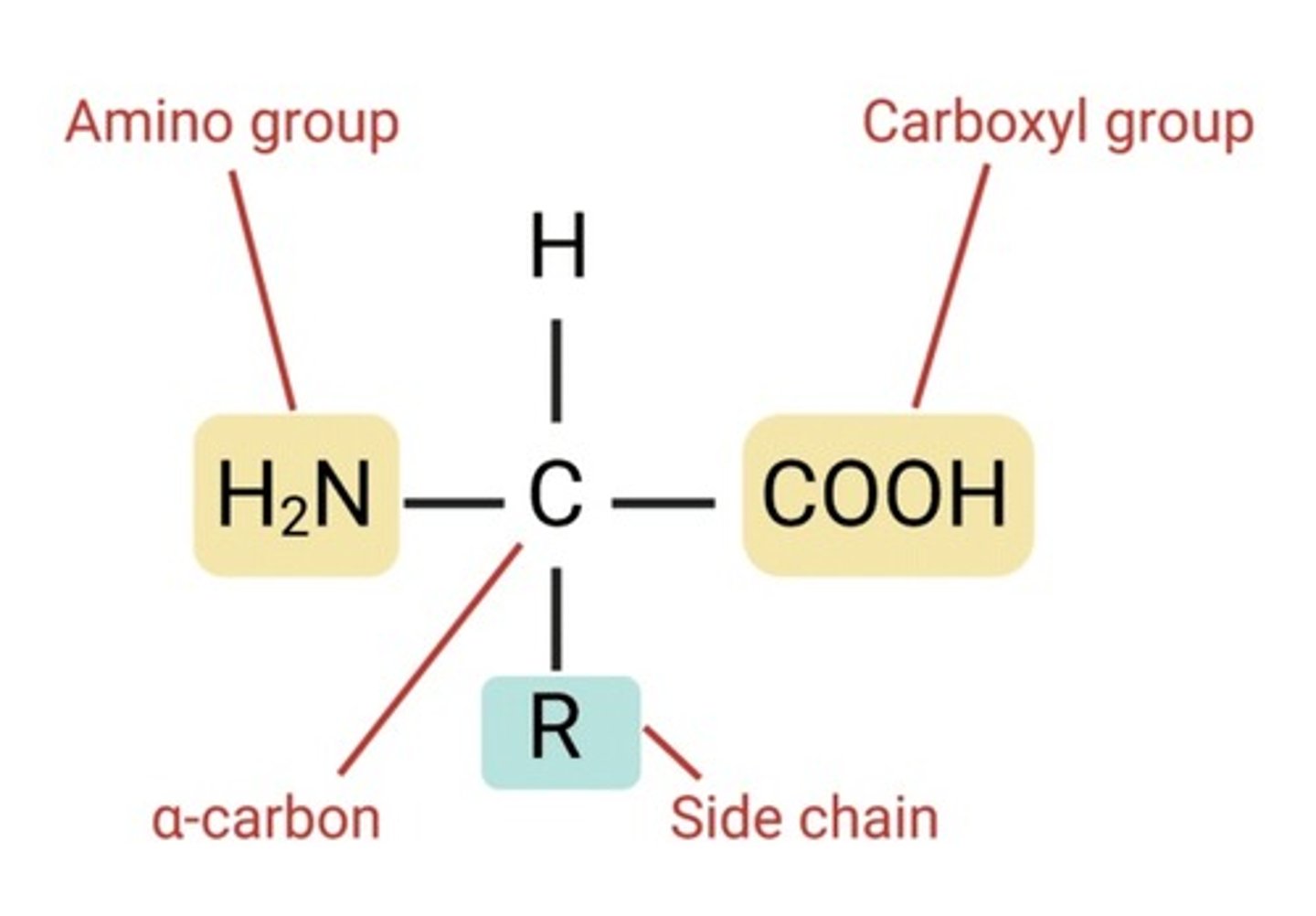
The ionizable groups (amino, carboxyl, R groups) and pH of environment
What influences amino acid charge
the presence of a central carbon (the alpha carbon) bonded to four different groups, making the molecule non-superimposable on its mirror image.
What is chirality in amino acids
Covalent bond between two amino acids
What is peptide bond
Primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids (unable to be changed by heat, acid etc)
Secondary structure
the folding of polypeptide chain as a result of hydrogen bonding between peptide groups along its length (alpha helix beta sheet)
Tertiary structure
the further twisting, folding and coiling of polypeptide chain as a result of interactions between the R group, result of intramolecular forces
Quaternary structure
The particular shape of a complex, aggregate protein, defined by the characteristic three-dimensional arrangement of its constituent subunits, each a polypeptide.
covalent bond
Bonds in primary structure
Hydrogen bond
Bonds in secondary structure (backbone of carbonyl and amide groups)
Hydrogen bonds - between side chains.
Ionic bonds (salt bridges) - between charged side chains (e.g. Lys⁺ and Asp⁻).
Hydrophobic interactions - nonpolar side chains cluster away from water.
Van der Waals forces - weak attractions between closely packed atoms.
Disulfide bonds (covalent) - between cysteine residues (S-S linkages).
Bonds in tertiary/quaternary structure
Alzheimer's disease
Accumulation of insoluble and neurotoxic Aβ peptides in the brain is the pathogenic event in
Prion disease
Normal prion protein (PrPc) contains α-helix while
Infectious PrPsc contains β-sheets, which resists to proteolytic degradation and form insoluble aggregates.
α-helix, β-sheets
Normal prion protein (PrPc) contains ____ while
Infectious PrPsc contains ______, which resists to proteolytic degradation and form insoluble aggregates.
What is an enzymes major role in biochemical reaction
An enzyme speeds up a biochemical reaction by lowering its activation energy.
What are properties of an enzyme
Enzymes are highly specific, reusable, work best at optimal pH and temperature, and speed up reactions by lowering activation energy without being consumed.
