Econometrics Midterm 2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Which of the following correctly identifies a difference between cross-sectional data and time series data?
time series data is based on temporal ordering, whereas cross-sectional data is not
The sample size for a time series data set is the number of
time period over which we observe the variables of interest
A static model is postulated when
a change in the independent variable at time “t” is believed to have an immediate effect on the dependent variable
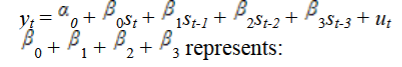
This model represents
a long-run change in y given a permanent increase in s
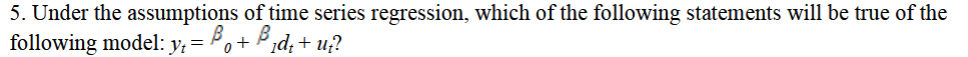
changes in the error term cannot cause future changes in d
If an explanatory variable is strictly exogenous it implies that:
the variable cannot react to what has happened to the dependent variable in the past
With base year 1990, the index of industrial production for the year 1999 is 112. What will be the value of the index in 1999, if the base year is changed to 1982 and the index measured 96 in 1982?
116.66 = (112/96) * 100
Which of the following statements is true?
when a series has the same average growth rate from period to period, it can be approximated with an exponential trend
A seasonally adjusted series is one which:
has seasonal factors removed from it
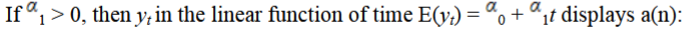
upward trend
A process is stationary if:
any collection of random variables in a sequence is taken and shifted ahead by h time periods, the joint probability distribution remains unchanged
A stochastic process {xt: t = 1,2, ….} with a finite second moment [E(xt2)< infinity] is covariance stationary if:
E(xt) is constant, Var(xt) is constant, and for any t, h >= 1, Cov(xt, xt+h) depends on h and not on t
Where et is an i.i.d. sequence with zero mean and variance sigmae2 represents a(n)
moving average process of order two
Which of the following is assumed in time series regression?
there is no perfect collinearity between explanatory variables
Which of the following statements is true?
a model with a lagged dependent variable cannot satisfy the strict exogeneity assumption
The model yt = yt-1 + et, t = 1,2, … represents a:
random walk process
If a process is said to be integrated of order one, or I(1), ____.
the first difference of the process is weakly dependent
Which of the following statements is true of dynamically complete models?
the problem of serial correlation does not exist in dynamically complete models
Which of the following is a strong assumption for static and finite distributed lag models?
dynamic completeness
If ut refers to the error term at time “t” and yt-1 refers to the dependent variable at time ‘t-1’, for an AR(1) process to be homoskedastic, it is required that:
Var(ut | yt-1 ) = Var(yt | yt-1 ) = sigma²
In the presence of serial correlation:
estimated OLS values are not BLUE
A smaller standard error means:
a larger t statistic
For a given significance level, if the calculated value of the Durbin Watson statistic lies between the lower critical value and the upper critical value, ___.
the test is inconclusive
The Breusch-Godfrey test statistic follows a:
X² distribution
Which of the following is an example of FGLS estimation?
Prais-Winsten estimation
Consistency of FGLS requires:
ut to be uncorrelated with xt-1, xt, and xt+1
Which of the following is a limitation of serial correlation-robust standard errors?
the serial correlation-robust standard errors can be behaved when there is substantial serial correlation and the sample size is small
In the time series literature, the serial correlation-robust standard errors are sometimes called:
heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent standard errors
Which of the following tests can be used to test for heteroskedasticity in a time series?
Breusch-Pagan test
The equation u²t = a0 +a1u²t-1 + vt is an autoregressive model in __.
u²t
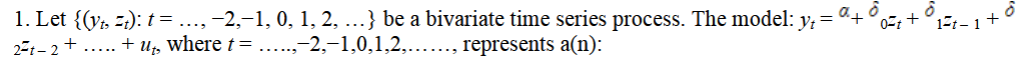
infinite distribution lag model
Where vt = ut - put-1 represents a:
rational distributed lag model
Which of the following is used to test whether a time series follows a unit root process?
augmented Dickey-Fuller test
A spurious regression refers to a situation where:
even though two variables are independent, the OLS regression of one variable on the other indicates a relationship between them
If two series have means that are not trending, a simple regression involving two independent I(1) series will often result in a significant ___ statistic.
t
Which of the following tests can be used to check for cointegration between two series?
Engle-Granger test
If ft denotes the forecast of yt-1 made at a time t, then the forecast error is given by:
et+1 = yt+1 - ft
Which of the following statements correctly identifies the difference between an autoregressive model and a vector autoregressive model?
in an autoregressive model one series is modeled in terms of its own past, whereas in a vector autoregressive model several series are modeled in terms of their past
A process {yt } is a martingale if ___ is equal to yt for all t >= 0
E(yt+1 | yt , yt-1 , …… , y0)
The value of the parameter a in the exponential smoothing method lies between ___.
0 and 1