Technical Considerations in Digital Imaging (Ch. 23)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Image resolution is improved by?
Small FSS
Short OID
Large SID
Shorter exposure times with high mA
What two things are very important with digital?
Grids
Tighter collimation
What two things are no longer directly related with digital that are with film?
kVp and contrast
What are the benefits of higher kVp with digital?
Reduction in ESE, and lower mAs values
What is the total exposure to the detector still significantly impacted by?
mAs
kVp
SID
OID
Collimation
Patient
Grids
Filters
What are the two major technique exposure systems?
Fixed kVp
Variable kVp
Fixed kVp systems: the kVp is held ______ for a given range of subject densities and contrasts with the mAs is ______ to achieve the appropriate image density
Constant, varied
When were fixed kVp systems developed and by who?
Fuchs in 1943
What are the advantages of fixed kVp systems?
Decrease patient dose
Consistent contrast levels
Increases tube life
What are the disadvantages of fixed kVp systems?
Provide lower contrast than variable kVp system
Exposure changes in small increments difficult to achieve due to less mA and time stations to choose from
Fixed kVp systems begin by establishing what?
Optimal kVp
What is optimal kVp selection?
The maximum kVp level that will produce images with appropriate contrast that are consistently within acceptable limits
The optimal kVp produces ______ contrast and ________ patient dose (not the best image)
Lower, minimum
For infant extremities, what is the optimal kVp range?
50-60 kVp
For adult extremities, what is the optimal kVp range?
65-75 kVp
For Bucky extremities, what is the optimal kVp range?
75-90 kVp
For the AP spine, what is the optimal kVp range?
85-95 kVp
For the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine, what is the optimal kVp range?
85-100 kVp
For the chest, what is the optimal kVp range?
110-130 kVp
For the skull, what is the optimal kVp range?
80-90 kVp
For barium-based contrast media, what is the optimal kVp range?
120 kVp
Once the optimal kVp is determined, adjust the mAs in increments by doubling or halving mAs for every _____ of subject thickness
5 cm
When were variable kVp systems introduced and by who?
Jerman in 1925
Variable kVp systems: use the rule that adjusts ____ kVp per cm of subject thickness and dose opposite of fixed kVp
2
Variable kVp systems: the ______ is held constant for a given range of subject densities
mAs
What are variable kVp systems consistent with?
15% rule
For variable kVp systems, what does the base of the chart begin with?
(2 kVp x part cm) + 30 kVp = new kVp
What kVp system is better suited for use with digital receptors?
Fixed
What are the steps when establishing an exposure technique system (fixed or variable)?
Phantom test exposures, produce range of acceptable images
Theoretical chart by extrapolation
Clinical trial
Clinical fine tuning
Continous quality assurance
When assessing digital exposure techniques, _______ affected by exposure quantity
Image noise
Digital image processing contains _____ latitude
Wider
DR accommodates _____ times overexposure and still produces acceptable image quality
4-5
Historically because of wide latitude, radiographers slightly _____ to their technique selection to decrease the chance of image noise and avoid repeats
Add
What is dose creep?
