Physics Radioactivity
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Define the term radiation
The emission and transfer of energy through space or a medium
What is the mass number
The number of an element which tells us the number of neutrons plus protons of the element
What is the atomic number
The number of an element which tells us the number of protons of the element
What is the charge of an atom
neutral (no. of protons = no. of electrons)
What is the charge and relative mass of protons
Charge= +1 and mass is 1
What is the charge and relative mass of neutrons
C= 0, M=1
What is the charge and relative mass of electrons
C= -1 , M= 0.00005
How much smaller is an electron than protons and neutrons
2000x
What are isotopes
atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but varying number of neutrons
What is the process radioactive decay
It is the process when unstable isotopes of elements decay intro other elements by emitting radiation (alpha, beta or gamma) or sometimes just emitting neutrons.
Describe what electron excitation is and why that releases energy in what form
When an atom absorbs energy (from heat or light), an electron can jump from a lower energy shell to a higher one (called excitation). The excited electron in the higher energy shell will eventually fall back down (because it would be unstable) and when it does, it releases energy in the form of EM radiation
What is ionisation
It is when an atom absorbs so much energy that the outermost electron will completely leave the atom, leaving it with a positive charge making it a positive ion. This is ionising radiation, a type of radiatuon that carries enough energy to remove electrons from the atoms, turning them into ions.
What is ionising Radiation
A type of radiation that has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, causing ions
What does it mean if a material is radioactive?
It contains unstable isotopes that can decay (emit radiation)
What is another name for ionising radiation
nuclear radiation, this is because, when unstable atoms release energy to become stable, that energy often comes from changes happening inside their nucleus and "Nuclear" refers to anything that comes from or involves the nucleus of an atom.
What are the 4 types of ionising radiation?
Alpha Radiation
Beta Particles
Gamma Rays
Emission of a neutron
Describe the structure of an alpha particle and why its often referred to as Helium (He)
Alpha particles are made up on 2 neutrons and 2 protons that comes from the nucleus of an unstable atom. This is often referred to as a helium particle as it has the same make up. They also have an overall charge of 2+
Describe the ionisng and penetrating power of alpha particles
Alpha particles are highly ionising due to their large mass and size. But they are the weakest in penetrating meaning they can only travel a few cm in air and are easily absorbed by a single piece of paper
Describe the structure of beta particle and how its made
Beta particles are just electrons, but they are made when an atom's neutron decays into a proton and electron. The proton stays in the neutron, but the electron is emitted at high speeds.
Describe the ionising and penetrating power of beta particles
Beta particles are moderately ionising and moderatly penetrating. For example, it would travel several meters in air but is stopped by 5mm of aluminium to stop. Beta particles are also less ionsing than alpha radiation as they are smaller.
What are gamma rays
electromagnetic waves that are often emitted after alpha or beta particles as a way of the nucleus getting rid of extra energy
Describe the ionisng and penetrating power of gamma radiation
Gamma rays are the most penetrating as they have no mass or charge and can therefore pass straight through materials. It takes thick pieces of lead or multiple layers of concrete to stop them. Gamma rays are however the least ionising.
