inheritance
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
what is an allele
different versions of the same gene that codes for a particular phenotype
what is genotype
all of the alleles present in an organism
what is phenotype
an individuals observable traits based on our genes. can be influenced by the environment
what is the dominant allele
the allele that is always expressed if present
what is the recessive allele
allele that needs two copies to be expressed
what is a gene
a length of dna that codes for a protein/characteristic.
what is the locus
the position of a gene on a chromosome
what is the mendelian law of inheritance.
in the f1 generation, 100% of the offspring show the dominant trait, and are 100% heterozygous. in the f2 generation, 75% will show the dominant trait and 25% will show the recessive trait. 25% of the offspring will be homozygous recessive, 25% will be homozygous dominant, and 50% will be heterozygous.
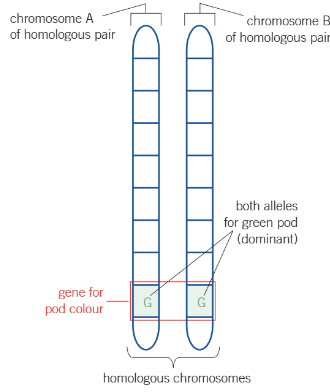
what genotype does this picture show?
homozygous dominant
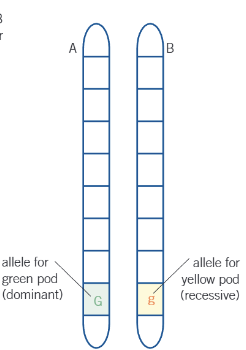
what genotype does this picture show?
heterozygous
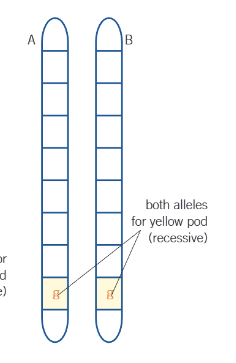
what genotype does this picture show?
homozygous recessive
what is a homozygote?
pair of chromosomes made of two of the same alleles of a gene, e.g. bb, BB. can be dominant or recessive
what is a heterozygote>
pair of chromosomes made of two different alleles of a gene. e.g. Bb
what is a diploid cell?
there are 2 copies of each allele- one copy inherited form the mother, one from the father
what is a codominant allele?
when two alleles both contribute to the phenotype. the phenotype is either a blend of both features or both features are represented
what did mendel study?
the colour of the pods of pea plants
what did mendels observations lead to?
the law of segregation
what is the law of segregation
pair of alleles of each parent separate and only one allele from each parent to the offspring. which allele is inherited is due to chance and segregation of alleles occurs during gamete formation in meiosis
how to simplify a ratio?
divide biggest number by smallest number
when do we use ratios when looking at monohybrid crosses?
we expect a 3:1 phenotype in the f2 generation, so can measure ratios to see how close it is to this theoretical value
why is it unlikely we will always find an exact 3:1 ratio in the f2 offspring?
statistical error due to chance and error due to gametes fusing
why is sample size important in terms of achieving the theoretical value?
larger sample size, data is more representative of the theoretical value. smaller sample size, data is less representative of the theoretical value
what is a homologous pair of chromosomes?
pair of chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal, that have the same gene loci, therefore determining the same features
what is the formula for degrees of freedom? (chi squared)
n-1, n is number of categories
if chi squared is below the critical value at p = 0.05, what do we do? (for inheritance)
accept the null- there is less than 5% probability that the difference between the observed and expected value is due to chance. the difference seen follows the laws of mendelian inheritance- 3:1 ratio
if chi squared is above the critical value at p = 0.05, what do we do? (for inheritance)
reject the null- there is more than 5% probability that the difference between the observed and expected value is due to chance. the observed ratio does not match the expected ratio. another factor is influencing results e.g. sex linkage. offspring doesn’t follow the laws of mendelian inheritance
define monohybrid inheritance
where one phenotypic characteristic is controlled by a single gene
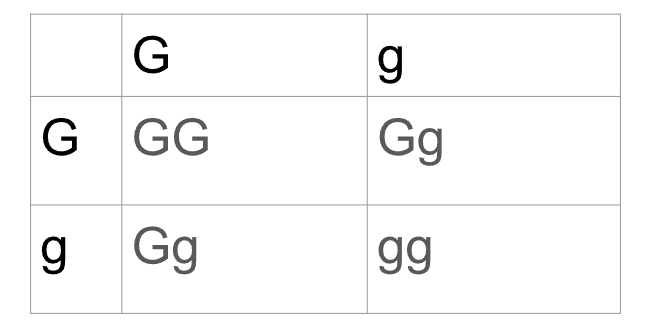
what does this image show?