When the whole system will need more radiation to do the same task because it is used to being overexposed
Aside from proper EI value, we must have correct _____ numbers, or __________
DI, deviation index
Calculation of exposure deviation index is formulated based upon target _____ values
EI
Indication of ________ from established target EI values
Variance
DI of 3+ considered possible ______ violations
ALARA
DI value: less than -3.0 =
Repeat
DI value: less than -1.0 =
Underexposure; consult radiologist for repeat (quantum mottle)
DI value: -0.5 to + 0.5 =
Target range
DI value: +1 to + 3.0 =
Overexposure; repeat only if relevant anatomy is clipped or “burned out”
DI value: > +3 =
Excessive radiation exposure, repeat only if anatomy is clipped, require immediate management follow-up
Photon starvation
Inadequate exposure to detector elements
Extreme overexposure yields ________
Data drop
Data drop
Detector elements are overwhelmed with photon energy; incapable of recognizing high-energy values
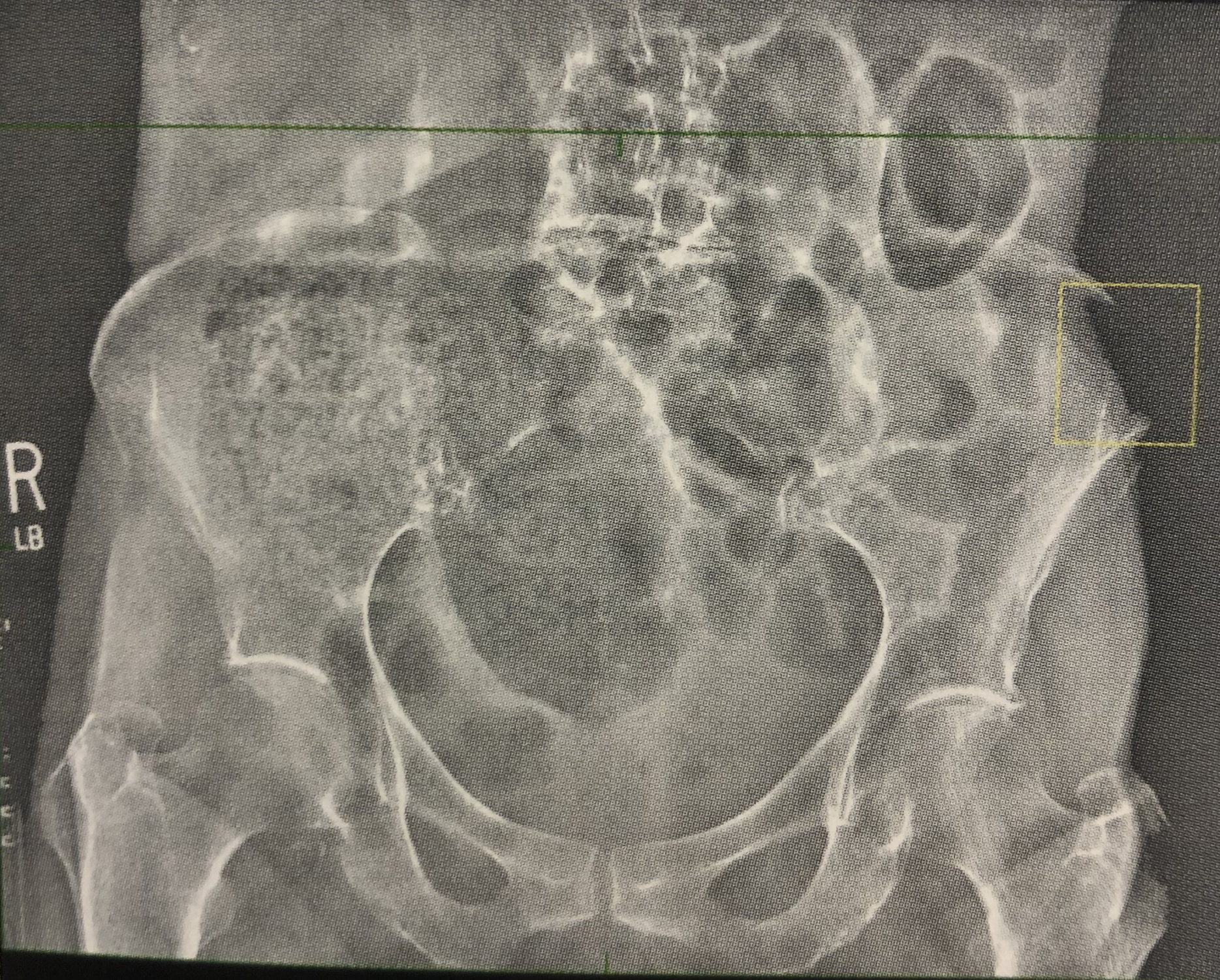
What is this image showing?
Data drop
What are the digital post-processing considerations?
Electronic masking
Electronic image annotation
Electronic masking
Cropping/shuttering display image; masking can impact the accuracy of exposure indicator values. Not a substitute for collimation
Electronic image annotation
Crucial to accuracy of medical image. Added R/L markers unacceptable and can be questioned legally
Medical radiographs are considered a _____ document, just like patients medical records
Legal
Radiologists assume the images are produced in _______ compliant manner
ALARA
Radiographers must be diligent in recognizing low-contrast image _______ and seek to remove them, or at minimum, alert the radiologist
Artifacts
Image artifacts: phantom/ghost images
Due to incomplete erasure of plate
Image artifacts: light spots
Caused by dust or foreign objects on IP
What is quantum mottle caused by?
