functional groups
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
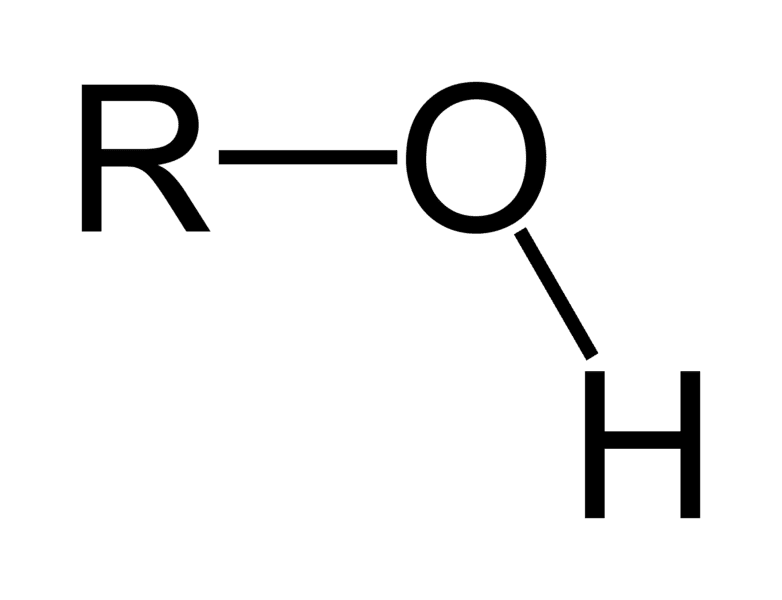
alcohol
-OH (hydroxyl group) attached to saturated C
~3200-3600
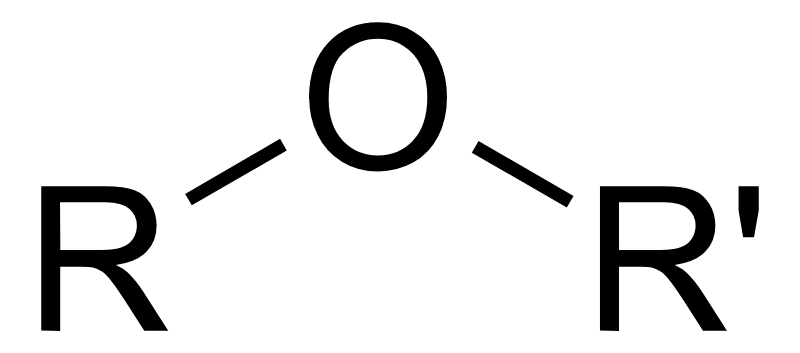
ether
single O is bonded to two separate C
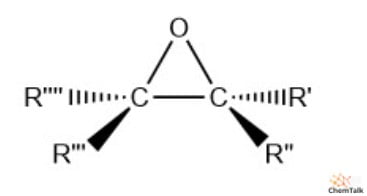
epoxide
three-membered cyclic ether where an O bridges two adjacent C, forming a ring
highly reactive
