SBI4U - Unit 1 - Biochemistry
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
electronegativity (En)
atom's attraction to shared electrons -- more orbits/electrons = less electronegativity
polar bond
covalent, En less than 1.7, nonequal En, nonequal sharing of electrons -- like other polars, do not like nonpolar
nonpolar bond
covalent, En less than 1.7, equal En, equal sharing of electrons
ionic bond
giving or taking electrons, En greater than 1.7
cohesion
water forms hydrogen bonds with each other
adhesion
water forms hydrogen bonds with other molecules -- good for transportation (ex. up xylem)
buffer
weak acids or bases that release or absorb H+ ions to compensate for changes in pH -- must be weak because strong acids or bases dissolve completely in water
functional groups
initiate chemical reactions, determine molecule's function, often ionic or strong polar
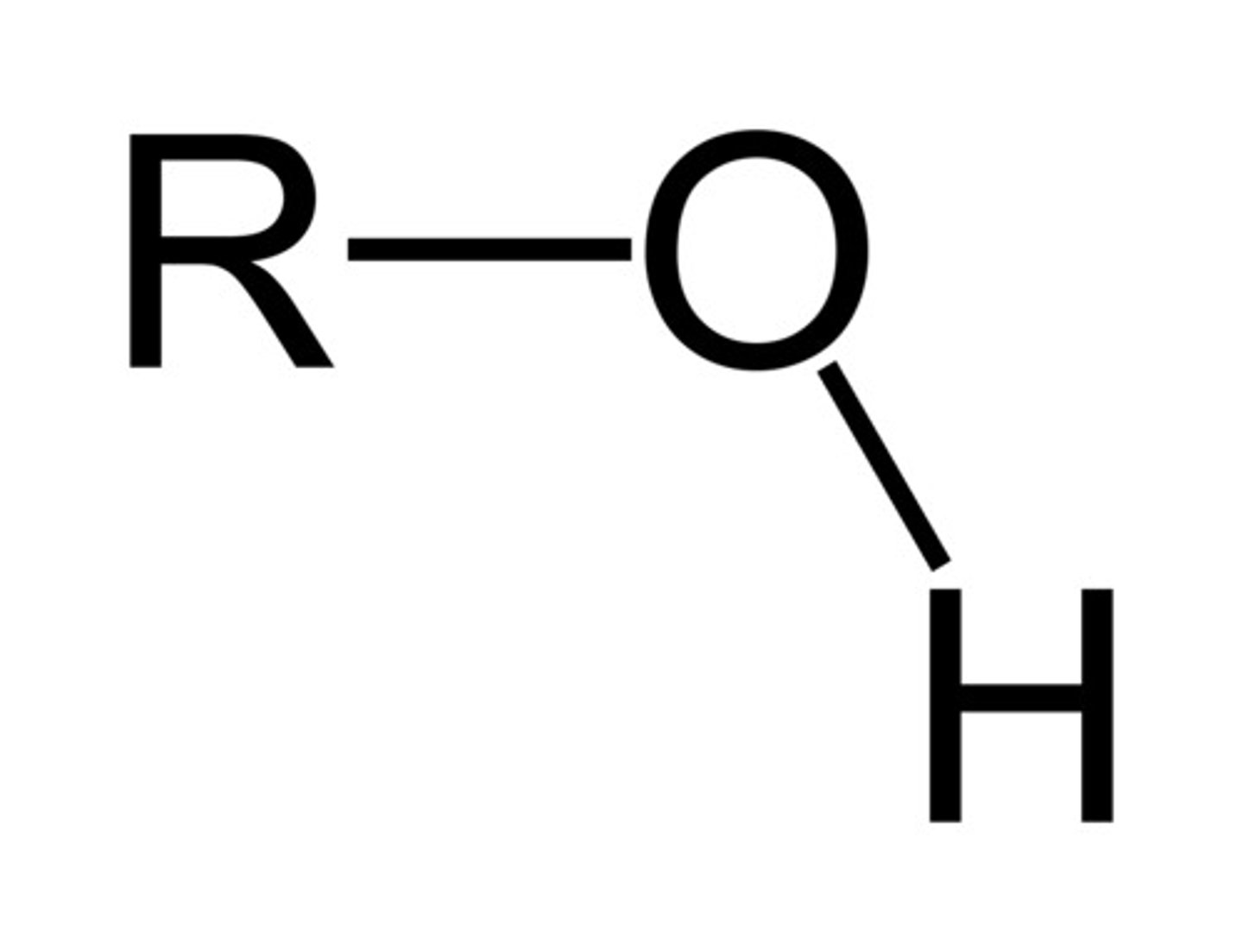
alcohol
functional group
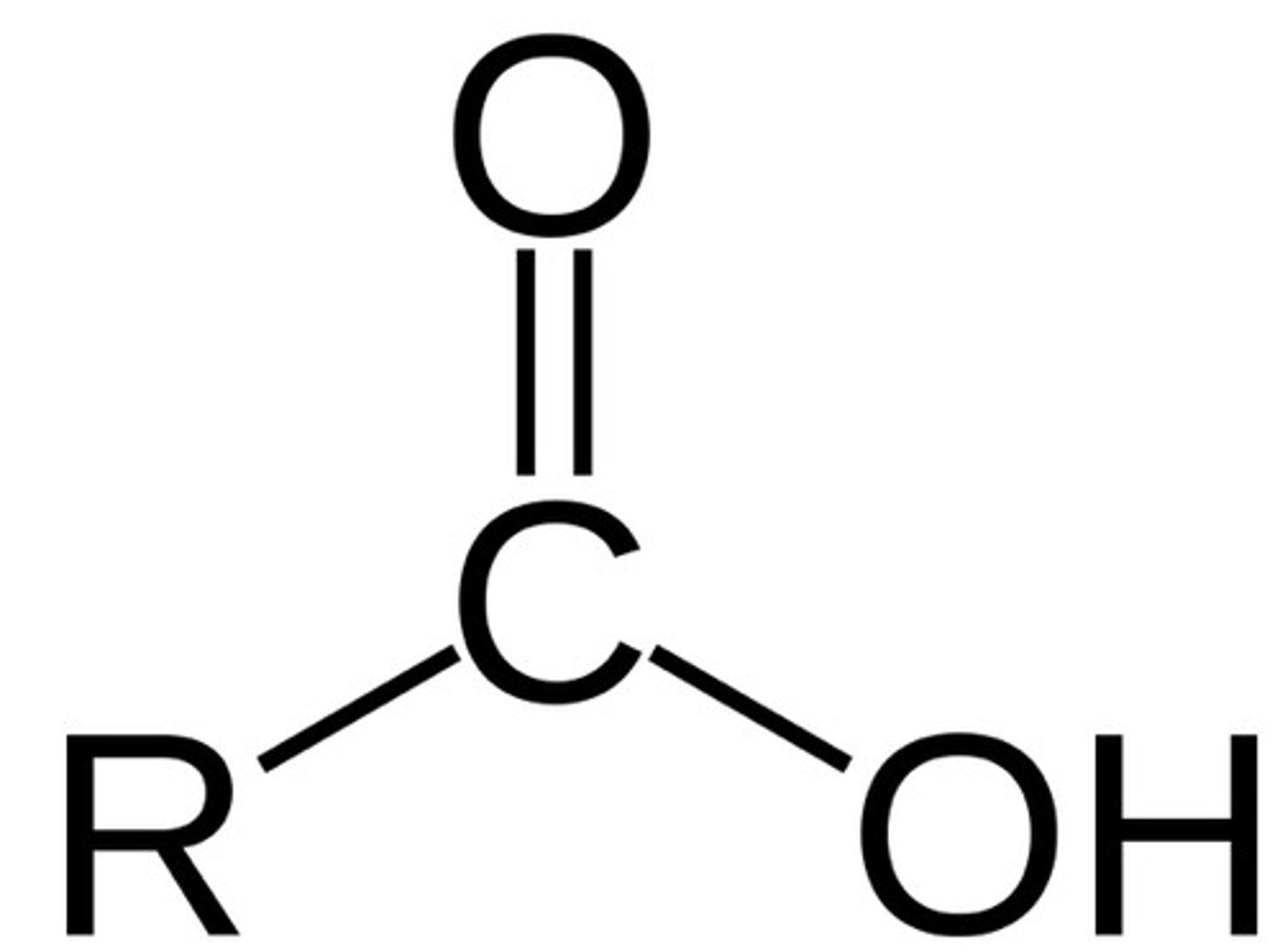
carboxyl
functional group
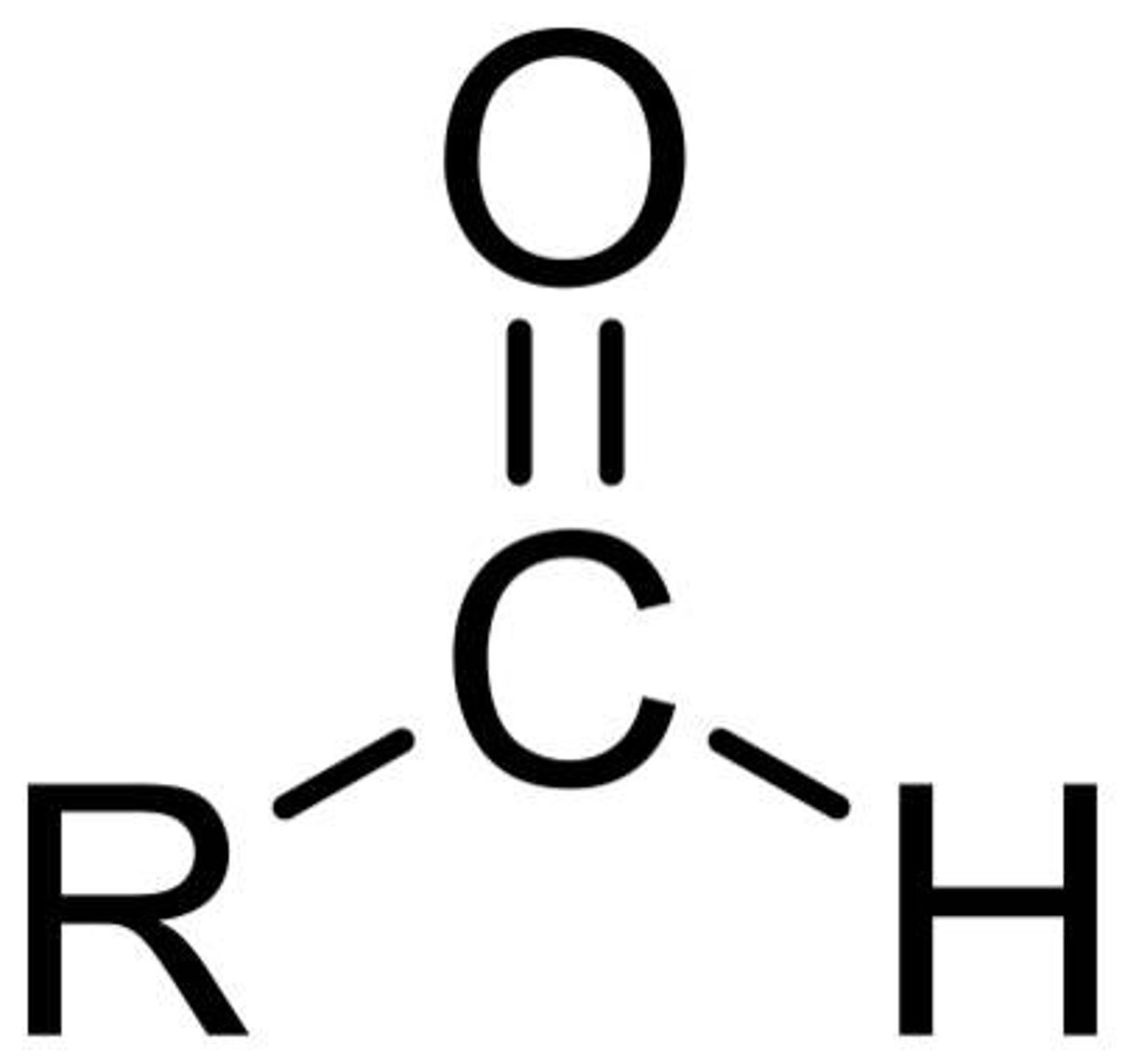
aldehyde (carbonyl)
functional group
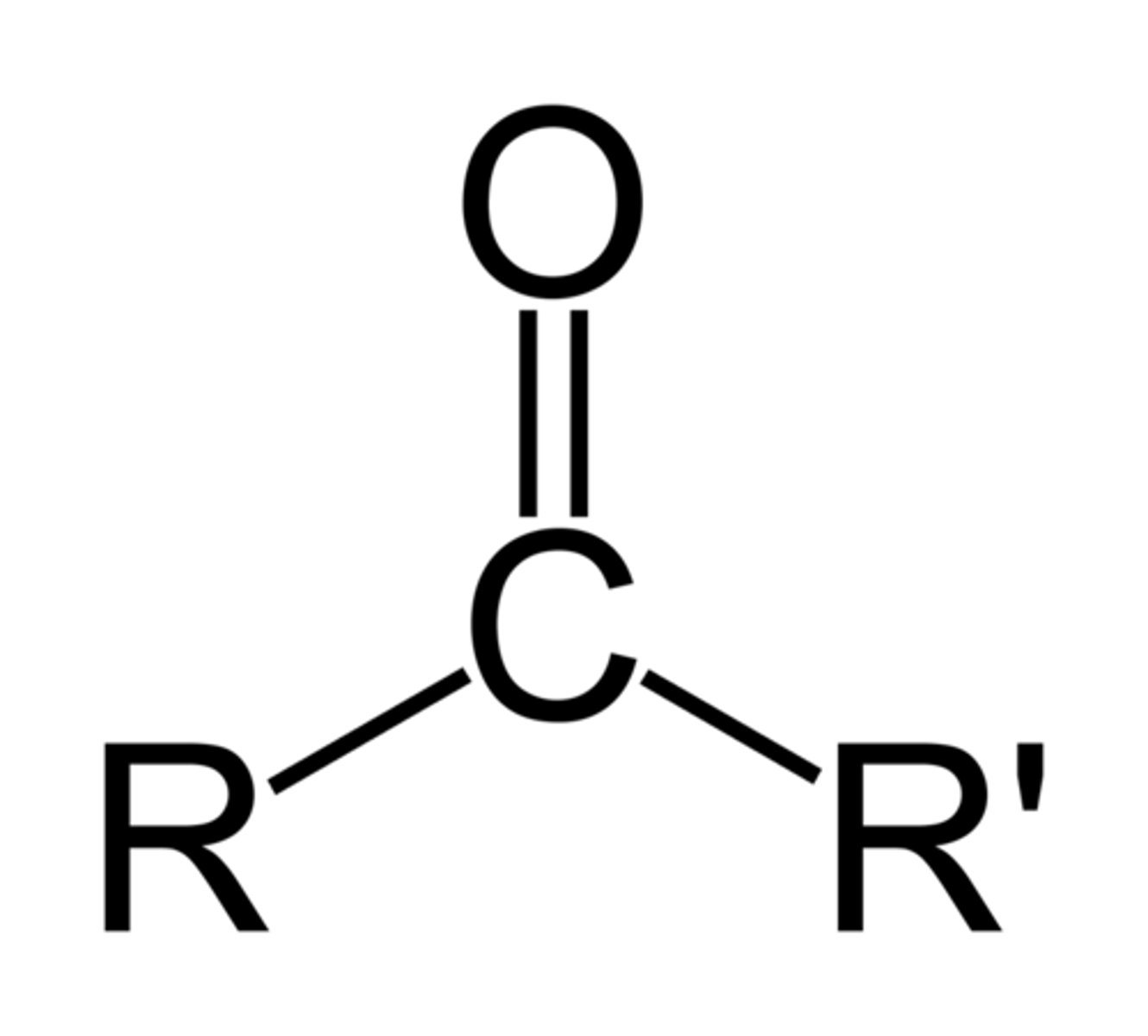
ketone (carbonyl)
functional group
amino
functional group
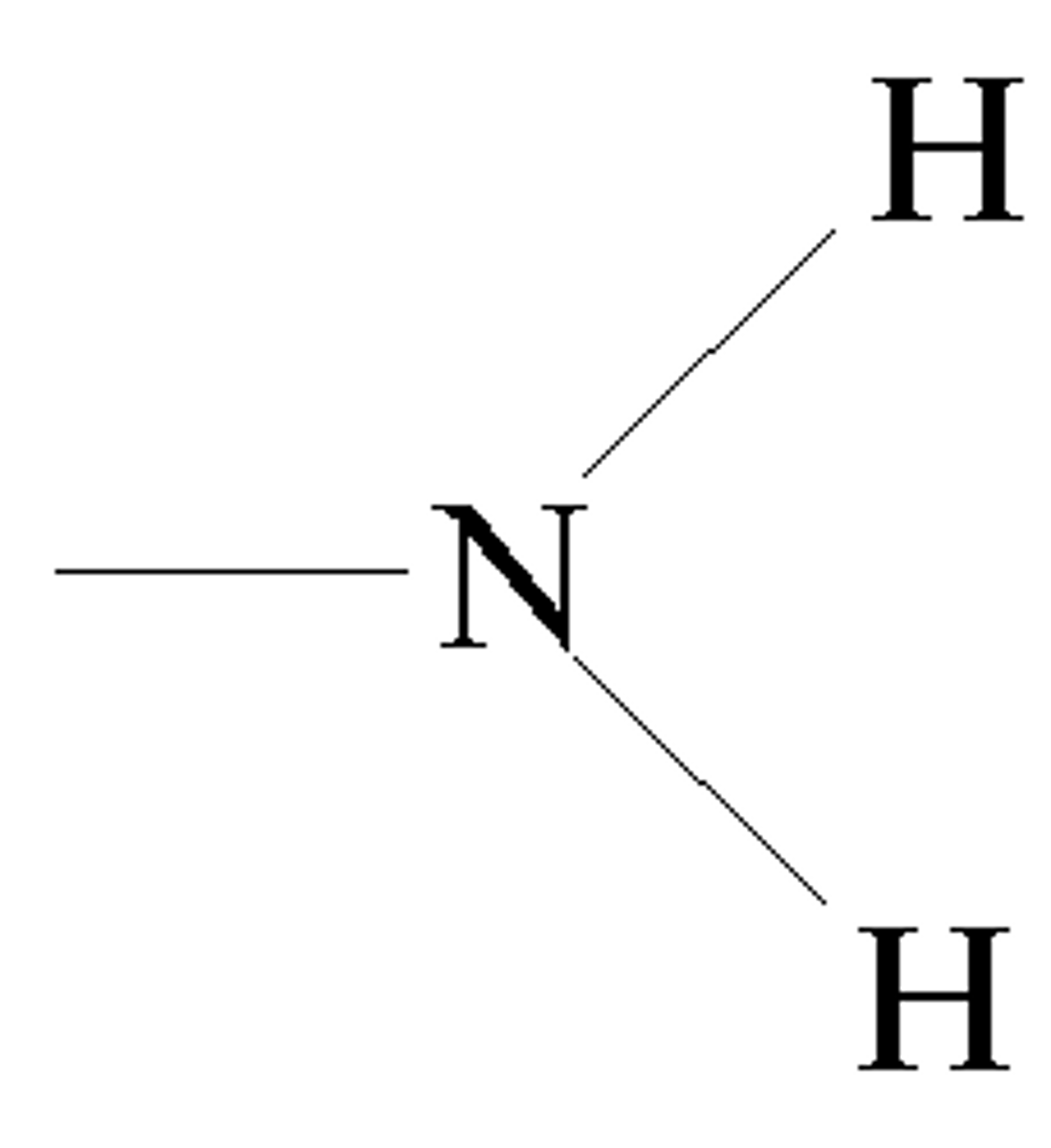
sulfhydral
functional group

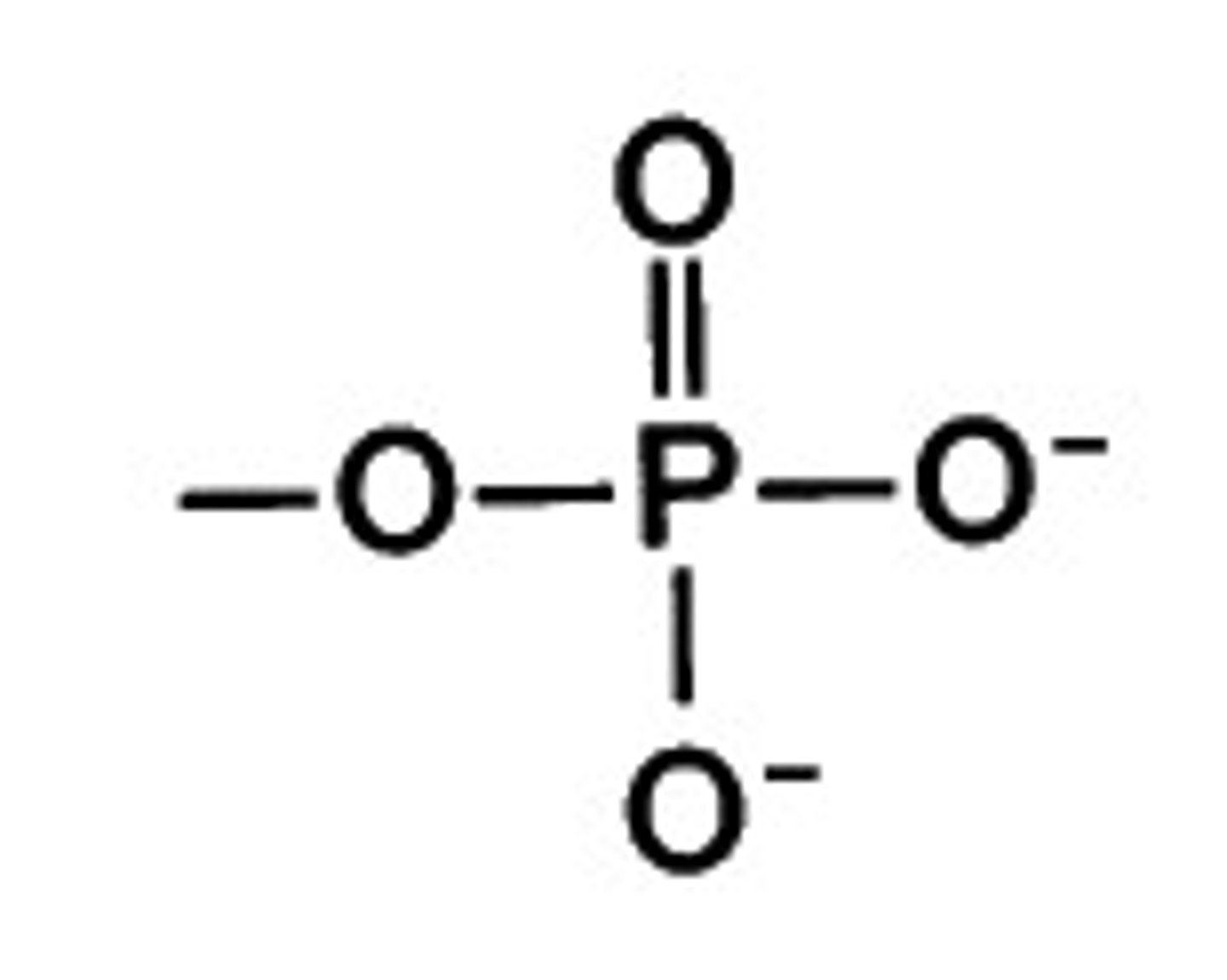
phosphate
functional group
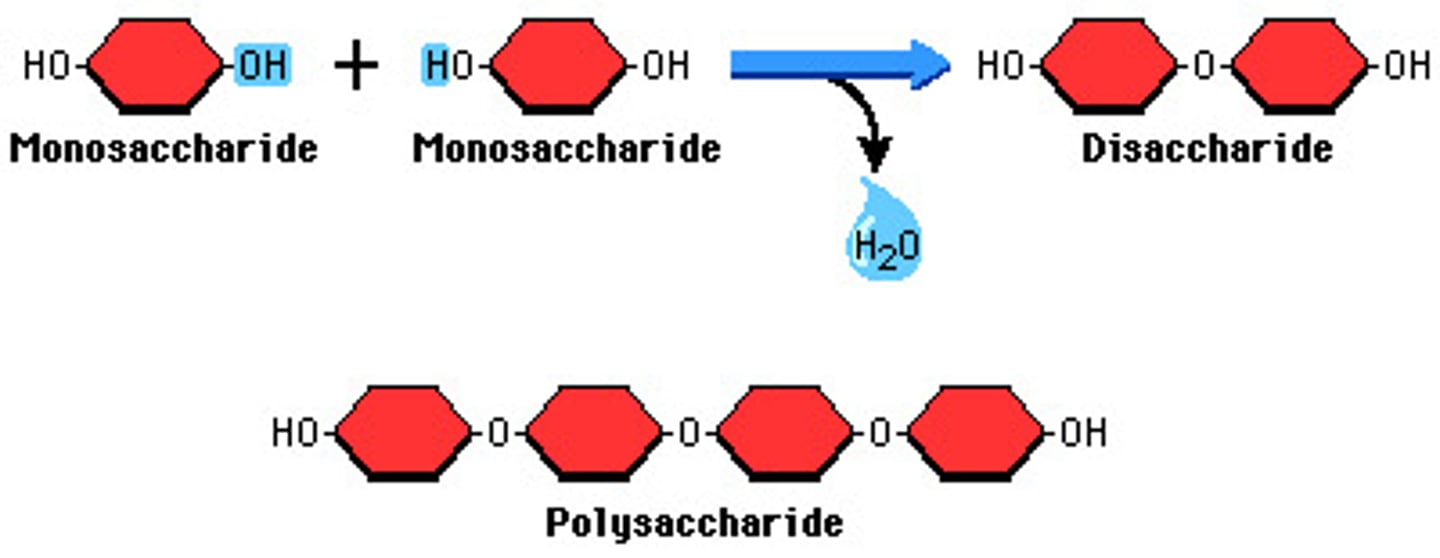
dehydration
water is removed from two molecules which then join up to form a larger molecule
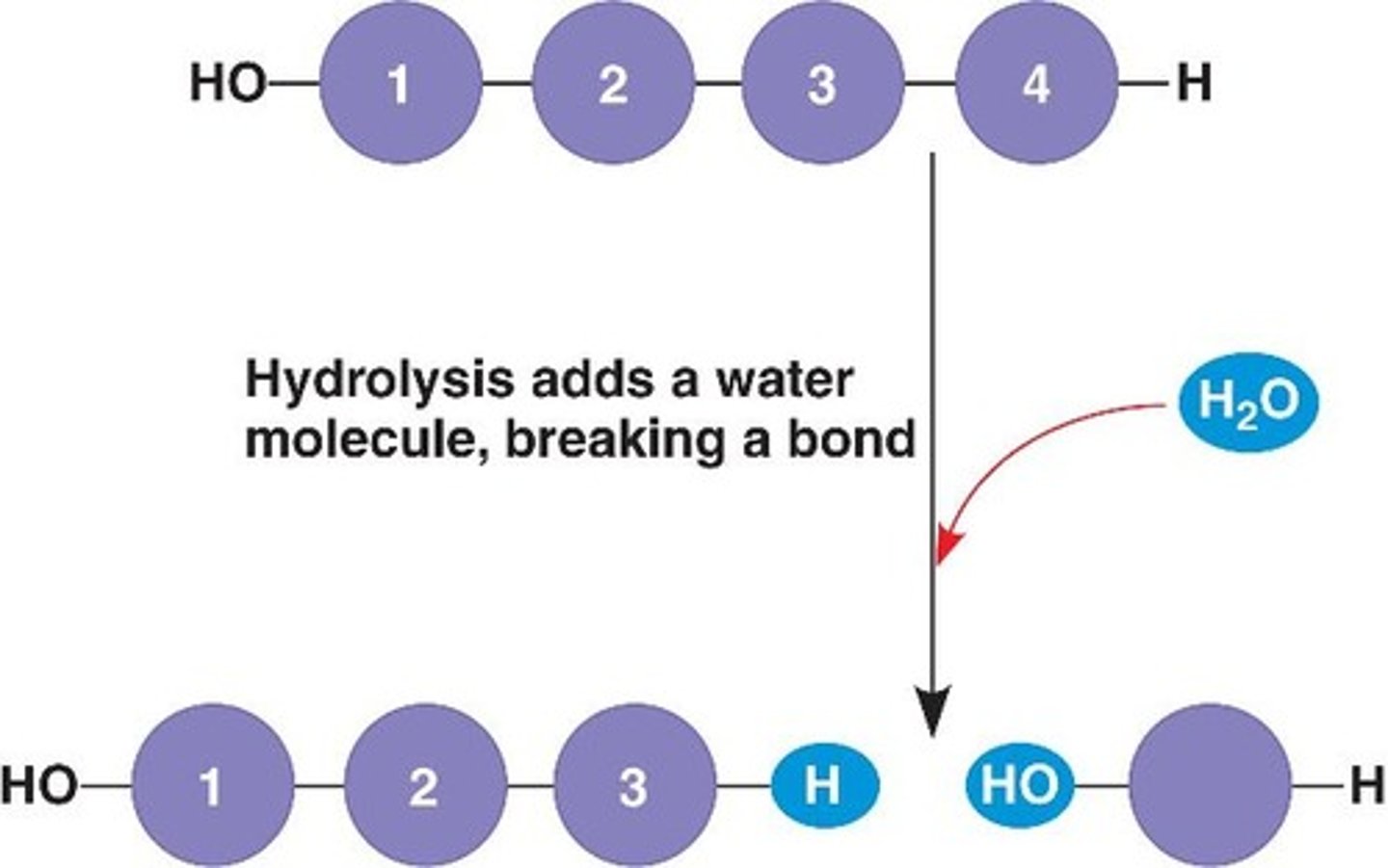
hydrolysis
water is added to a larger molecule, which breaks up into smaller subunits
