Chapter 2: The Marketing Environment
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Marketing environment
environment in which companies operate
consists of external, exogenous forces (eg. climate change) = uncontrollable factors
The business and its marketing environment
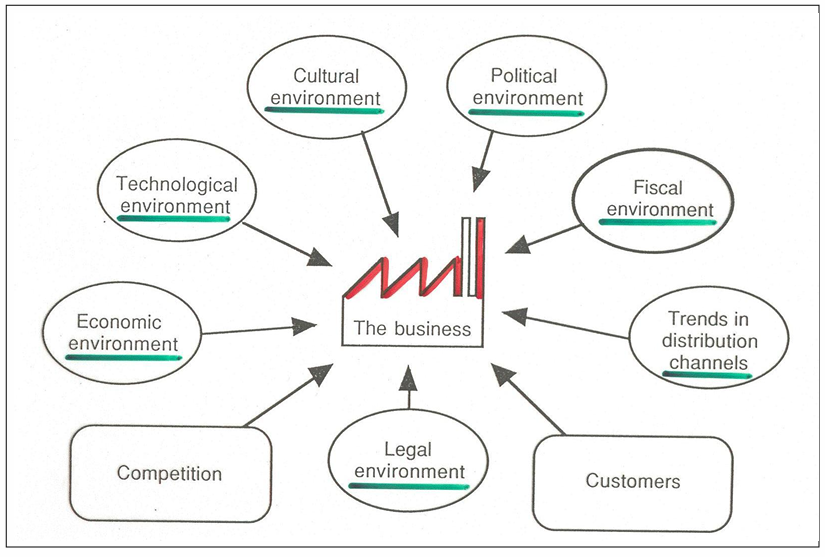
Components of the marketing environment
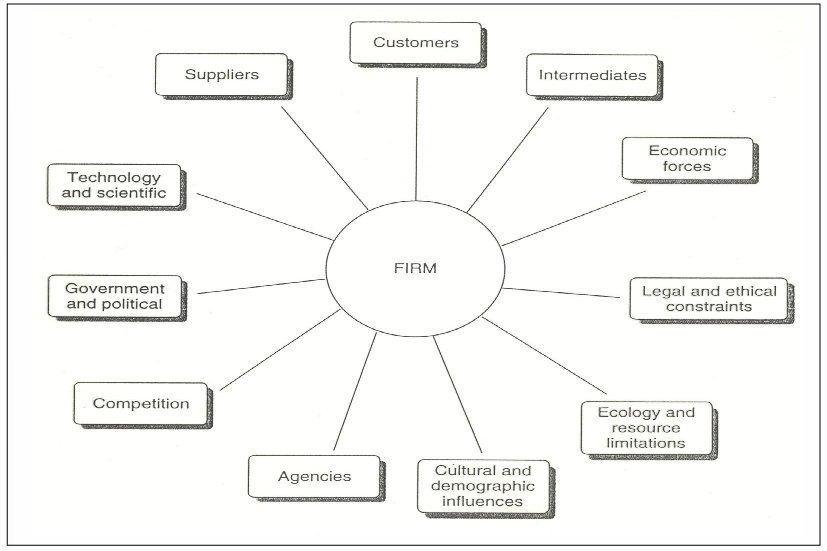
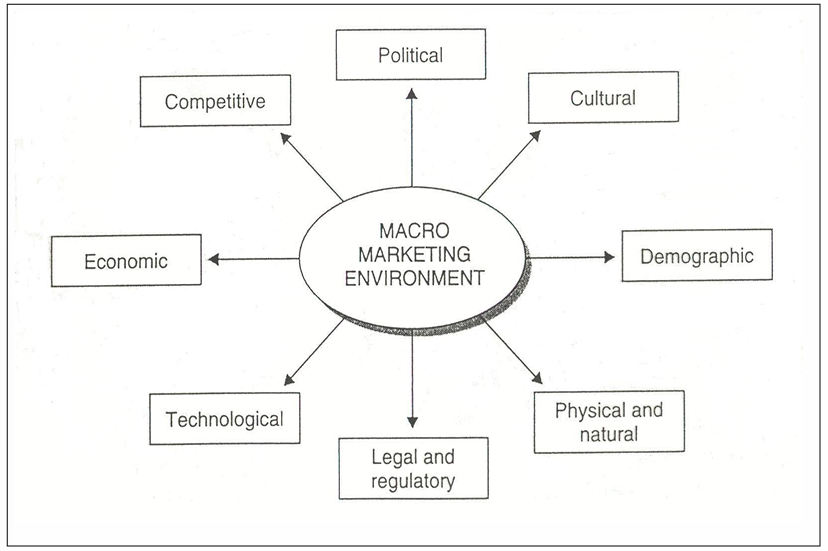
Components of the (macro-)marketing environment
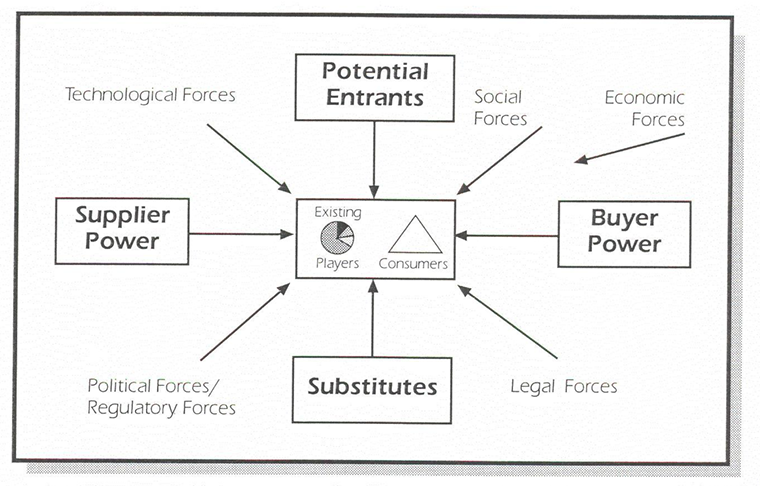
5 exogenous forces in the marketing environment (Forces + impact + how to cope with it)
Forces
Economic forces (Eg. inflation, interest rate…)
Structural forces
Political forces (Eg. government, changes in leadership…)
Social forces (Eg. cultural trends and patterns in society)
Technological forces (Eg. innovation, scientific breakthroughs…)
Impact on
individual firms
competitors
whole industry
How to cope with it
Keep informed
Act collectively
Develop contingency plans
Beware of the Boiled Frog Syndrome
Boiled frog syndrome
Literally
You place a frog directly in a pot of boiling water → the frog will scramble out
You place a frog in room temperature water → the frog will stay in the pot → you heat up the water → the frog enjoys it → you heat up the water further → the frog becomes groggier and is unable to climb out of the pot → the frog stays in the pot and boils to death
Message
Everybody notices revolutionary changes in the environment
Slow gradual changes are the most dangerous ones