haloalkane
C bonded to a halogen
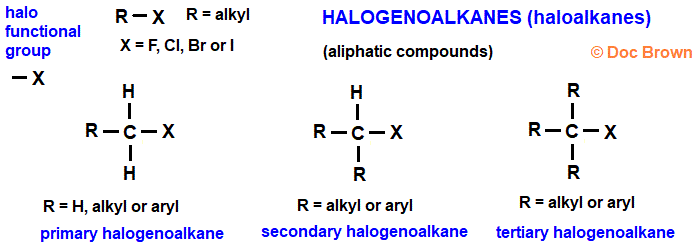
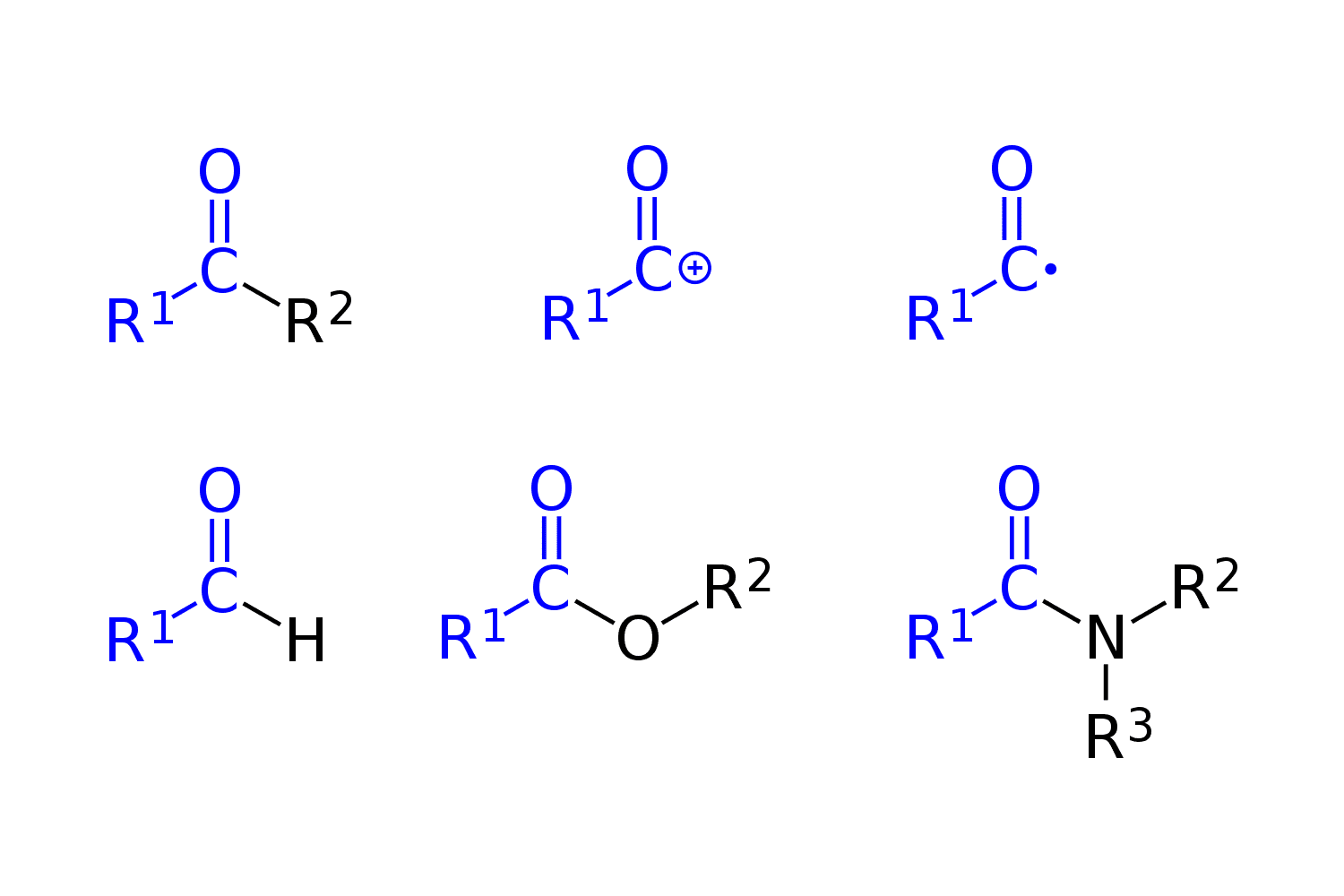
aldehyde
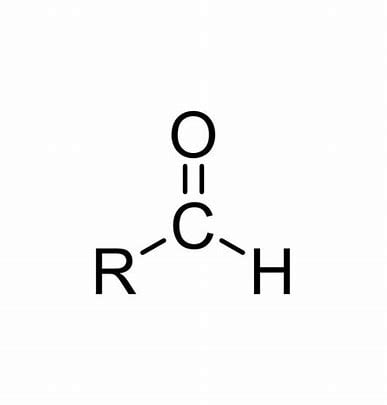
carbonyl carbon
C=O
~1700
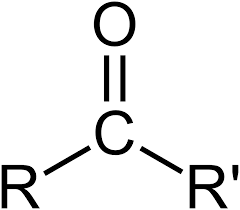
ketone
carboxylic acid
carbonyl & hydroxyl group attached to same C

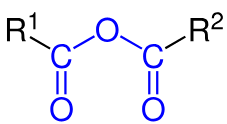
acid anhydride
two acyl groups linked by an oxygen atom
