9. Ciliary Body
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
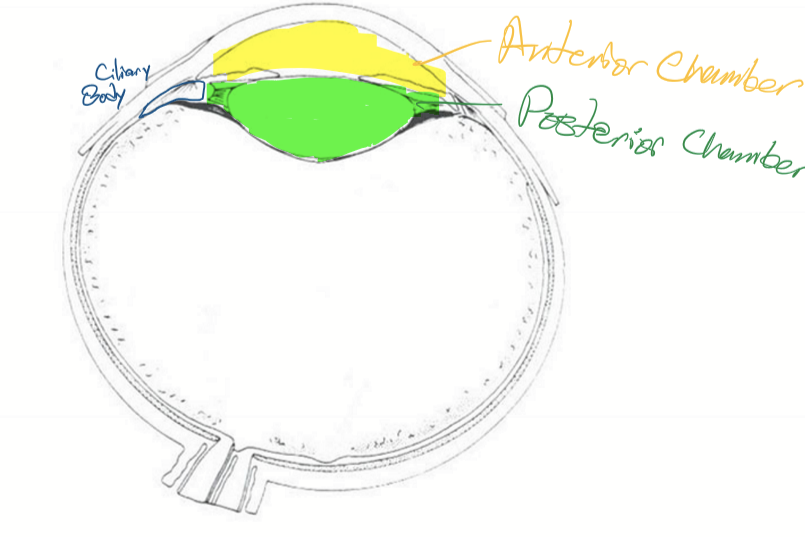
Anterior chamber
Bordered anteriorly by the cornea and posteriorly by the iris and lens
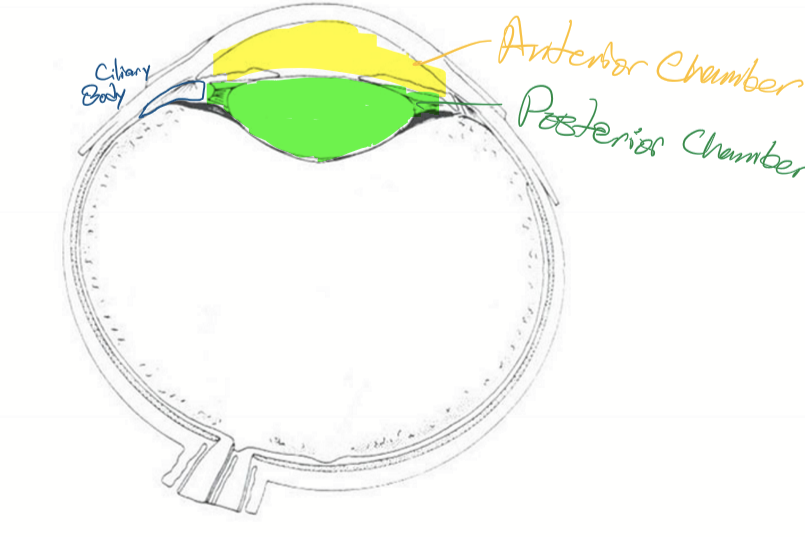
Posterior chamber
Space between the posterior surface of the iris and the anterior surface of the vitreous
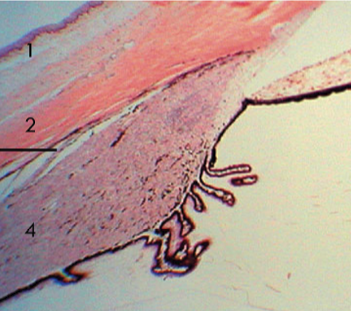
Parts of Ciliary Body
Base
Outer Side
Inner Side
Apex
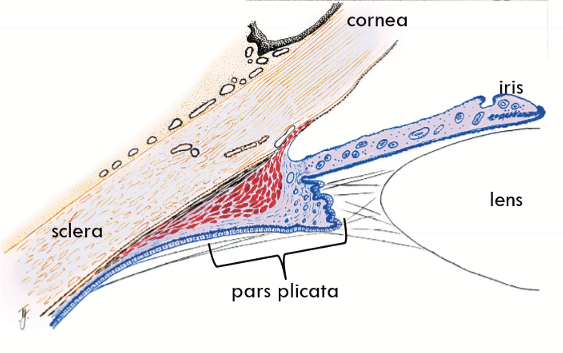