Inadequate exposure, insufficient mAs
Image artifacts: laser film transport artifacts
Caused by uneven transport of film material through a laser imaging system
Image artifacts: algorithm artifacts
Has to do with manufacturers preset values
Image artifacts: white line
Caused by bad DELs in TFT (requires correction program)
Image artifacts: white line along the length of travel
Caused by dust on the light guide blocking light from CR plate
Image artifacts: scratches or tears or peeling
Caused by damage to CR plates
Image artifacts: fogging
From background radiation or scatter due to IP being must more sensitive
Image artifacts: histogram analysis error
Due to improper collimation (edges must be parallel to sides of IP), improper technique, beam alignment, scatter, extreme density differences
Image artifacts: poor grid alignment
Results in grid lines or only as poor image quality because the computer may not necessarily display the grid lines
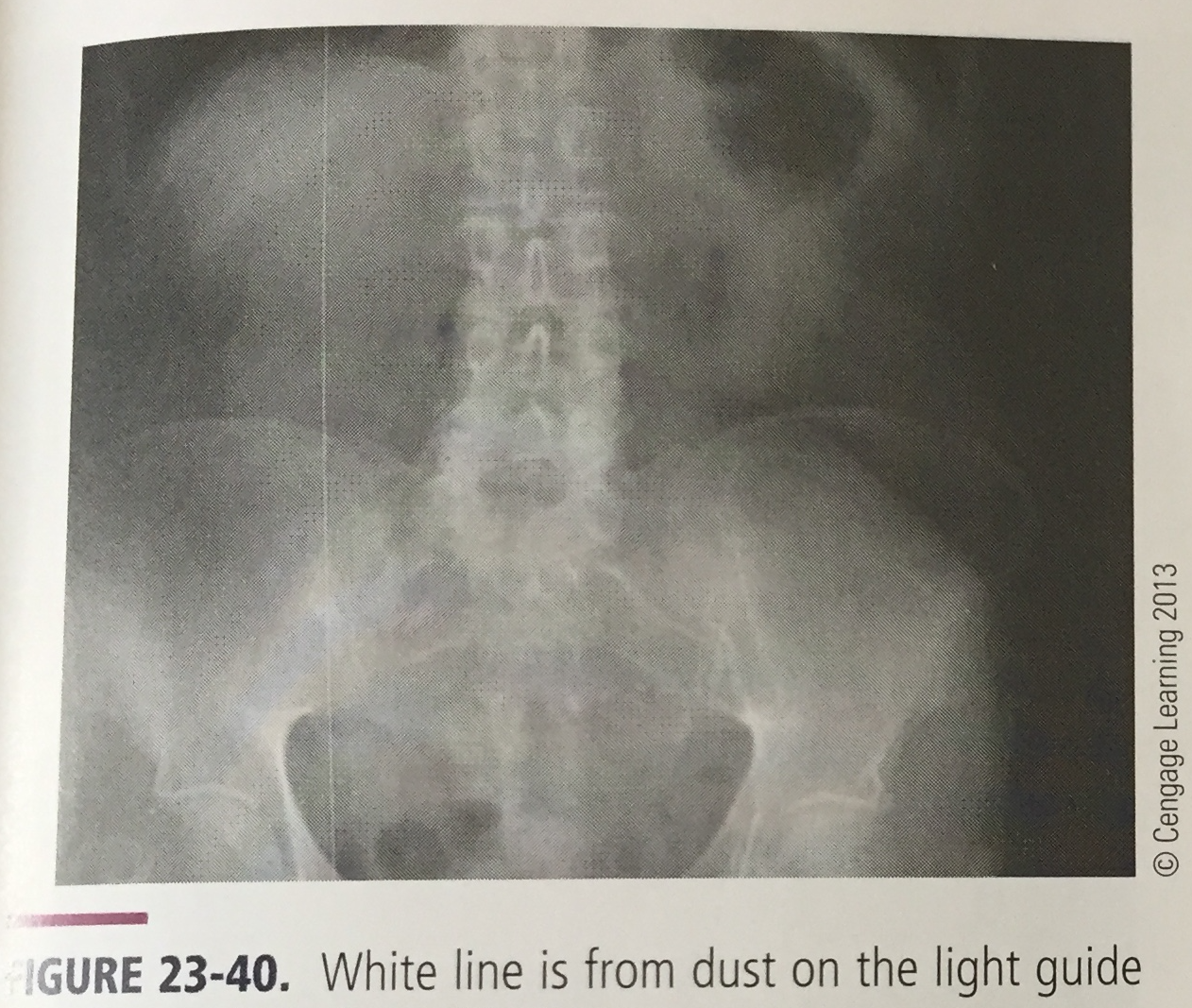
What is the artifact and what is it caused by?
