Pharmacology Osmosis Q's
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
A novel compound is currently being studied to potentially treat pancreatic cancer. The compound is being tested in pancreatic cell cultures for efficacy and in rats to evaluate for adverse effects. Which of the following phases of development is this medication currently undergoing?
Preclinical
-when a compound is tested in animal models or cell cultures to evaluate efficacy and safety.
A new medication is currently being studied, and attempts are being made to understand its pharmacodynamic profile better. The median toxic dose is found to be 55 mg/ml, and the median effective dose is found to be 20 mg/ml. Which of the following is the therapeutic index of this medication?
55/20 =2.75
A group of researchers is studying a novel therapeutic agent and performing experiments to better understand this compound's properties. One of the researchers is assigned to study the pharmacokinetics of the compound. Which of the following describes a pharmacokinetic process?
Plasma concentration of a medication over time
What is pharmokinetics
Pharmacokinetics is the study of the activity of a drug in the body and its concentration in the body’s compartments over time, including the processes by which drugs are absorbed, distributed in the body, metabolized and localized in the tissues, and excreted
A 66-year-old man presents to the emergency department with crushing substernalchest pain. He is found to have an inferior wall myocardial infarction per ECG criteria, and the cardiac catheterization lab is activated. Before transferring, this patient is treated with aspirin and clopidogrel since the sum of their anti-platelet effects together is more significant than their individual effects. Which of the following best describes this type of pharmacodynamic medication interaction?
Synergistic
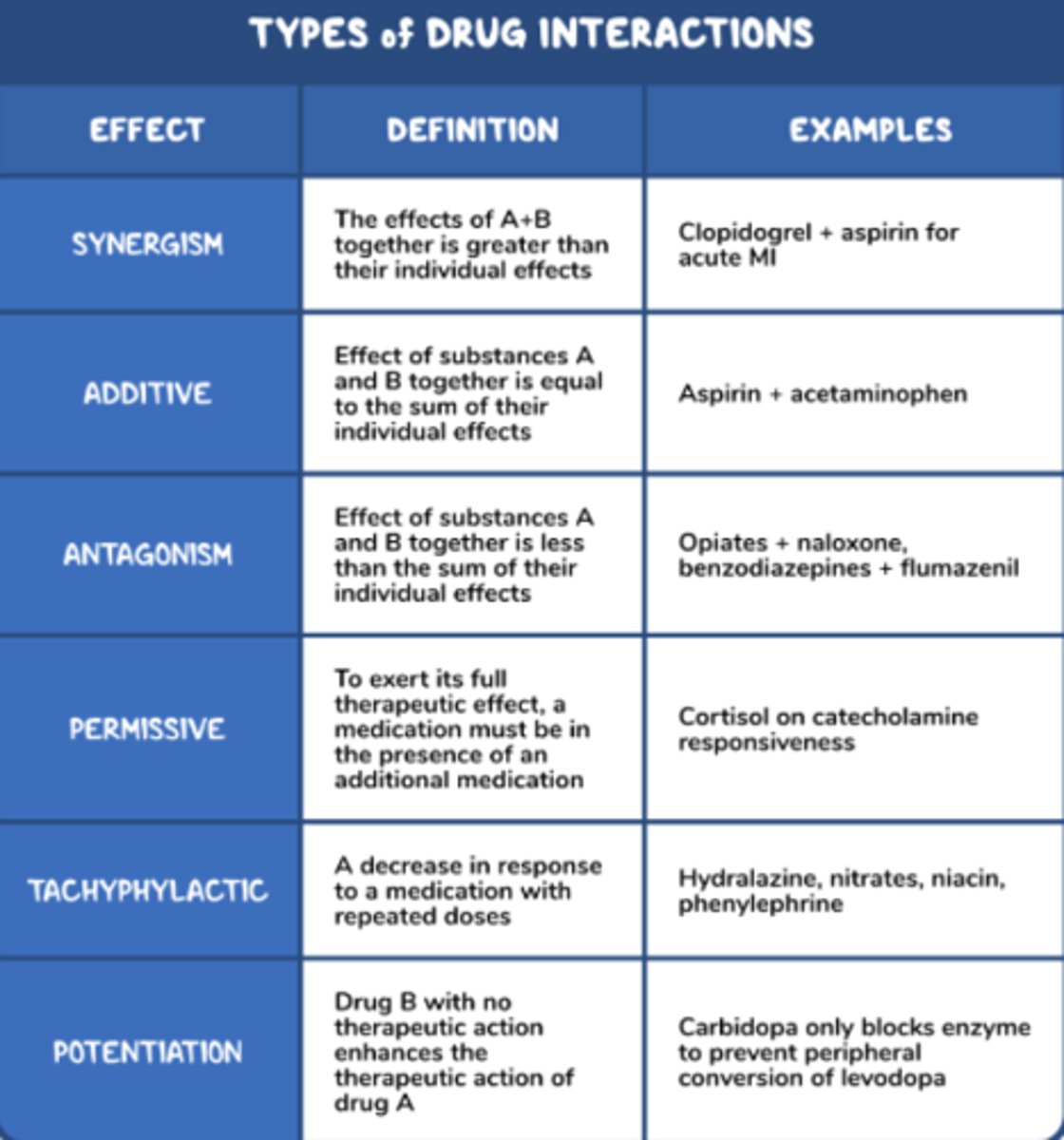
A new medication is currently being studied, and attempts are being made to understand its pharmacodynamic profile better. Which of the following correctly identifies the median toxic dose of this medication on the graph below?
