Alkyl Halides
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Alkyl halides
organic compounds in which one or more halogen atoms- fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine- are substituted for one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon
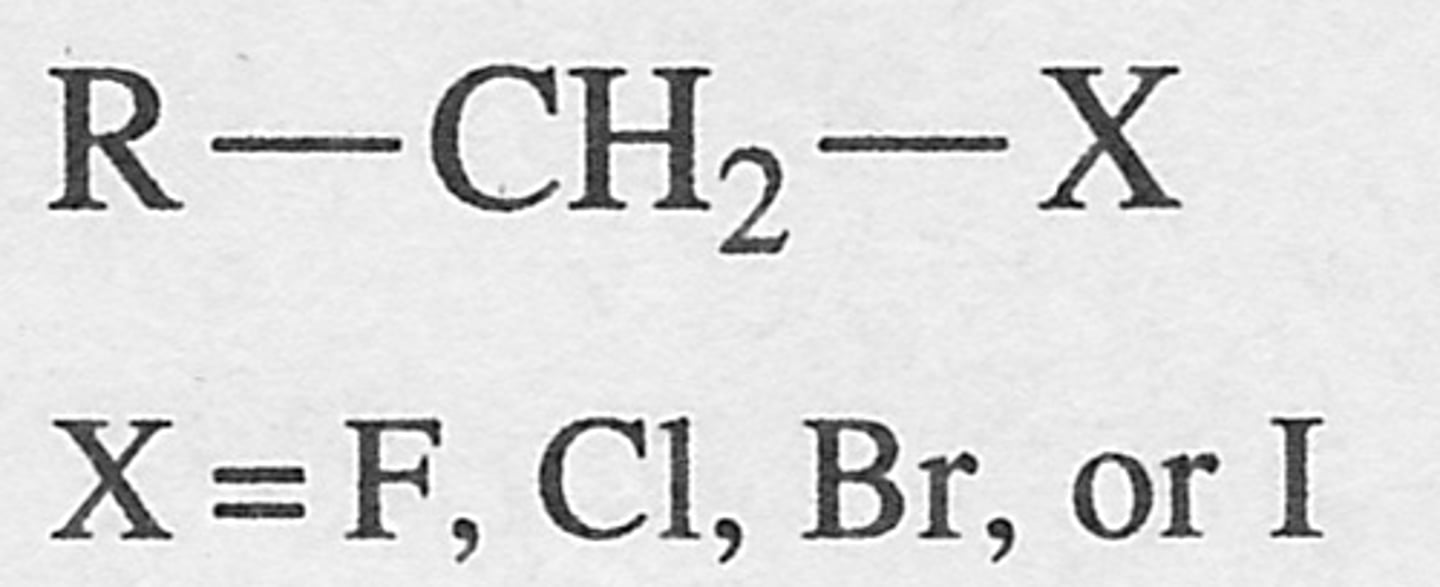
