EKG review: Arrhythmia rules
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Rhythms: sinus, atrial, junctional, ventricular, paced, heart blocks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
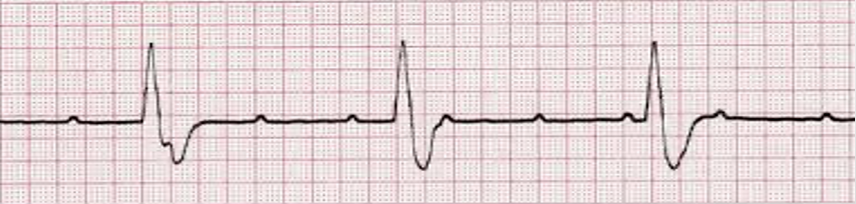
Sinus exit block
absence of cardiac cycle(s); P-P intervals still march out across the rhythm once activity resumes
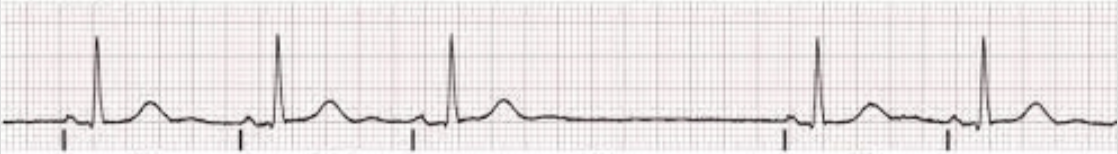
Sinus pause
absence of cardiac cycles(s); P-P intervals will not march out across rhythm strip due to SA node restarting
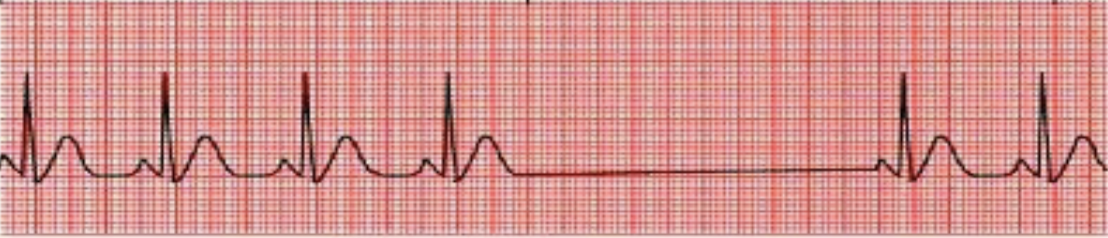
Sinus arrest
absence of at least 3 cardiac cycles; P-P intervals will not march out across the rhythm strip due to SA node restarting
normal sinus rhythm
RRR, intervals map out evenly

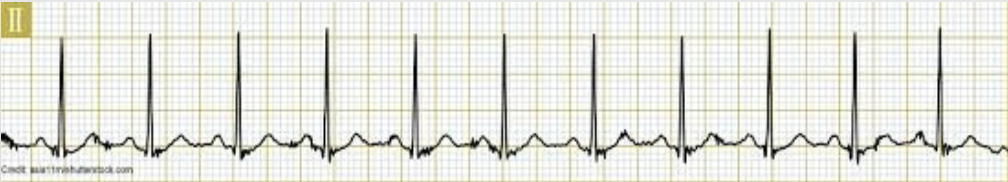
sinus bradycardia
regular rhythm, HR < 60
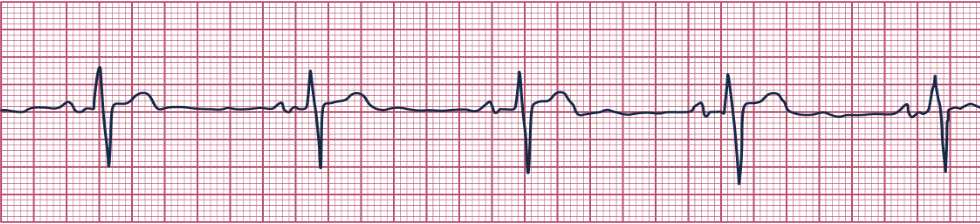