A
What is the the therapeutic index of a drug
Toxic dose (TD50) / Effective dose (ED50)
is a quantitative measurement of the relative safety of a drug. It is calculated by taking the median toxic dose divided by the median effective dose, as detailed in the formula below.
Lower number (1 being the worst) is less favorable/safe
A 73-year-old man is found to have a deep vein thrombosis following an uncomplicated total left hip arthroplasty. The patient and physician decide to pursue anticoagulation with a medication with a low therapeutic index and requires frequent laboratory monitoring to ensure that the medication is in the therapeutic window. Which of the following medications is most likely being administered to this patient?
-Clopidogrel
-Aspirin
-Warfarin
-Enoxaparin sodium
-Apixaban
Warfarin
Low TI
A group of researchers is studying a novel therapeutic agent and performing experiments to better understand this compound's properties. One of the researchers is assigned to investigate the pharmacodynamics of the compound. Which of the following describes a pharmacodynamic process?
-Absorption rate
-Half-life of elimination
-Clearance
-Volume of distribution
-Receptor binding sites
Receptor binding sites
What is pharmacodynamics?
Pharmacodynamics is the study of a drug's molecular, biochemical, and physiologic effects or actions on the body.
All drugs produce their effects by interacting with biological structures or targets (e.g. receptors) at the molecular level to induce a change in how the target molecule functions regarding subsequent intermolecular interactions. These interactions include receptor binding, post-receptor effects, and chemical interactions.
The graph below shows the concentration-dependent effects of morphine in comparison to drug X, where both act at opioid μ-receptors. Which of the following best describes drug X?
Noncompetitive antagonist
Reversible competitive antagonist
Chemical antagonist
Irreversible competitive antagonist
Partial agonist
Partial agonist
A partial agonist produces a lower response at full receptor occupancy than do full agonists.