Transition state of uncatalyzed reaction
Red
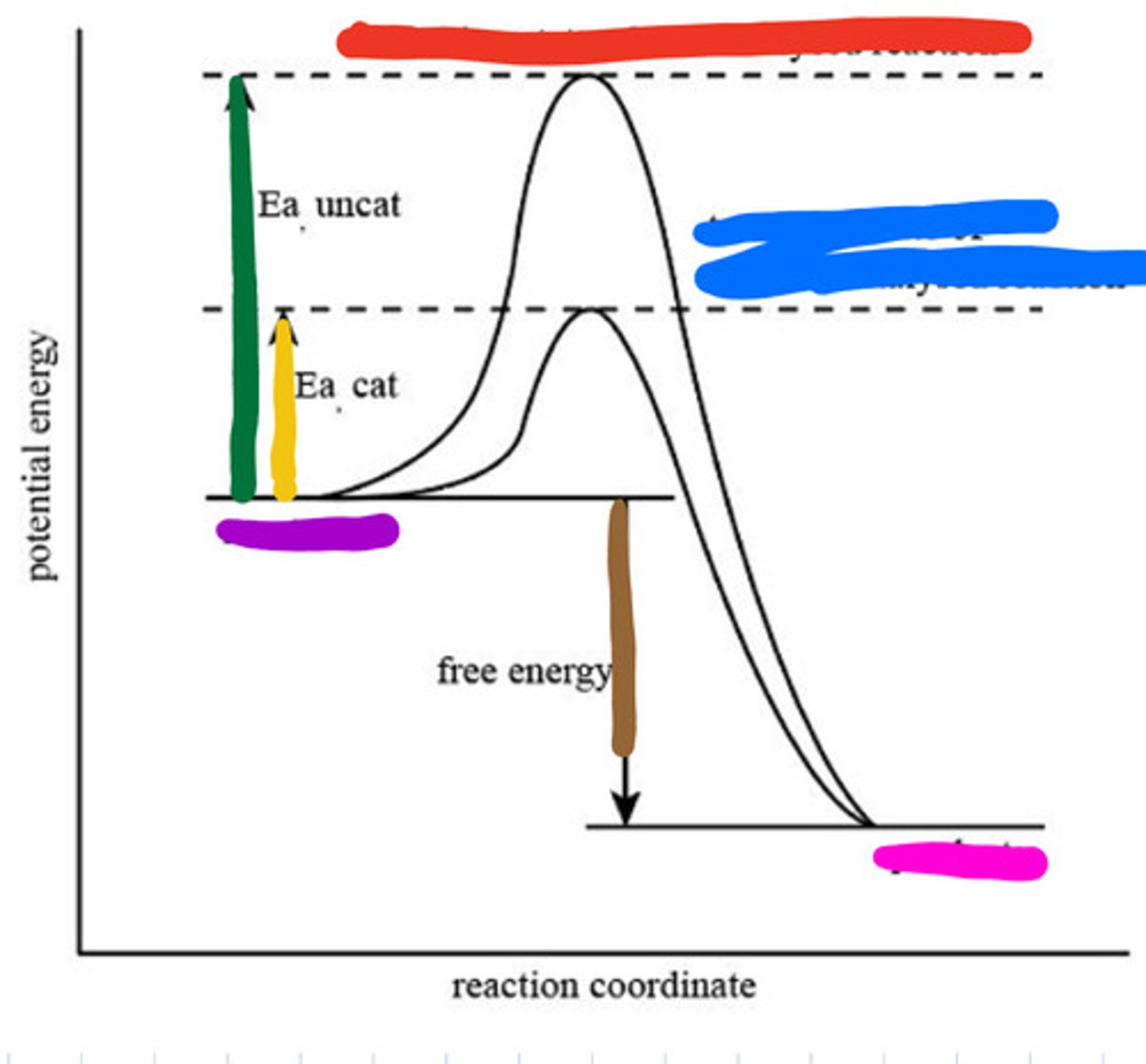
Transition state of catalyzed reaction
Blue
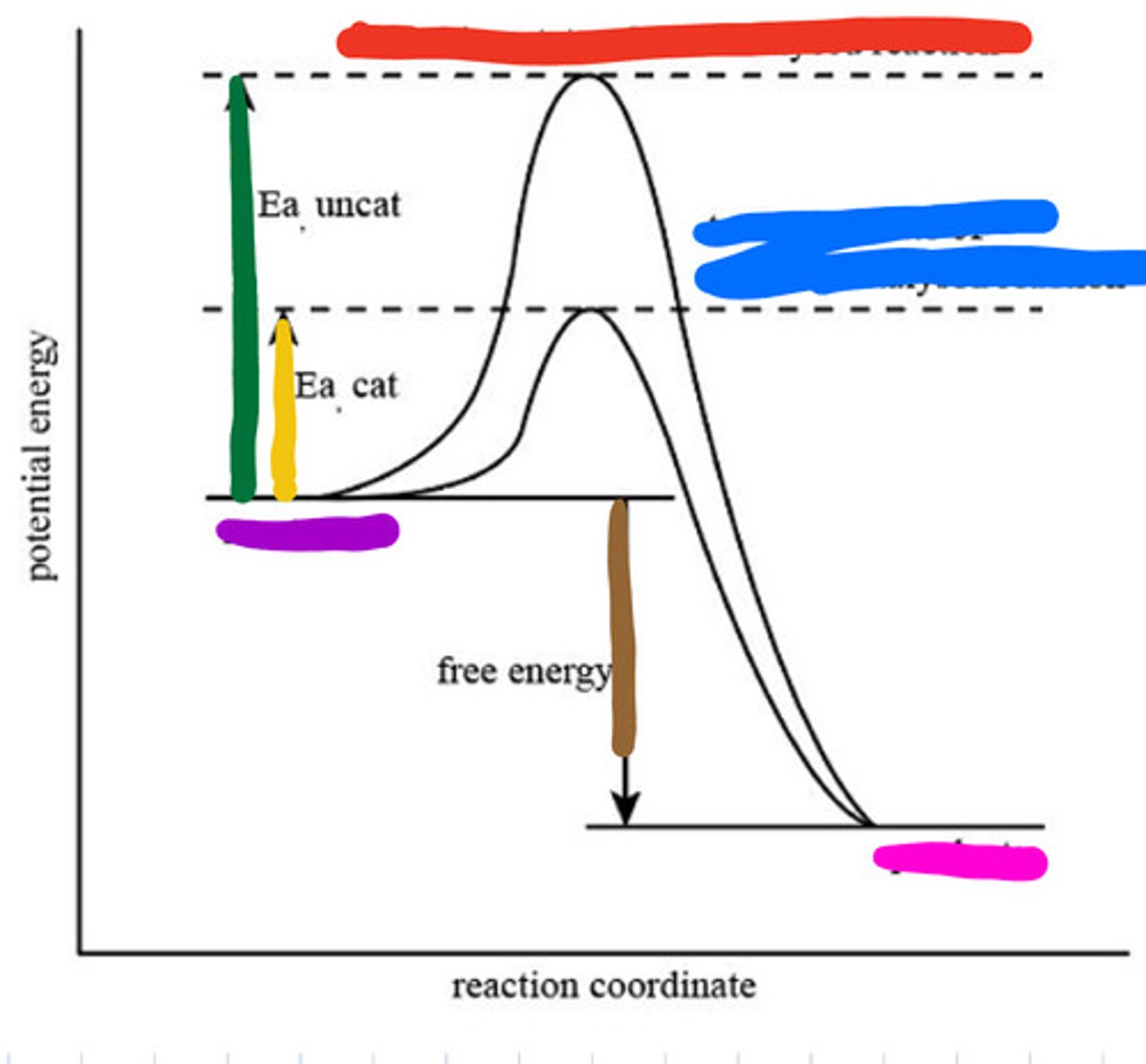
Substrate
Purple
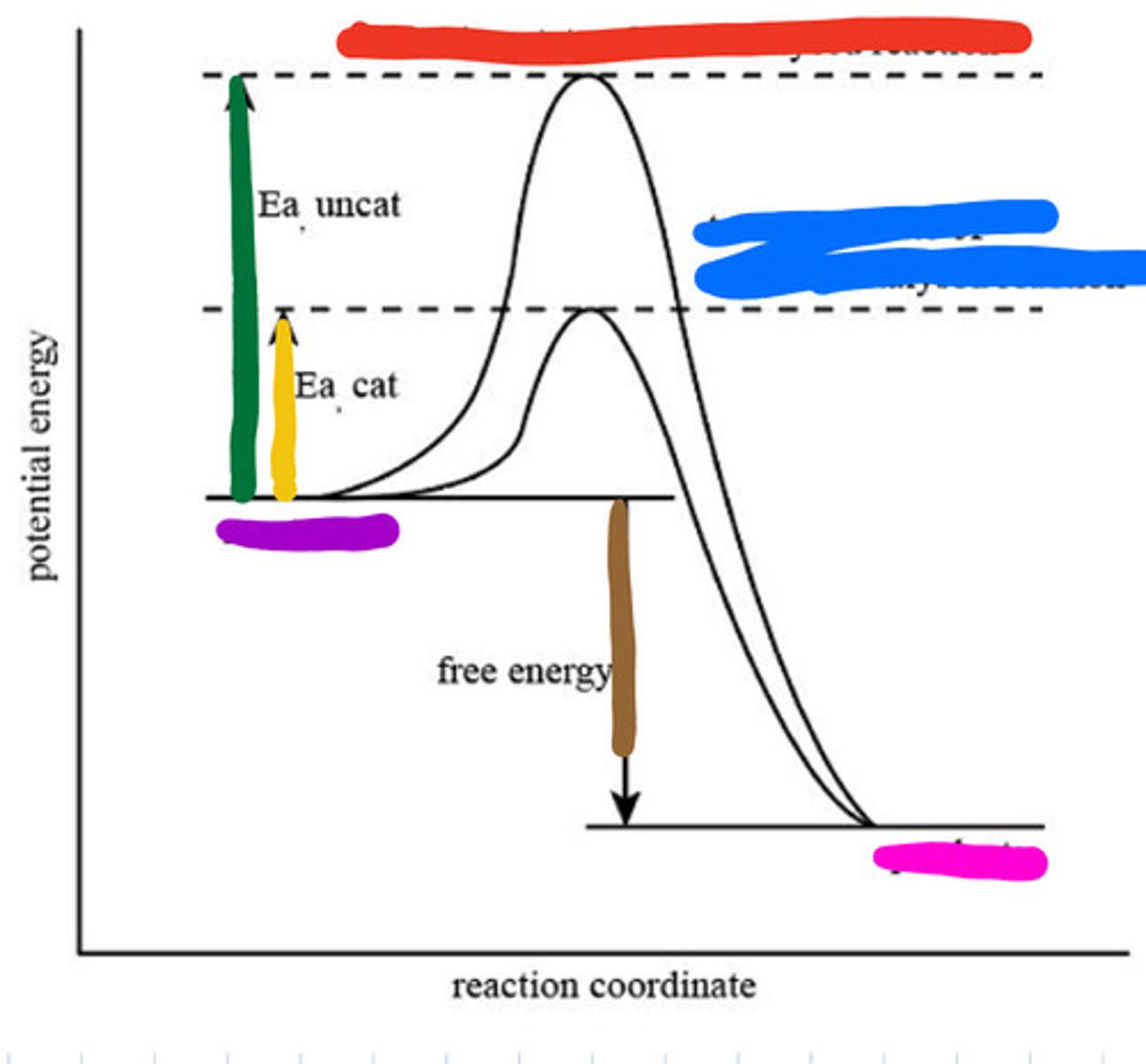
Product
Pink
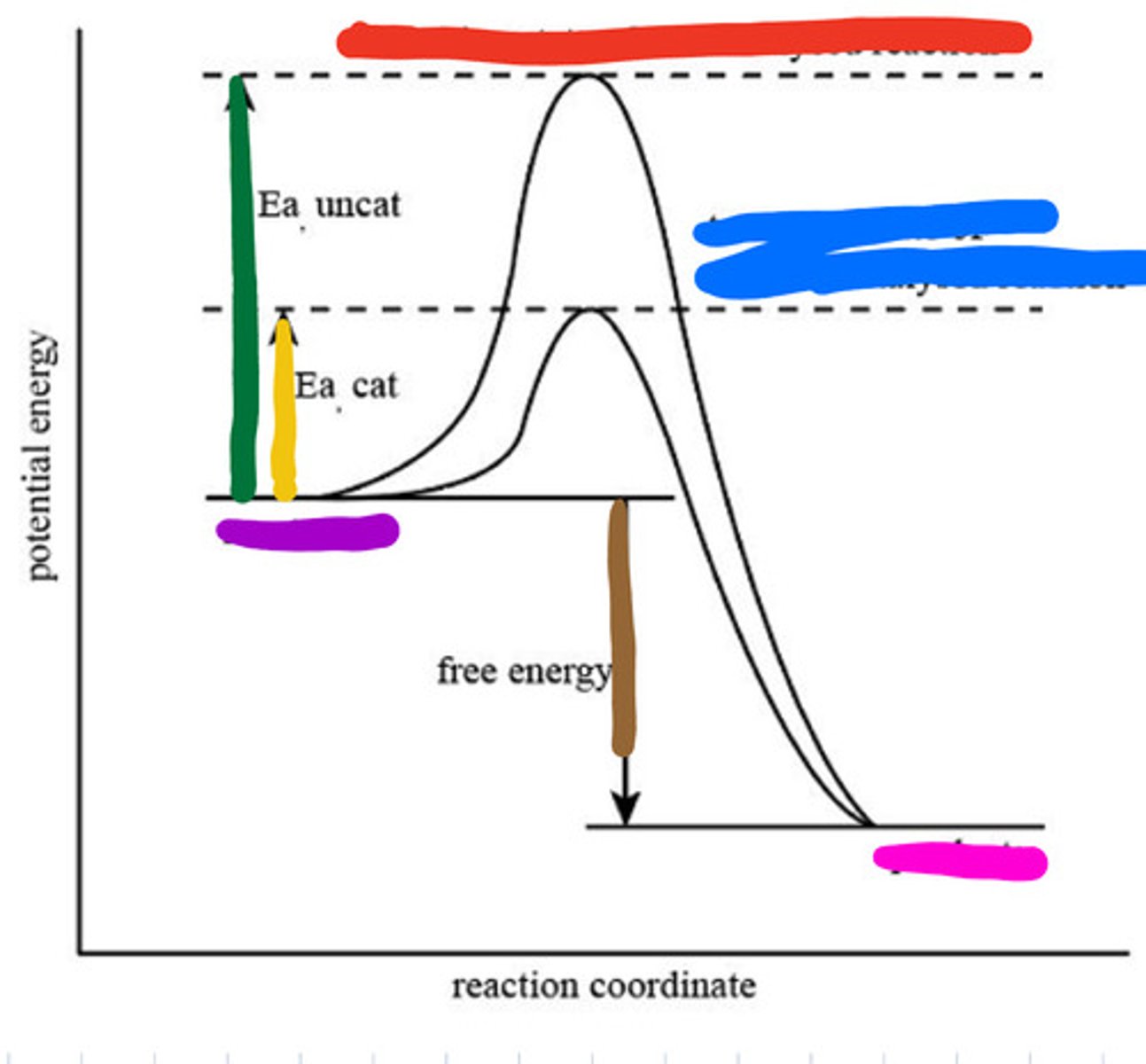
Activation energy for uncatalyzed
Green