punnet square for a monohybrid cross
define dihybrid inheritance
two phenotypic characteristics are inherited from two different genes which have different alleles
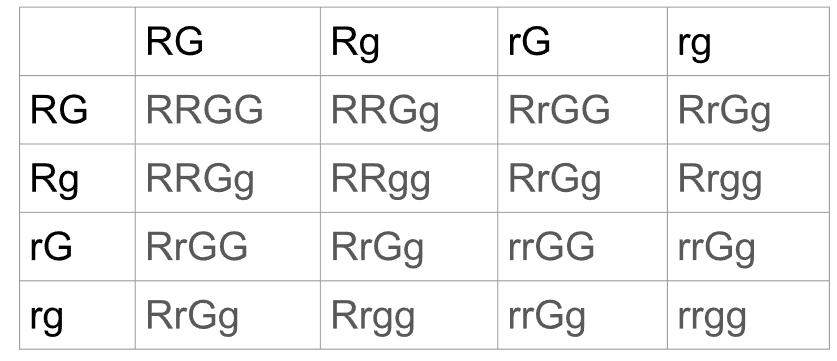
what does this image show?
punnet square for dihybrid cross
If an organism has the genotype RrTt, what are the gamete possibilities?
RT, Rt, rT, rt
how to determine the gamete possibilities from a genotype? (e.g. RrTt)
FOIL
What sample size do you need for chi squared?
20
in a dihybrid cross, how many offspring should have each characteristic?
9,3,3,1
give an example of codominance
blend of both features (e.g. roan coat colour in shorthorn cattle from red and white alleles) or both features are represented (e.g. a and b antigens for ab blood type)
how does codominance occur?
both alleles are equally dominant, meaning both are expressed in the phenotype
what are the 3 coat colours (not just red and white) in shorthorn cows, as they are codominant for an allele controlling coat colour?
homozygous for first allele (red coat), homozygous for other allele (white), heterozygous, both are produced and coat is light red/roan
in codominant alleles, what cant we do? what must we do instead?
use uppercase and lower case as this would imply that the capital is dominant. therefore we use subscript for the allele on the letter for the gene, e.g. allele for no pigment is cw and allele for red is cr
give an example of when multiple alleles may be inherited + explain what alleles this has
human ABO blood groups- 3 alleles associated with Gene i, different antigens on CSM of red blood cells. allele Ia, (produces antigen a) allele Ib (produces antigen b) and allele Io (doesnt lead to production of either antigen)
how many alleles can be present in an individual, even if there are 3 alleles, and why?
2- only 2 homologous chromosomes and gene loci
which blood type alleles are dominant, and which are recessive?
Ia and Ib are codominant, Io is recessive to both
which allele combinations can cause the blood group A
Ia Ia or Ia Io
which allele combinations can cause the blood group B
Ib Ib or Ib Io
which allele combinations can cause the blood group AB
IaIb
which allele combinations can cause the blood group O
IoIo
a cross between someone with blood group O and someone with blood group AB produces what?
only individuals of the other 2 groups, A and B
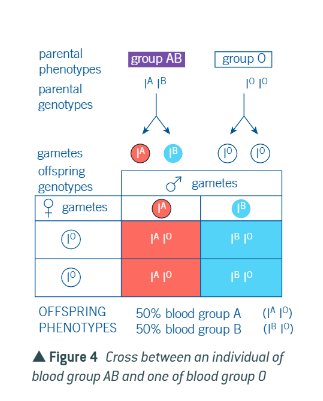
when certain individuals of blood group A are crossed with certain individuals of blood group B, their children have what?