acyl
C double-bonded to an O and single-bonded to another atom or group of atoms (R)
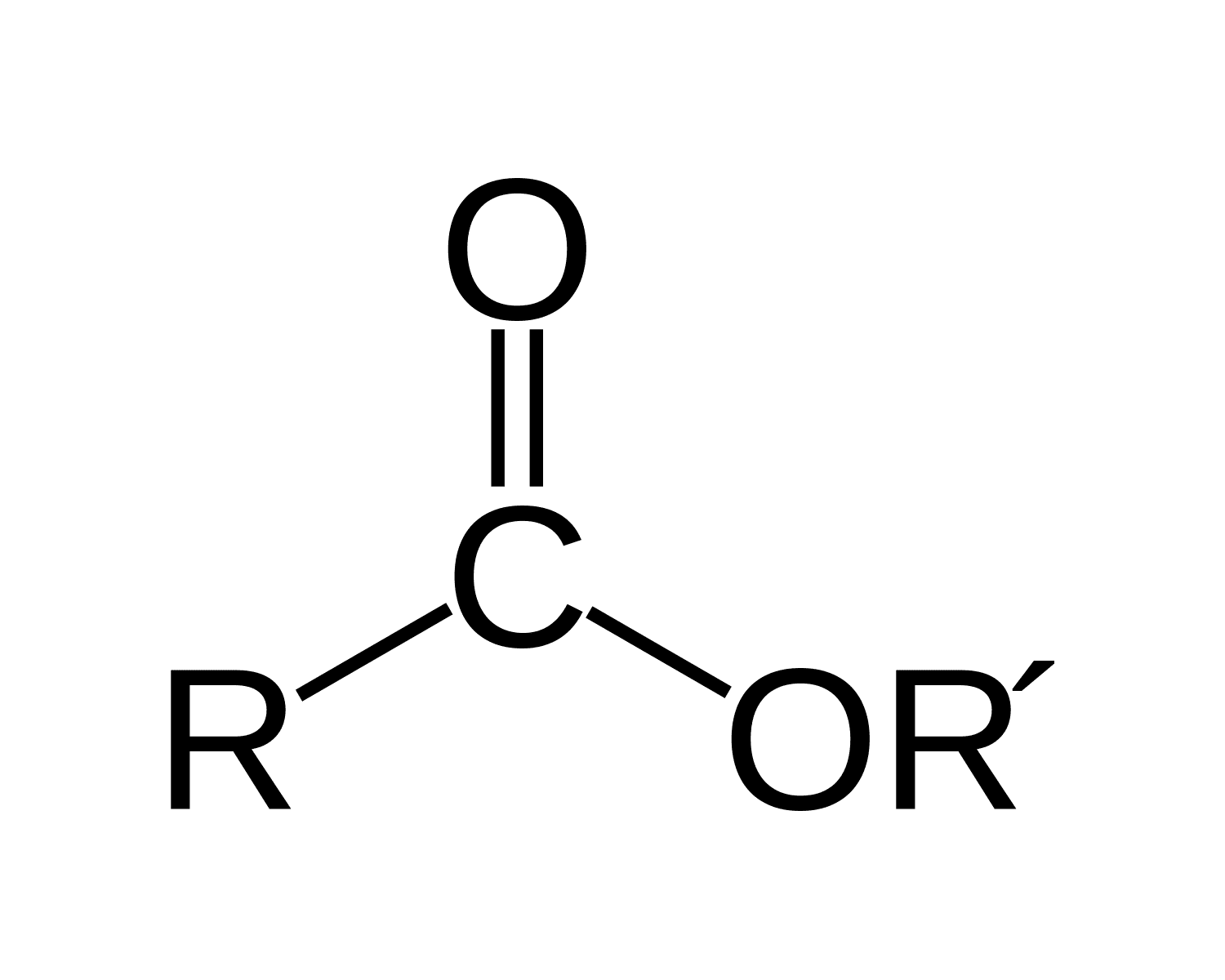
ester
C double-bonded to an O (carbonyl group) and single-bonded to another O, which is then single-bonded to a different C
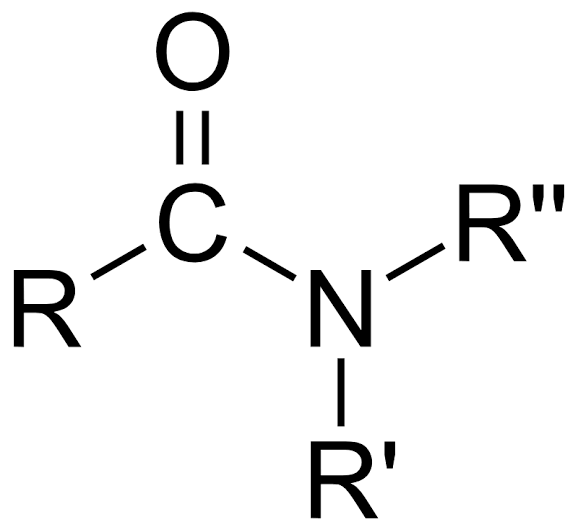
amide
carbonyl group (C=O) directly bonded to a N
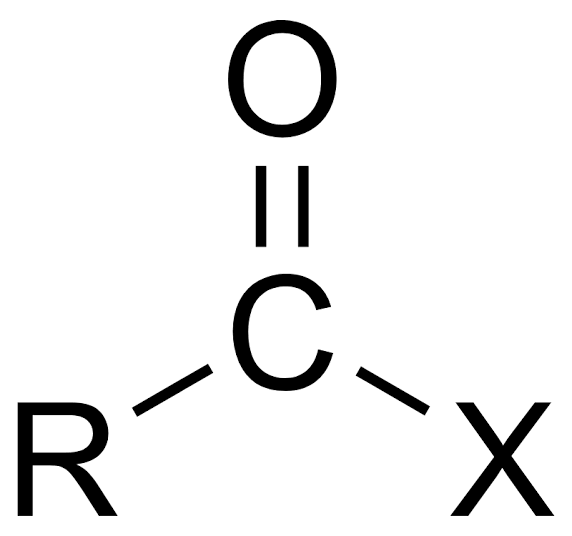
acyl halide