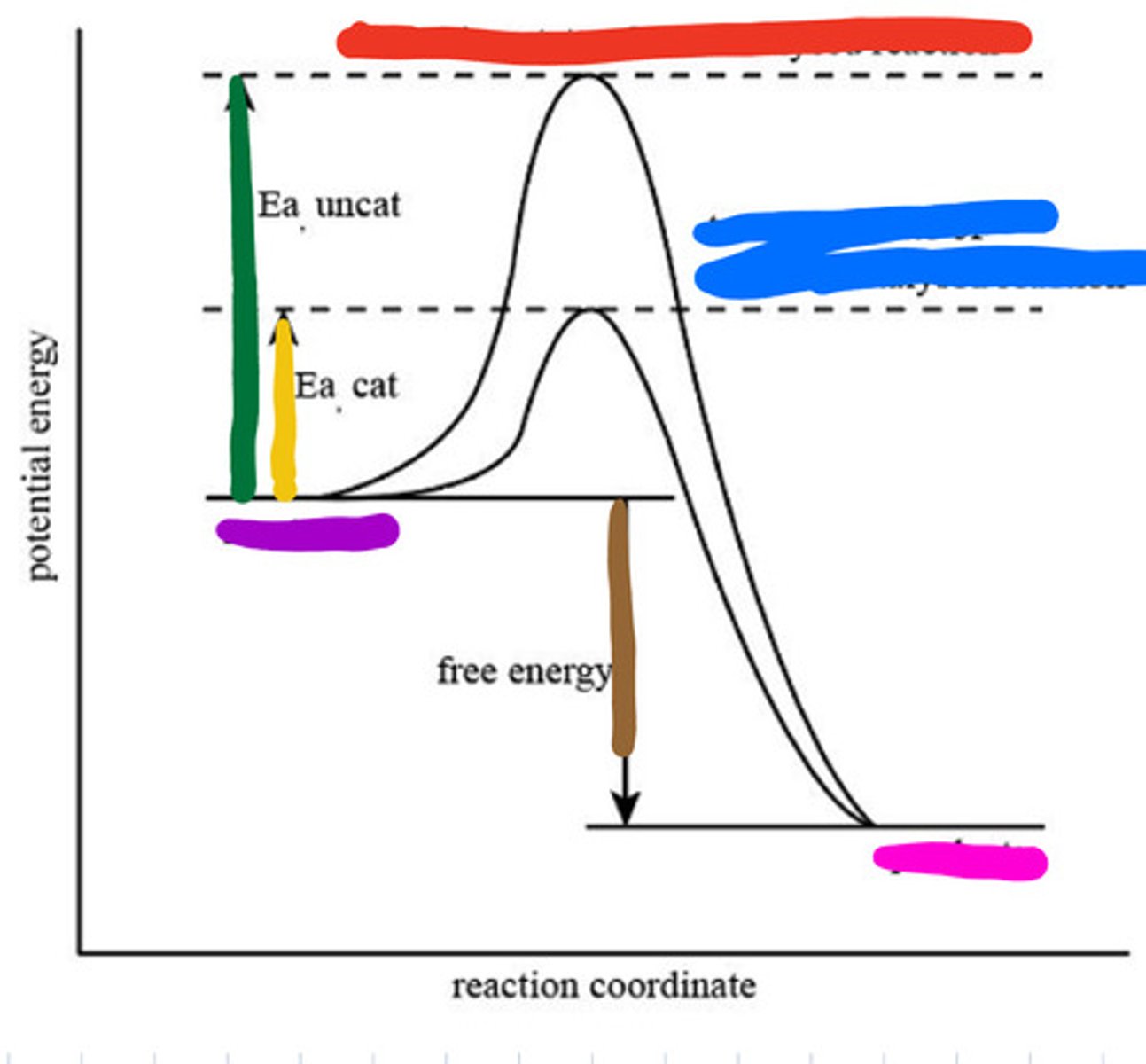
Activation energy for catalyzed
Yellow
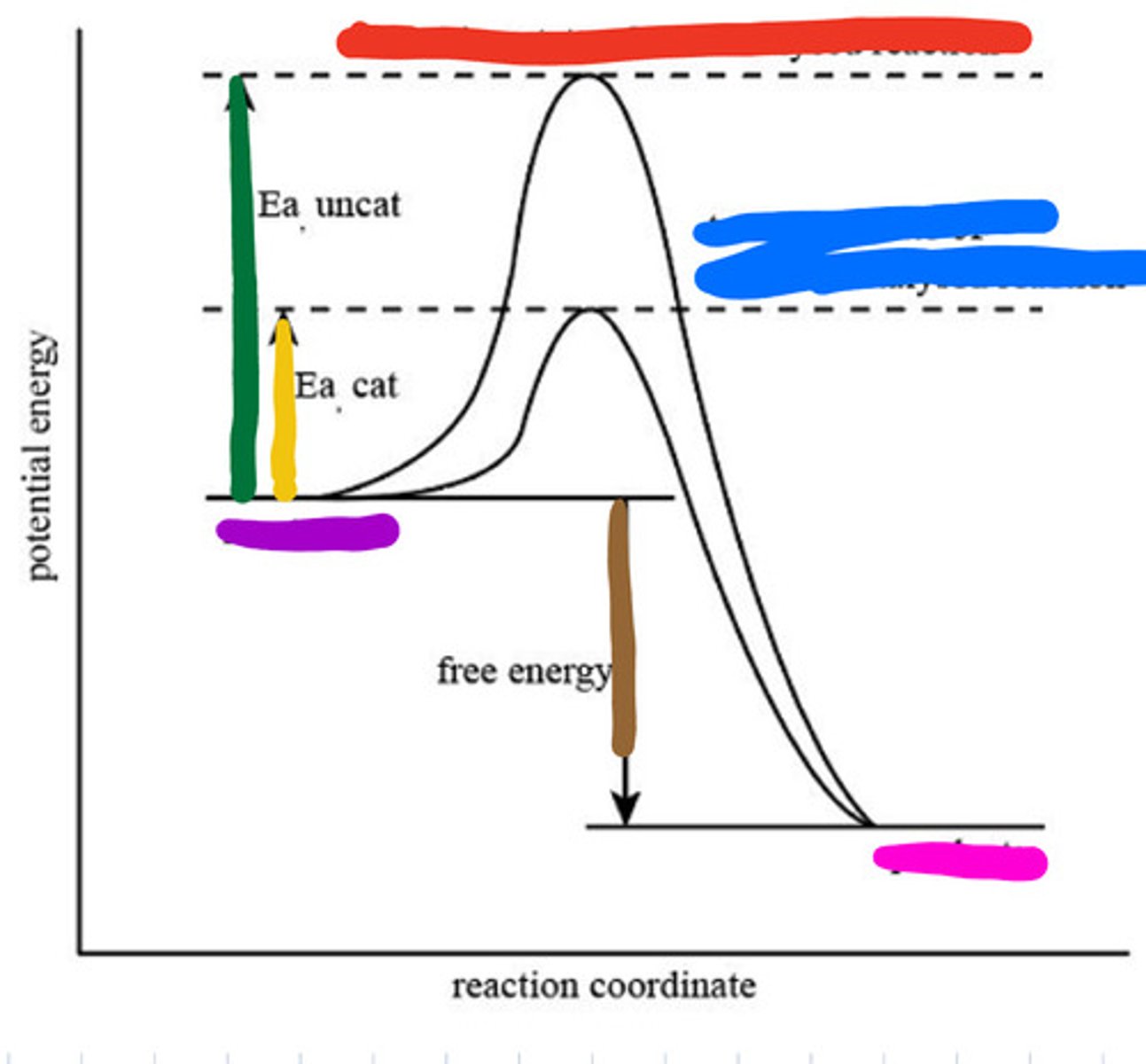
Reaction energy
Brown
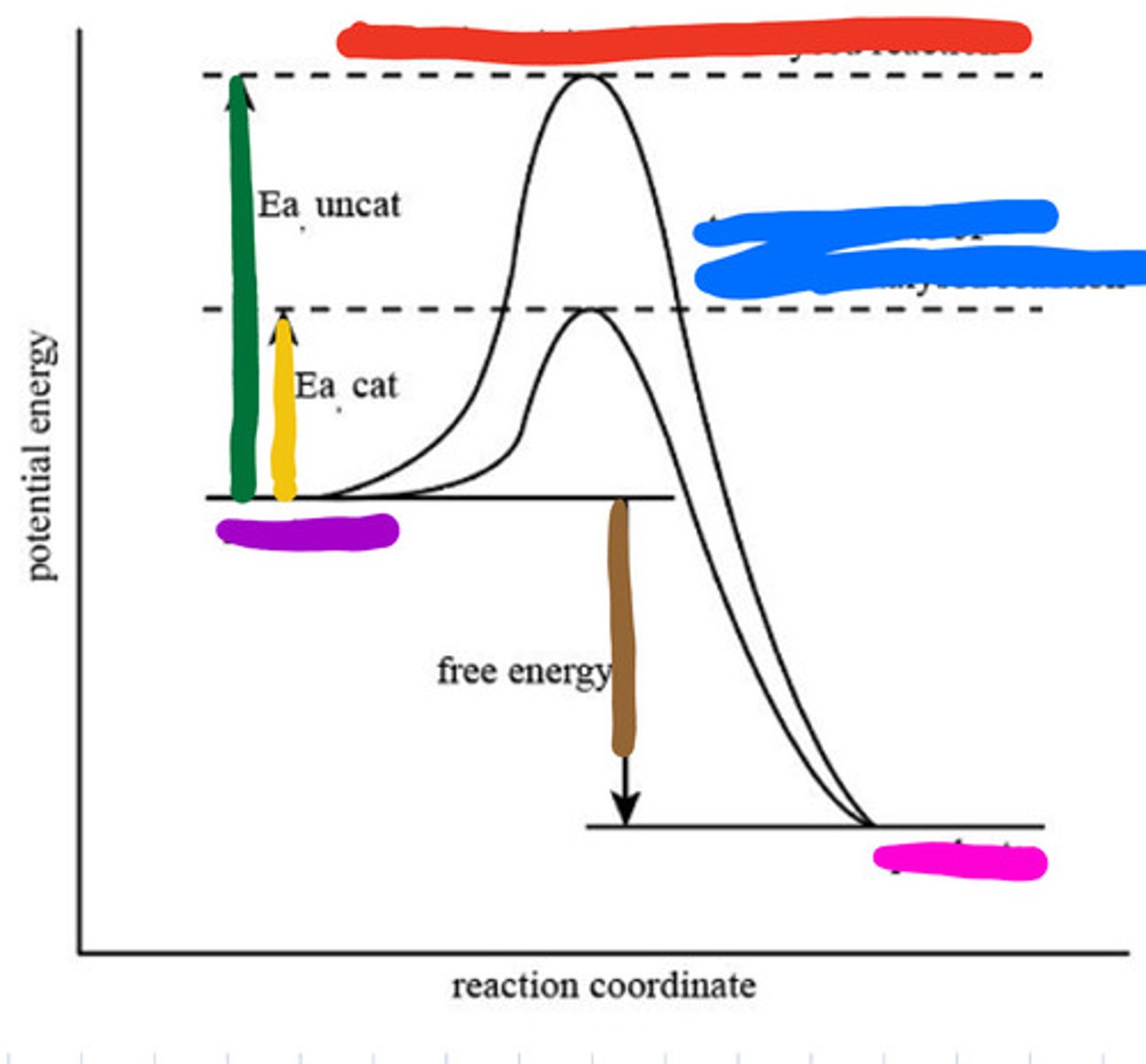
Active site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
catalytic efficiency
Kcat/Km
Kcat
turnover number (molecules catalyzed per second in optimal conditions)