Primary alkyl halide
An alkyl halide in which the carbon atom bonded to the halogen is also bonded to 1 other carbon atom.
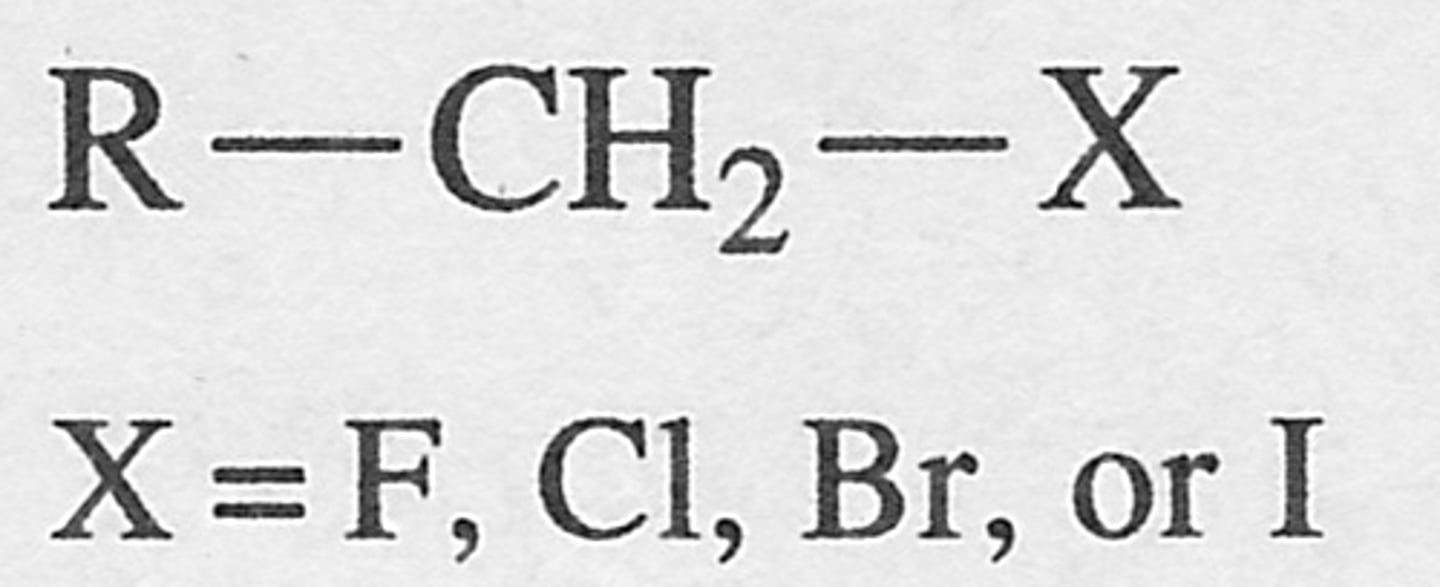
Secondary alkyl halide
an alkyl halide in which the halogen is bonded to a secondary carbon
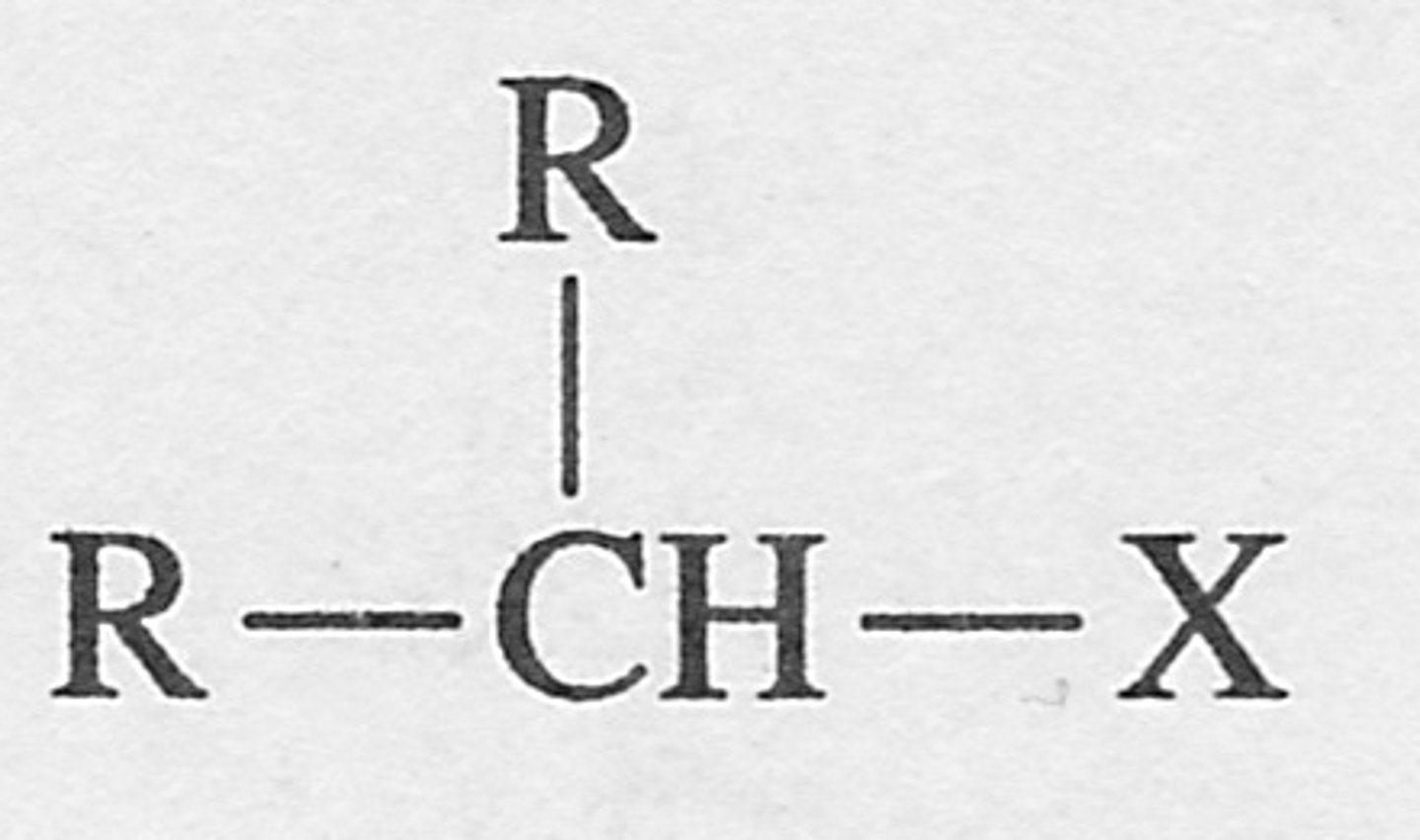