polymerization
process of smaller subunits joining together
saturated fat
single bond, animal fats
unsaturated fat
double bond, oils
fatty acid vs fat
fatty acid: long straight chain, carboxyl acids // fat (triglycerol): 3 fatty acids + glycerol
when fatty acid -- fat
glycerol removes carboxyl acid from fatty acid when it joins to form a fat
steroids
uses: growth, hormonal signalling, regulation of metabolic processes
lipid
nonpolar, do not dissolve in water
protein
many amino acids joined by peptide bonds
amino acids
carboxyl group + aminon group
denaturation
loss of structure + function of protein -- usually occurs as a result in change of temperature or pH level
protein primary structure
the linear structure of amino acids
protein secondary structure
folds (β-pleated) or coils (α-helix) that are formed through interactions between atoms in the backbone
protein tertiary structure
3D shape of polypeptide chain formed through interactions between R groups
protein quaternary structure
2 > polypeptides joining together
nucleotide
building block of nucleic acid -- 5 carbon sugar + nitrogenous base + 1-3 phosphate groups
pyrimidines nitrogenous bases
single organic ring: uracil (U), thymine (T), cytosine (C)
purine nitrogenous bases
double organic ring: adenine (A) and guanine (G)
DNA nitrogenous pairs
A+T / C+G
RNA nitrogenous pairs
A+U / C+G
enzyme
biological catalyst -- jumpstarts chemical reactions without being used up
competitive inhibition
where a molecule mimics a substrate and binds to the active site of an enzyme so that the actual substrate cannot bind there