White line, caused by dust on the light guide blocking light from CR plate
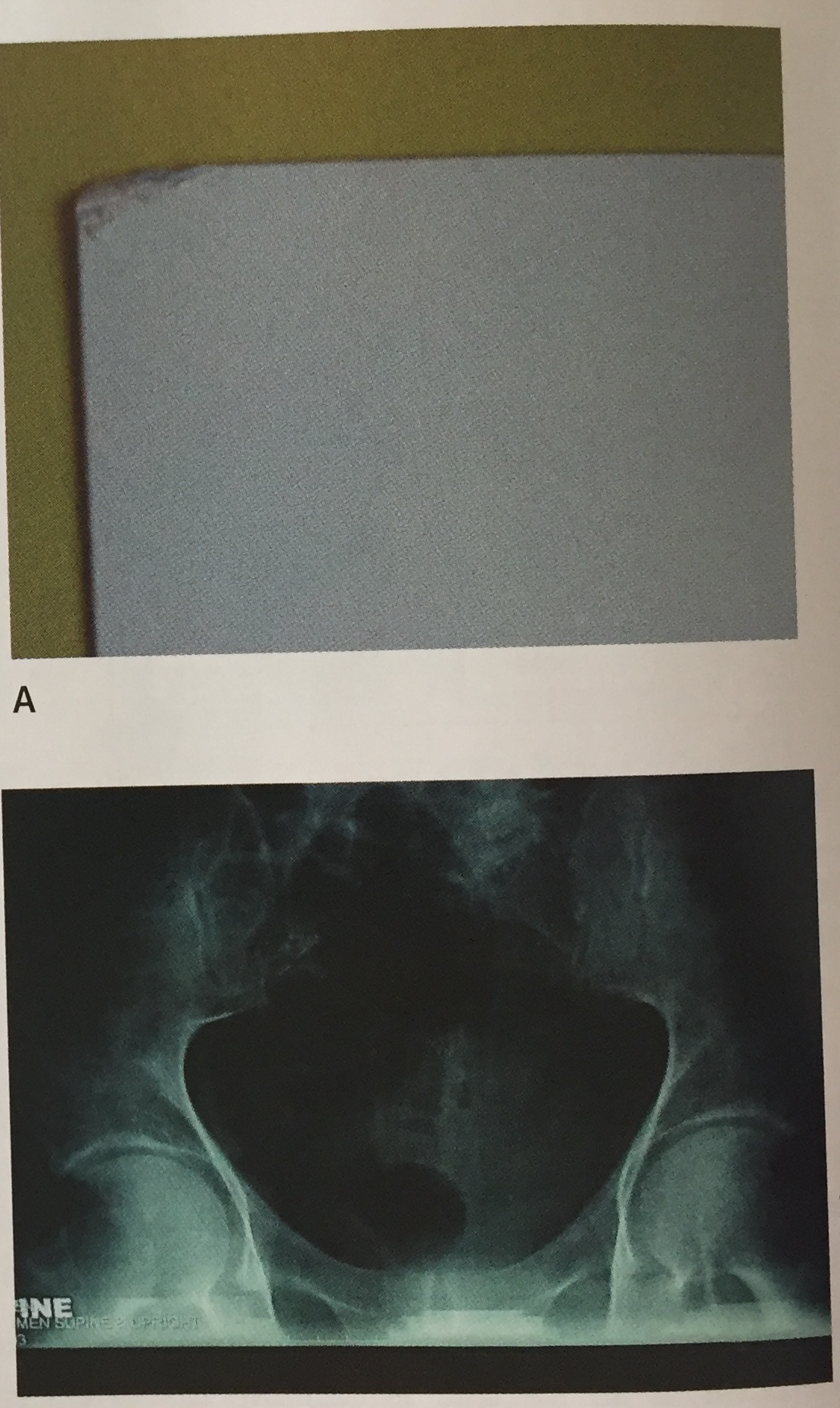
What is the artifact and what is it caused by?