Conclusion: you have to constantly monitor changes in the environment and also slow and gradual changes because they are the most dangerous oones
Forces: Economic forces
Performance of the economy = facts
gross national product
economic growth vs recession
family income
un(employment) rate
business investments
Consumer confidence = perception of the facts
Disposable income
inflation rate
media information
internal and national events
Impact of economic forces
“good” vs “bad” times
Forces: Structural forces
market structure of an industry
Eg. farms → slaughter house → process → retail → consumer
vertical and horizontal integration
Market entry barriers
Market entry barriers (Porter): attractive industry vs unattractive industry
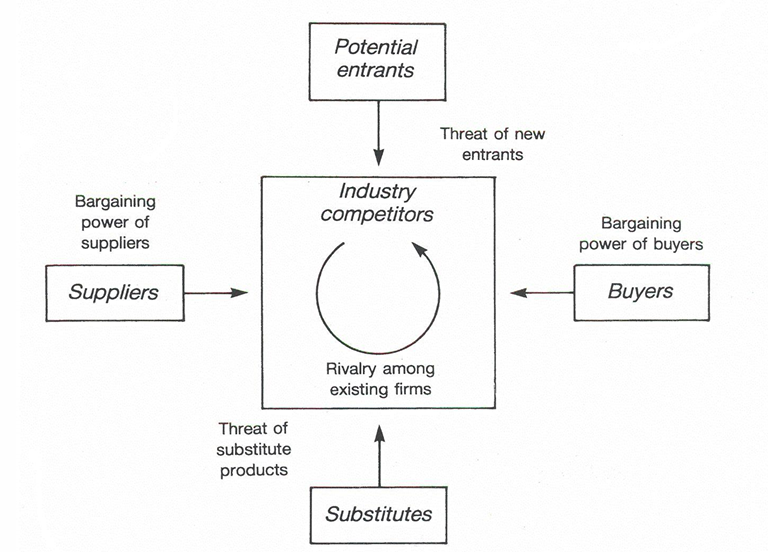
unattractive industry | attractive industry |
→ Low profit potential |
→ High profit potential |
Monopoly = market where 1 single company has developped a unique product |
Forces: Political forces
Domestic politics
Consumerism: safe, informed, choice, voice
Legal/Regulatory environment
Consumer protection regulations
Competition regulation
Information regulations
International politics
situations of cooperation ←> situations of conflict
Forces: Social forces
Social values / factors
Environmental consciousness, Animal welfare
Health consciousness, Quality orientation
Involvement in labour force
Less time for leisure/ But interest in quality time
Religion
Demographics
Age structure: « double-ageing » evolution
Population growth or decline
Emigration / Immigration
Forces: Technological forces