Location of Ciliary Body
Behind the Iris and runs circumferential (triangular cross section)
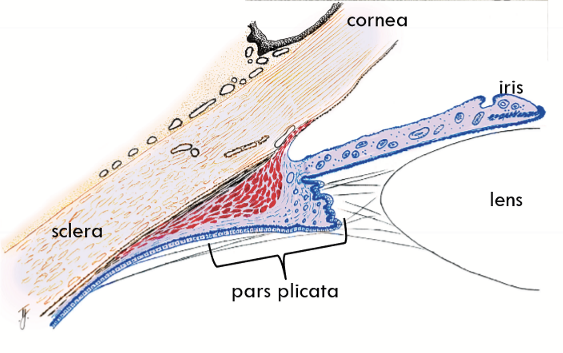
Base of Ciliary Body
Anterior; at the limit of the iris root and scleral spur
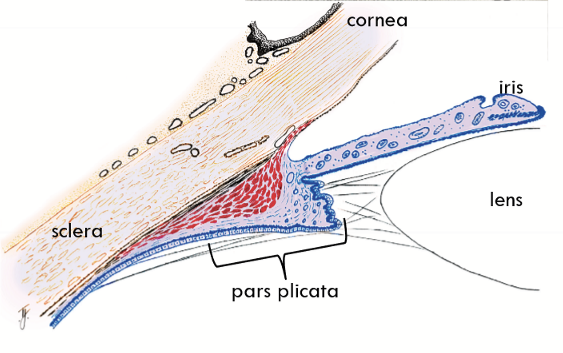
Outer Side of Ciliary Body
Lies against the sclera
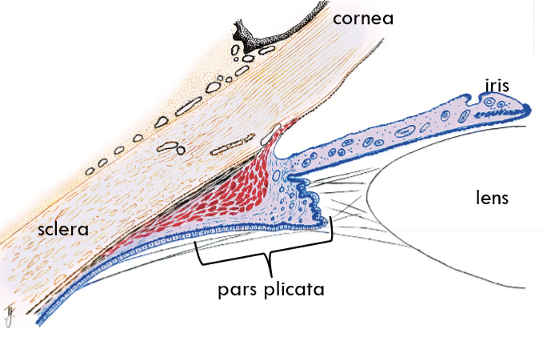
Inner Side of Ciliary Body
Faces aqueous humour (posterior chamber)
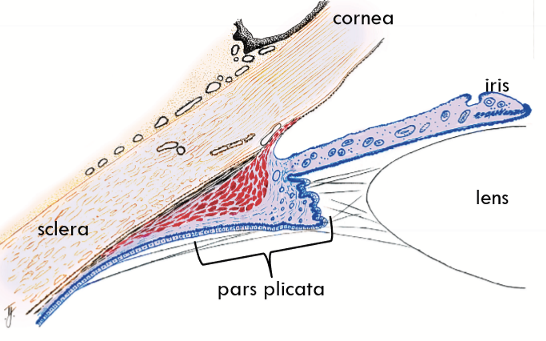