Scratches or tears caused by damage to CR plates, and peeling of IP
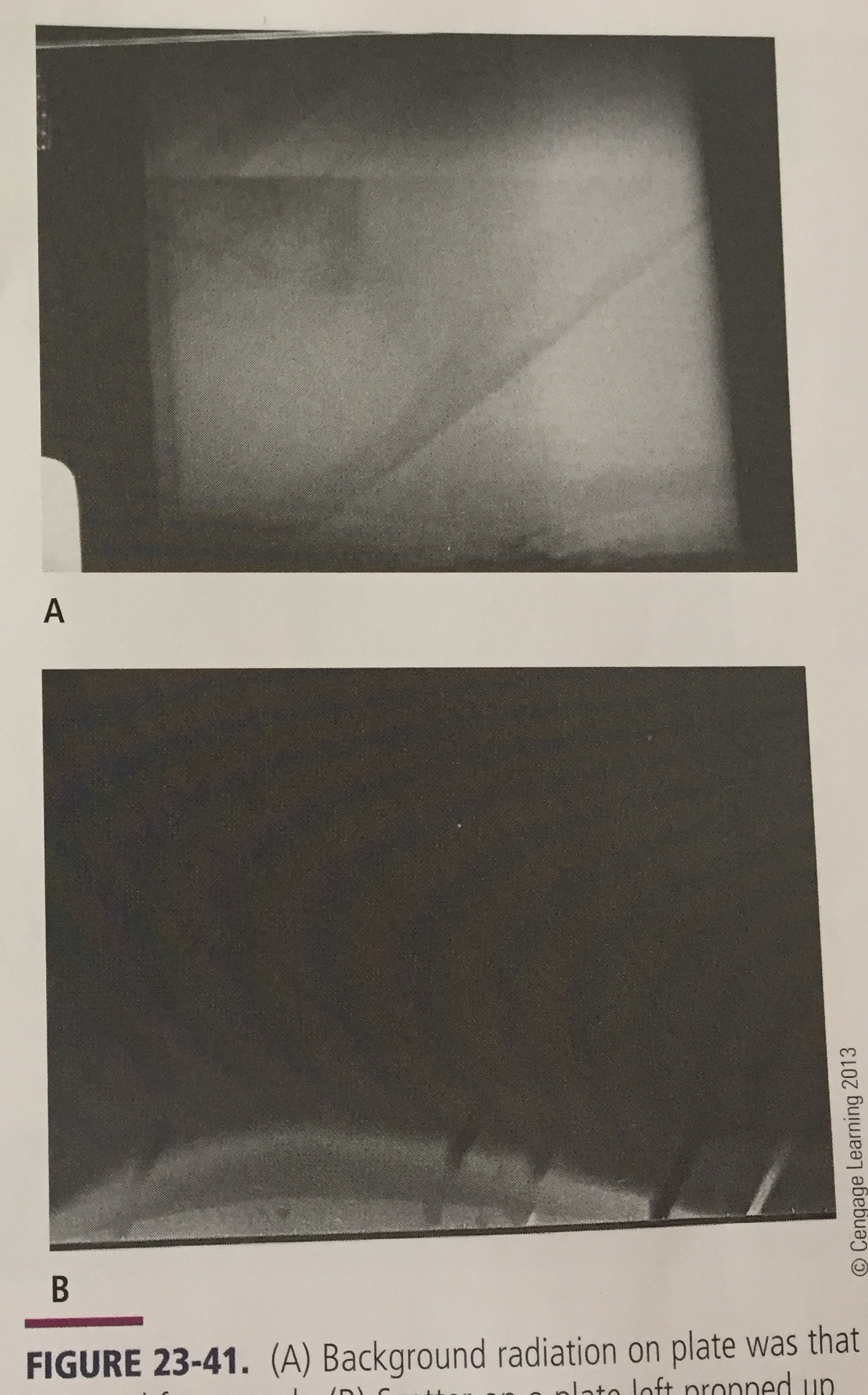
What is the artifact and what is it caused by?
