Milady Chapter 5-1
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Cleaning
A mechanical process (scrubbing) using soap and water or detergent and water to remove all visible dirt, debris and many disease-causing germs.
Sanitizing
A chemical process for reducing the number of disease-causing germs on cleaned surfaces to a safe level.

Disinfection
A chemical process that uses specific products to destroy harmful organisms on environmental surfaces.

Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
Contains 16 categories that are required by law to be present on all chemical products.

Disinfectants
chemical products that destroy most bacteria (excluding spores), fungi, and viruses on surfaces.

Hospital Disinfectants
Designated by the EPA as being effective to clean blood and body fluids.

Nonporous
Made/constructed of material that has no pores or openings and cannot absorb liquid

Disease
Abnormal condition of all or part of the body, or its systems or organs, which makes the body incapable of carrying on normal functions
Tuberculocidal Disinfectants
Proven to kill the bacteria that causes tuberculosis in addition to the pathogens destroyed through the use of hospital disinfectants.
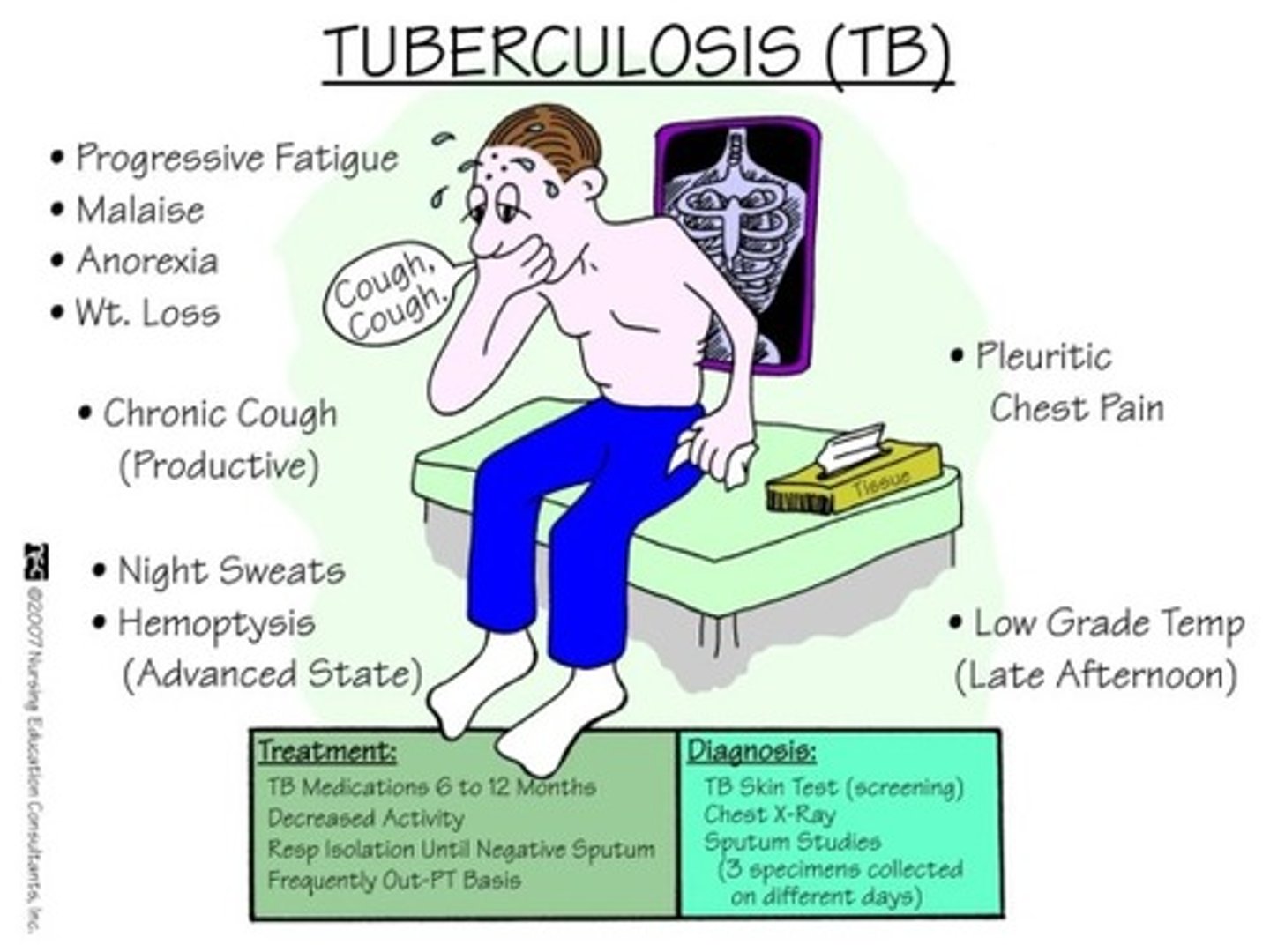
Tuberculosis
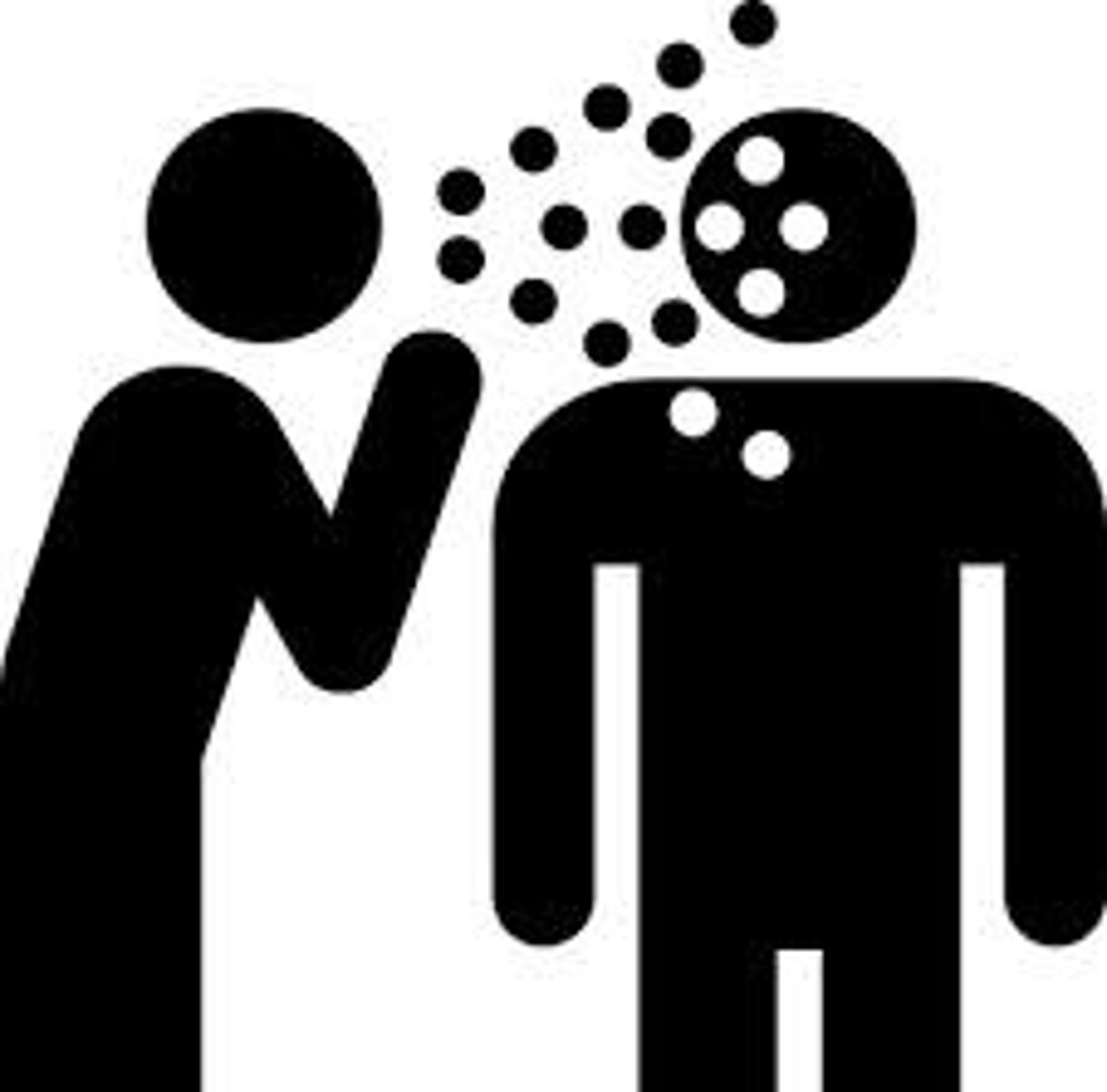
a disease caused by bacteria that are transmitted through coughing or sneezing and is not transmitted on surfaces