Tertiary alkyl halide
an alkyl halide in which the halogen is bonded to a tertiary carbon
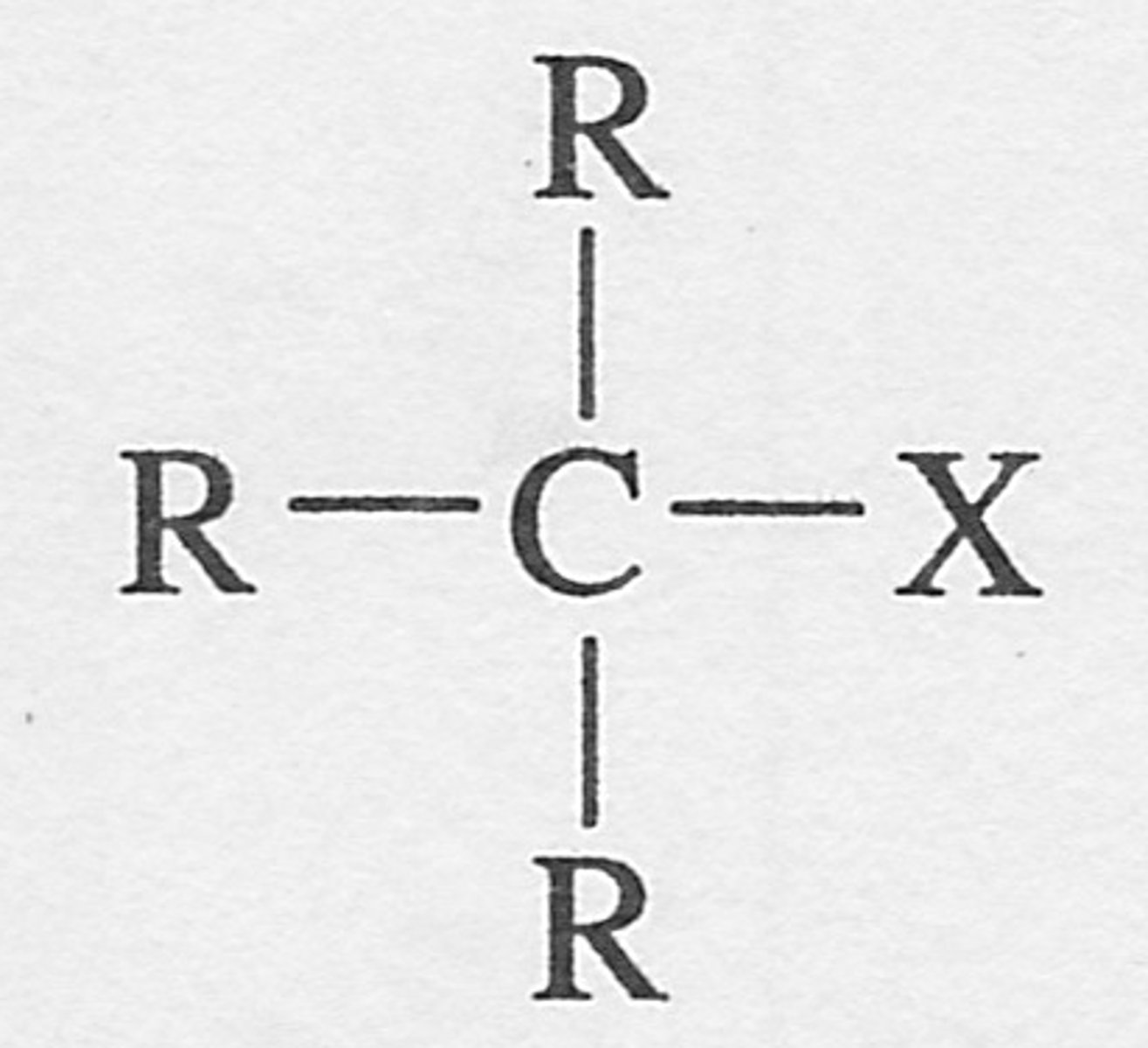
Halogenoalkane
An alkane with at least one halogen atom in place of a hydrogen atom
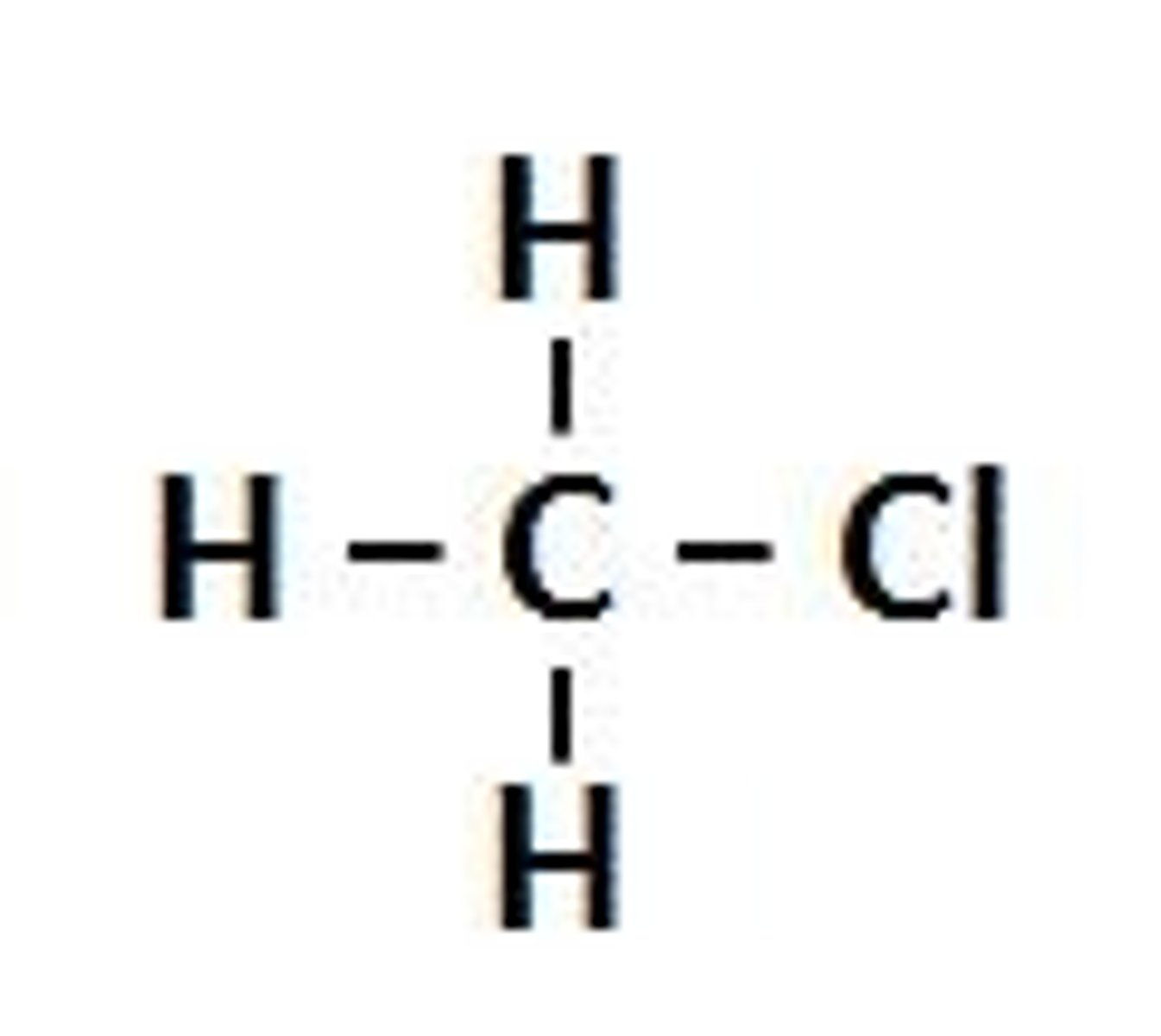
CFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons.