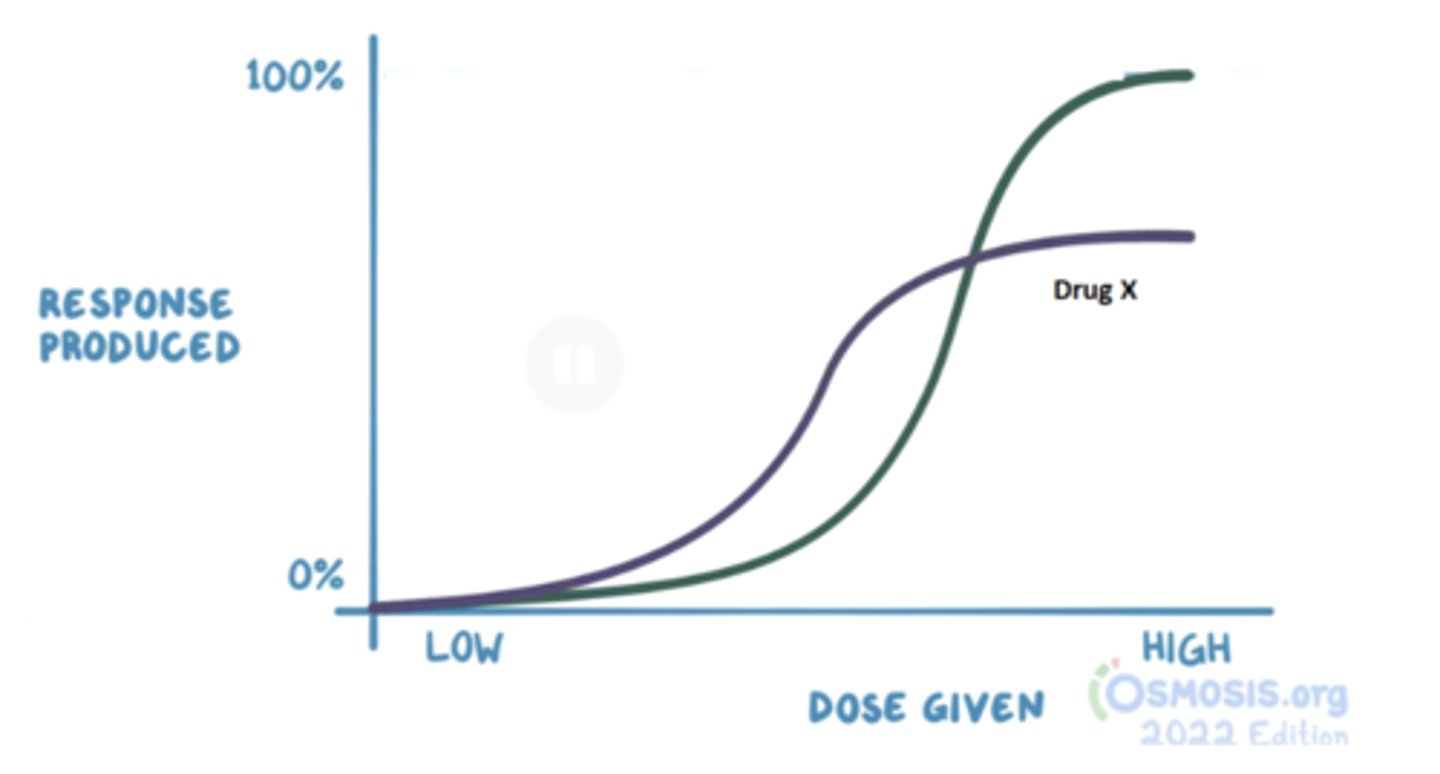
What is an agonist
An agonist can be a drug or the endogenous ligand for the receptor. Increasing concentrations of the agonist will increase the biological response until there are no more receptors for the agonist to bind or a maximal response has been reached.
The graph below shows the concentration-dependent effects of diazepam on GABAa receptors, both alone and in the presence of a fixed concentration of Drug B. Which of the following best describes drug B?