Vmax / [E]
Km
Substrate concentration at 1/2 Vmax
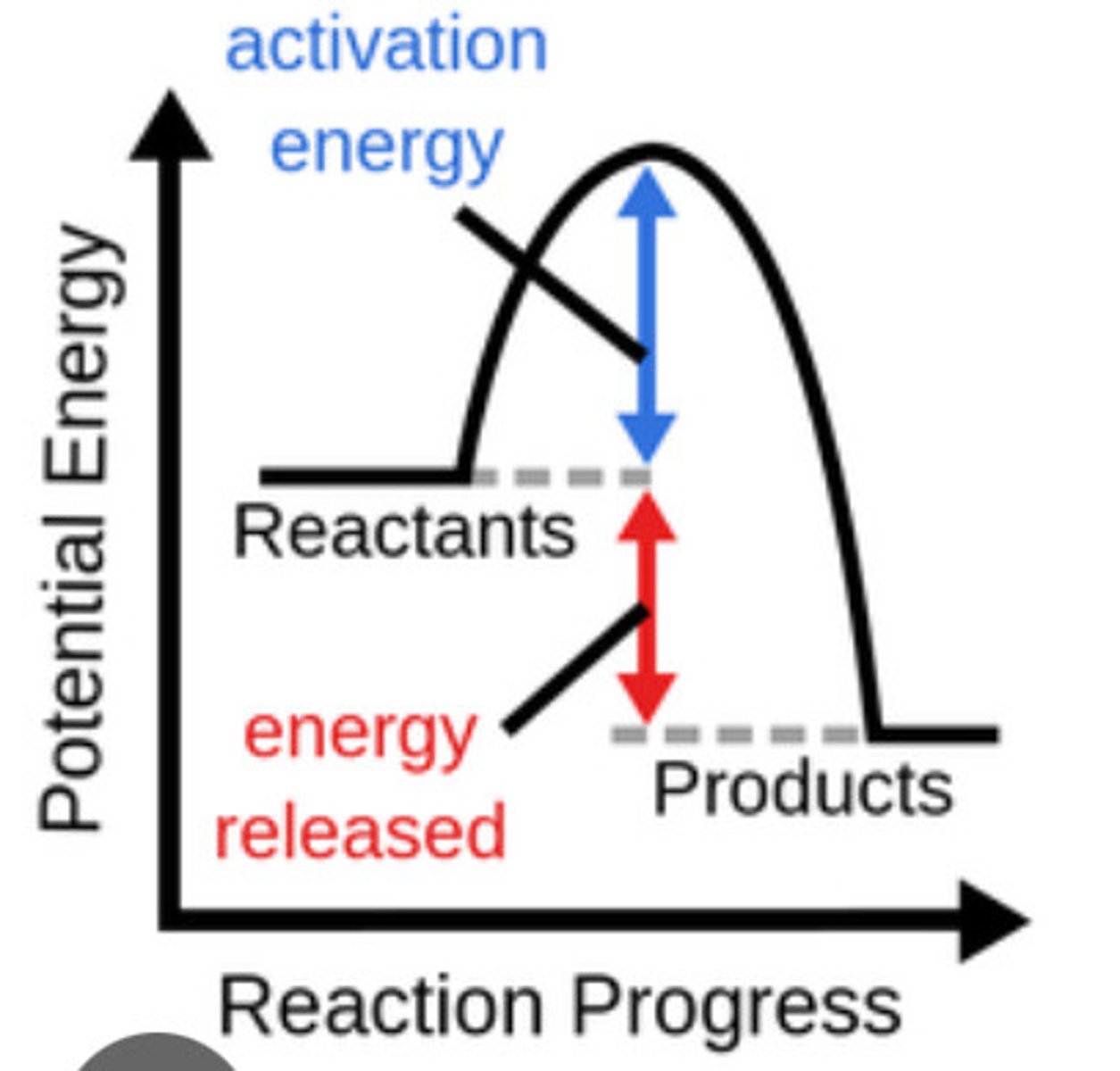
Exothermic reaction
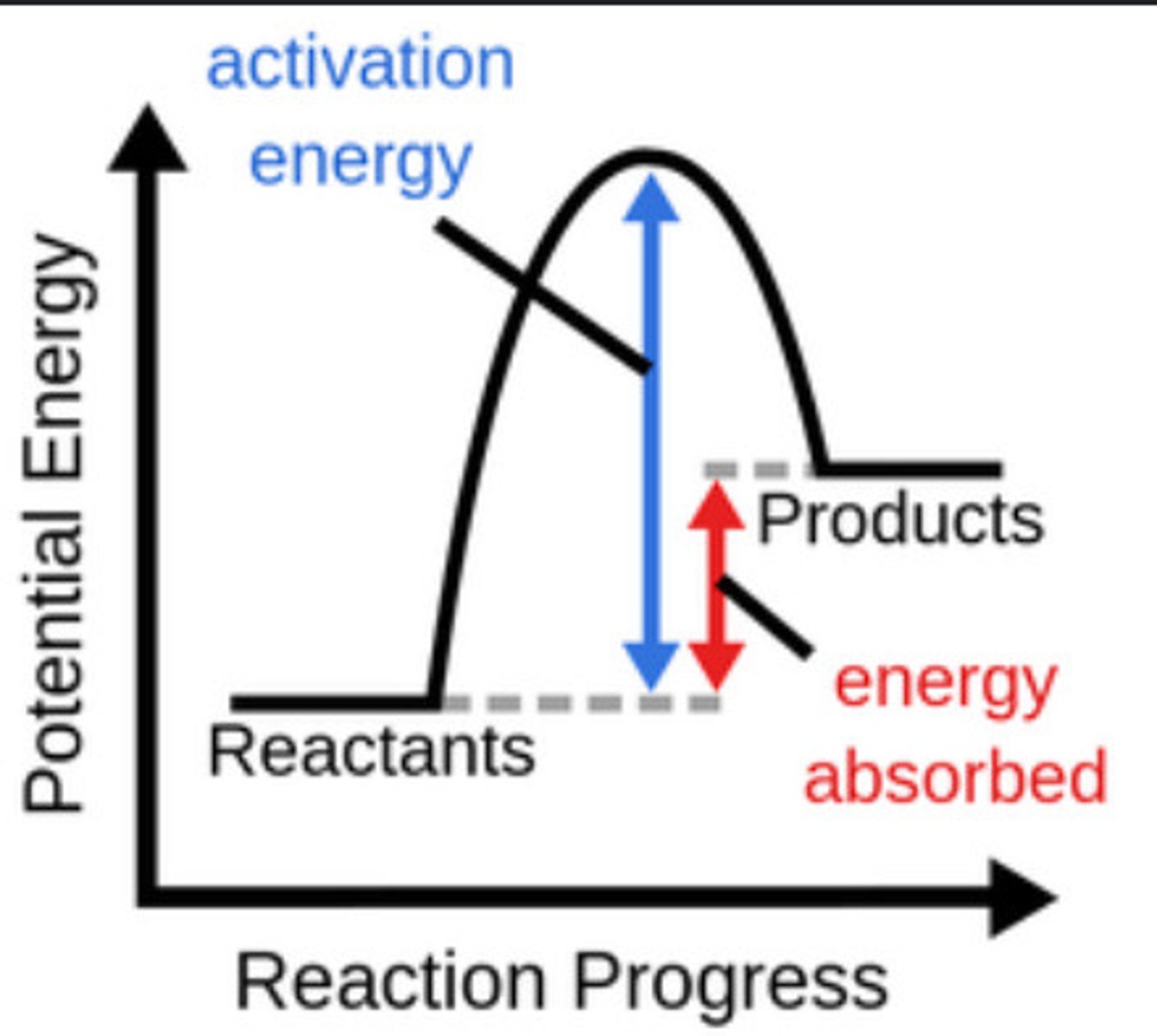
Endothermic reaction
Specificity
The ability of an enzyme to choose the exact substrate from a group of similar chemical molecules.
• Only one substrate is complementary to the active site.