Non flammable, not toxic.
Used in refrigerants, aerosols, propellants, plastics, degreasing.

Dangers of CFC
Destroy the ozone layer.
Carbon-chlorine bond breaks into chlorine free radicals, which break down ozone.
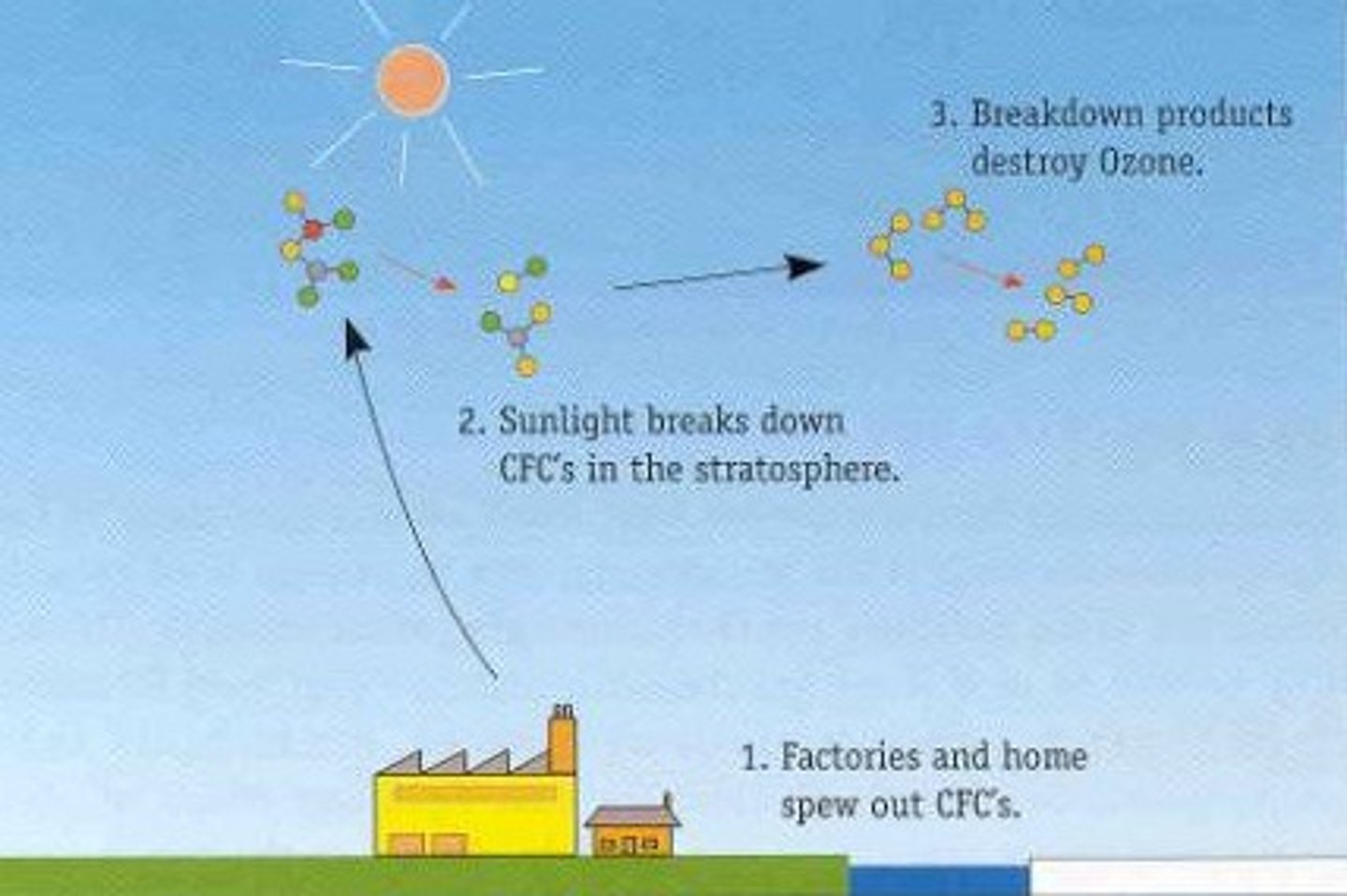
CFC-11
5000x greater global warming potential that CO2
Halothanes
Only inhalation anesthetic agent containing a bromine atom.