sinus tachycardia
regular rhythm; HR > 100
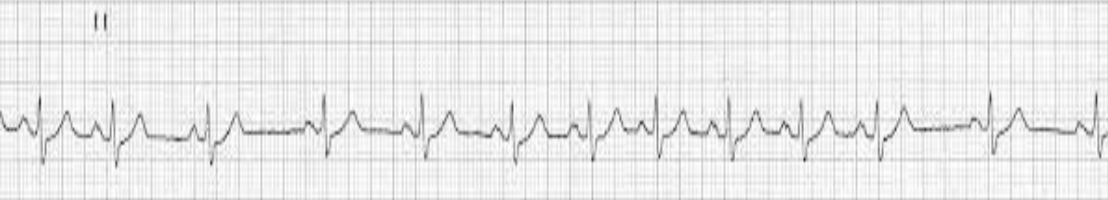
sinus arrhythmia
benign variation in beat intervals; regular rate, irregular rhythm
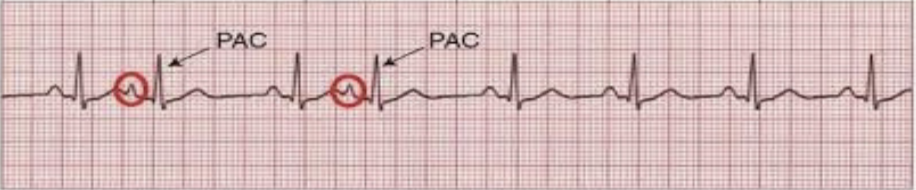
premature atrial complex (PAC)
arrive early in the cardiac cycle → longer PR; have different morphologies than normal waves
wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP)
pacemaker site shifts → at least 3 different P wave morphologies
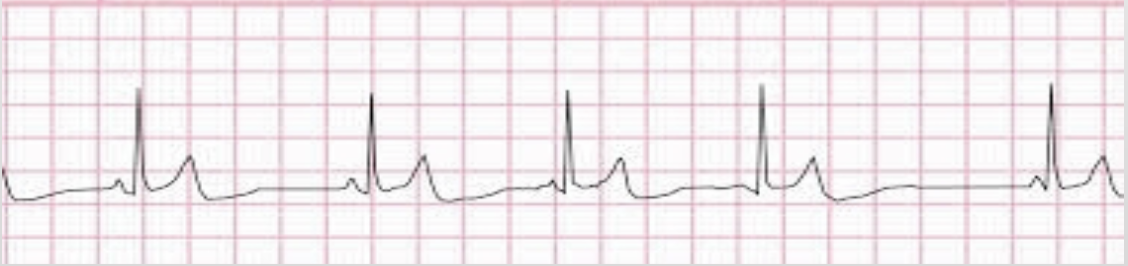
multifocal atrial pacemaker (MAT)
pacemaker site shifts → at least 3 different P wave morphologies ; HR > 100
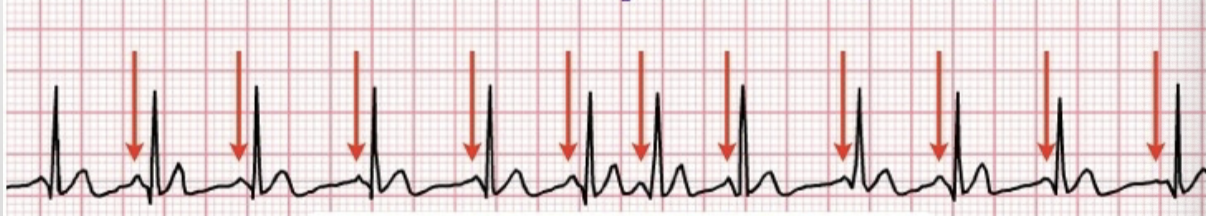
atrial flutter (A-flutter)
sawtooth pattern; no P waves; irregular

atrial fibrillation (A-fib)
no P waves; irregularly irregular, HR usually > 100;
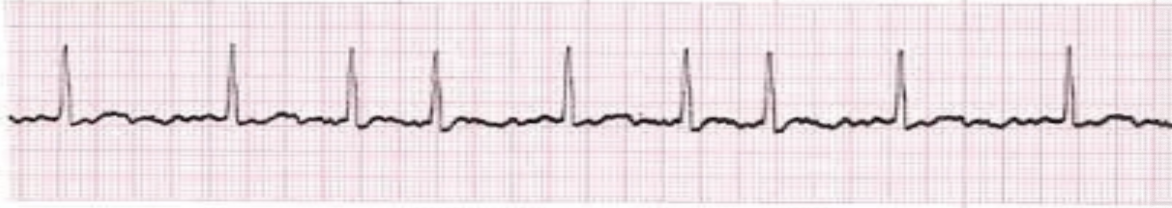
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) (SVT)
