Unit 2 Cells and Cell Transport
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Microscopes are
the #1 tool in cell biology
microscopes help
the development of the cell theory
the two types of microscopes are?
Electron and Light
Electron microscope views
dead cells
Electron microscopes use
beams of electron and magnets
In electron microscopes what cannot be seen
color
Light microscopes use
light and lenses
light microscopes view
living cells
light microscopes require
a stain to see the color
electron microscopes are
expensive & clear
light microscopes are
blurry and not as zoomed in
specimen are placed on the
stage
what do objective lens do
magnifies the specimen
adjustment knobs are for
focus
Ocular lens does what
magnifies it more (again)
electron beams are used to produce what?
images
magnification and resolution are
higher than a light microscope
all organisms are made up of
one or more
the cell is the
basic unit of life
all cells come from
pre existing cells
Robert Hooke was famous for?
naming cells
Why did Robert call cells cells?
When he looked through the lenses at the cork he saw tiny squares which reminded him of jail cells
Antonie Von Leeuwenhoek was famous for?
looking at a pond of water and identifying cells
Cells can be different shapes but they are limited by-
surface area and volume ratio
cells absorb nutrients through
their membranes
as cells get bigger
surface area gets smaller
a cells membrane represent the cells-
surface area
the cytoplasm and all the organelles represent
the cells volume
surface area formula is
length x width x number of sides
types of prokaryotes
unicellular, circular dna,
prokaryotes have
no embrane bound organelles nor a nucleus
circular dna looks like
a rubber band with double curves
flagella is a tail that turns into
boat propeller
capsules
provide protection from white blood cells
an example of something with a capsule is
salmonella
protein tubes that extend from the membrane enable
attachment to things to help exchange DNA and DNA is in the nucleoid region
prokaryotes do not have
inner membranes
prokaryotes have ribosomes but they are
different from eukaryote ribosomes
how many chromosomes do humans have
46
Eukaryote examples
plants, animals, protists, and fungal cells
Eukaryote cells may be
unicellular or multicellular
membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotes have
DNA is in a
nucleus
linear DNA
has a beginning and a end
prokaryotic cells are
unorganised and simple
eukaryotic cells are
organised and complex
circular shape equals
either animal or protists
Endosymbiosis means
to work together
endosymbiosis is a
theory used to explain how eukaryotic cells could have evolved from prokaryotic cells
endo means
inside
sym means
together
bio means
life
endosymbiotic theory means
evidence
mitochondria and chloroplasts were once
free-living bacteria
mitochondria and chloroplasts have
DNA inside the organelle
mitochondria and chloroplasts can
reproduce the same as extant bacteria by binary fission (splits into two)
mitochondria and chloroplasts also have
the same size similar to extent bacteria
mitochondria and chloroplasts are about
the same size as bacteria
plants contain
cell walls,chloroplasts, and large water vacuoles
plants dont have
mitochondria
Animals contain
small vacuoles, and maybe cilia/flagella
animals do not have
cell walls or chloroplasts
the nucleus
contains DNA which are instructions for making proteins
the nucleus has a nuclear membrane made up of
phospholipids
in the inside of the Nucleus it makes
ribosomes
cilia helps push out
mucus
ribosomes do what
turn amino acids into proteins
ribosomes look like
small dots in an electron microscope
ribosomes could be in the
cytoplasm fluid or attached to endoplasmic reticulum
cells that need a lot of protein have a lot of
ribosomes
ribosomes are also found in prokaryotes because
its not surrounded by a membrane
the endomembrane system are also called
multiple organelles
what is a folded membrane inside the cell
the endomembrane system
is the endomembrane system inside prokaryotes
No
How are multiple organelles divided?
by a phospholipid membrane
what are multiple organelles called when divided?
compartments
what does the endoplasmic reticulum membrane do?
twists and folds forming tubes and pockets
endoplasmic reticulum creates
compartiments for many chemical reactions
what are the types of endoplasmic reticulum?
rough and sooth ER
Smooth ER contains
no ribosomes
Smooth ER makes
lipids (steroids)
smooth ER does what
detoxifies drugs and poisons
Lots of smooth ER are located in the
liver
explain why someone with alcohol problems might have liver problems
because smooth ER is stored in the liver your body which breaks down alcohol and other drugs the over usage of the smooth ER can be damaging towards the liver
Rough ER have
ribosomes
ribosomes in rough ER make
proteins that enter the rough ER and are folded before being packaged to leave
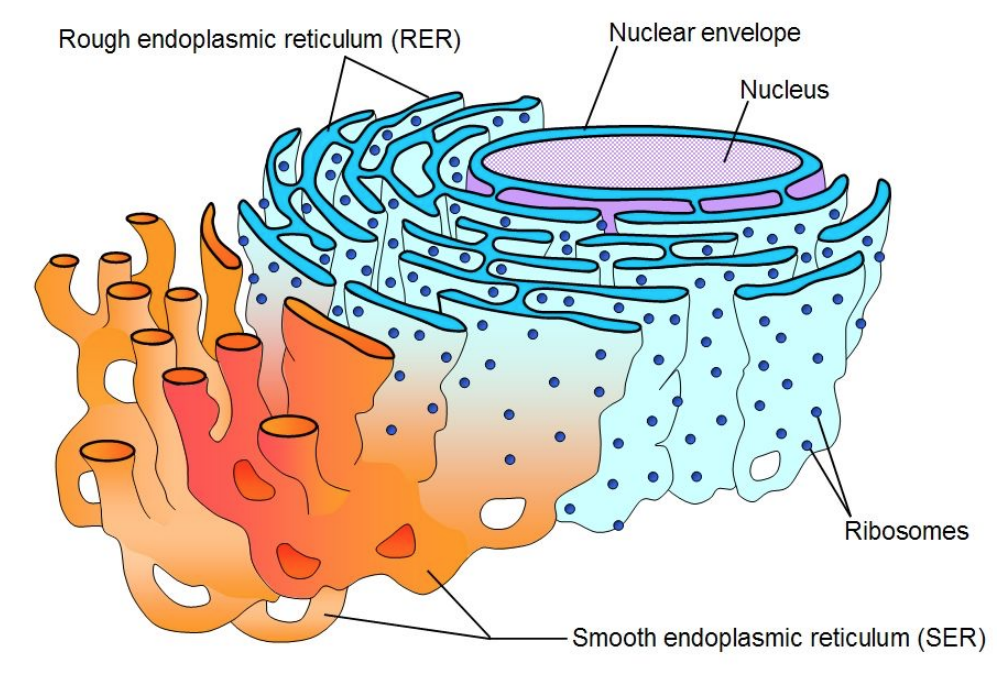
What is this image of?
endoplasmic reticulum
what does the Golgi apparatus do?
sends out proteins from the cell to other parts of the body
what is an example of golgi apparatus?
pancreas secretes
Transport Vesicles move unfinished ER products to?
golgi to be processed
some protein need to be folded or have some chemical groups to-
function
what is the function of Golgi apparatus?
package proteins to move to other places
what do secretory vesicles do?
leave the cell
transport vesicles are?
membrane bound spheres that pinch off of ER
lyse means
to split
digestion contain
enzymes
lysosomes do what?
digest old or broken cell organelle and pathogens
vacuoles are?
phospholipid membrane sacs
vacuoles are used as
temporary storages for food, water, and poisons
central vacuole stores?
water and minerals