Holoenzymes
enzymes with their cofactors
Regulation of enzyme
-enzymes can be activated or inhibited so the rate of product formation responds to the need of the cell
-feed back inhibition of metabolic pathway
-most rate limiting steps are at the beginning
Cytoplasm
Enzymes are located in the
Enzyme Kinetics
The study of how fast enzyme-catalyzed reactions occur and how they're affected by factors like substrate or enzyme concentration.
Michalis-Menten Equation
Vo = (Vmax x [S])/(Km + [S])
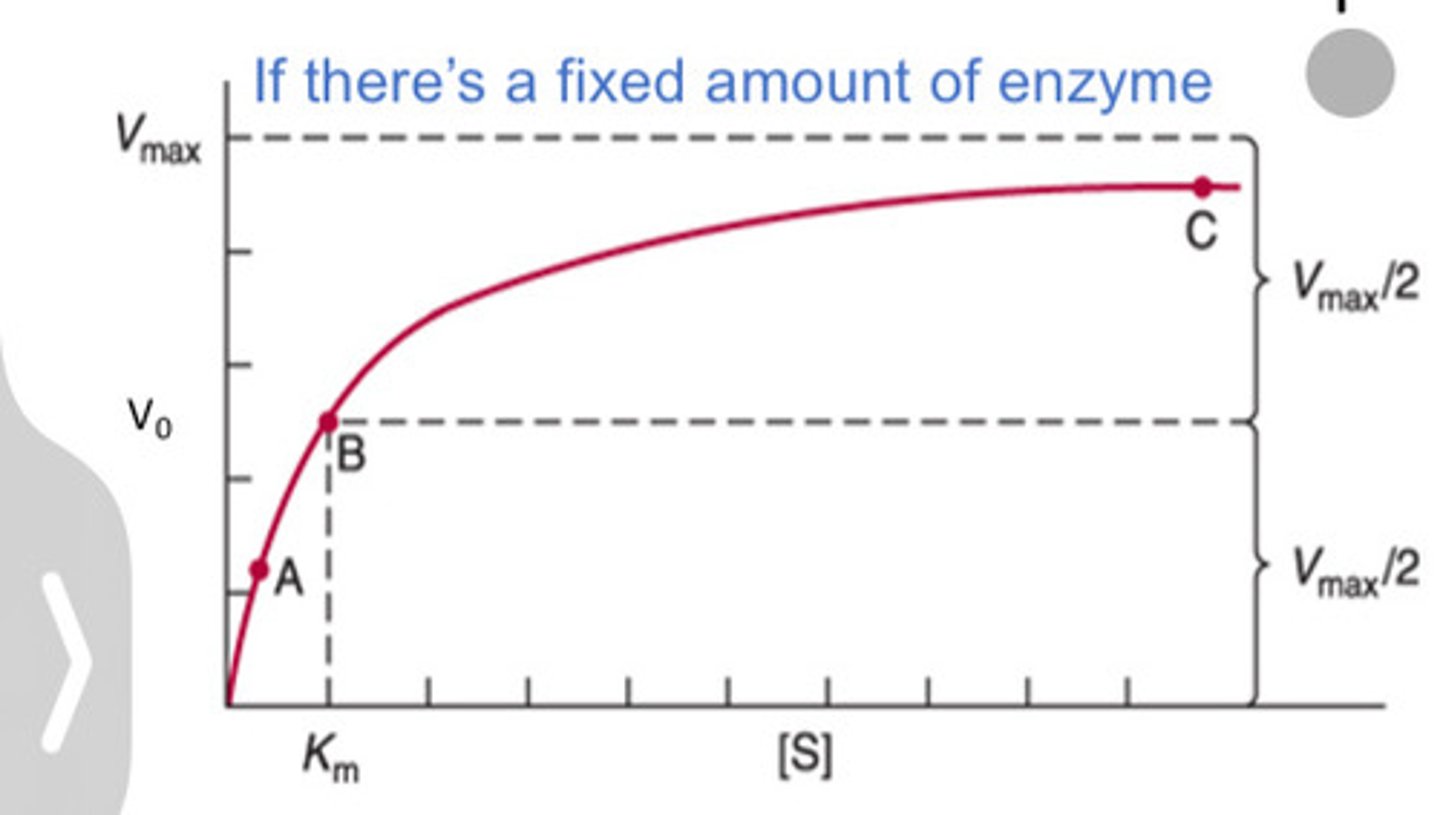
Km
Substrate concentration at 1/2 Vmax
V max
The maximum rate of the reaction when all enzyme active sites are saturated.
