Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic, Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Last updated 10:59 PM on 10/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
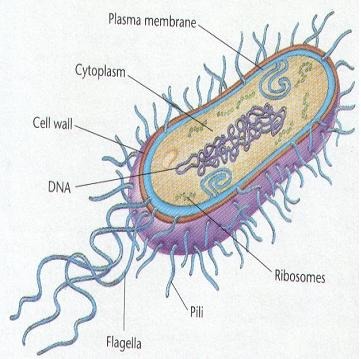
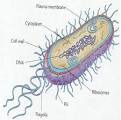
Prokaryotic cell
a cell that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles; including bacteria
2
New cards
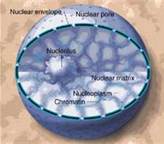
Nucleus
a part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
3
New cards
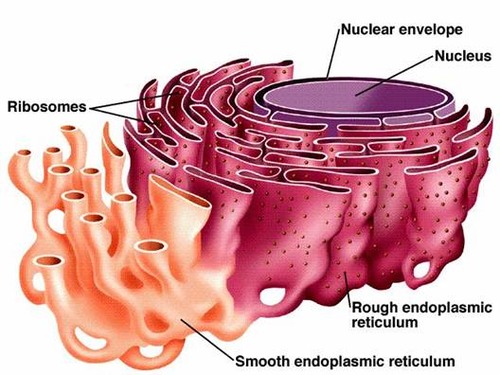
Ribosomes
non membrane bounded organelles responsible for protein synthesis;found in eukaryotes and porkaryotes
4
New cards
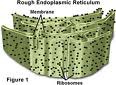
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
5
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
6
New cards
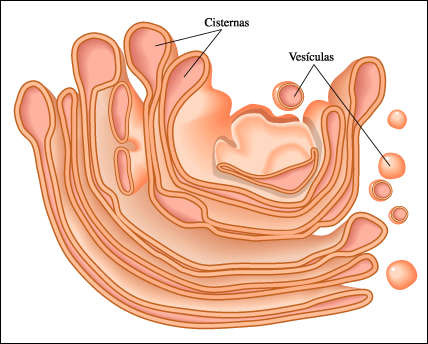
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of stacks of flat membranous sacs that modify, store, and route products of the endoplasmic reticulum.
7
New cards
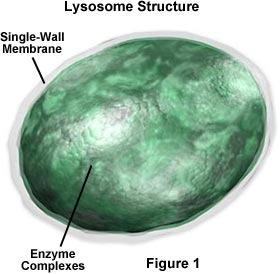
Lysosome
membrane-bound sac containing digestive enzymes that can break down proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides
8
New cards
Central Vacuole
a large, fluid-filled organelle that stores not only water but also enzymes, metabolic wastes, and other materials;provides turgor pressure in plant cells

9
New cards
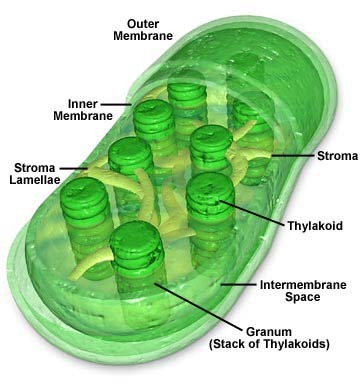
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy; contains DNA
10
New cards
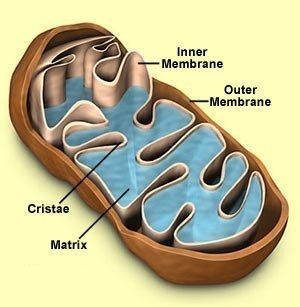
Mitochondrion
in eukaryotic cells, the cell organelle that is surrounded by two membranes and that is the site of cellular respiration, which produces ATP;contains DNA
11
New cards
Cell wall
strong wall outside a plant cell's plasma membrane that protects the cell and maintains its shape
12
New cards
Cilia
short structures projecting from a cell and containing bundles of microtubules that move a cell through its surroundings or move fluid over the cell's surface
13
New cards
Flagella
A long cellular appendage specialized for locomotion, formed from a core of nine outer doublet microtubules and two inner single microtubules, ensheathed in an extension of plasma membrane.
14
New cards
Centrioles
One of two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope; play a role in cell division. NOT in PLANT CELLS
15
New cards
Cell membrane
a phospholipid layer that covers a cell's surface and acts as a barrier between the inside of a cell and the cell's environment
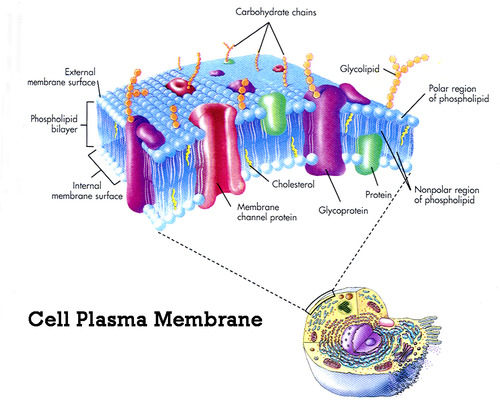
16
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
17
New cards
Plasmid
a circular DNA molecule that is usually found in bacteria and that can replicate independent of the nucleoid DNA
18
New cards
Chromosome
threadlike structure within the nucleus containing the genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next Prokaryotic cells do not have them.
19
New cards
Eukaryote
A cell with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles; these include human, animal, plant, and fungi cells
20
New cards
Organelles
Tiny membrane bound compartments inside cells that do specific jobs; these are found in Eukaryotes
21
New cards
Ribosomes only
Prokaryotic
22
New cards
Prefix means "before"
Prokaryotic
23
New cards
Prefix means "true"
Eukaryotic