any of the four blood groups
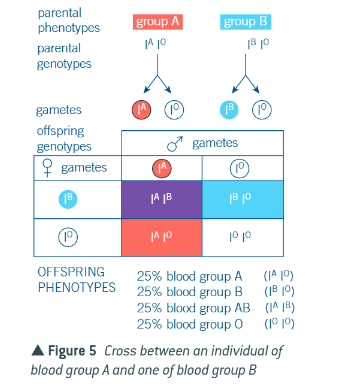
what is a test cross and when do we use it?
when we dont know whether an organism is homozygous or heterozygous from inspection of genotype. cross a dominant phenotype with recessive phenotype. if homozygous recessive in offspring, parent must be heterozygous. working backwards
what genotype trait does the unknown parent show when doing a dihybrid test cross?
dominant trait- YYRR (homozygous dominant) or YyRr (heterozygous)
what do we cross the unknown parent with in a dihybrid test cross?
double recessive- yyrr
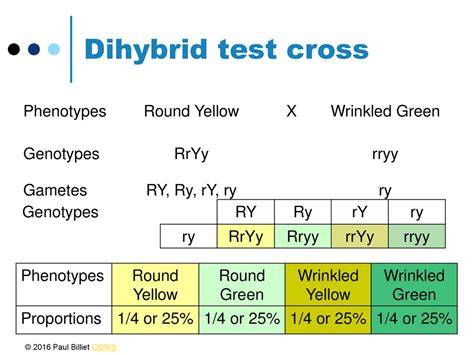
what must we do when doing a dihybrid test cross, before determining the offspring?
identify the gametes
in a dihybrid test cross, when crossing with a double recessive, what does all heterozygous offspring mean about the parent?
it is homozygous dominant
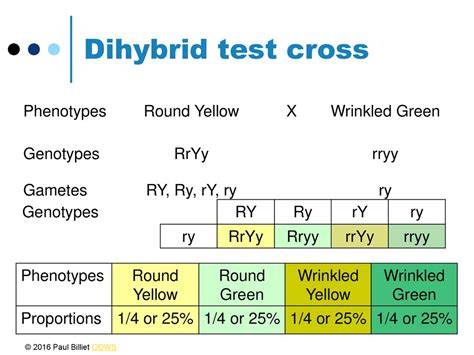
in a dihybrid test cross, when crossing with a double recessive, what does all 1:1:1:1 offspring mean about the parent?
it is heterozygous
when breeding two homozygous codominant parents (1st generation), what genotypes and phenotypes are produced in the offspring?
100% heterozygous- blend of both features
discuss the significance of genes existing as alleles.
genes must exist as alleles to give increased variation in offspring. more likely some of the population have adaptations to survive rapid environmental chance
explain how codominance of alleles can result in offspring with a phenotype that is different from either parent.
both alleles are expressed in their phenotype
describe the classical phenotypic ratio for a codominant gene resulting from the cross of two heterozygous (blend) parents
1:2:1, 1 homo dom, 2 heterozygous, 1, homo recessive
explain one way in which the behaviour of chromosomes during meiosis produces genetic variation in gametes
crossing over gives different allele combinations
name the relationship between the two alleles that control coat colour
codominant
why are humans diploid organisms?
we have two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent
what does f1 mean?
the first set of offspring from 2 parents
what is monohybrid inheritance?
involves inheritance of characteristics which are controlled by a singular gene
what is the expected ratio of phenotypes for 2 heterozygous parents?
3:1 dom to recessive
why arent expected ratios always observed?
fertilisation/fusion of gametes is random, small sample size, codominance, sex linkage
how does meiosis produce genetic variation in crossing over and gametes?
crossing over between chromatids produces different allele combinations. independent assortment of chromosomes produces different combination of maternal and paternal alleles
what is meant by sex-linkage?
where an allele is located on one of the sex chromosomes, meaning its expression depends on the sex of the individual
why are males more likely to express a recessive sex-linked allele
most sex linked alleles are located on the X chromosome. males only get 1 copy of the allele so will express this characteristic even if its recessive. females get two x alleles so its less likely
which parent do males inherit sex linked characteristics from?
the mother: the Y chromosome can only come from their father. therefore if the mother is heterozygous for sex-linked alleles, she is a carrier and may pass the trait on
what is an X linked genetic disorder?
disorder caused by a defective gene on the x chromosome, e.g. haemophilia
give a cause of a x linked genetic disorder.
recessive allele with an altered sequence of DNA nucleotide bases that therefore codes for a faulty protein, which doesnt function.