Describe what emission of a neutron is
it is when a nucleus has too many neutrons (making it unstable), it can throw out a neutron to increase its stability
How do u do a nuclear decay equation for alpha particles
Using the example of Uranium-238
The Uranium 238 mass number will minus 4
The atomic number of uranium 238 will minus 2
Because the result will have a different atomic number, use the periodic table to find the new element
to the new element as He- 4 (2 atomic number)
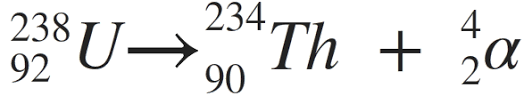
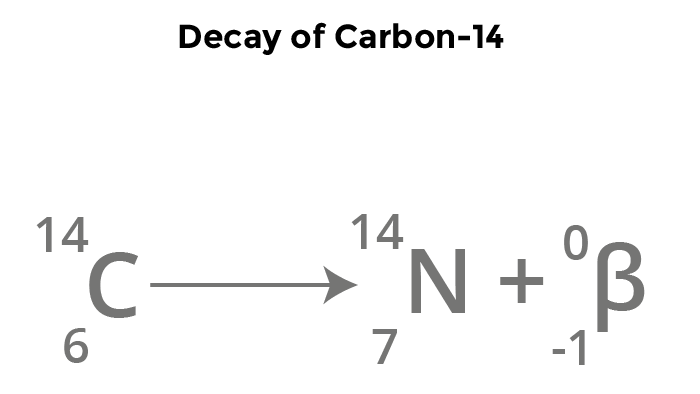
How do u write the nuclear decay equation for beta decay
for example using C-14
The mass number of carbon stays the same but the atomic numnber gains 1
find out the new element and add e- 0 (M) and 1 (A)
How do u write the nuclear decay equation for gamma radiation
for thorium-234
It will be the same it will be th 234 → th 234 + gamma ray
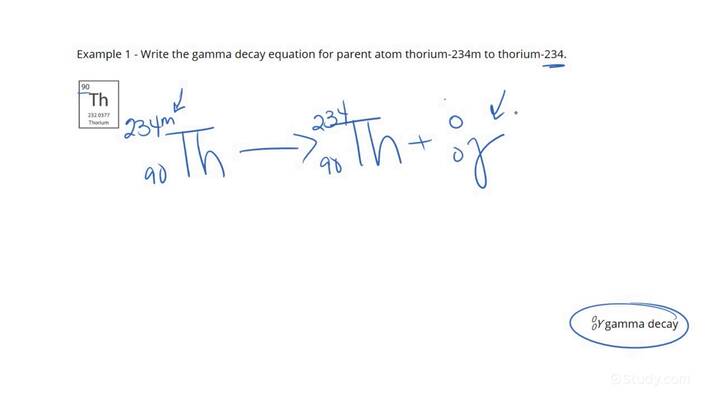
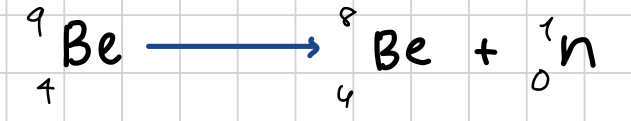
How do u write the nuclear decay equation for neutron emission
for example Be 9
The mass number of Be 9 loses 1 but teh atomic number stays the same (same element therefroe)
So Be 9 would equal Be 8 + a neutron (1 and 0)
Define the term activity
a samples overall rate of decay
What is activity measured in
Becquerels (1 Bq = 1 decay per second)
What are the two definitions for half-life
The time taken for the no. of radioactive nuclei in a sample to half
The time taken for the no. of decays, or activities to half
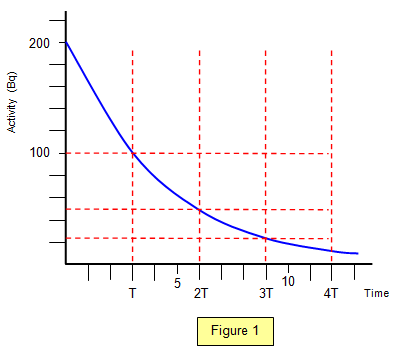
Explain the graph of activty by time
This is because as time goes on the number of particles remaining and activity of the sample will decline. the rate of decline will also fall as shown through the curve
What instrument is used to measure activity in real life and how does it work
a geiger- muller tube and counter. The instrument records all the decays that reach them each second
Define the term irradiation
the process by which objects are exposed to radiation
Define the term contamination
When radioactive particles get onto or into other objects
What are the three factors that determine how harmful radiation is
Type of Radiation
Where you’re exposed to it
The amount
Why is beta and gamma radiation harmful to you and not alpha when its outside of the body
This is because beta and gamma radiation can penetrate through the skin and thorugh tissues to reach vital organs. Alpha radiation however cannot penetrate through and harm u when outside the body
What is the most harmful type of radiation and why
Ionising radiation because they enter living cells and interact with the molecules inside. It can ionise our DNA and cause mutations (cancer)
What is the most dangerous type of radiation when the source is inside the body
alpha
What does the dosage of radiation depend on
How far from the source you are
how long you’re exposed
how radioactive the substance is
What are some precautions you can take whilst being around a radioactive source
Wearing gloves and overalls
Handling the radioactive material with tongs
Keeping the radioactive material in a lead lined box
Where can you find low level radioactivity and how do you dispose of it
in clothes and syringes
disposed by burying in secure landfill sites
Where can you find intermediate level radioactivity and how do you dispose of it
found in nuclear reactors, radioactive sources in medicine
disposed by burying it in concrete
Where can you find high level radioactivity and how do you dispose of it
found in nuclear fuel and chemical waste
disposed by encasing it in concrete and burying it deep underground
What are for uses for nuclear radiation
Medical tracers
Radiotherapy
Sterilisation
Industry
How do medical tracers works
a source that emits beta or gamma radiation is injected into the patient