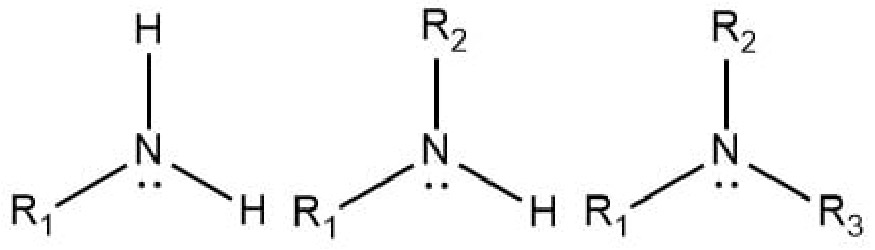
amine
N with a lone pair, bonded to 1, 2, or 3 alkyl groups
nitrile
C triple-bonded to a N
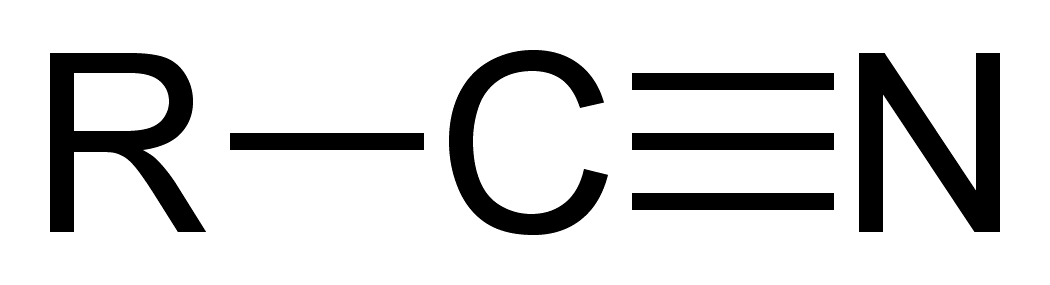
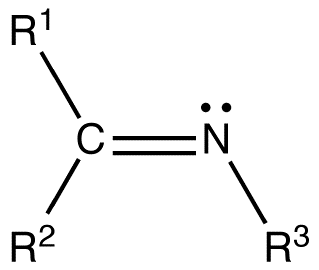
imine
C double bonded to N
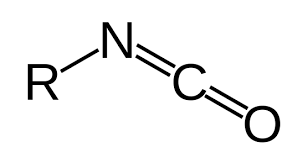
isocyanate
azo compound
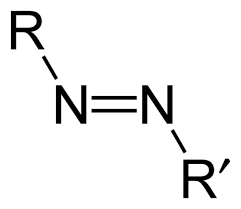
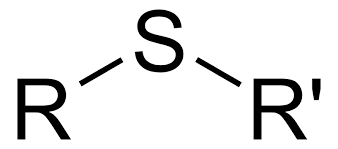