At different stages in the agro-food chain
Fertilizer and seeds (innovation)
Biotechnology - Genetic modification
Harvest and processing technologies
Packaging and preservation technologies
New methods of sales and distribution
Direct sales
Internet sales
Consumer acceptance? To be monitored
SWOT-analysis (components and how to rank them)
Mainly descriptive analysis
Strategic planning tool
Opportunities
Outside the company, external factors/forces
Offers new perspectives, chances
Threats
Outside the company, external factors/forces
Can cause problems, losses
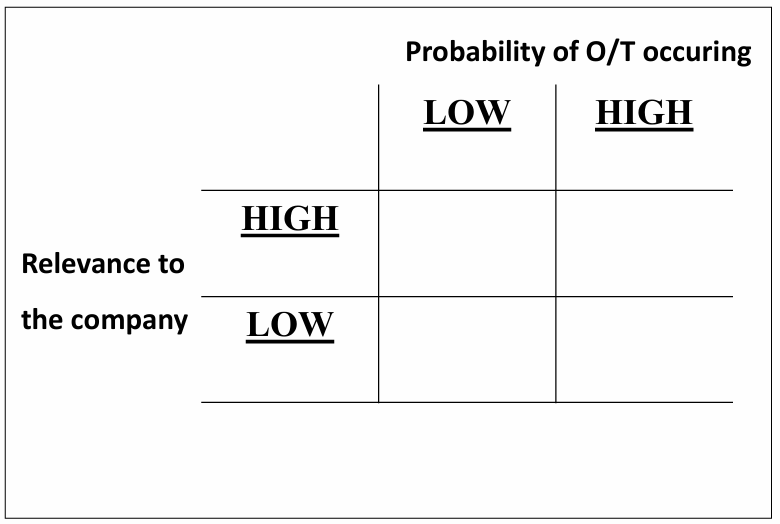
Strengths
Inside the company, internal factors
Enable the company to
Benefit from opportunities
Cope with threats
Weaknesses
Inside the company, internal factors
Prevent the company to
Benefit from opportunities
Cope with threats
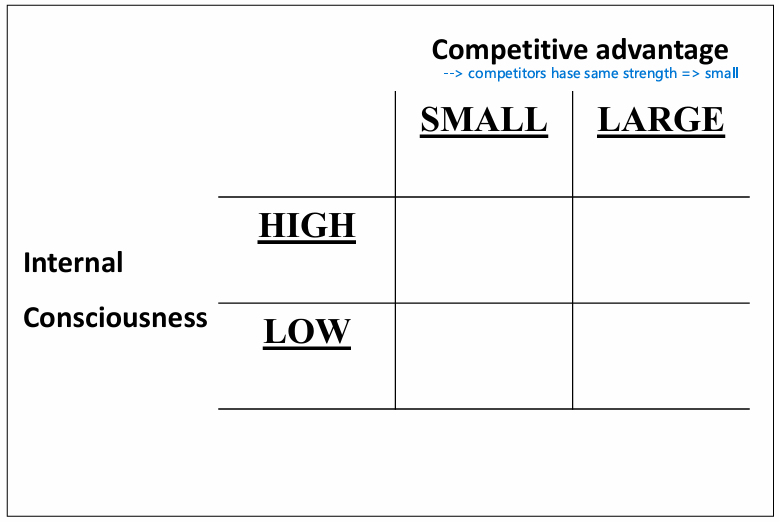
Strengths/ Weaknesses: Examples
1) Marketing
Company image and reputation
Market share
Own sales force
Own distribution channels
Research & Development
2) Financial
Cost of capital
Financial stability
Profitability
3) Manufacturing
Facilities, technical and manufacturing skills
Economies of scale
Own work force
4) Organisatorial
Visionary leadership
Managing capability
Flexibility
Dedicated workers
Entrepreneurial orientation
SWOT-grid
O (eg. international networking) | T (eg. language) | |
S (eg. you’re easy with learning languages) | Does this strength enable us to benefit from this opportunity? To what extent Strategic choice = ATTACK | Does this strength enable us to cope with this threat? To what extent? Strategic choice = DEFEND |