As the source moves around the body, it can be detected using a radiographer
doctors use this method to check whether vital organs are working as they should be
the radioactive soruce has to have as short a half-life as possible so they only emit radiation for a short period and stop being harmful
How does radiotherapy work
high doses of radiation can be used to kiss cancer cells and stop them divided. Gamma rays are used
How does steriliastion work
food and medical equipment can ve irradiated with a high dose of gamma rays to kill all microbes
How is nuclear radiation used in industry
gamma emitting tracers are used to detect leaks in underground pipes. a crack in the pipe will show extra high radiation. use short half life
Define nuclear fission
The division of a large and unstable nuclei into a smaller nuclei (with the release if energy) and neutrons
What is spontaneous fission and how often does it happen
when fission occurs by itself (is unforced), rare
What is the process of nuclear fission in a nuclear reactor (4)
A slow moving neutron is fired at an unstable nucleus like uranium-235
The unstable nucleus absorbs the neutron and splits into two daughter nuclei and 2-3 nuetrons whilst emitting energy in the form of gamma radiation
The 2-3 nuclei that were released are then absorbed by other unstable nuclei and the process repeats creating a chain reaction
The gamma radiation released is used to boil water into steam which turns turbines, converting kinetic energy into electricity by a generator
Why is it important that nuclear chain reactors are kept under control
to avoid a nuclear meltdown.
What are pros of nuclear energy
The uranium fuel is relatively cheap
it produces a large and steady amount of energy
doesn’t produce greenhouse gases
What are cons of nuclear energy
The powerplant itself is very expensive to build
the produced nuclear waste is expensive to dispose
theres always a risk of major disaster (alck of public support)
what is the purpose of control rods in a nuclear reactor
absorb neutrons and slow down the fission process
what is the purpose of containment building in a nuclear reactor
absorb dangerous radiation
what is the purpose of the moderator in a nuclear reactor
slows down the neutrons so that it can be absorbed by the unstable nuclei
what is the purpose of fuel rods in a nuclear reactor
contains the uranium for fission
Define the process of nuclear fusion and give examples
when two lighter nuclei, join to form a single larger nuclei. an example is 2 hydrogen nuclei fusing together to form a single helium nuclei
why is nuclear fusion beneficial
it releases alot of energy (from some of the mass of the original two nuclei) and fuels stars
It is how all elements heavier than hydrogen are made
it doesn’t produce any nuclear waste
why is nuclear fusion not done on earth
because it only happens at really high temperatures and pressures for it to overcome the repulsion of a positively charged nucleus
Describe the uses of radioactivity in household smoke alarms
An alpha source ionises air between 2 electrodes causing a constant current. Smoke blocks the alpha so tthe he current stops
What is carbon dating
The determination of an organic matter by finding the amount of carbon-14 that it contains
Describe the logic behind how carbon dating works
All living organisms absorb carbon, carbon -12 (stable) and carbon -14 (unstable)
when an organism dies, it stops absorbing carbon
The carbon - 12 stays the same
the carbon-14 begins to decay and reduces
Scientists can use the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 in an organism to find its age
what is the equation for the formation of a carbon-14 isotope
14N + 01N → 14C + 11P
What is the equation for the decay of carbon-14
14C → 14N + Beta radiation