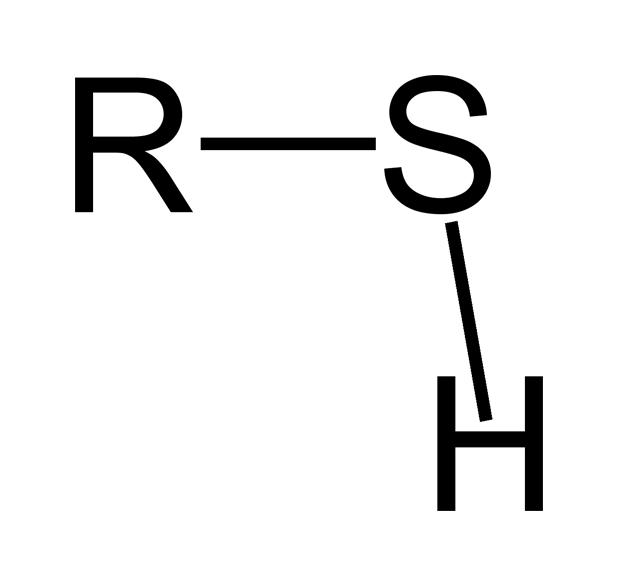
thiol
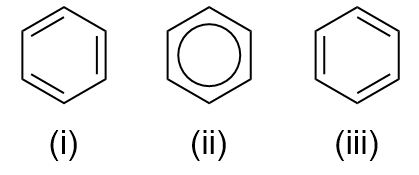
arene
cyclic, unsaturated structure, most commonly a benzene ring
aromatic hydrocarbon
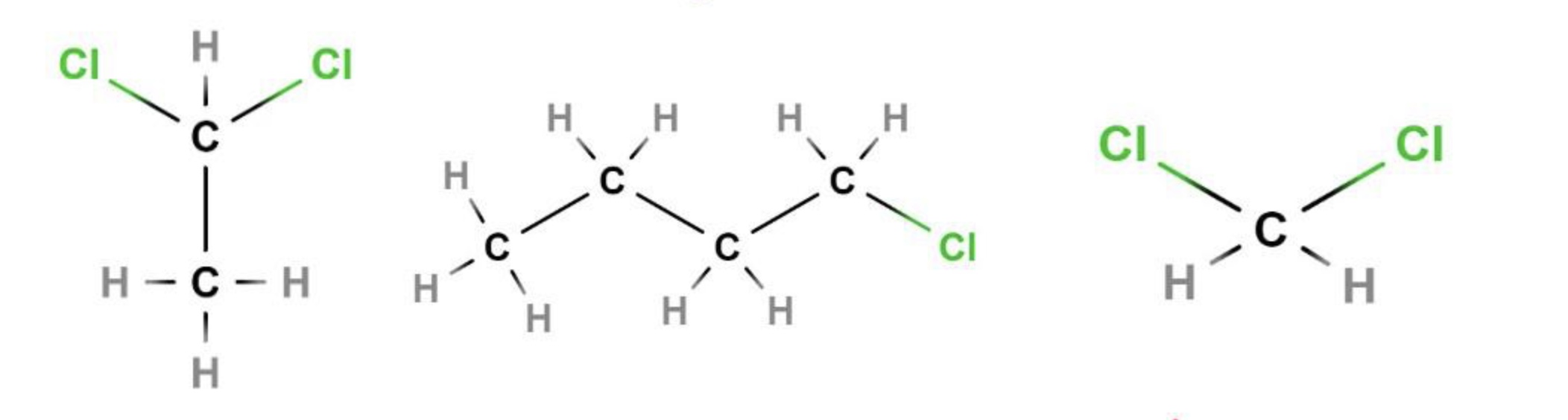
alkyl halide
at least one of an alkane's H is replaced by a halogen (F, Cl, Br, or I)
nitroalkane
N bonded to two O and attached to an aliphatic (alkane) C
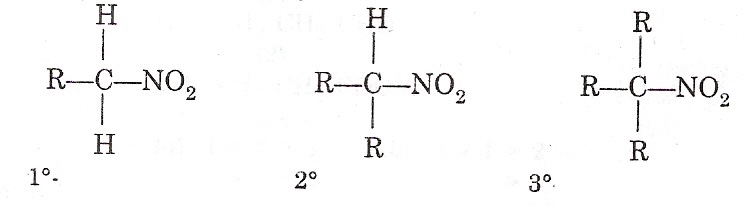
sulfide