Apex of Ciliary Body:
Ora Serrata, which is also the transition zone between the ciliary body and the retina
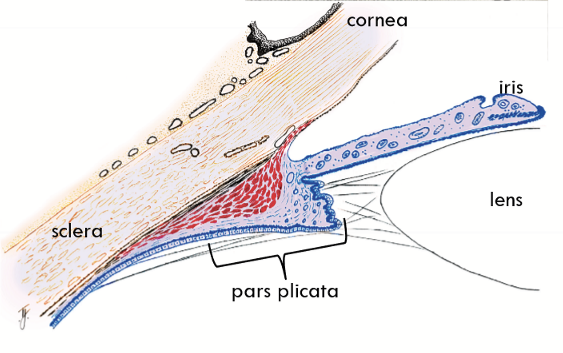
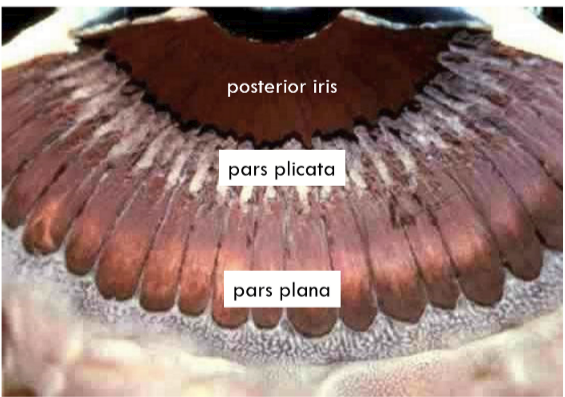
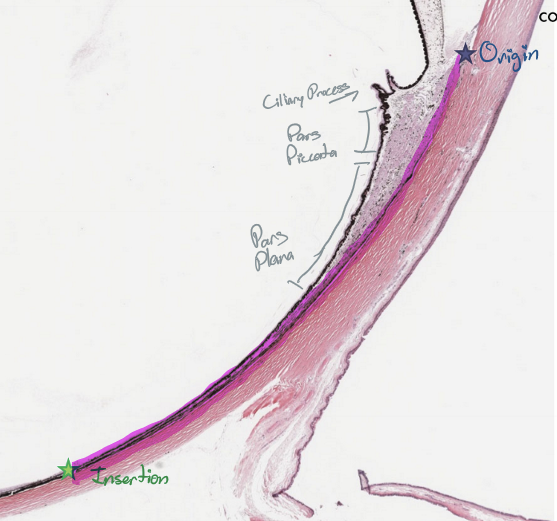
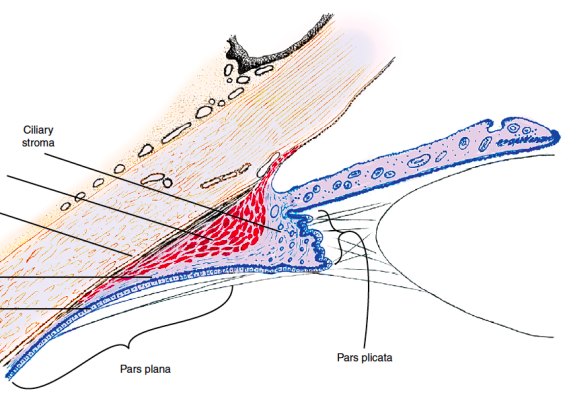
Pars plicata = Corona ciliaris
Ciliary processes are the tissue crests
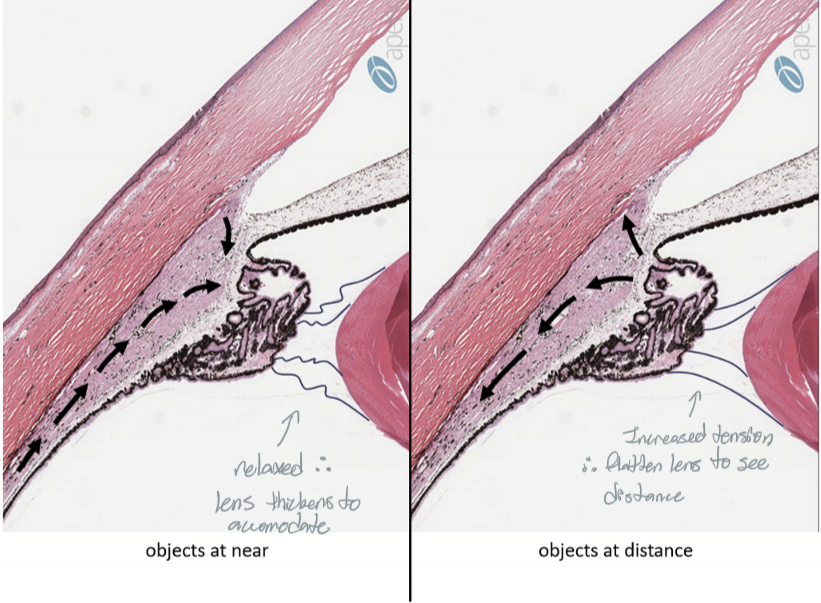
Function is aqueous humour production and assists in accomodation.