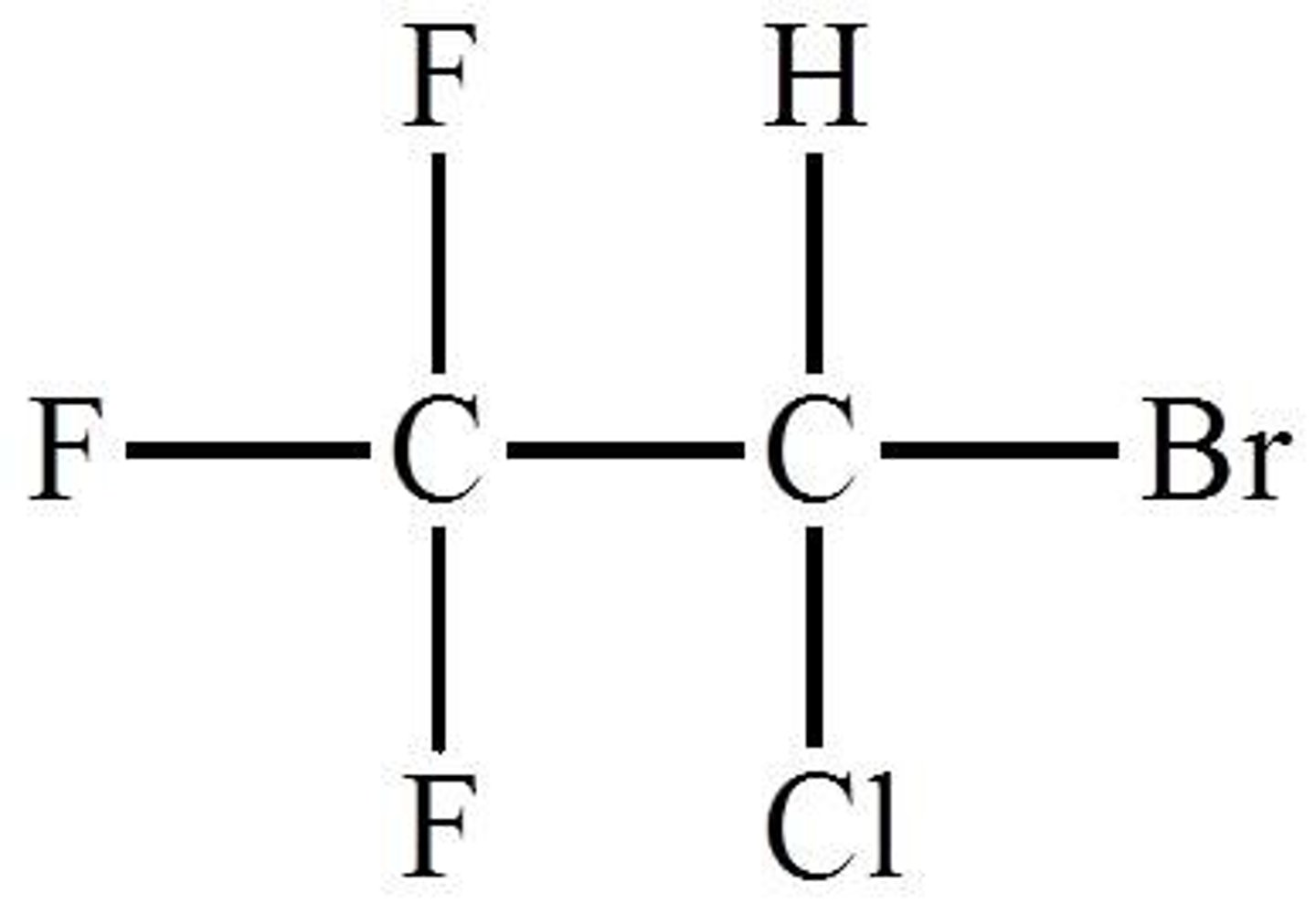
CCl4 uses
Used in fire extinguishers,
precursor to refrigerants,
cleaning agent.
Halothanes characteristics
Colorless,
Pleasant smelling,
Unstable in light
CCl4 (Carbon tetrachloride) characteristics
Colorless liquid,
sweet smell that can be detected at low levels
CCl4 other names
Halon
Freon
in HV AC
CHCl3 (Chloromethane) uses
Used to be used as a refrigerant, but not anymore because it is toxic.
Used for making lead based additives for gasoline.
Chemical intermediate in the production of silicone polymers.
Solvent in the manufacture of butyl rubber.
Methylating and chlorinating agent.
Many other uses
Teflon (PTFE) uses
Non stick coating for pans,
Containers and pipework for reactive and corrosive chemicals.