Lower
____ Km means higher affinity between enzyme and substrate
Lineweaver-Burk Plot
the double reciprocal graph of the Michaelis-Menten equation
Reaction rate
The MM equation solves for the _____ (v) of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction based on substrate concentration, Km, and Vmax.
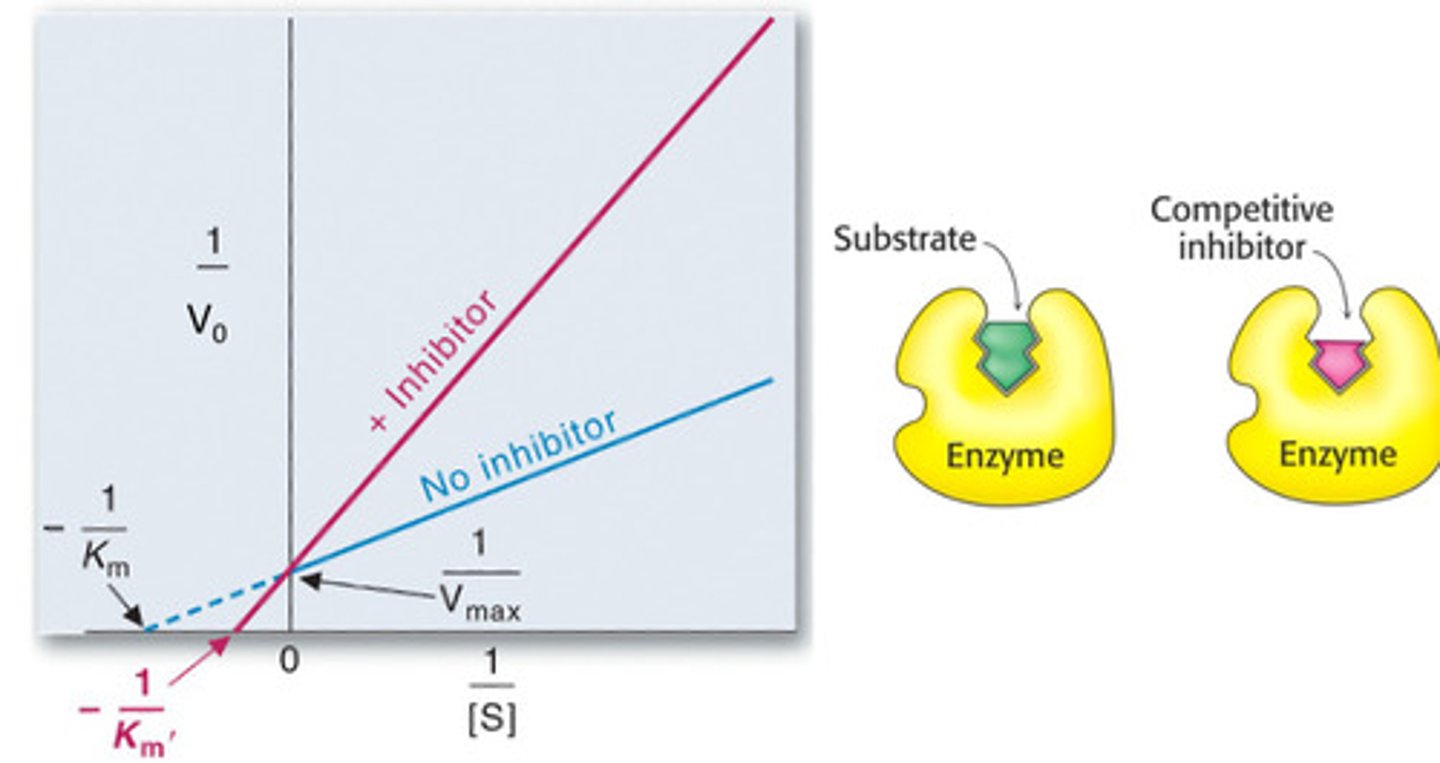
Competitive inhibition
Km increases, Vmax stays the same
Increases
Increasing enzyme concentration _________ Vmax but does not change Km.
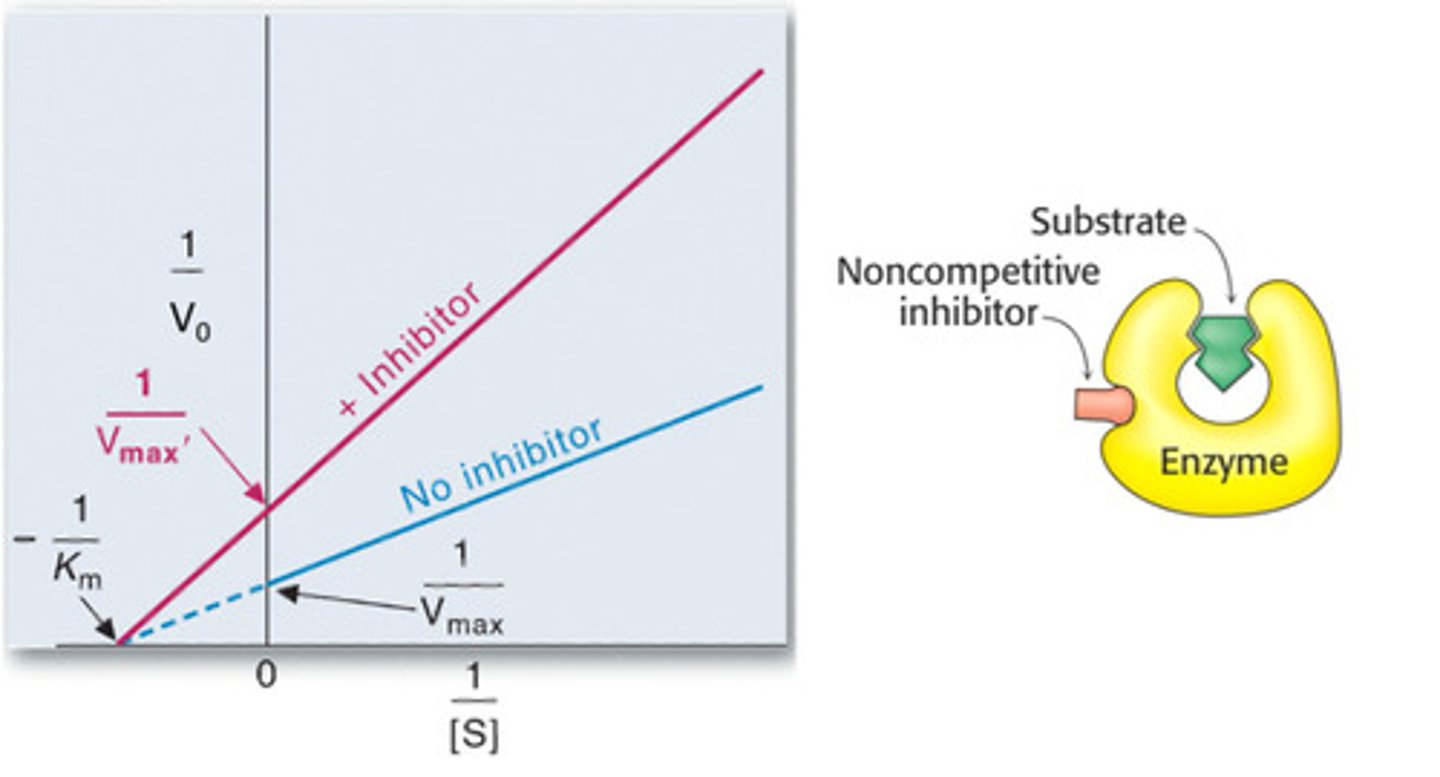
Non competitive inhibition
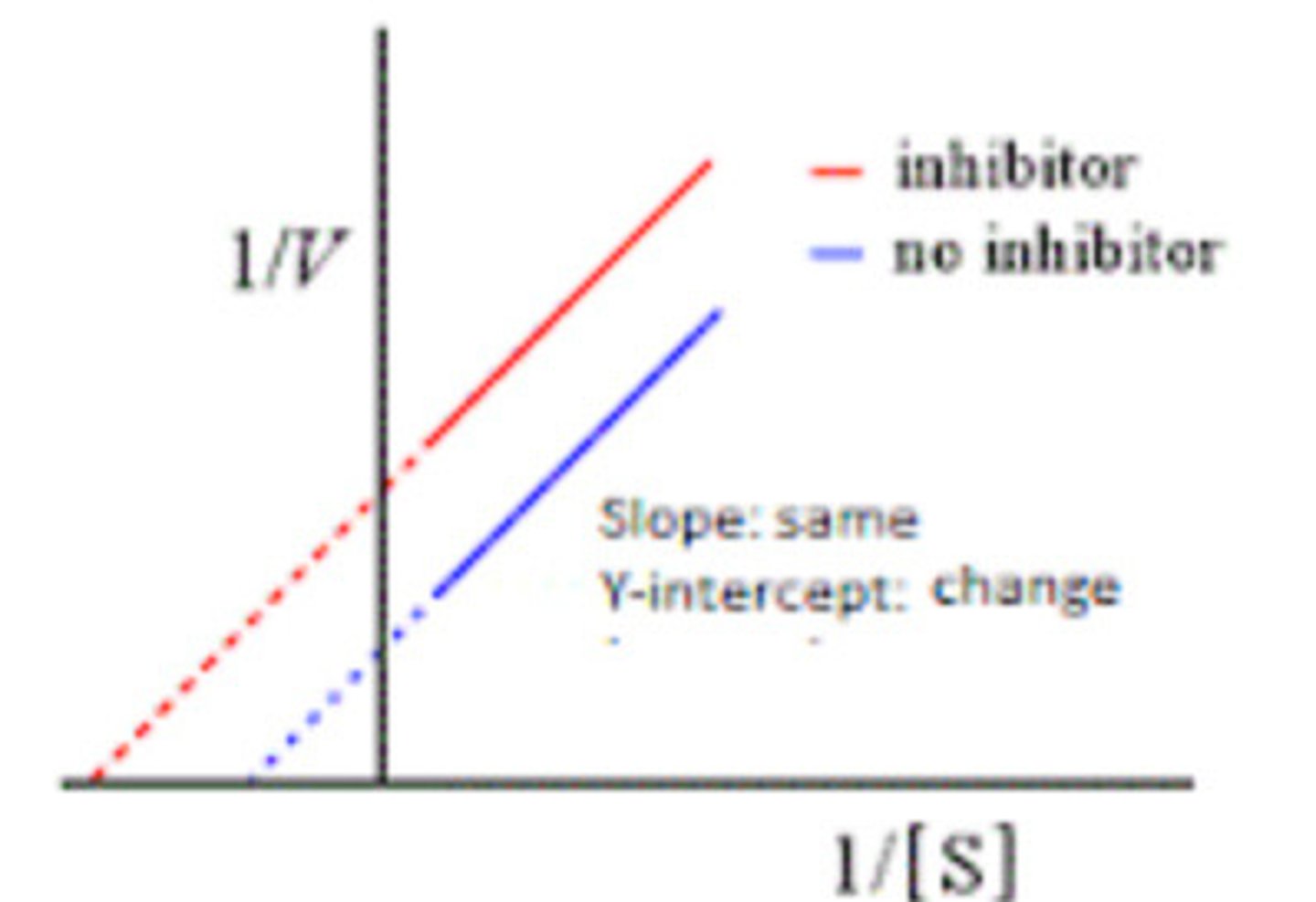
Km unaffected, Vmax reduced
Uncompetitive inhibition
inhibitor binds only to enzyme-substrate complex
Lower Km and vmax
-1/Km
What is the x-intercept of a Lineweaver-Burk plot?
1/Vmax
What is the y-intercept of a Lineweaver-Burk plot?
Allosteric control, covalent modification, feedback inhibition
Enzyme activity is regulated through ______, _________(like phosphorylation), __________, and changes in gene expression.
Competitive and noncompetitive inhibition
What are the two most common types of reversible enzyme inhibition?
Michaelis Menten graph
hyperbolic
Competitive inhibition
Km increases (lower affinity), Vmax stays the same.
Noncompetitive inhibition
Vmax decreases, Km stays the same
[S] in enzyme kinetics
concentration of substrate
Allosteric regulation
The binding of a regulatory molecule to a protein at one site that affects the function of the protein at a different site.
Homotropic/heterotropic effectors
What are types of allosteric regulation
Homotropic effectors
when the substrate itself serves as an effector (oxygen binds to hemoglobin)
Heterotropic effector
effector is different from substrate (PFK1 is inhibitated by citrate)
Covalent modification
phosphorylation and dephosphorylation by ATP or other enzymes
Beta-lactam antibiotics