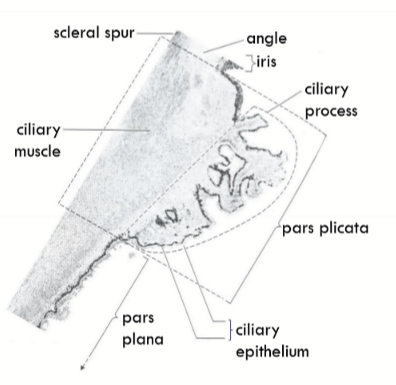
Pars plana = Orbicularis ciliaris
Flatter portion of ciliary body and extends from ora serrata to ciliary processes
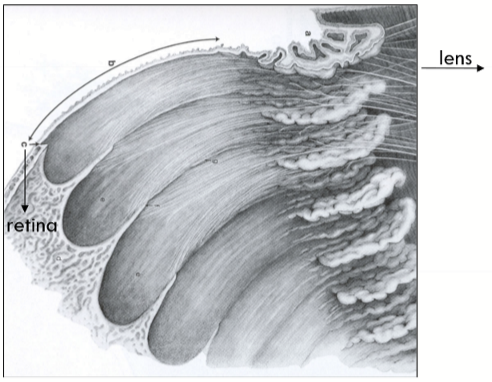
Ora Serrata
Transition zone; termination of the retina
Supraciliaris = supraciliary lamina = anterior lamina fusca
Outermost layer of the ciliary body which lies adjacent to the sclera
Composed of pigmented ribbon like layers of loose connective tissue
contains collagen type I, melanocytes, fibroblasts
Runs diagonal to stroma and ciliary body
Function of Supraciliaris
Serves as an intermediate
Creates a potential space
Fluid can drain here
Expandable piece of tissue for muscle movement
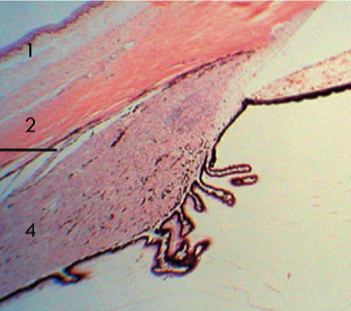
Ciliary muscle layer
Reticulum of smooth muscle with interweaving layer to layer
Sphincter-like contraction of the ciliary muscle
Fibers are subdivided into regions
Longitudinal fibers
Radial fibers
Circular fibers
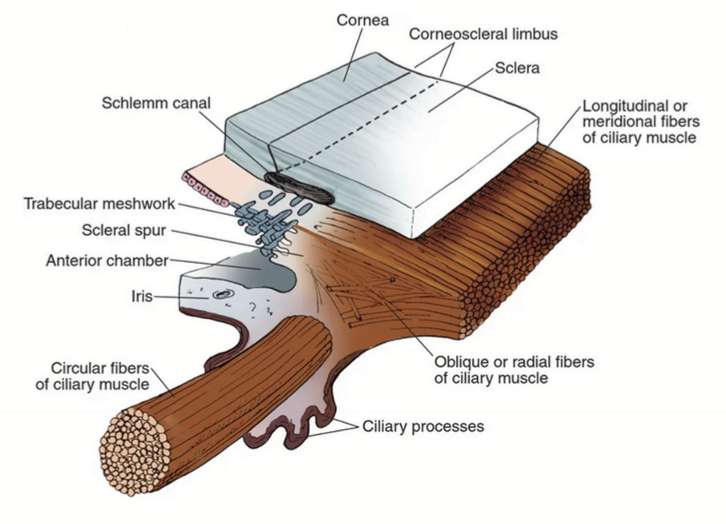
Scleral spur
Located anterior to the ciliary body and composed of sclera; acts as an attachment for ciliary muscle and trabecular meshwork; Aids in aqueous humor drainage.