Lubricant for machinery
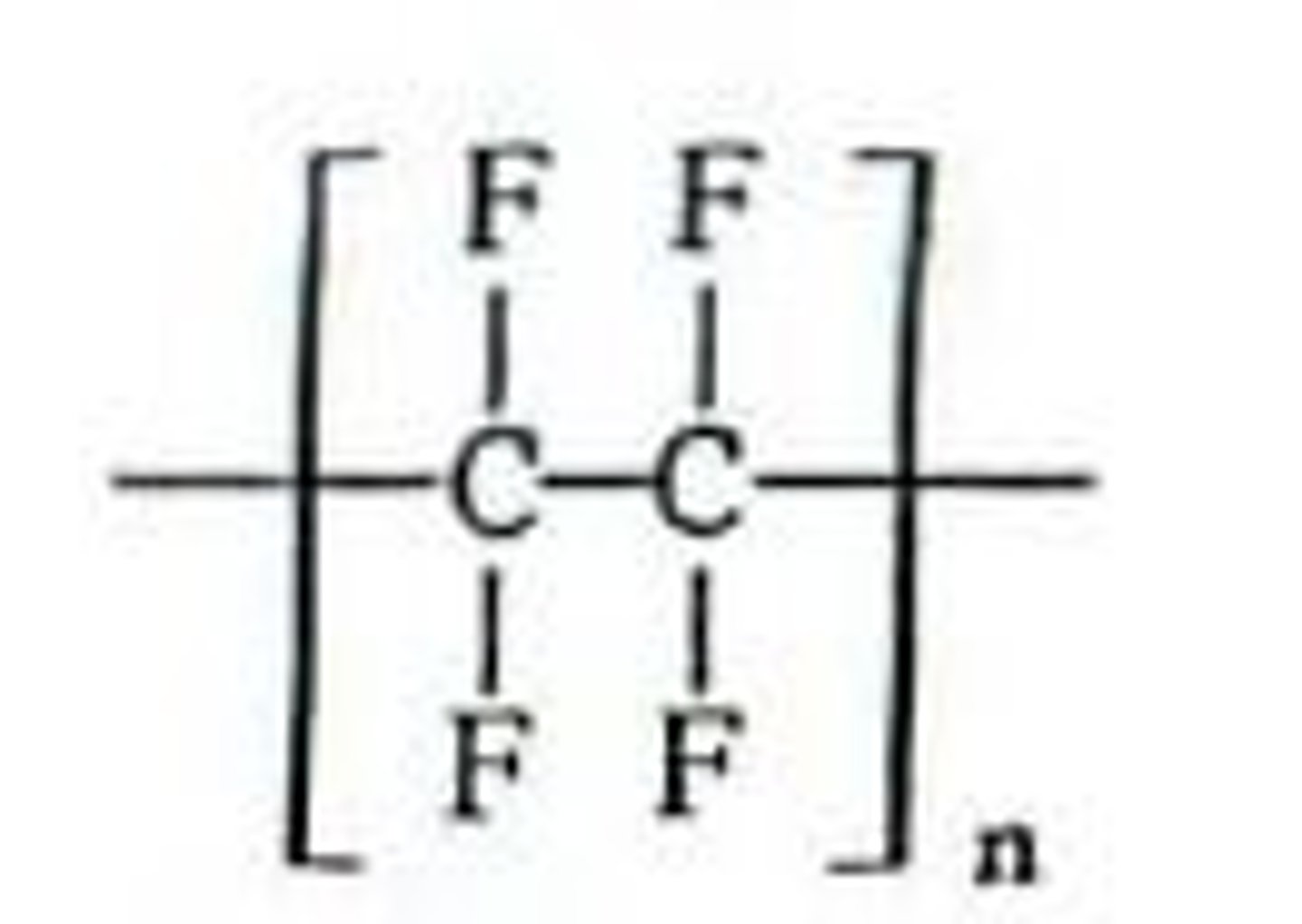
Teflon (PTFE) characteristics
Non reactive because of the strength in the carbon-fluorine bonds.
What does the reactivity of alkyl halides depend upon?
C-X bond energy and polarity
The greater the bond energy of R-X,
The greater the stability,
The less reactivity
The greater the electronegative difference (bond polarity) of R-X,
The greater will be the stability and the lesser the reactivity
Reactivity of halogens in order
I > Br > Cl > F
When is R-F the most reactive?
If an electrophile is attacking the reagent.
Which two types of reactions do alkyl halides show generally?