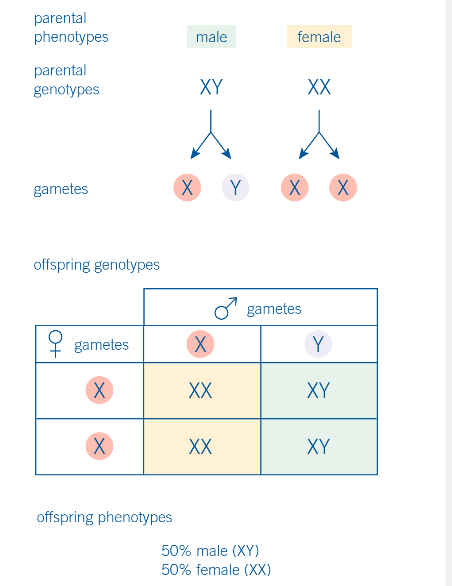
what does this image show
sex inheritance in humans
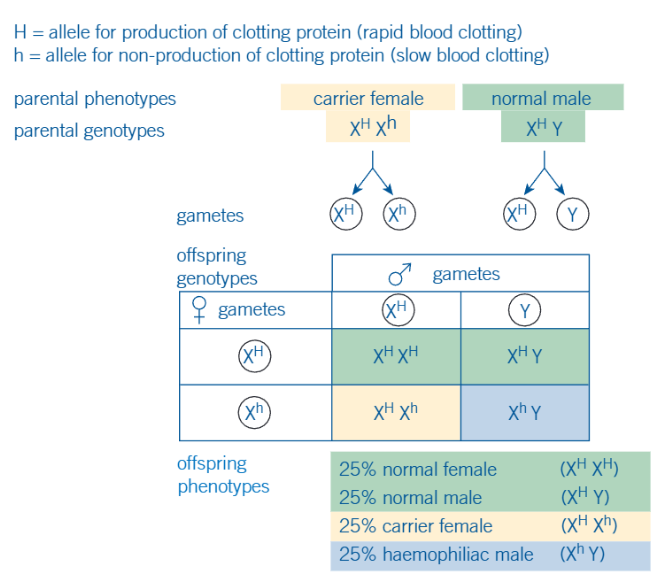
what does this image show
inheritance of haemophilia from a carrier female
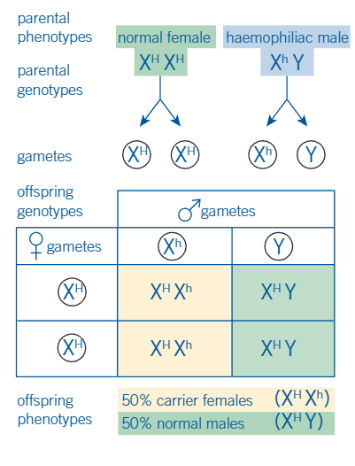
what does this image show
inheritance of the haemophiliac allele from a haemophilic male
how are sex-linked alleles presented?
the allele in subscript on the X gene e.g. XH and Xh
why cant males pass haemophilia to their sons?
as they pass the Y chromosome to their sons, however they can pass it to a daughter via their X chromosome
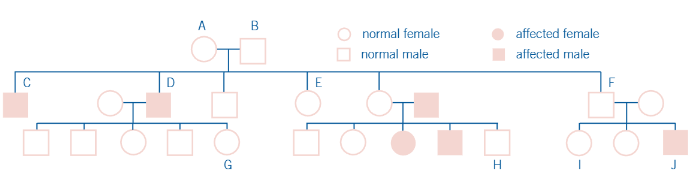
what is a way to trace the inheritance of sex-linked characteristics?
pedigree chart
in a pedigree chart, how are males and females represented? what does the shading mean?