Longitudinal fibers
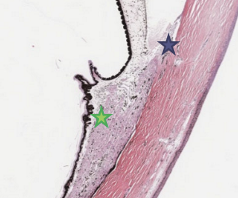
Run longitudinally; Origin = scleral spur; Insertion = “muscle stars” in suprachoroid
Radial fibers
Interdigitating V-shaped bundles; Origin = Scleral spur; Insertion = connective tissue near the posterior ciliary processes
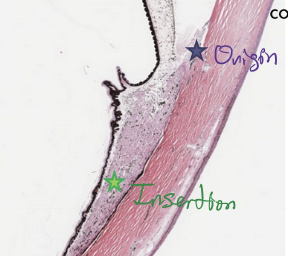
Circular fibers
Lies nearest lens/posterior chamber; Origin = scleral spur; Insertion = connective tissue mid-ciliary processes; Sphincter action
Stroma of Ciliary Body
Continuous with Iris stroma and the Choroidal stroma
Composed of LCT, highly vascularized and capillaries are fenestrated
Contains melanocytes
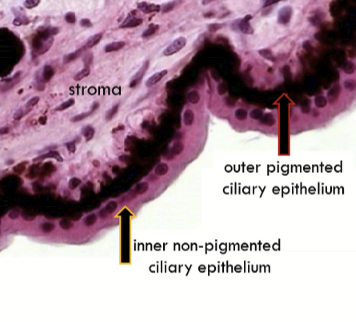
Outer pigmented ciliary epithelium
Continuous with anterior epithelium of iris and pigmented epithelium of retina
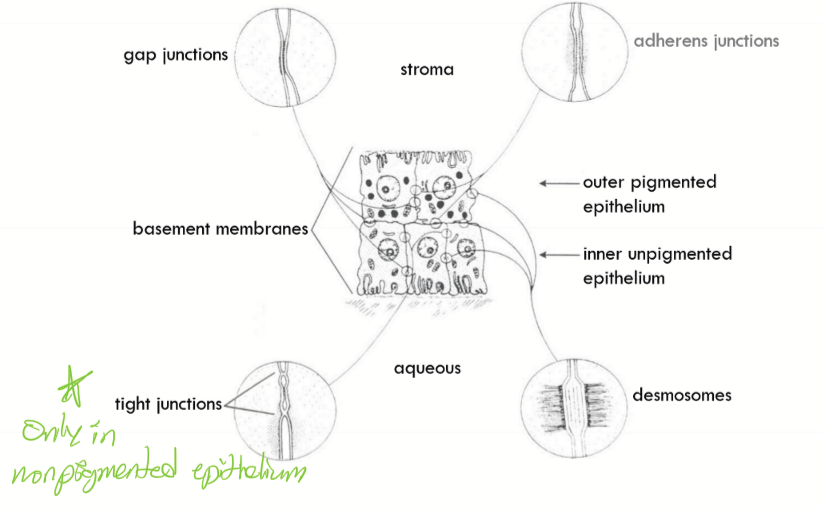
Contains desmosomes, adherens junctions, gap junctions
The basement membrane attaches to the outer pigmented ciliary epithelium to the stroma
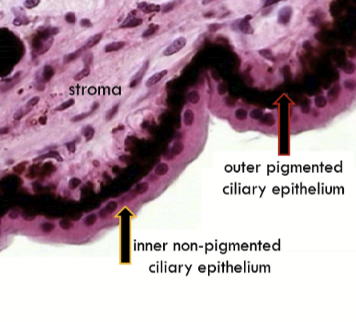
Inner non-pigmented ciliary epithelium
Continuous with posterior epithelium of iris and neural layers of retina
Contains desmosomes, interdigitations, gap junctions, and tight junctions
The internal limiting membrane is the basement membrane.
It is continuous with internal limiting membrane of the retina and posterior iris epithleium.
Which junction is found only in the inner unpigment epithelium and not in the outer pigmented epithelium?
Tight junctions
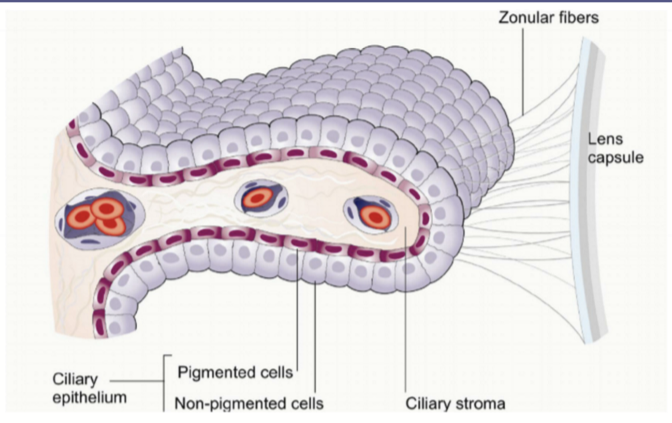
Ciliary Processes
Ciliary processes that arise from the ciliary body and are largely masses of small blood vessles.
Each consists of a central core of stroma covered by a double layer of epithelium: inner nonpigmented and outer pigmented epithelium and their associated basement membranes.