noncompetitive inhibition
inhibitor binds somewhere that isn't the active site, changing the shape of the enzyme and changing the active site so that the substrate cannot fit
allosteric site
where regulatory molecules bind to enzymes
allosteric regulation
one site on a protein is affected by the binding of a molecule to a different site (ie noncompetitive inhibition)
endomembrane system
group of interacting organelles b/w the nucleus and plasma membrane -- nucleus (DNA with instructions for creating proteins -> RNA -> cytosol) --> rough ER (ribosomes turn RNA into proteins -> rough ER packages them) --> vesicles (carry proteins to golgi body OR from rough ER to smooth ER) --> smooth ER (proteins from rough ER get packaged and sent to golgi / others become enzymes which create lipids) --> golgi body (proteins are modified and sent to plamsa membrane) --> plasma membrane (vesicles fuse with and let proteins/lipids out to the exterior of the cell)
vesicles
many different types and functions -- ie vacuoles: huge trashcans, isolate/dispose of water/debris/toxins / in plant cells: maintain cell shape/rigidity // lysosomes: contain digestive enzymes, kill the cell
microtubule
long hollow cylinder w/ tubulin protein -- within flagella and cilia -- form pseudopods (false feet)
sterol
steroid with an OH group at one end and a non polar hydrocarbon on the other -- prevent fatty acids from forming a gel at normal temperatures
integral membrane protein
a protein that is embedded in the lipid bilayer
peripheral membrane protein
a protein on the surface of the membrane
passive transport
movement of a substance across a membrane without expending energy -- diffusion
simple diffusion
movement of small/non polar substances to move across a membrane unassisted
facilitated diffusion
transport of ions/polar substances across a membrane via proteins
transport protein
proteins that help substances move across the membrane
channel protein
pathway for water and ions to pass through the membrane like a gate
carrier protein
bind to a specific solute and change shape in order to allow solutes through
hypotonic
lower solute / higher water concentration than what is in it
hypertonic
higher solute / lower water concentration than what is in it
osmosis
diffusion from higher solute (hypertonic) to lower solute concentration (hypotonic)
active transport
movement of a substance across a membrane against the concentration gradient using energy
primary active transport
result of chemical reaction: ATP -> ADP + phosphate group, phosphate group binds to carrier protein and tricks it into binding with a substance it otherwise would not
secondary active transport
transport using the ion concentration gradient created by the primary active transport
exocytosis
secretory vesicles bind with plasma membrane which opens up to release components from the vesicle to the exterior of the cell
endocytosis
plasma membrane folds in and either takes in the extracellular water and whatever's in it or components bind to receptors and the folded membrane pinches off and releases the stuff within the vesicles into the cell