Chemical antagonist
Partial agonist
Reversible competitive antagonist
Irreversible competitive antagonist
Noncompetitive antagonist
Reversible competitive antagonist
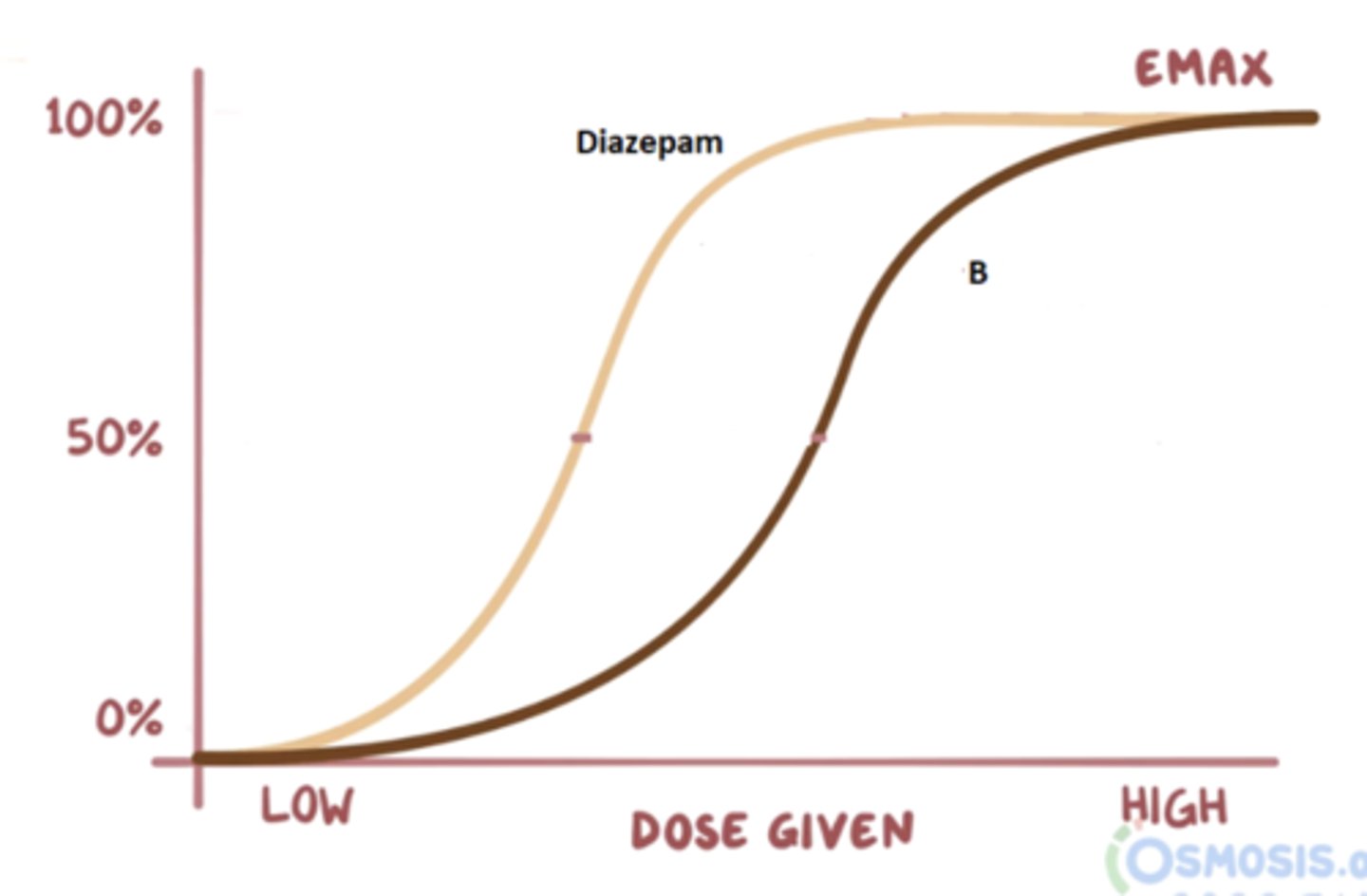
What is a competitive antagonist
A competitive antagonist is a pharmacologic antagonist that can be overcome by increasing the agonist concentration.
The inhibition caused by reversible competitive antagonists can be overcome when more ligands are floating around. So when it unbinds, it’s more likely for one of the ligands to bind. On the dose-response graph, reversible competitive antagonists shift the curve to the right, increasing the dose required to achieve ed50 without affecting Emax.