regular, narrow, HR >100 (usually >150); no P or retrograde P waves
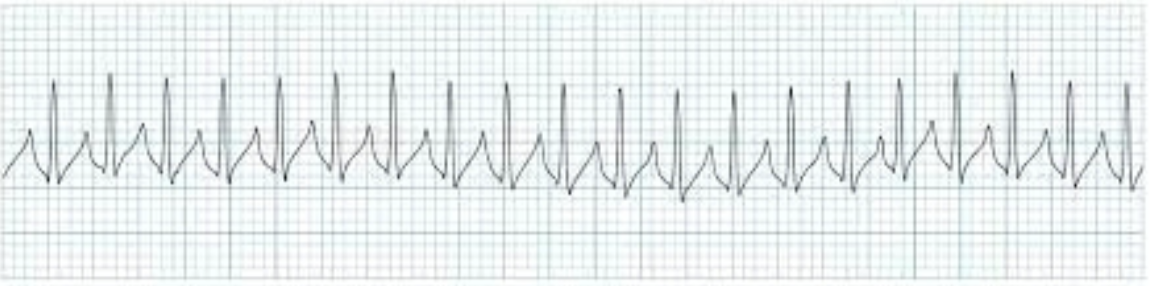
Premature junctional complex (PJC)
early in the cardiac cycle; no P, inverted P, or post-QRS P wave

Junctional escape beat (JEB)
late in the cardiac cycle -where next R wave should’ve been; no P, inverted P, or post-QRS P wave
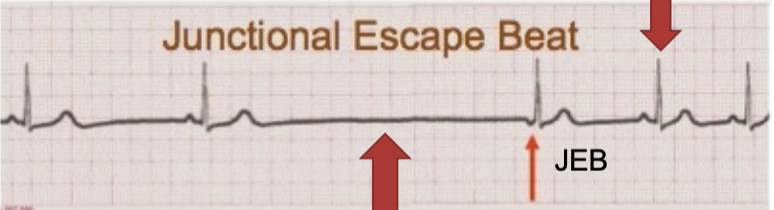
Junctional escape rhythm (Junctional rhythm)
regular rhythm; HR 40-60 bpm; no P, inverted P, or post-QRS P wave
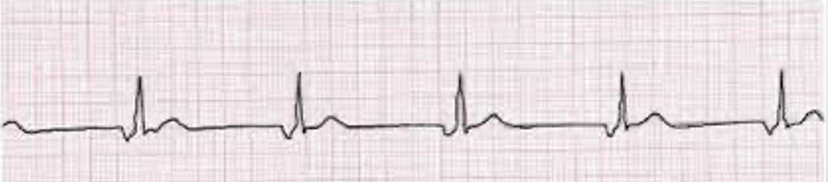
Accelerated junctional rhythm
regular rhythm; HR 60-100 bpm; no P, inverted P, or post-QRS P wave

Junctional tachycardia
regular rhythm; HR >100 bpm; no P, inverted P, or post-QRS P wave
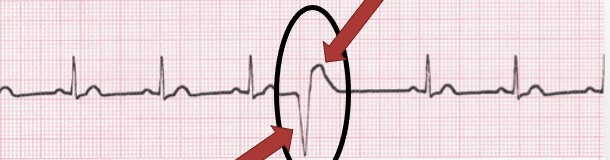
Premature ventricular complex (PVC)
early in the cardiac cycle; R on T; wide QRS; can be grouped
Ventricular escape complex