Characteristics of the capillaries in the Ciliary Processes
Capillaries in the ciliary processes are highly permeable (d/t fenestration, no endothelial cell overlap, no complete tight junctions)
Allows for easy movement of fluid and molecules
Ciliary Body Functions
Aqueous production; Produces some vitreal components; controls accommodation
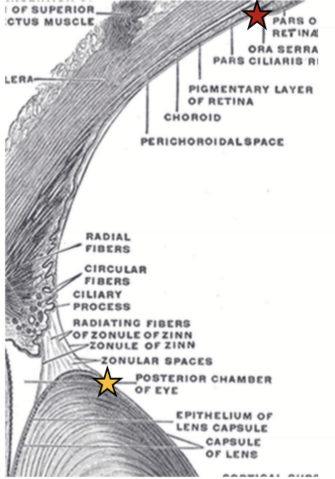
Zonules
Composed of dense aggregates of microfilaments
Fibrillin is a critical glycoprotein (principle component)
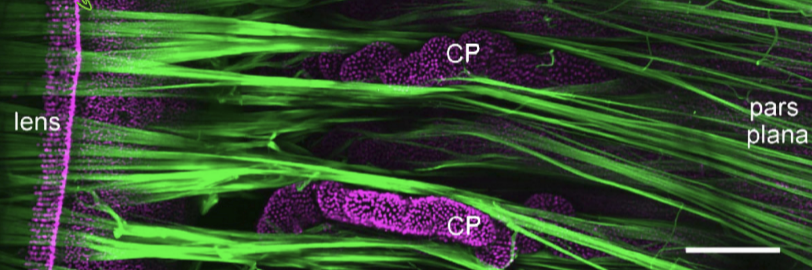
Classification of main fibers
Orbiculoposterior
Orbiculoanterior
Cilioposterior
Cilioequatorial
Orbiculoposterior
Origin = ora serrata
Insertion = into posterior capsule (at ligament of Weiger)
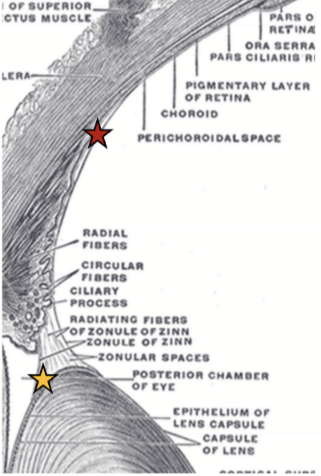
Orbiculoanterior
Origin = CB pars plana
Insertion = Into the anterior lens capsule
Thickest and strongest zonules & attached to thickest part of lens capsule
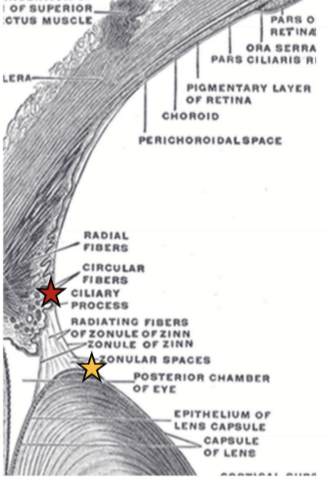
Cilioposterior
Origin = CB valleys
Insertion = Into posterior lens capsule
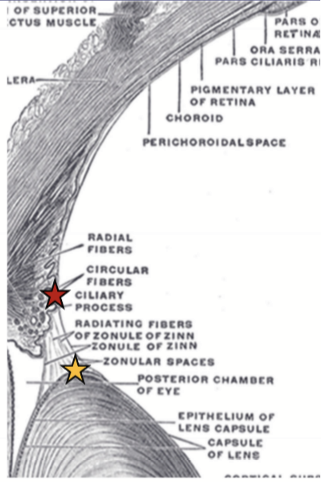
Cilioequatorial
Origin = CB valleys
Insertion = Into equator of lens capsule
Classification of auxiliary fibers
Orbiculociliary: from pars plana to posterior ciliary process
Interciliary: from ciliary process to process
Function is to provide stability for primary zonules & hold ciliary body in place
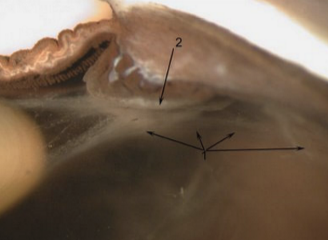
Zonular Failure
Zonular tears or dehiscence
Lens destabilization or luxation (completely fallen out)

Ciliary Muscle
Action:
Contraction of muscle → eye focused for near
Relaxation of muscle → eye focused for distance
Innervation:
Parasympathetic stimulation activates muscle (contraction)
Sympathetic has an inhibiting effect; reduces activation