An irreversible competitive antagonist competes with the agonist for the same receptor site, but the binding is irreversible. The receptor will not activate, no matter how many agonists are around. Agonist will have increased effective dose and a reduced maximal effect of Emax (right downward shift)
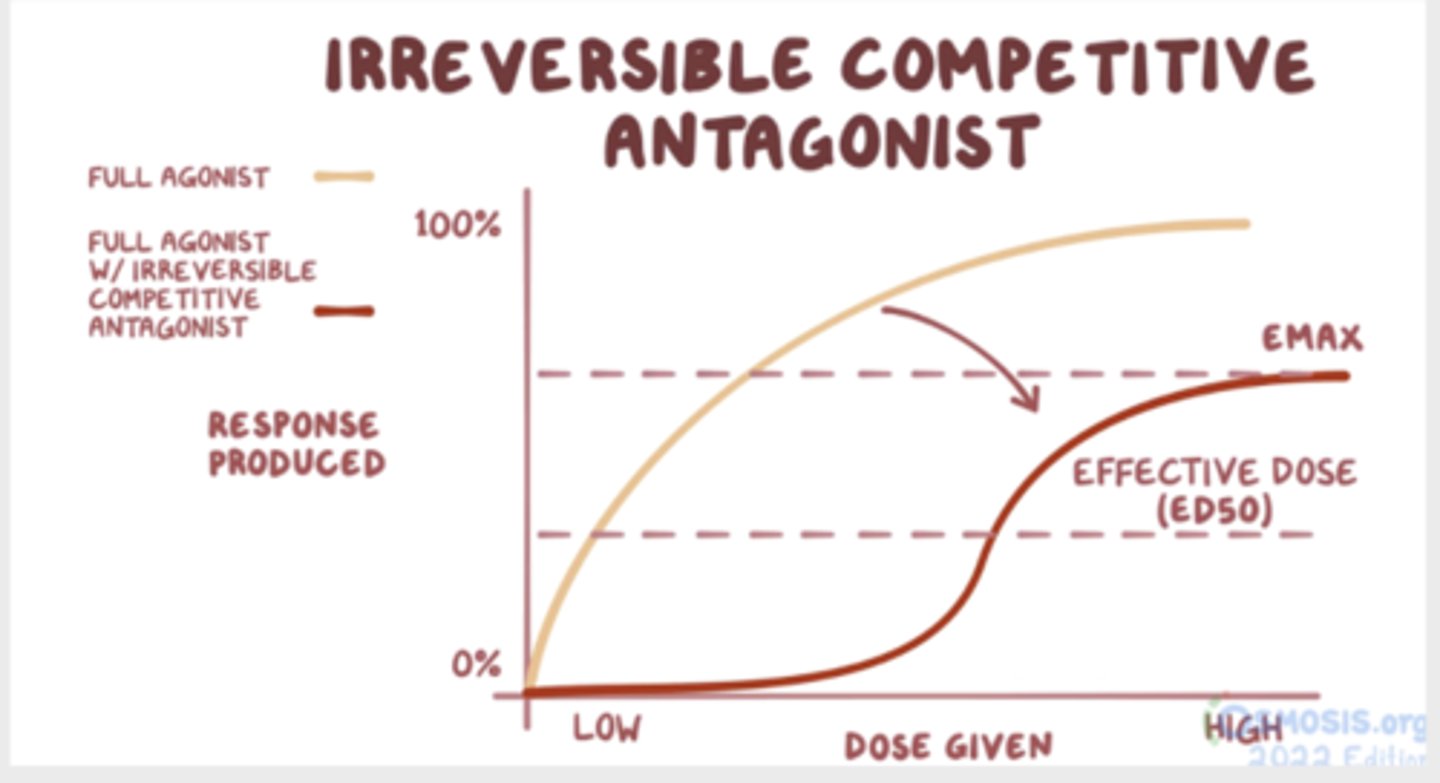
What is a non competitive antagonist
Non-competitive antagonists do not bind to the same site as an agonist; they bind to a spot called an allosteric site. When they bind, they cause the receptor's shape changes so the ligand can no longer recognize it as a binding site.
The dose-response curve shifts to the right, increasing the effective dose (ED50), and reducing the maximal effect (Emax). Non-competitive antagonists reduce the extent of the maximum response that any dose of an agonist can achieve.
Antagonists can be divided into competitive antagonists and non-competitive antagonists. Once a non-competitive antagonist binds a receptor, agonists cannot surmount the inhibitory effect, irrespective of their concentration. Which of the following is the most appropriate statement concerning noncompetitive antagonism?
-There is a right and downward shift on the dose-response curve.
-It acts at the same site as a full agonist.
-Its effect can be eliminated by increasing the concentration of agonist.
-The potency of the drug decreases.
-The action of buprenorphine at opioid μ-receptors is an example of non-competitive antagonism.
-There is a right and downward shift on the dose-response curve.