Fogging from background radiation or scatter due to IP being much more sensitive than film
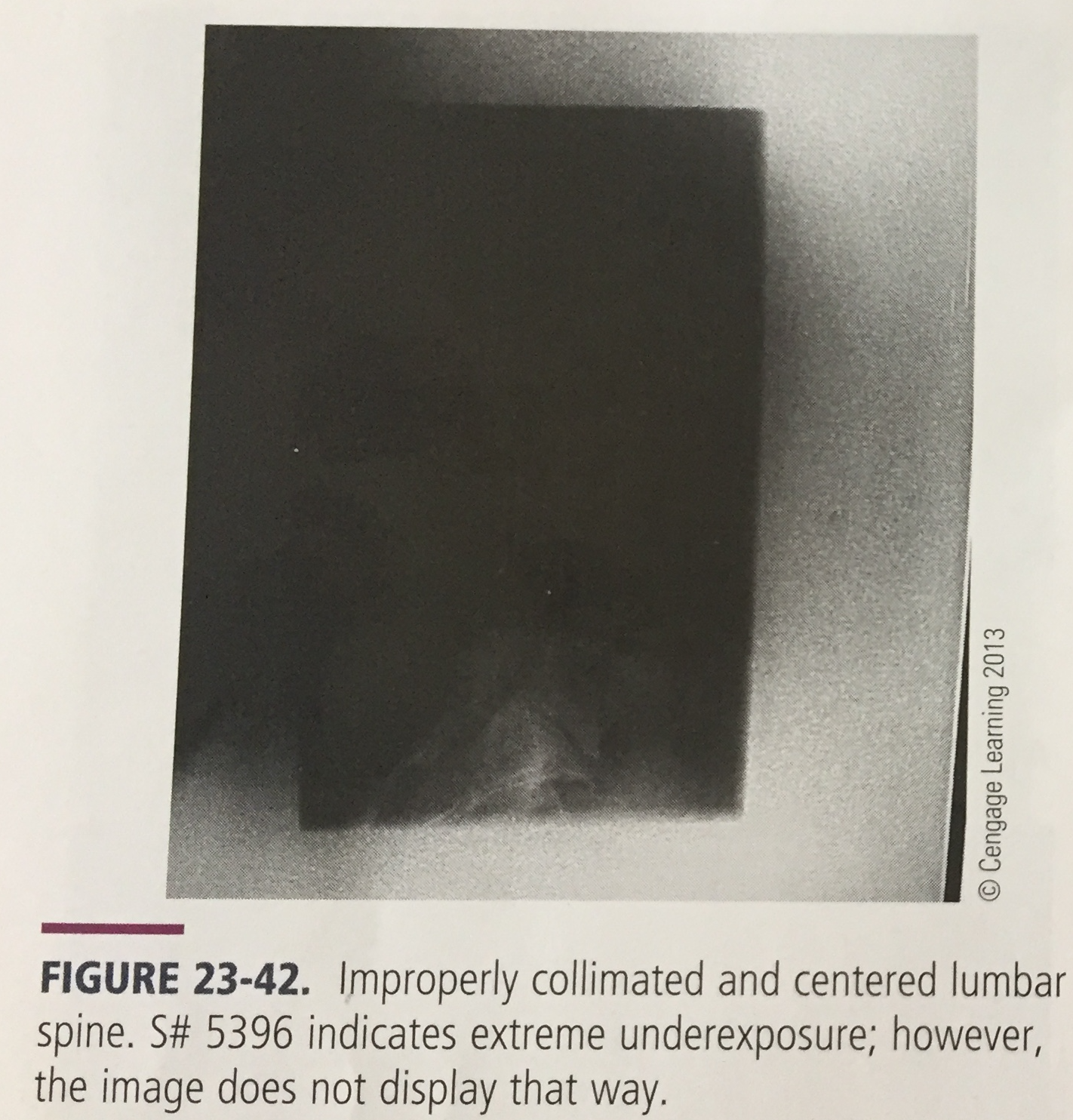
What is the artifact and what is it caused by?