Nucleophilic substitution,
Elimination
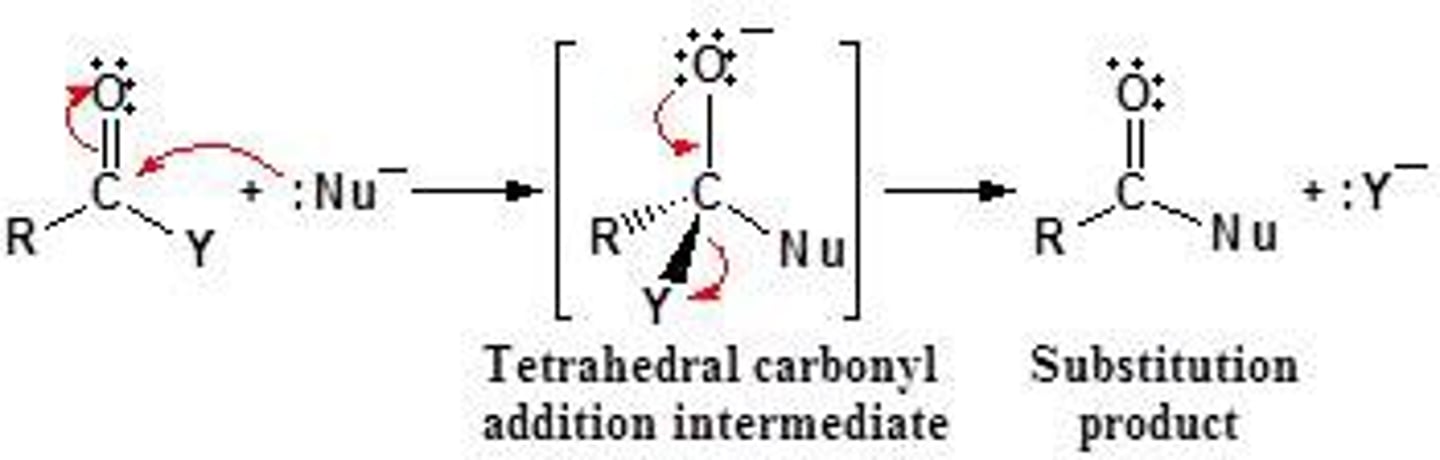
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
-SN1 and SN2
- Reactions in which the halogen is replaced by some other atoms or a group
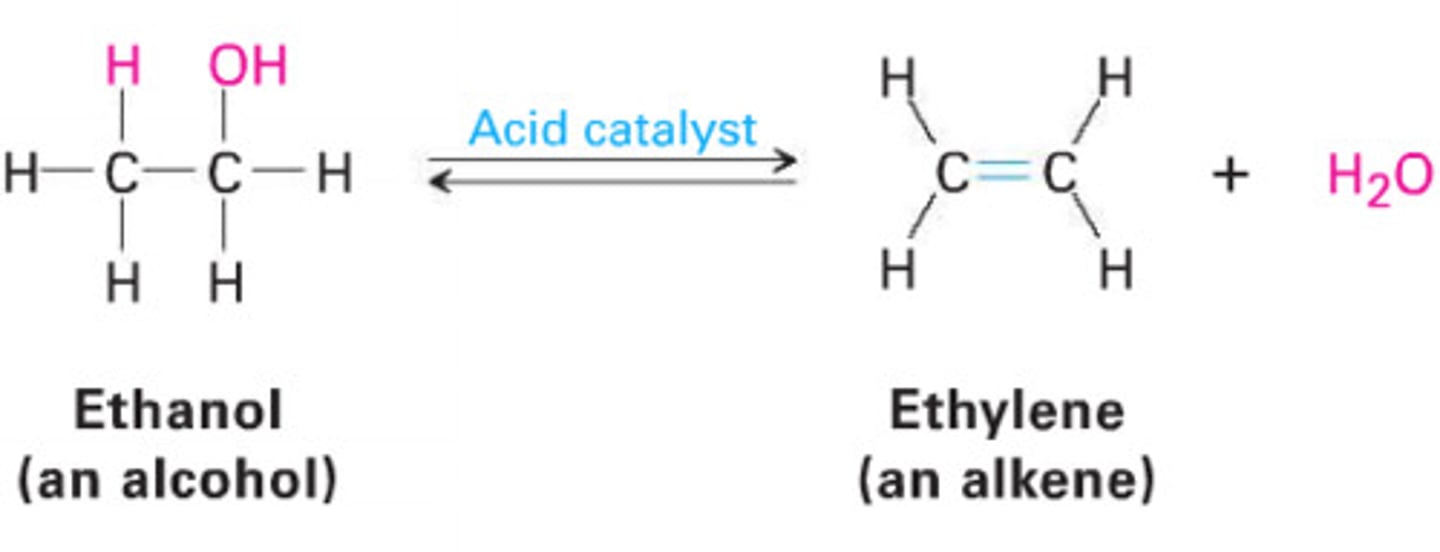
Elimination reaction
The removal of HX from the halide,
E reactions
Electrophile
Electron deficient molecules which accept electron pairs to make new covalent bonds
Examples of electrophiles
Positive ions,
Neutral molecules (SO3, AICI3, BF3),
Carbon atom bearing positive charge in a partially ionic covalent molecule
Nucleophiles
Electron rich molecules which donate electron pairs
Examples of nucelophiles
Negative ions,
Molecules with lone pairs (NH3, H2O, -NH2),
A molecule with a pi electron (C2CH, C2H4),
Carbon bearing partial negative charge in organometallic compounds (Grignard's reagent)
Leaving group
The group that departs with an unshared pair of electrons.
Sn reactions, the incoming nucleophile must be stronger than the leaving one.
Sn reactions
Nucleophilic substitution reactions
Which two ways can Sn reactions occur?