male is square, circle is female, shaded = characteristic in the phenotype
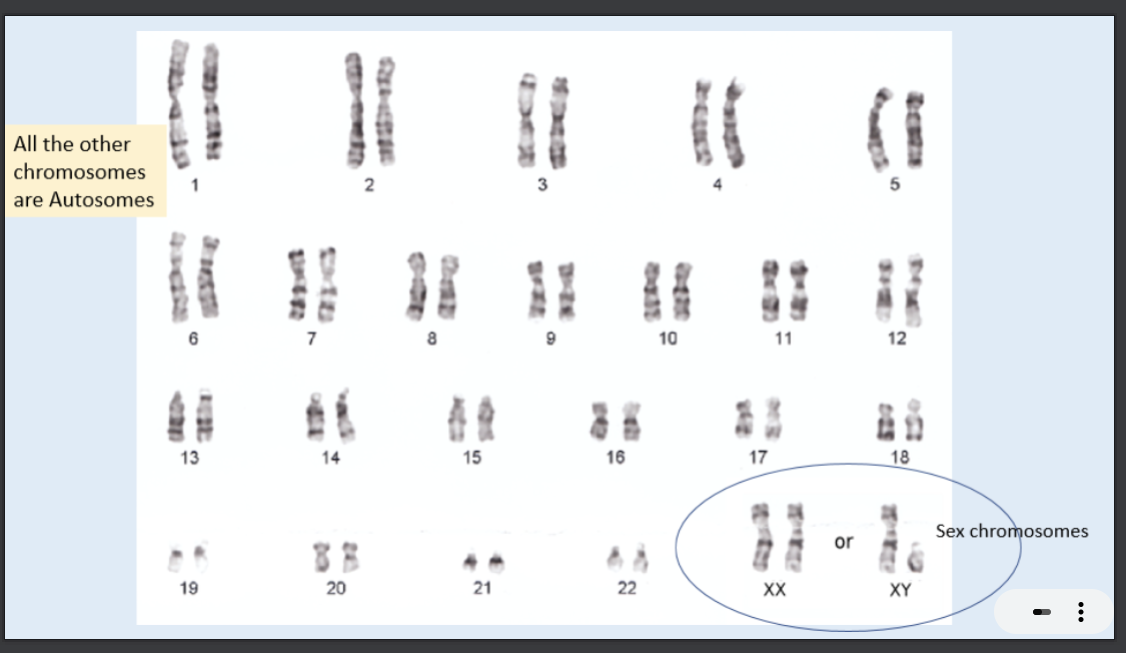
what does this picture show?
carrier types- image of chromosomes found inside an individuals cells. carrier type in image: diploid cells as chromosomes in homologous pairs. two circle homologous chromosomes hold same gene at same loci. pairs called autosomes (except pair 23)
what is pair number 23 in humans?
sex chromosomes
when determining sex, do the offspring inherit alleles or genes?
sex gene
what happens when recombination during meiosis, moving SRY from Y chromosome to X chromosome?
boy child inherits one X chromosome and one X(SRY+) chromosome. infertile as adult
what are the sex chromosomes for chickens?
zz for cockrels, zw for hen
what are the sex genes in crickets?
XX for females, X for males
what are genes on sex chromosomes called?
sex linked genes
what happens if a sex linked trait is due to a recessive allele?
female will only express the phenotype if she is homozygous recessive, yet a male will express the phenotype if he receives 1 recessive allele from his mother
What are the genes for red green colourblindness
XN (normal vision, dom) and Xn (colour blindness, recessive)
what is colourblindness caused by
faulty recessive gene on the x chromosome
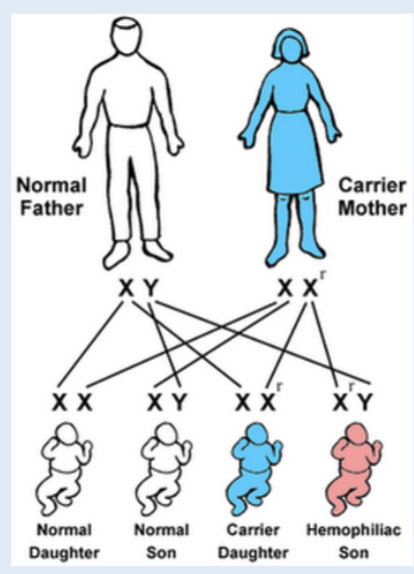
what is haemophilia caused by?
faulty recessive x linked gene