Hepatitis Virus Types: Transmission, Prevention, and Clinical Features
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the primary transmission route for RNA viruses related to hepatitis?
Fecal-oral route, sexually, and IV drug use.
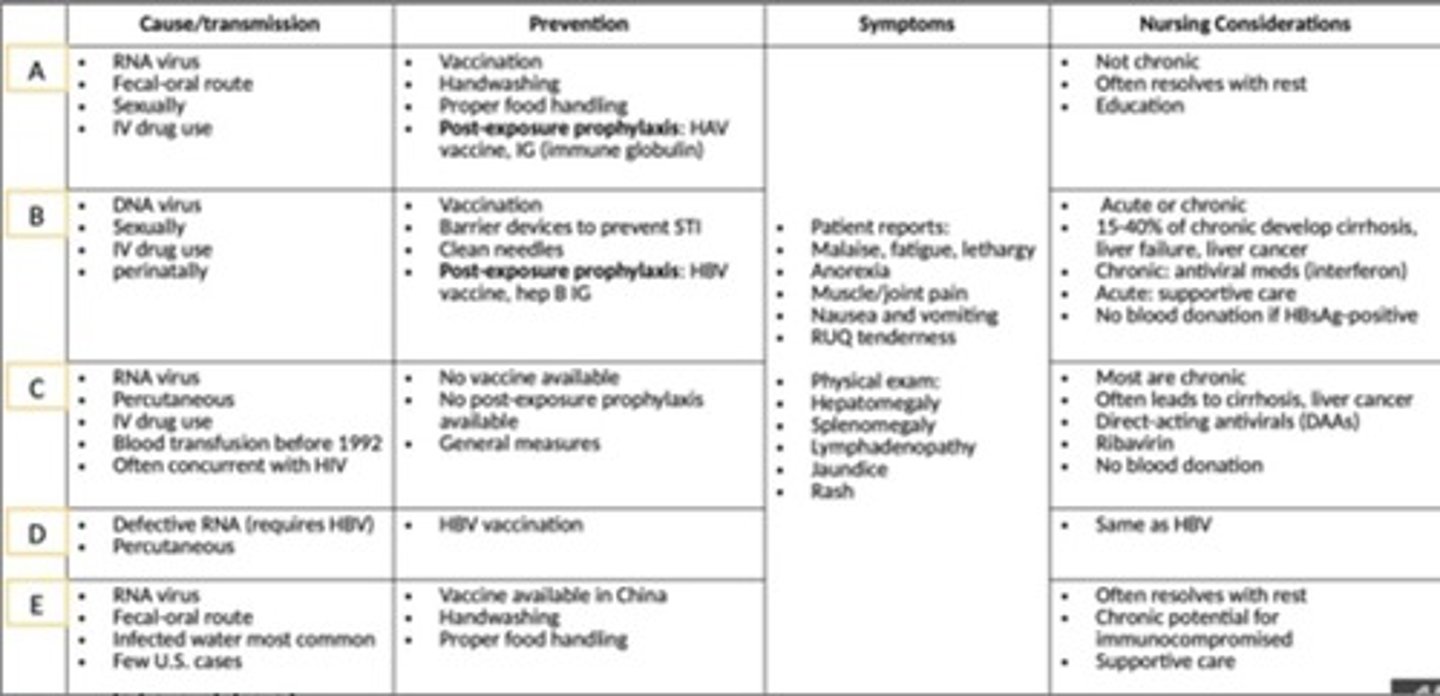
What are the transmission routes for DNA viruses related to hepatitis?
Sexually, IV drug use, and perinatally.
What is a common co-infection with hepatitis C viruses?
HIV
What are some prevention methods for hepatitis A?
Vaccination, handwashing, proper food handling, and post-exposure prophylaxis with HAV vaccine and immune globulin (IG).
What prevention methods are available for hepatitis B?
Vaccination, barrier devices to prevent STIs, clean needles, and post-exposure prophylaxis with HBV vaccine and hepatitis B IG.
What is the status of vaccination and post-exposure prophylaxis for hepatitis C?
No vaccine or post-exposure prophylaxis available.
What is the post-exposure prophylaxis for hepatitis B?
Defective RNA (requires HBV) and HBV vaccination.
What symptoms might a patient report with hepatitis?
Malaise, fatigue, lethargy, anorexia, muscle/joint pain, nausea, vomiting, and RUQ tenderness.
What physical exam findings are associated with hepatitis?
Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, jaundice, and rash.
What nursing considerations are important for hepatitis A patients?
Most cases are not chronic and often resolve with rest.
What percentage of chronic hepatitis cases can develop into cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer?
15-40%.
What treatments are available for chronic hepatitis?
Antiviral medications such as interferon and direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) like Ribavirin.
What should patients with HBsAg-positive status avoid?
Blood donation.
What is the primary transmission route for hepatitis E?
Fecal-oral route, often through infected water.
What is the common outcome for hepatitis E in immunocompromised individuals?
Chronic potential.