Penicillins and amoxicillin act by inhibiting enzymes in bacterial cell wall synthesis
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
lower blood pressure by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I (an inactive enzyme) to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor) drugs include captopril, enalapril, and lisinopril
Plasma enzymes
Active secreted into blood like clotting factors and released during cell turnover (indicate tissue damage)
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
Liver function test panel (type of plasma enzyme)
Creatine Kinase (CK)/Cardiac troponin I (cTnI)
Myocardial infarction test (type of plasma enzyme)
Glucose meter
Provide fast analysis of blood glucose levels and allow management of both hypo/hyperglycermic disorders to adjust glucose to normal level
Enzymatic reaction and detector
What are the two parts of a glucose meter
Enzymatic reactions
Glucose oxidase, glucose dehydrogenase, hexokinase
Biosensor
Those meters incorporate the enzymes into a ______ that generates an electron that is detected by the glucose meter
PCR
detects the presence of viral genetic material (RNA or DNA)—during COVID-19, RT-PCR was used to amplify and identify SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient samples to confirm infection.
salivary amylase
Breakdown dietary carbohydrate for digestion (plaque formation by binding to bacterial surfaces and enamel providing simple sugars to bacteria)
lysozyme, lactoferrin, lactoperoxidase system, histatins
What are antimicrobial and protective salivary enzymes
matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
A family of zinc-containing enzymes that act in the extracellular space to digest various extracellular proteins and proteoglycans
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs)
Natural inhibitors to MMPs, balance is needed for homeostasis