Sn1: Nucleophilic substitution unimolecular,
Sn2: Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular
Sn 1 reaction molecularity
1
Molecularity
the number of molecules that participate as reactants in an elementary reaction
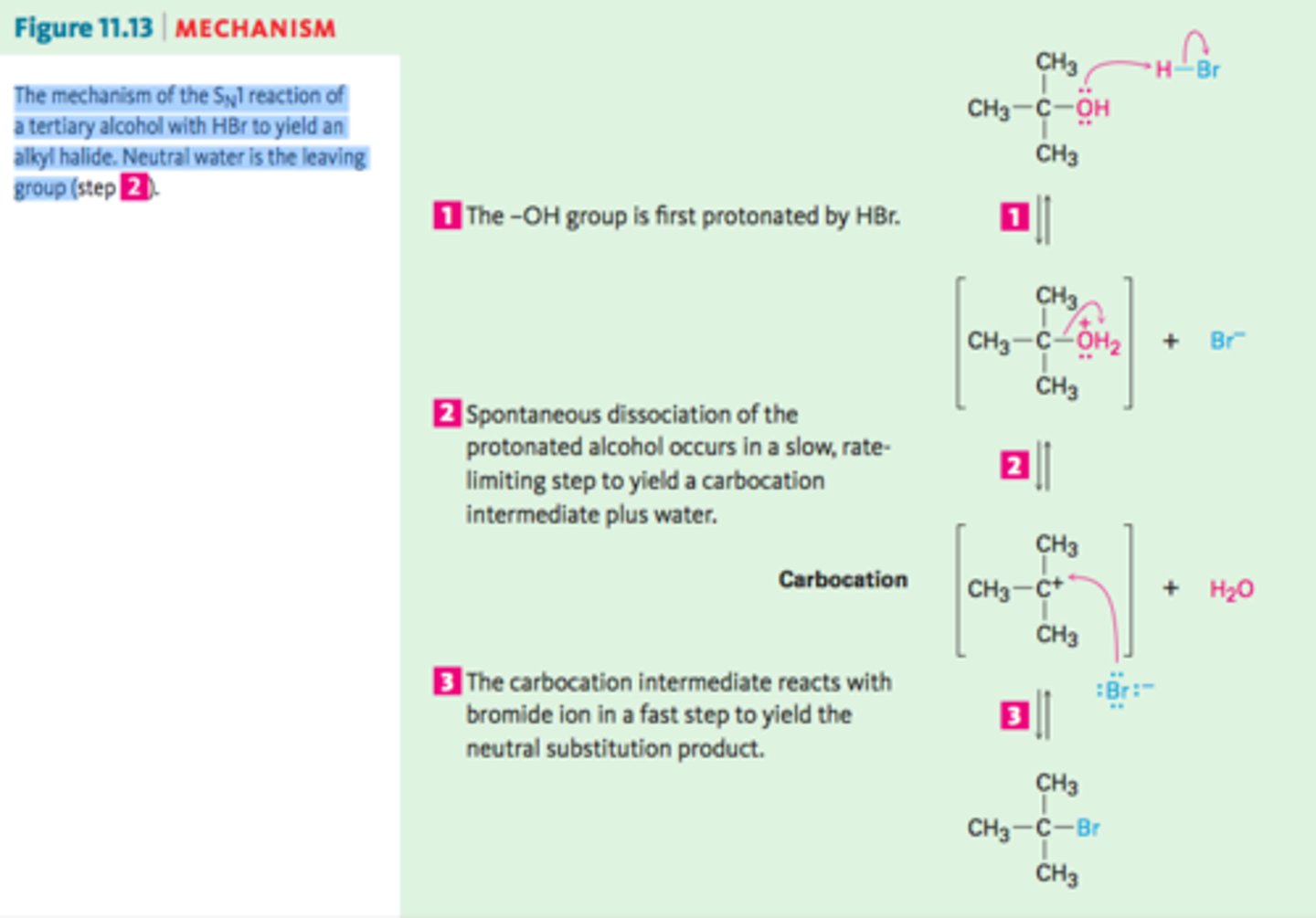
Sn 1 reaction mechanism
2 step mechanism.
R-X --> R+ X- (slow),
R+ + Nu- --> R--Nu (fast)
Sn 1 reaction rate
Rate α [R-X]
Rate = k[R-X]
Sn 1 reaction order
1
Sn 1 reaction
In tertiary alkyl halides.
Coming nucleophile may attack from any side.
Favored in polar solvents
Sn 2 reaction molecularity
2
Sn 2 reaction mechanism
Single step.
R-X + Nu- --> R-Nu + X- (slow)
Sn 2 reaction rate
Rate α [R-X][Nu-]
Rate = k[R-X] [Nu]
Sn 2 reaction order
2
Sn 1 reaction product
Racemic mixture.
50% inversion
50% retention of configuration
Sn 2 reaction product
100% inversion of configuration
Sn 2 reaction
In primary alkyl halides.
Coming nucleophile attacks from backside.
Favored in non polar solvents.
What kind of reactions does a secondary alkyl halide give?
Sn 1 and 2, depending on the structure of alkyl group or nature of the solvent
Processes in Sn reactions
1) Breakage of C-L or C-X bond.
2) Formation of C-Nu bond.
What does the mechanism of the Sn reaction depend on?
Timing of the 2 main processes.
If the processes occur simultaneously, its Sn2.
If the bond breaks first and then the formation happens, it is Sn1.
When purely alcoholic solution of sodium/potassium hydroxide and halogenoalkanes are reacted an alkene is formed, what is the mechanism of reaction
Elimination
The organic compound carbon tetrachloride is used as
Solvent
Hydrolysis of bromoethene condition
Dilute NaOH warm
In substitution reactions, dihaloalkane or secondary halogenoalkane give / show
Both SN1 and SN2
The order of reactivity of alkyl halides towards nucleophile is
RI > RBr > RCl > RF
The halothane used in hospitals as an anesthetic is chemically
2-Bromo-2-chloro-1, 1, 1-trifluroethane
Is BF3 a nucleophile?
No