W (eg. sociability) | Does this weakness prevent us to benefit from this opportunity? To what extent? Strategic choice = CLEAN UP | Does this weakness prevent us to cope with this threat? To what extent? Strategic choice = CRISIS |
How to implement new strategy
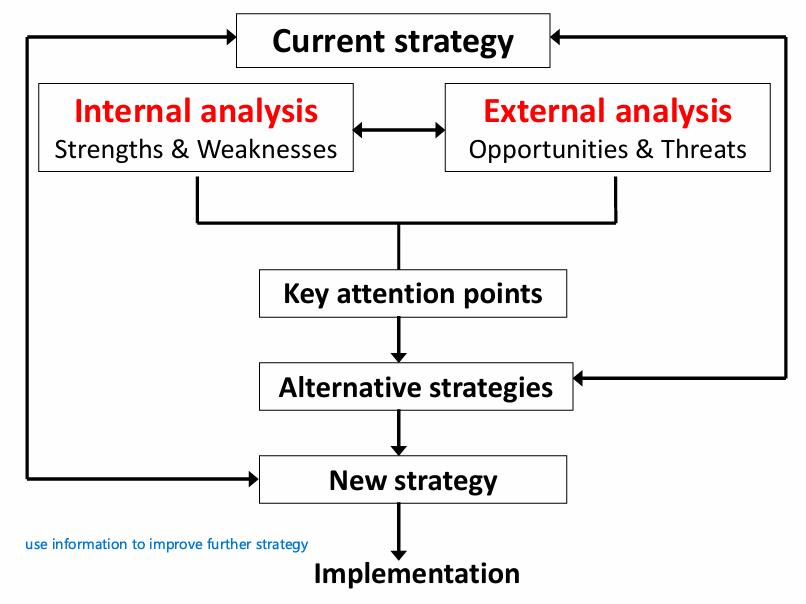
SWOT examples:
You are the marketing manager of a start-up company that produces plant-based meat alternatives with protein from microalgae. Your case looks as follows:
(1) You do not produce microalgae yourself but source microalgae protein from a multinational food ingredient supplier.
(2) The production of microalgae and the extraction of protein thereof are expensive processes.
(3) The plant-based meat alternatives that you produce have a lower carbon footprint than animal-based meat.
(4) An increasing number of consumers care about the environment and make environmentally conscious decisions.
(5) Food price inflation is still high and it is expected to remain high throughout 2024.
(6) As a start-up company, your company has a substantial amount of outstanding bank loans.
(7) You managed to bring together and employ a team of food scientists and technologists with excellent skills.
(8) Due to climate change, the environmental conditions in the area where you are located are becoming more suitable for microalgae production.
1) Threat
2) Threat
3) Strength
4) Opportunity
5) Threat
6) Weakness
7) Strength
8) Opportunity
More explanation → see ppt