come late in the cardiac cycle, past when next expected R wave; wide QRS
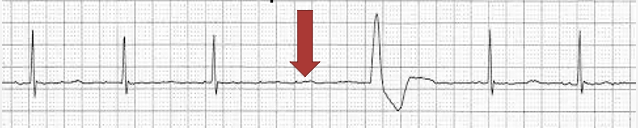
Idioventricular rhythm (IVR)
regular, HR 20-40, wide QRS, no P waves
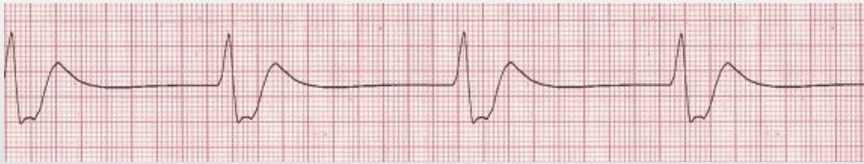
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
regular, HR 40-100, wide QRS, no P waves
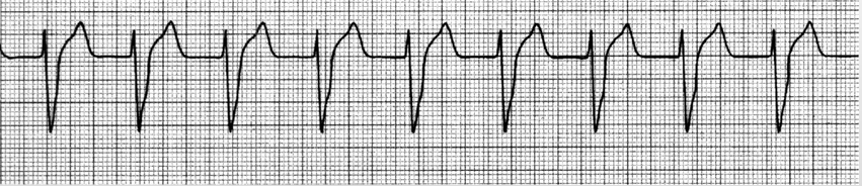
ventricular tachycardia (V-tach)
regular, wide; HR >100; no P; can be polymorphic or monomorphic
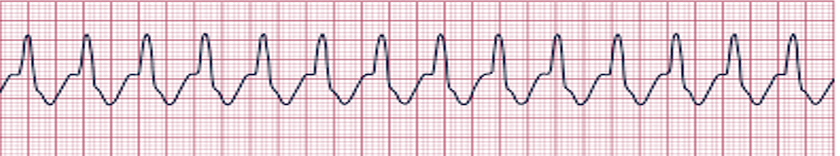
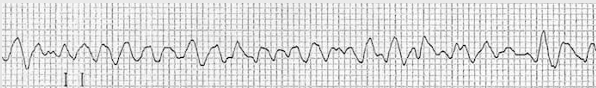
ventricular fibrillation (V-fib)
irregular; no P waves, QRS complexes, or T waves
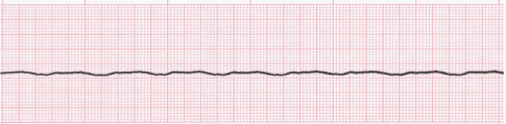
asystole
flat line, no pulse; lack of electrical activity
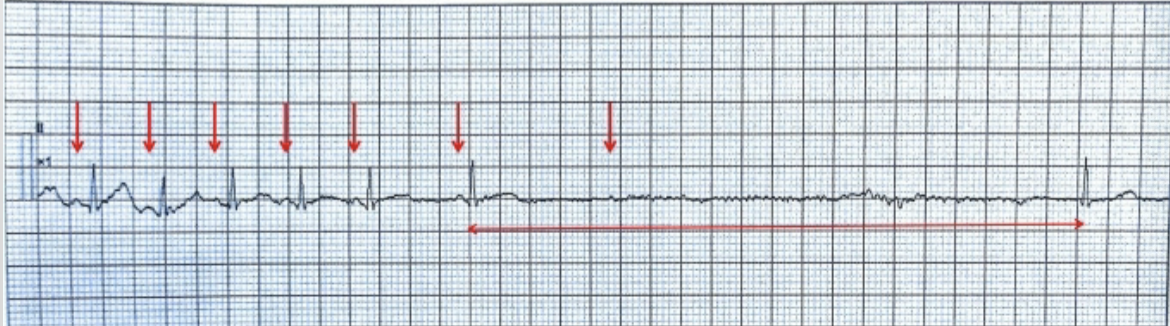
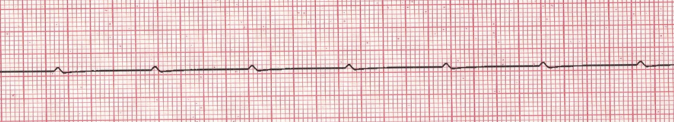
ventricular standstill
P waves only; can be present in paroxysmal episdoes