Histogram analysis error due to improper collimation, improper technique, beam alignment, scatter, extreme density differences
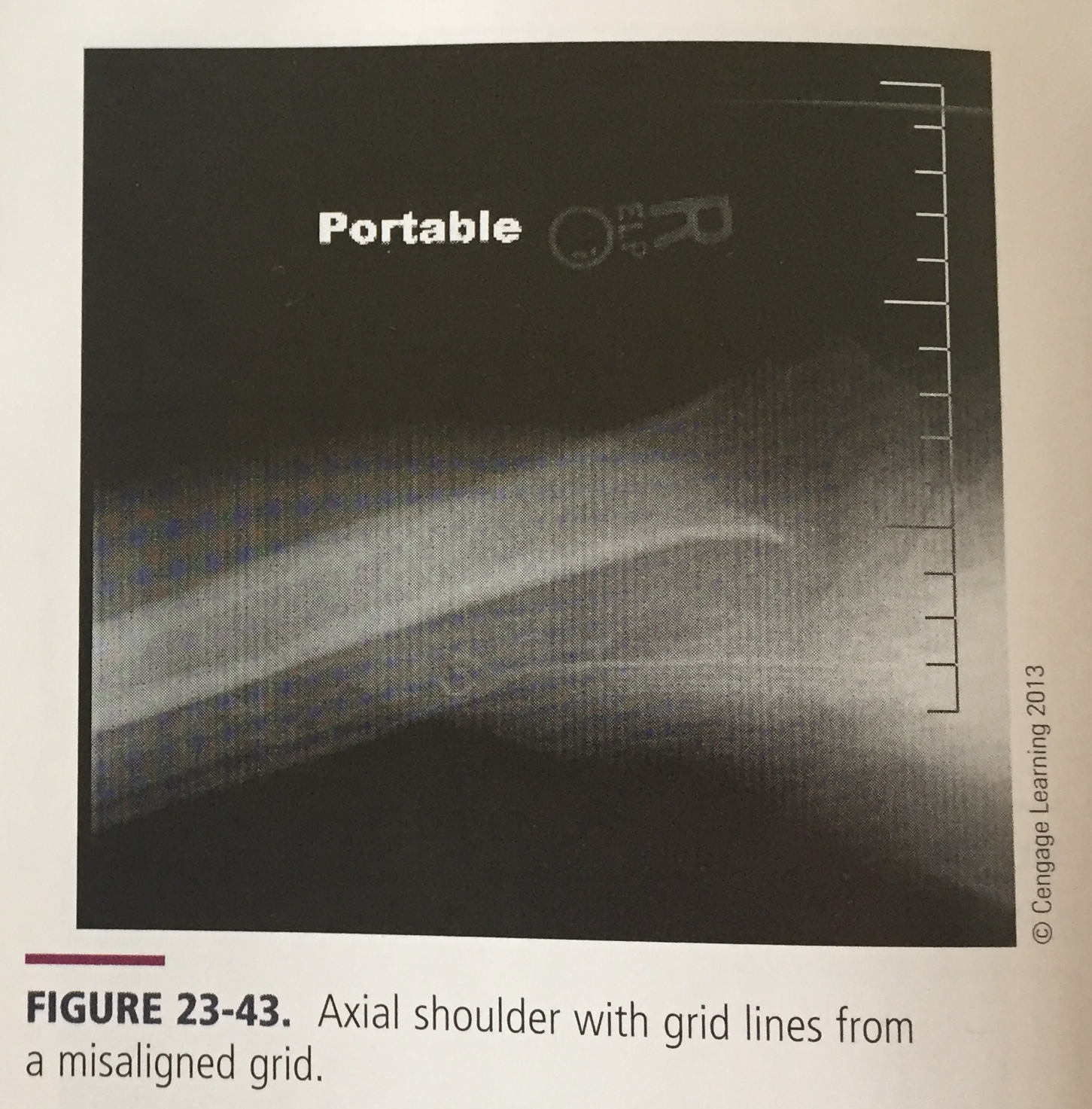
What is the artifact and what is it caused by?
Poor grid alignment leading to grid lines or poor image quality