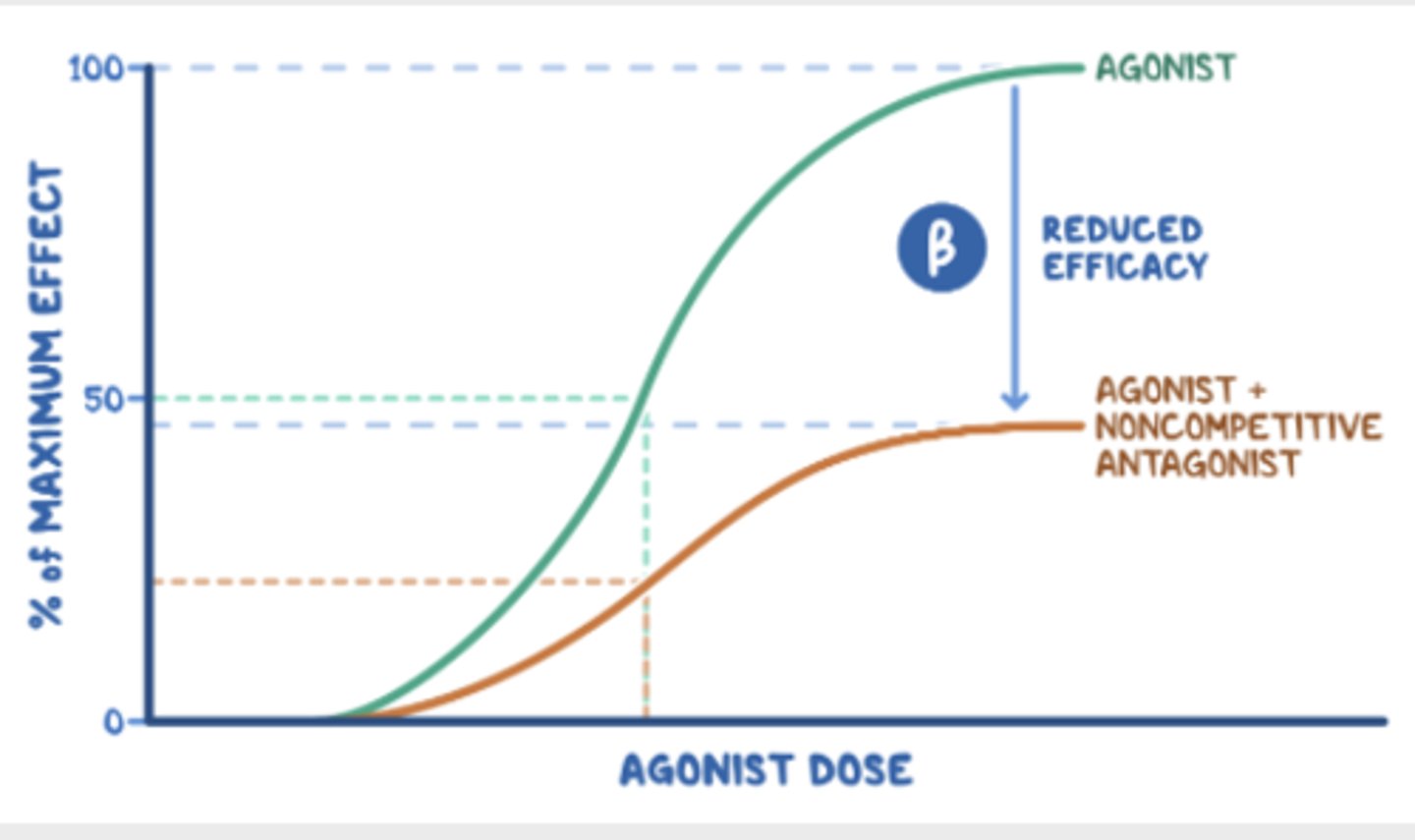
Naloxone binds to opioid receptors without activating them; instead, it decreases the receptor's ability to be activated by another agonist. Its blocking effect can be overcome by increasing the concentration of opioid receptor agonists. Naloxone can be classified as which of the following classes of drug?
competitive antagonist
A new medication is currently being studied, and attempts are being made to understand its pharmacodynamic profile better. The median toxic dose is found to be 55 mg/ml, and the median effective dose is found to be 20 mg/ml. Which of the following is the therapeutic index of this medication?