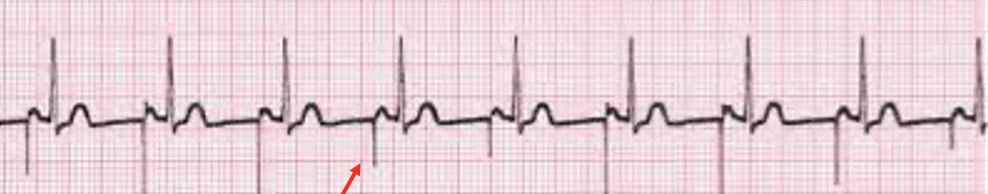
atrial paced
pacer spike followed by normal PQRST cycle
ventricular paced
pacer spike followed by a wide QRS complex and contralateral T wave
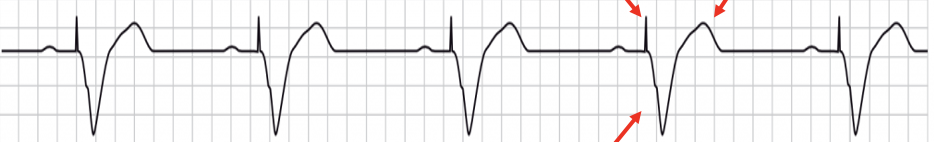
AV paced
pacer spike preceding P wave; 2nd pacer spike followed by a wide QRS and contralateral T wave
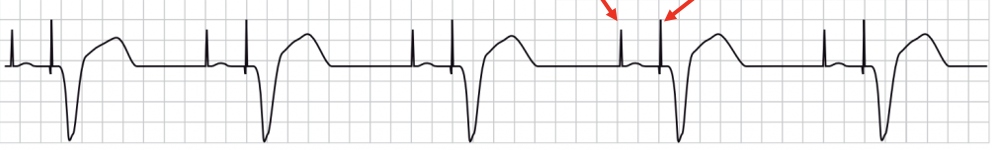
First degree AV block
RRR, long PR interval (>0.2 sec)
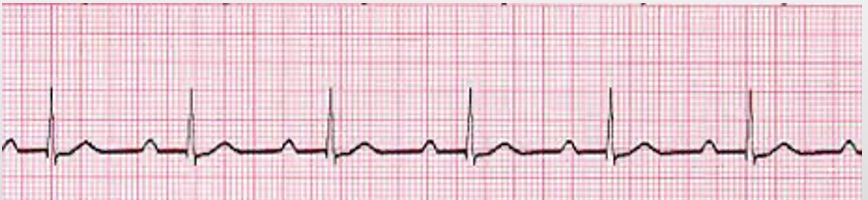
2nd degree AV block Type 1 (Wenckebach)
irregular, increasing PR intervals followed by a dropped beat -cycle repeats
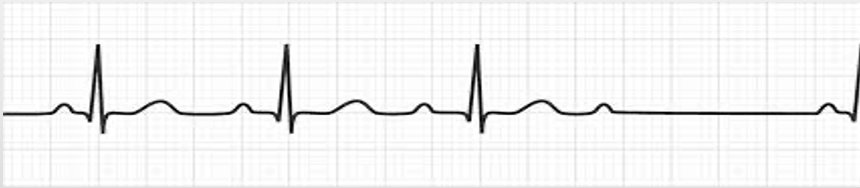
2nd degree AV block Type 2 (Mobitz II)
constant PR intervals, QRS usually wide; occasional dropped QRS complexes
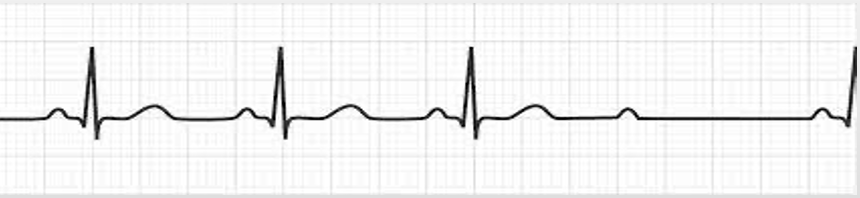
3rd degree AV block (complete heart block)
regular R-R unrelated to regular P-P; P & QRS don’t line up