Infection Control
the methods used to eliminate or reduce the transmission of infectious organisms
Infectious Disease
caused by harmful pathogenic organisms that enter the body
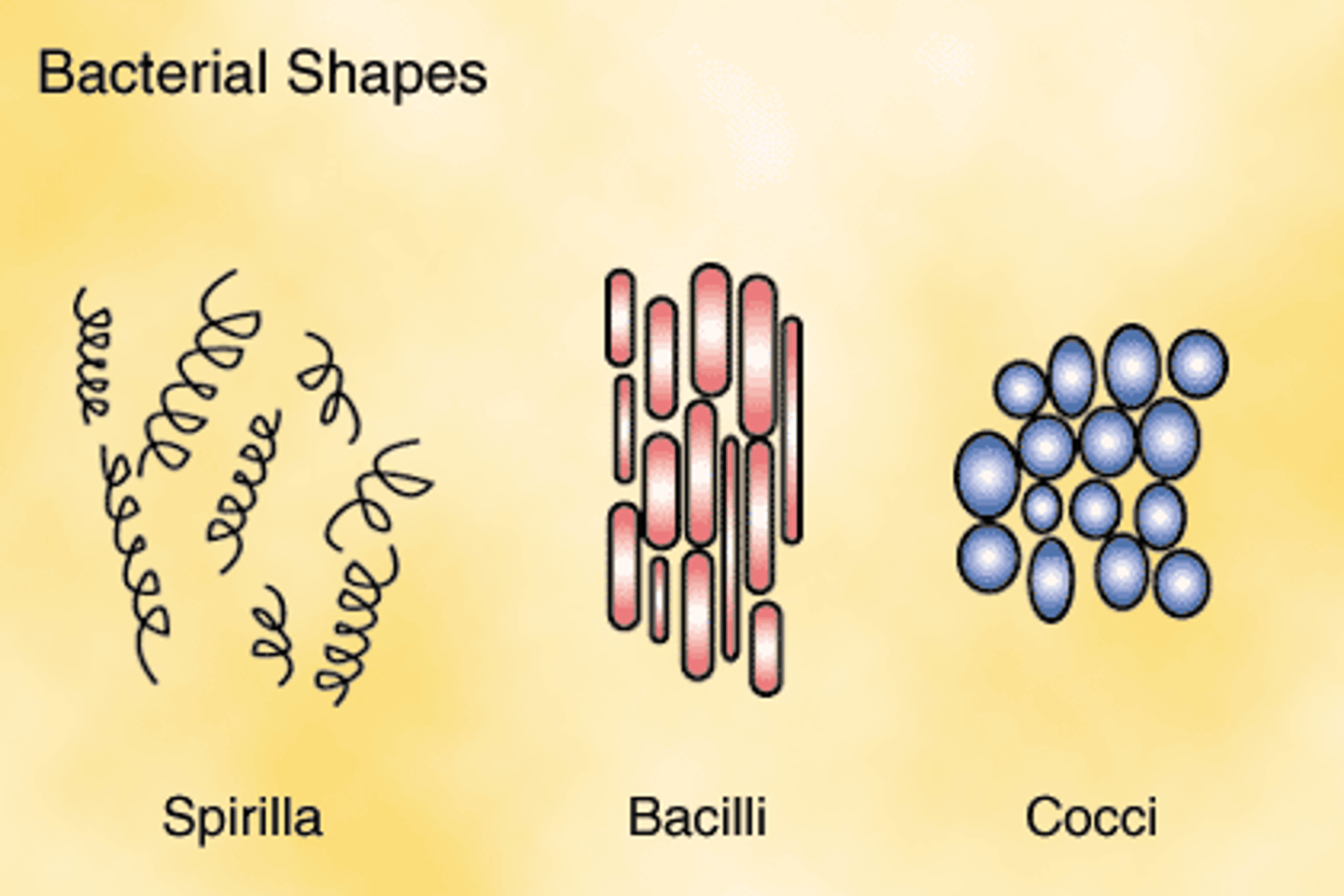
Bacteria
one-celled microorganisms that have both plant and animal characteristics
Microorganism
any organism of microscopic or submicroscopic size

Non pathogenic
Harmless microorganisms that may perform useful functions
(most bacteria are non pathogenic)

Pathogenic
harmful microorganisms that can cause disease or infection in humans when they invade the body
Bactericidal
Capable of destroying bacteria
Fungicidal
Capable of destroying fungi
Virucidal
Capable of destroying viruses